《LeetCode》位运算详解
位运算
^ : 按位异或
& : 按位与
| : 按位或
~ : 取反
<< : 算术左移
>> : 算术右移
0s和1s分别表示只由0或1构成的二进制数字
x ^ 0s == x;
x ^ 1s == ~x;
x ^ x == 0;
x & 0s == 0;
x & 1s == 1;
x & x == x;
x | 0s == x;
x | 1s == 1s;
x | x == x;
//n & (n-1)可以去除n的位级表示中最低的那一位
n = 11110100
n & (n-1) == 11110000
//n & (-n)可以得到n的位级表示中最低的那一位
n = 11110100
n & (-n) == 00000100
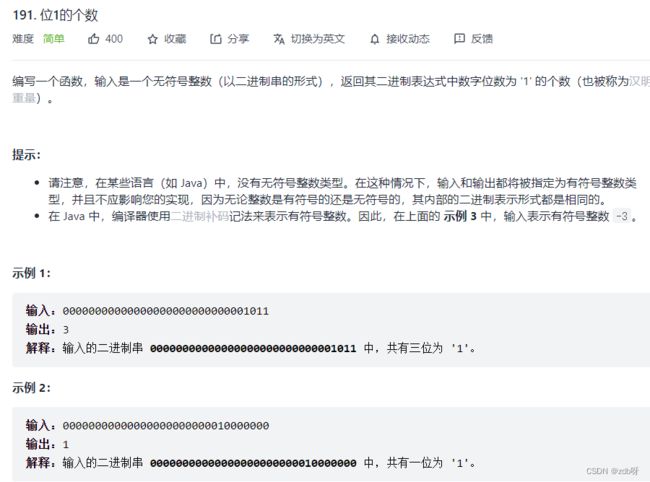
191. 位1的个数【简单】
题目:输入为长度32的二进制串
思路一:循环检查二进制位
时间复杂度:O(k),k为二进制位数,k=32
空间复杂度:O(1)
class Solution {
public:
int hammingWeight(uint32_t n) {
int ret = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= 31; i++) {
if (n & (1 << i)) { //检查每一位是否为1 从低位到高位检查
ret++;
}
}
return ret;
}
};
思路二:位运算优化
时间复杂度:O(logn) 循环次数 = 1的个数
空间复杂度:O(1)
class Solution {
public:
int hammingWeight(uint32_t n) {
int ret = 0;
while (n) {
n = n & (n - 1); //n & (n - 1) 每次把最低位的1 变成 0
ret++;
}
return ret;
}
};
461. 汉明距离【简单】
方法二:移位实现位计数
时间复杂度:O(logC),其中C是元素的数据范围,在本题中logC = 31
空间复杂度:O(1)
class Solution{
public:
int hammingDistance(int x, int y){
int diff = x ^ y; //异或
int res = 0;
while(diff){
res += diff & 1; //看低位是否为1
diff >>= 1; //右移
}
return res;
}
};
优化:0的位可以不判断
- 方法:Brian Kernighan 算法
时间复杂度:O(m),m为1的位数
空间复杂度:O(1)
class Solution{
public:
int hammingDistance(int x, int y){
int diff = x ^ y; //异或
int res = 0;
while(diff){
diff &= diff - 1; //从低位到高位将1变0
res++;
}
return res;
}
};
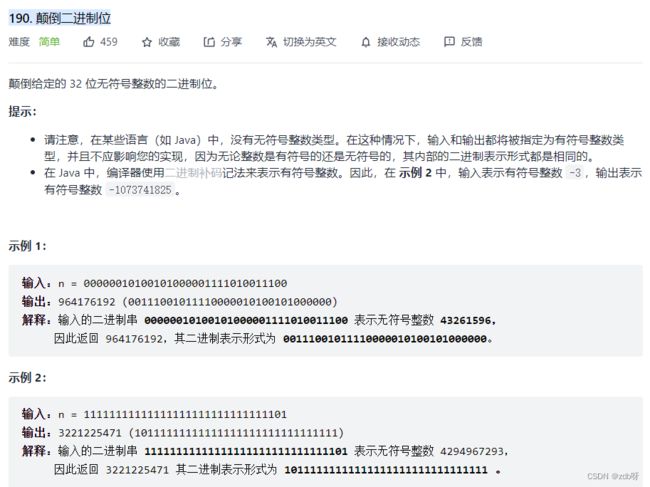
190. 颠倒二进制位【简单】
- 思路一:逐位颠倒
时间复杂度:O(logn),即循环32次
空间复杂度:O(1)
class Solution {
public:
uint32_t reverseBits(uint32_t n) {
uint32_t res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= 31; i++) {
res <<= 1; //扩充一位
res |= n & 1; //扩充位上填数
n >>= 1; //舍弃低位
}
return res;
}
};
- 优化:不记0位
class Solution {
public:
uint32_t reverseBits(uint32_t n) {
uint32_t rev = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= 31 && n > 0; i++) {
rev = rev | ((n & 1) << (31 - i)); //|相当于保留1
n >>= 1; //n右移一位
}
return rev;
}
};
思路二:分而治之
时间复杂度:O(1)
空间复杂度:O(1)
class Solution {
public:
uint32_t reverseBits(uint32_t n) {
n = (n >> 16) | (n << 16);
n = ((n & 0xff00ff00) >> 8) | ((n & 0x00ff00ff) << 8); // 00000000111111110000000011111111
