二叉树遍历的应用
1. 翻转二叉树
题目描述
力扣链接
给你一棵二叉树的根节点 root ,翻转这棵二叉树,并返回其根节点。
示例:
输入:root = [4,2,7,1,3,6,9]
输出:[4,7,2,9,6,3,1]
代码
//递归
class Solution {
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
//前/后序遍翻转字符串
if(root == null) return root;
swap(root);//前序遍历
invertTree(root.left);
invertTree(root.right);
// swap(root);//后序遍历
return root;
}
public void swap(TreeNode root){
//交换节点位置
TreeNode temp = root.left;
root.left = root.right;
root.right = temp;
}
}
//BFS
class Solution {
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {return null;}
Deque<TreeNode> deque = new ArrayDeque<>();
deque.offer(root);
while (!deque.isEmpty()) {
int size = deque.size();
while (size-- > 0) {
TreeNode node = deque.poll();
swap(node);
if (node.left != null) {deque.offer(node.left);}
if (node.right != null) {deque.offer(node.right);}
}
}
return root;
}
public void swap(TreeNode root) {
TreeNode temp = root.left;
root.left = root.right;
root.right = temp;
}
}
2. 对称二叉树
题目描述
力扣链接
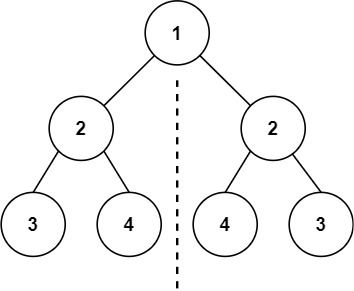
给你一个二叉树的根节点 root , 检查它是否轴对称。
示例:
输入:root = [1,2,2,3,4,4,3]
输出:true
代码
class Solution {
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
Deque<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offerFirst(root.left);
queue.offerLast(root.right);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
TreeNode leftNode = queue.pollFirst();
TreeNode rightNode = queue.pollLast();
if (leftNode == null && rightNode == null) {
continue;
}
// if (leftNode == null && rightNode != null) {
// return false;
// }
// if (leftNode != null && rightNode == null) {
// return false;
// }
// if (leftNode.val != rightNode.val) {
// return false;
// }
// 以上三个判断条件合并
if (leftNode == null || rightNode == null || leftNode.val != rightNode.val) {
return false;
}
queue.offerFirst(leftNode.left);
queue.offerFirst(leftNode.right);
queue.offerLast(rightNode.right);
queue.offerLast(rightNode.left);
}
return true;
}
}
3. 二叉树的最大深度
题目描述
力扣链接
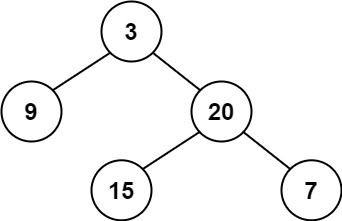
给定一个二叉树,找出其最大深度。
二叉树的深度为根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例:
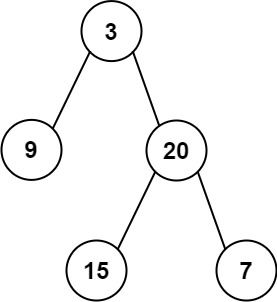
给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
代码
递归
class solution {
/**
* 递归法
*/
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int leftDepth = maxDepth(root.left);
int rightDepth = maxDepth(root.right);
return Math.max(leftDepth, rightDepth) + 1;
}
}
非递归
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
queue.offer(root);
int ans = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
while (size > 0) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
if (node.left != null) {
queue.offer(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
queue.offer(node.right);
}
size--;
}
ans++;
}
return ans;
}
}
N叉树的最大深度
题目描述
力扣链接
给定一个 N 叉树,找到其最大深度。
最大深度是指从根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点总数。
N 叉树输入按层序遍历序列化表示,每组子节点由空值分隔(请参见示例)。
输入:root = [1,null,3,2,4,null,5,6]
输出:3
代码
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public int val;
public List children;
public Node() {}
public Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
public Node(int _val, List _children) {
