JAVA 3层架构及其实例文件/代码规范
目录
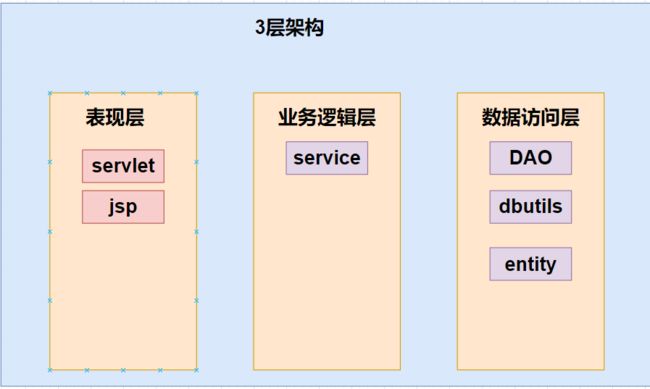
架构图
为什么要使用3层架构
各个部分应有的文件
表现层
业务逻辑层
数据访问层
各层示例代码
表现层
jsp
servlet
业务逻辑层
service 接口
service逻辑
数据访问层
dao 接口
dao 操作
entity
dbutils
一图胜万言
架构图
为什么要使用3层架构
1 方便团队分工 利于维护
2 规范代码,在开发软件时对每个层的代码进行规范,固定开发语言的风格。
3 降低更新难度,当软件系统要换数据库时,只要将数据访问层的代码修改就好了。
4 实现"高内聚、低耦合"。易于分配资源。
5 是使得代码逻辑清晰。
各个部分应有的文件
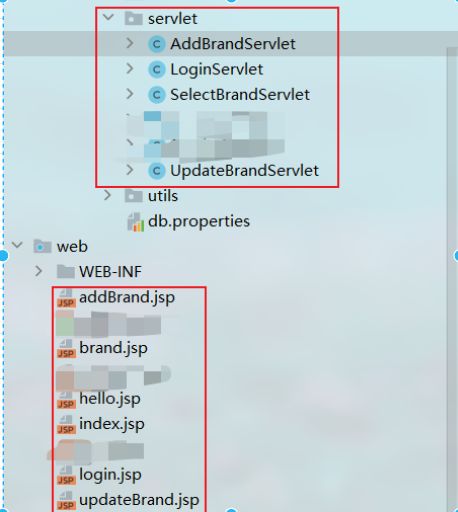
表现层
应该有的文件(jsp+servlet)
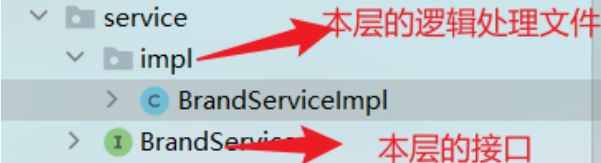
业务逻辑层
应该有的文件(service的接口,及其实现的逻辑代码)
具体的逻辑代码应该包括,多次对Dao层的操作(多次查询,修改,登陆的检验,用户在线状态的检验等等)也包括对数据库的连接,关闭等等
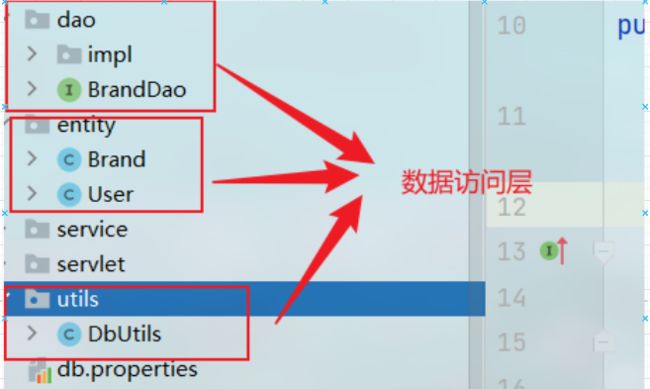
数据访问层
应该有的
DAO(全称Data Access Object,意为数据访问接口/对象)
DAO中也应该定义接口,及其实现(具体指增删改查的代码)
entity(意为实体类是数据库表的映射)
utils是工具集的意思,其中连接数据库,关闭数据库/数据源/对象的一些操作应该写在这里的某个类里面
各层示例代码
表现层
jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %>
Title
序号
品牌名称
企业名称
排序
品牌介绍
状态
操作
${brand.id}
${brand.brandName}
${brand.companyName}
${brand.ordered}
${brand.description}
${brand.status}
修改 删除
servlet
package com.teaching.jsp.servlet;
import com.teaching.jsp.entity.Brand;
import com.teaching.jsp.service.BrandService;
import com.teaching.jsp.service.impl.BrandServiceImpl;
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.http.*;
import javax.servlet.annotation.*;
import java.io.IOException;
@WebServlet(name = "AddBrandServlet", value = "/addBrand")
public class AddBrandServlet extends HttpServlet {
BrandService brandService=new BrandServiceImpl();
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
request.setCharacterEncoding("utf8");
//接收参数
String brandName = request.getParameter("brandName");
String companyName = request.getParameter("companyName");
String ordered = request.getParameter("ordered");
String description = request.getParameter("description");
String status = request.getParameter("status");
//封装Brand
Brand brand = new Brand();
brand.setBrandName(brandName);
brand.setDescription(description);
brand.setCompanyName(companyName);
brand.setOrdered(Integer.valueOf(ordered));
brand.setStatus(Integer.valueOf(status));
//调用Service去处理业务
brandService.insertBrand(brand);
//转发到selectAll
response.sendRedirect("/teachingJsp/selectBrand");
}
}
业务逻辑层
service 接口
package com.teaching.jsp.service;
import com.teaching.jsp.entity.Brand;
import java.util.List;
public interface BrandService {
List selectAllBrand();
boolean insertBrand(Brand brand);
Brand selectBrandById(String id);
boolean updateBrand(Brand brand);
}
service逻辑
package com.web.serivce.impl;
import com.web.dao.Impl.UserDaoImpl;
import com.web.dao.UserDao;
import com.web.entity.User;
import com.web.serivce.UserServlet;
import com.web.utils.DbUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class UserService implements UserServlet {
private UserDao userDao=new UserDaoImpl();
//使用Dao查询当前的用户
@Override
public User getUserByUserEntity(User user) {
//service是有多个dao方法组成
//和数据库交互相关的方法调用
//其中获取数据库连接,关闭连接 应该写在本层
User u= null;
