C++轻量级Web服务器TinyWebServer源码分析之threadpool篇
文章目录
- threadpool线程池篇简介
- 一、线程池的创建与回收
- 二、向请求队列添加请求任务
- 三、worker函数内部访问run函数,完成线程处理
- 四、run函数执行任务
- 原文链接
threadpool线程池篇简介
空间换时间,浪费服务器的硬件资源,换取运行效率.
池是一组资源的集合,这组资源在服务器启动之初就被完全创建好并初始化,这称为静态资源.
当服务器进入正式运行阶段,开始处理客户请求的时候,如果它需要相关的资源,可以直接从池中获取,无需动态分配.
当服务器处理完一个客户连接后,可以把相关的资源放回池中,无需执行系统调用释放资源.
线程池的设计模式为半同步/半反应堆,其中反应堆具体为Proactor事件处理模式。
具体的,主线程为异步线程,负责监听文件描述符,接收socket新连接,若当前监听的socket发生了读写事件,然后将任务插入到请求队列。工作线程从请求队列中取出任务,完成读写数据的处理。以下为具体类的定义源码:
class threadpool
{
public:
/*thread_number是线程池中线程的数量,max_requests是请求队列中最多允许的、等待处理的请求的数量*/
threadpool(int actor_model, connection_pool *connPool, int thread_number = 8, int max_request = 10000);
~threadpool();
bool append(T *request, int state);
bool append_p(T *request);
private:
/*工作线程运行的函数,它不断从工作队列中取出任务并执行之*/
static void *worker(void *arg);
void run();
private:
int m_thread_number; //线程池中的线程数
int m_max_requests; //请求队列中允许的最大请求数
pthread_t *m_threads; //描述线程池的数组,其大小为m_thread_number
std::list<T *> m_workqueue; //请求队列
locker m_queuelocker; //保护请求队列的互斥锁
sem m_queuestat; //是否有任务需要处理
connection_pool *m_connPool;//数据库
int m_actor_model; //模型切换
};
需要注意的问题:
threadpool也是采用RALL机制,并且是类内声明,类外初始化;
线程处理函数和运行函数设置为私有属性;
1、worker为啥要采用静态成员函数的方法?
理由一、pthread_create的函数原型中第三个参数的类型为函数指针,指向处理线程函数的地址。
该函数,要求为静态函数。如果处理线程函数为类成员函数时,需要将其设置为静态成员函数。(或者可以采用强制类型转换?)
理由二、pthread_create的函数原型中第三个参数的类型为函数指针,指向的线程处理函数参数类型为(void *),
若线程函数为类成员函数,则this指针会作为默认的参数被传进函数中,从而和线程函数参数(void*)不能匹配,不能通过编译。
静态成员函数就没有这个问题,里面没有this指针。
2、为啥要定义worker函数调用run,不能直接run吗?
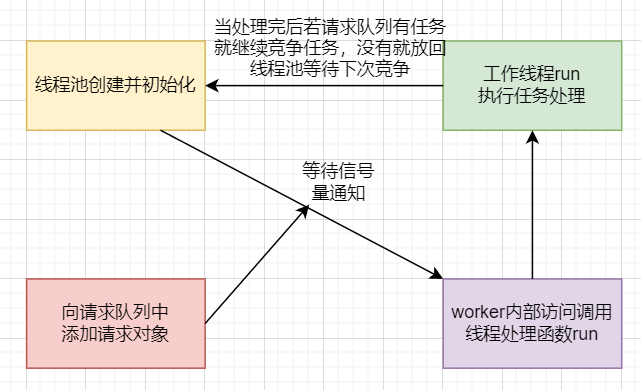
一、线程池的创建与回收
构造函数中创建线程池,pthread_create函数中将类的对象作为参数传递给静态函数(worker),在静态函数中引用这个对象,并调用其动态方法(run)。
具体的,类对象传递时用this指针,传递给静态函数后,将其转换为线程池类,并调用私有成员函数run。
template <typename T>
threadpool<T>::threadpool( int actor_model, connection_pool *connPool, int thread_number, int max_requests) : m_actor_model(actor_model),m_thread_number(thread_number), m_max_requests(max_requests), m_threads(NULL),m_connPool(connPool)
{
if (thread_number <= 0 || max_requests <= 0)
throw std::exception();
m_threads = new pthread_t[m_thread_number];
if (!m_threads)
throw std::exception();
for (int i = 0; i < thread_number; ++i)
{
if (pthread_create(m_threads + i, NULL, worker, this) != 0)
{
delete[] m_threads;
throw std::exception();
}
if (pthread_detach(m_threads[i]))
{
delete[] m_threads;
throw std::exception();
}
}
}
二、向请求队列添加请求任务
通过list容器创建请求队列,向队列中添加时,通过互斥锁保证线程安全,添加完成后通过信号量提醒有任务要处理,最后注意线程同步。
template <typename T>
bool threadpool<T>::append(T *request, int state)
{
m_queuelocker.lock();//加锁保证线程安全
if (m_workqueue.size() >= m_max_requests)//根据硬件,预设请求队列最大值
{
m_queuelocker.unlock();//超出请求队列最大值就解锁返回false
return false;
}
request->m_state = state;
m_workqueue.push_back(request);//添加任务
m_queuelocker.unlock();
m_queuestat.post();//信号量提醒线程池有任务要处理
return true;
}
三、worker函数内部访问run函数,完成线程处理
内部访问私有成员函数run,完成线程处理要求。
template <typename T>
void *threadpool<T>::worker(void *arg)
{
threadpool *pool = (threadpool *)arg;将参数强转为线程池类,调用成员方法
pool->run();
return pool;
}
四、run函数执行任务
从请求队列中取出任务进行具体的业务逻辑处理
void threadpool<T>::run()
{
while (true)
{
m_queuestat.wait();//信号量等待
m_queuelocker.lock();//被唤醒后先加互斥锁
if (m_workqueue.empty())
{
m_queuelocker.unlock();
continue;
}
T *request = m_workqueue.front();//从请求队列中取出第一个任务
m_workqueue.pop_front();//将任务从请求队列删除
m_queuelocker.unlock();
if (!request)
continue;
if (1 == m_actor_model)//模式判断
{
if (0 == request->m_state)
{
if (request->read_once())
{
request->improv = 1;
connectionRAII mysqlcon(&request->mysql, m_connPool);//从连接池中取出一个数据库连接
request->process();//process(模板类中的方法,这里是http类)进行处理
}
else
{
request->improv = 1;
request->timer_flag = 1;
}
}
else
{
if (request->write())
{
request->improv = 1;
}
else
{
request->improv = 1;
request->timer_flag = 1;
}
}
}
else
{
connectionRAII mysqlcon(&request->mysql, m_connPool);
request->process();
}
}
}
原文链接
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzAxNzU2MzcwMw==&mid=2649274278&idx=5&sn=87470bb3ade0150bb94fcbf33c43c2f8&chksm=83ffbefeb48837e843cfc8258248a1e1b69b48ed993c51861ec63e3b0541fa4714a3846adf90&scene=178&cur_album_id=1339230165934882817#rd