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(Node root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
int depth = 0;
if (root.children != null){
for (Node child : root.children){
depth = Math.max(depth, maxDepth(child));
}
}
return depth + 1; //中节点
}
}
4. 完全二叉树的节点个数
题目描述
力扣链接
给你一棵 完全二叉树 的根节点 root ,求出该树的节点个数。
完全二叉树 的定义如下:在完全二叉树中,除了最底层节点可能没填满外,其余每层节点数都达到最大值,并且最下面一层的节点都集中在该层最左边的若干位置。若最底层为第 h 层,则该层包含 1~ 2h 个节点。
示例 1:
输入:root = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
输出:6
代码
class Solution {
// 通用递归解法
public int countNodes(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) {
return 0;
}
return countNodes(root.left) + countNodes(root.right) + 1;
}
}
class Solution {
// 迭代法
public int countNodes(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
int result = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
while (size -- > 0) {
TreeNode cur = queue.poll();
result++;
if (cur.left != null) queue.offer(cur.left);
if (cur.right != null) queue.offer(cur.right);
}
}
return result;
}
}
5. 平衡二叉树的判断
题目描述
力扣链接
给定一个二叉树,判断它是否是高度平衡的二叉树。
本题中,一棵高度平衡二叉树定义为:
一个二叉树每个节点 的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过 1 。
示例 1:
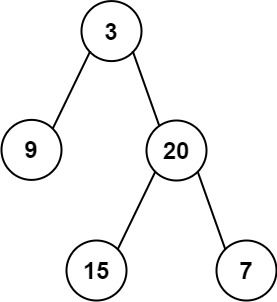
输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
输出:true
代码
class Solution {
/**
* 递归法
*/
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
return getHeight(root) != -1;
}
private int getHeight(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int leftHeight = getHeight(root.left);
if (leftHeight == -1) {
return -1;
}
int rightHeight = getHeight(root.right);
if (rightHeight == -1) {
return -1;
}
// 左右子树高度差大于1,return -1表示已经不是平衡树了
if (Math.abs(leftHeight - rightHeight) > 1) {
return -1;
}
return Math.max(leftHeight, rightHeight) + 1;
}
}
6. 二叉树的所有路径(回溯)
题目描述
力扣链接
给你一个二叉树的根节点 root ,按 任意顺序 ,返回所有从根节点到叶子节点的路径。
叶子节点 是指没有子节点的节点。
输入:root = [1,2,3,null,5]
输出:["1->2->5","1->3"]
代码
class Solution {
public List<String> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode root) {
List<String> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) {
return res;
}
List<Integer> stack = new ArrayList<>();
preorderTraversal(root,stack,res);
return res;
}
public void preorderTraversal(TreeNode root,List<Integer> stack,List<String> res) {
//讲节点加入栈,以便回溯
stack.add(root.val);
//叶子节点处理
if(root.left == null && root.right == null){
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < stack.size() - 1; i++) {
sb.append(stack.get(i)).append("->");
}
sb.append(stack.get(stack.size() - 1));
res.add(sb.toString());
return;
}
if (root.left != null) {//防止空指针异常
preorderTraversal(root.left, stack, res);
stack.remove(stack.size() - 1);// 回溯
}
if (root.right != null) {//防止空指针异常
preorderTraversal(root.right, stack, res);
stack.remove(stack.size() - 1);// 回溯
}
}
}
7. 找树左下角的值
题目描述
力扣链接
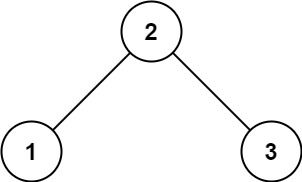
给定一个二叉树的 根节点 root,请找出该二叉树的 最底层 最左边 节点的值。
假设二叉树中至少有一个节点。
示例 1:
输入: root = [2,1,3]
输出: 1
代码
class Solution {
public int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode root) {
Deque<TreeNode> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
//根节点入队
queue.offerLast(root);