Connection connection =null;
try {
connection = DbUtils.getConnection();
connection.setAutoCommit(false);
u = userDao.selectUserByEntity(user,connection);
connection.commit();
} catch (SQLException e) {
try {
connection.rollback();
} catch (SQLException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
}
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
if (connection!=null){
try {
DbUtils.close(connection);
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
return u;
}
//判断用户是否注册
@Override
public boolean registryUser(User user) {
User u= null;
Connection connection =null;
int row=0;
try {
connection = DbUtils.getConnection();
connection.setAutoCommit(false);
int i=userDao.selectUserByUsername(user.getUsername(),connection);
if (i>0){
throw new RuntimeException("username已经存在");
}
row+=userDao.insertUser(user,connection);
connection.commit();
} catch (SQLException e) {
try {
connection.rollback();
} catch (SQLException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
}
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
if (connection!=null){
try {
DbUtils.close(connection);
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
return row>0;
}
}
数据访问层
dao 接口
package com.teaching.jsp.dao;
import com.teaching.jsp.entity.Brand;
import java.util.List;
//DAO 的全称是Data Access Object
public interface BrandDao {
List selectAll();
boolean insert(Brand brand);
Brand selectBrandById(String id);
boolean updateBrand(Brand brand);
}
dao 操作
对数据库的连接不应该写在此层,应该写在serivce层
package com.teaching.web.dao;
import com.teaching.web.entity.User;
import com.teaching.web.utils.DbUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao {
@Override
public User selectUserByEntity(User user, Connection connection) throws SQLException {
String sql="select id,username,password from user where username=? and password=?";
User u = null;
PreparedStatement ps = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setString(1, user.getUsername());
ps.setString(2, user.getPassword());
ResultSet rs = ps.executeQuery();
if (rs.next()){
u =new User(
rs.getInt(1),
rs.getString(2),
rs.getString(3)
);
}
return u;
}
@Override
public int insertUser(User user, Connection connection) throws SQLException {
String sql="insert into user values (null,?,?)";
PreparedStatement ps = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setString(1, user.getUsername());
ps.setString(2, user.getPassword());
int i = ps.executeUpdate();
DbUtils.close(ps,null,null);
return i;
}
@Override
public int selectUserByUsername(String username, Connection connection) throws SQLException {
PreparedStatement ps=null;
ResultSet resultSet=null;
int anInt=0;
try {
String sql="select count(*) from user where username=?";
ps = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setString(1,username);
resultSet = ps.executeQuery();
if (resultSet.next()){
anInt = resultSet.getInt(1);
}
} finally {
