算法题:正则表达式匹配(题目+思路+代码+注释)
题目
- 正则表达式匹配
给你一个字符串 s 和一个字符规律 p,请你来实现一个支持 ‘.’ 和 ‘*’ 的正则表达式匹配。
‘.’ 匹配任意单个字符
‘*’ 匹配零个或多个前面的那一个元素
所谓匹配,是要涵盖 整个 字符串 s的,而不是部分字符串。
示例 1:
输入:s = “aa” p = “a”
输出:false
解释:“a” 无法匹配 “aa” 整个字符串。
示例 2:
输入:s = “aa” p = “a*”
输出:true
解释:因为 ‘*’ 代表可以匹配零个或多个前面的那一个元素, 在这里前面的元素就是 ‘a’。因此,字符串 “aa” 可被视为 ‘a’ 重复了一次。
示例 3:
输入:s = “ab” p = “."
输出:true
解释:".” 表示可匹配零个或多个(‘*’)任意字符(‘.’)。
示例 4:
输入:s = “aab” p = “cab”
输出:true
解释:因为 ‘*’ 表示零个或多个,这里 ‘c’ 为 0 个, ‘a’ 被重复一次。因此可以匹配字符串 “aab”。
示例 5:
输入:s = “mississippi” p = “misisp*.”
输出:false
提示:
0 <= s.length <= 20
0 <= p.length <= 30
s 可能为空,且只包含从 a-z 的小写字母。
p 可能为空,且只包含从 a-z 的小写字母,以及字符 . 和 *。
保证每次出现字符 * 时,前面都匹配到有效的字符
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/regular-expression-matching
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
思路
s为待匹配字符串,p为正则表达式字符串
- 特殊情况直接处理掉,返回结果,比如两个空字符串等情况(在实际情况,正则为空,无论被匹配的是不是空字符串都能匹配上,而题目中要求的是正则表达式为空,待匹配字符串为空则匹配上,待匹配字符串不为空则匹配不上)
if (s == null || p == null){
return false;
}
if (p.length() == 0){
if (s.length() ==0){
return true;
}else {
return false;
}
}
- 正则匹配其实就是若干中匹配可能性的在不断的尝试,而我们可以设置一个待匹配字符串下标标兵,正则表达式字符串下标标兵,用来表示匹配到哪里了,直到两边全部匹配完成,两个标兵都走到字符串长度位置则证明匹配成功,则设置标志位为true,以直接结束其他的递归。
- 递归的思路,把匹配整个表达式拆分为每次匹配一个正则最小项,一直把整个正则表达式匹配完,这样就把匹配整个正则表达式这样的一个大难题拆分为了一个小难题就是匹配一个正则表达式项。然后利用递归再加上优化就可以完成整个匹配
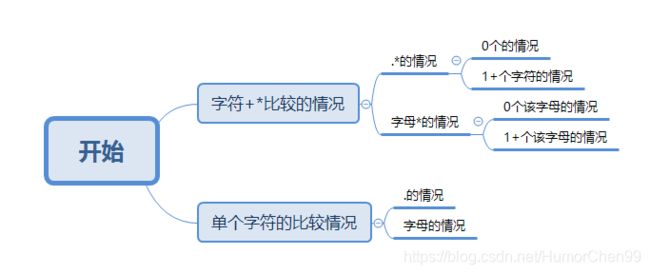
- 在匹配的过程中可能遇到的每种情况进行分类讨论,并做对应处理,如下图:
代码
调用函数 isMatch(String s, String p)进行匹配
public class Solution {
private volatile Boolean finish = false;
public boolean isMatch(String s, String p) {
synchronized (finish){
finish = false;
//特殊情况处理
if (s == null || p == null){
return false;
}
if (p.length() == 0){
if (s.length() ==0){
return true;
}else {
return false;
}
}
//开始匹配
isMatch(s.toCharArray(),s.length(),0,p.toCharArray(),p.length(),0);
return finish;
}
}
public void isMatch(char[] str,int strLen,int strPosition,char[] regex,int regexLen,int regexPosition){
//找到了就出去
if (finish){
return;
}
//正则用完了就出去
if (regexPosition == regexLen){
//正则用完了,字符串用完了,就是匹配成功了
if (strPosition == strLen){
finish = true;
}
return;
}
//从正则字符串拿一个字符
char now = regex[regexPosition];
//由于存在*代表零个或者若干个前一个字符,所以需要试探性的去取下一个正则的字符
char next = ' ';
if (regexPosition < regexLen -1){
next = regex[regexPosition+1];
}
//开始分类讨论
//有下一个并且下一个是个*
if (next == '*'){
//零个或者若干个
if (now == '.'){
//匹配0个
isMatch(str,strLen,strPosition,regex,regexLen,regexPosition+2);
if (finish){
//匹配到了就直接结束掉
return;
}
//匹配1+个字符
for (int i =1;i<=strLen-strPosition;i++){
isMatch(str,strLen,strPosition+i,regex,regexLen,regexPosition+2);
}
}else {
boolean failed = false;
//匹配0个now字符
isMatch(str,strLen,strPosition,regex,regexLen,regexPosition+2);
if (finish){
//匹配到了就直接结束掉
return;
}
//匹配1个以上now 字符
for (int i =1;i<=strLen-strPosition;i++){
//检查若干长度个
for (int j = 0;j<i;j++){
if (str[strPosition+j] != now){
//不相等直接退出
failed = true;
break;
}
}
if (failed){
//如果短的都匹配不上直接退出,比如匹配1个a 都匹配不上那么就不可能匹配上2个a
break;
}
//通过了检查
isMatch(str,strLen,strPosition+i,regex,regexLen,regexPosition+2);
}
}
}else {
//单个字符比较
//字符串用完了直接出去
if (strPosition == strLen){
return;
}
//匹配当前字符
char strNow = str[strPosition];
if (now == strNow || now == '.'){
//相同继续递归比较(如果比较完了,则进函数的时候检查会检查出来)
isMatch(str,strLen,strPosition+1,regex,regexLen,regexPosition+1);
}else {
//不相同结束
return;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(new Solution().isMatch("ab",".*c"));
}
}
![]()