int ret = 0;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
//弹出元素
TreeNode node = queue.pollFirst();
//注意灵活使用层序遍历 从右向左
if(node.right != null) queue.offerLast(node.right);
if(node.left != null) queue.offerLast(node.left);
ret = node.val;
}
return ret;
}
}
8. 路径总和
题目描述
力扣链接
给你二叉树的根节点 root 和一个表示目标和的整数 targetSum 。判断该树中是否存在 根节点到叶子节点 的路径,这条路径上所有节点值相加等于目标和 targetSum 。如果存在,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
叶子节点 是指没有子节点的节点。
示例 1:
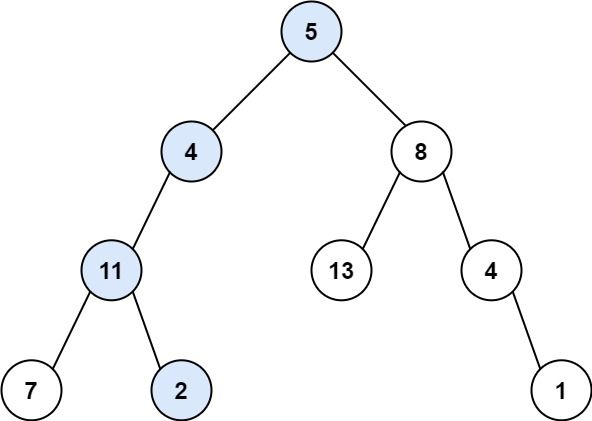
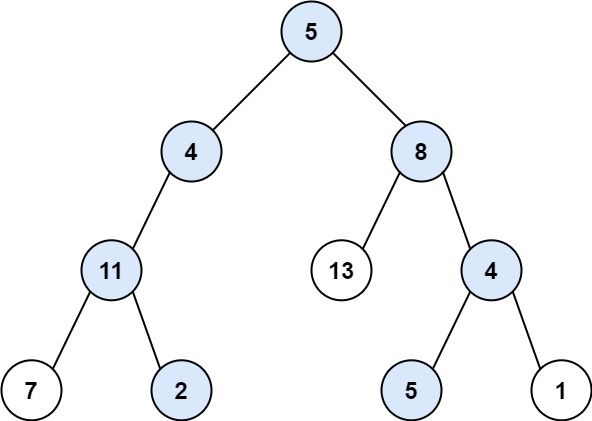
输入:root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,null,1], targetSum = 22
输出:true
解释:等于目标和的根节点到叶节点路径如上图所
代码
class Solution {
public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) {
if (root == null) {
return false;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queNode = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
Queue<Integer> queVal = new LinkedList<Integer>();
queNode.offer(root);
queVal.offer(root.val);
while (!queNode.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode now = queNode.poll();
int temp = queVal.poll();
if (now.left == null && now.right == null) {
if (temp == sum) {
return true;
}
continue;
}
if (now.left != null) {
queNode.offer(now.left);
queVal.offer(now.left.val + temp);
}
if (now.right != null) {
queNode.offer(now.right);
queVal.offer(now.right.val + temp);
}
}
return false;
}
}
//递归
class Solution {
public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
if(root == null) return false;
//不断减减路径总和
targetSum -= root.val;
// 叶子结点
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
return targetSum == 0;
}
if(root.left != null){
boolean left = hasPathSum(root.left,targetSum);
if(left){//已经找到
return true;
}
}
if(root.right != null){
boolean right =hasPathSum(root.right,targetSum);
if(right){//已经找到
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
路径之和2(回溯 + 重要)
题目描述
力扣链接
给你二叉树的根节点 root 和一个整数目标和 targetSum ,找出所有 从根节点到叶子节点 路径总和等于给定目标和的路径。
叶子节点 是指没有子节点的节点。
示例 1:
输入:root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,5,1], targetSum = 22
输出:[[5,4,11,2],[5,8,4,5]]
代码
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null) return res;
List<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();
preorderdfs(root, targetSum, res, path);
return res;
}
public void preorderdfs(TreeNode root, int targetsum, List<List<Integer>> res, List<Integer> path){
path.add(root.val);
if(root.left == null && root.right == null){
// 找到了和为 targetsum 的路径
if (targetsum - root.val == 0) {
res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
}
return; // 如果和不为 targetsum,返回
}
if (root.left != null) {
//这种写法更能体现回溯
targetsum -= root.val;
preorderdfs(root.left, targetsum , res, path);
targetsum += root.val;
path.remove(path.size() - 1); // 回溯
}
//注意两种写法的区别
if (root.right != null) {
preorderdfs(root.right, targetsum - root.val, res, path);
path.remove(path.size() - 1); // 回溯
}
}
}
9. 从中序与后序遍历构建二叉树
题目描述
力扣链接
给定两个整数数组 inorder 和 postorder ,其中 inorder 是二叉树的中序遍历, postorder 是同一棵树的后序遍历,请你构造并返回这颗 二叉树 。
示例 1:
输入:inorder = [9,3,15,20,7], postorder = [9,15,7,20,3]
输出:[3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
代码
class Solution {