DbUtils.close(ps,resultSet,null);
}
return anInt;
}
}
entity
package com.teaching.jsp.entity;
public class Brand {
// id 主键
private Integer id;
// 品牌名称
private String brandName;
// 企业名称
private String companyName;
// 排序字段
private Integer ordered;
// 描述信息
private String description;
// 状态:0:禁用 1:启用
private Integer status;
public Brand() {
}
public Brand(Integer id, String brandName, String companyName, String description) {
this.id = id;
this.brandName = brandName;
this.companyName = companyName;
this.description = description;
}
public Brand(Integer id, String brandName, String companyName, Integer ordered, String description, Integer status) {
this.id = id;
this.brandName = brandName;
this.companyName = companyName;
this.ordered = ordered;
this.description = description;
this.status = status;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getBrandName() {
return brandName;
}
public void setBrandName(String brandName) {
this.brandName = brandName;
}
public String getCompanyName() {
return companyName;
}
public void setCompanyName(String companyName) {
this.companyName = companyName;
}
public Integer getOrdered() {
return ordered;
}
public void setOrdered(Integer ordered) {
this.ordered = ordered;
}
public String getDescription() {
return description;
}
public void setDescription(String description) {
this.description = description;
}
public Integer getStatus() {
return status;
}
public void setStatus(Integer status) {
this.status = status;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Brand{" +
"id=" + id +
", brandName='" + brandName + '\'' +
", companyName='" + companyName + '\'' +
", ordered=" + ordered +
", description='" + description + '\'' +
", status=" + status +
'}';
}
}
dbutils
package com.teaching.jsp.utils;
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSourceFactory;
import com.sun.scenario.effect.impl.sw.sse.SSEBlend_SRC_OUTPeer;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.Properties;
public class DbUtils {
private static DataSource dataSource;
static {
Properties prop=new Properties();
try {
prop.load(new FileInputStream("F:\\JAVA EE Preject\\课堂练习\\src\\com\\teaching\\jsp\\db.properties"));
System.out.println("iiii");
dataSource = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(prop);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public static void test(){
System.out.println(DbUtils.class.getClassLoader().getResource("db.properties"));
}
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
System.out.println("iiii111");
return dataSource.getConnection();
}
public static void close(Connection connection) throws SQLException {
if (connection!=null){
connection.close();
}
}
public static void close(PreparedStatement ps, ResultSet rs,Connection connection) throws SQLException {
if (rs!=null){
rs.close();
}
if (ps!=null){
ps.close();
}
if (connection!=null){
connection.close();
}
}
}