Map<Integer,Integer> map; //使用map方便的到中序遍历元素在数组的索引
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) {
map = new HashMap<>();
int inLen = inorder.length;
int postLen = postorder.length;
// 将中序遍历的元素存入map
for(int i = 0;i < inLen;i++){
map.put(inorder[i],i);
}
return getTree(inorder, 0, inLen, postorder, 0, postLen);//左闭右开
}
public TreeNode getTree(int[] inorder,int inBegin, int inEnd, int[] postorder, int postBegin, int postEnd){
//如果前后索引不满足左闭右开,也就是无法创建节点
if(inBegin >= inEnd || postBegin >= postEnd){
return null;
}
//找到根节点的索引
int rootIndex = map.get(postorder[postEnd - 1]);
//创建节点
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(inorder[rootIndex]);
//保存左子树的个数
int leftLen = rootIndex - inBegin;
//递归构建子树
root.left = getTree(inorder, inBegin, rootIndex, postorder, postBegin, postBegin + leftLen);
root.right = getTree(inorder, rootIndex + 1, inEnd, postorder, postBegin + leftLen, postEnd - 1);
return root;
}
}
10. 从前序与后序遍历构建二叉树
题目描述
力扣链接
给定两个整数数组 preorder 和 inorder ,其中 preorder 是二叉树的先序遍历, inorder 是同一棵树的中序遍历,请构造二叉树并返回其根节点。
示例 1:
输入: preorder = [3,9,20,15,7], inorder = [9,3,15,20,7]
输出: [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
代码
class Solution {
Map<Integer,Integer> map; //存储中序遍历元素和索引的对应关系
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
map = new HashMap<>();
int n = preorder.length;
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++){
map.put(inorder[i],i);
}
return getTree(preorder, 0, n, inorder,0, n);
}
public TreeNode getTree(int[] preorder, int preBegin, int preEnd, int[] inorder, int inBegin, int inEnd){
//区间不满足左闭右开就结束
if(preBegin >= preEnd || inBegin >= inEnd) return null;
//获取根节点索引,前序遍历第一个元素
int rootIndex = map.get(preorder[preBegin]);
//创建结点
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(inorder[rootIndex]);
//根据中序遍历获取左子树长度
int leftLen = rootIndex - inBegin;
//创建左右子树
root.left = getTree(preorder, preBegin + 1,preBegin + leftLen + 1, inorder, inBegin,rootIndex);
root.right = getTree(preorder, preBegin + leftLen + 1, preEnd, inorder, rootIndex + 1,inEnd);
return root;
}
}
11. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
题目描述
力扣链接
给定一个二叉树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。
百度百科中最近公共祖先的定义为:“对于有根树 T 的两个节点 p、q,最近公共祖先表示为一个节点 x,满足 x 是 p、q 的祖先且 x 的深度尽可能大(一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先)。”
示例 1:
输入:root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 1
输出:3
解释:节点 5 和节点 1 的最近公共祖先是节点 3 。
代码
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(p == root || q == root || root == null){
return root;
}
//后序遍历
TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
//回溯
if(left == null && right == null){//两个节点都未找到
return null;
}else if(left == null && right != null){
//找到一个
return right;
}else if(left != null && right == null){
return left;
}else{// 若找到两个节点
return root;
}
}
}
二叉搜索树的最近祖先
本题是二叉搜索树,二叉搜索树是有序的,那得好好利用一下这个特点
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if (root.val > p.val && root.val > q.val) return lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
if (root.val < p.val && root.val < q.val) return lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
return root;
}
}