n = ((n & 0xf0f0f0f0) >> 4) | ((n & 0x0f0f0f0f) << 4); // 00001111000011110000111100001111
n = ((n & 0xcccccccc) >> 2) | ((n & 0x33333333) << 2); // 00110011001100110011001100110011
n = ((n & 0xaaaaaaaa) >> 1) | ((n & 0x55555555) << 1); // 01010101010101010101010101010101
return n;
}
};
136. 只出现一次的数字【简单】
思路一:哈希表计数
时间复杂度:O(n)
空间复杂:O(n)
思路二:异或运算
时间复杂度:O(n) n为数组长度
空间复杂度:O(1)
- [x]
class Solution {
public:
int singleNumber(vector& nums) {
int ret = 0;
for (auto e: nums) ret ^= e; //两个相同的值做异或结果为0 任何数和0异或等于它本身
return ret;
}
};
骚一点,一个多余空间都不用
class Solution {
public:
int singleNumber(vector& nums) {
for (int i = 1; i < nums.size(); i++) {
nums[0] ^= nums[i];
}
return nums[0];
}
};
260. 只出现一次的数字 III【中等】
思路一:哈希表
时间复杂度:O(n)
空间复杂度:O(n)
- 思路二:位运算
时间复杂度:O(n)
空间复杂度:O(1)
思路:
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> singleNumber(vector<int>& nums) {
unsigned int target = 0; //unsigned不能少
// 一对相同的数字异或为0
// 所以target为两个只出现了一次的元素的异或
for (auto n: nums) {
target ^= n;
}
// 因为两数不同,lowbit必然不为0
// 物理意义就是两个不同的数字不同的最低的位在哪
int lowbit = target & (-target);
int a1 = 0;
int a2 = 0;
// 重复上述的过程,但是将nums按照lowbit为1或者为0分类
// 则两个数必然被分到不同的类目;而相同的数字一定在同一个类目
// 所以按类目分别异或就可以得到两个不同的数字
for (auto n: nums) {
if (n & lowbit) {
a1 ^= n;
} else {
a2 ^= n;
}
}
return {a1, a2};
}
};
231. 2 的幂【简单】
思路一:一直÷2,除到不能除再判断是否为1
时间复杂度:O(logn)
空间复杂度:O(1)
思路四:(2^30) % n ==0?
//时间复杂度:O(1)
//空间复杂度:O(1)
class Solution {
//private:
//static constexpr int BIG = 1 << 30; //最大的2的幂数 即BIG=2^30
public:
bool isPowerOfTwo(int n) {
return n > 0 && 1073741824 % n == 0;
}
};
- 思路二:位运算
时间复杂度:O(1)
空间复杂度:O(1)
思路:2的幂的二进制只有一位是1,其他全是0
class Solution {
public:
bool isPowerOfTwo(int n) {
return n > 0 && (n & (n - 1)) == 0; //抹掉1,判断是否等于0
}
};
版本二:
class Solution {
public:
bool isPowerOfTwo(int n) {
return n > 0 && (n & -n) == n; //提取1,判断是还等于n,等于说明原来的数只有一个1
}
};
342. 4的幂【简单】
类似上一题
思路:n>0 && 1的位数只有一位 && 出现在奇数位上
时间复杂度:O(1)
空间复杂度:O(1)
bool isPowerOfFour(int n){
return n > 0 && !(n & (n - 1)) && (n & 1431655765); //与10101..101的十进制数按位与
};
class Solution {
public:
bool isPowerOfFour(int n) {
return n > 0 && (n & (n - 1)) == 0 && (n & 0xaaaaaaaa) == 0;
}
};
思路二:4的幂 % 3 == 1
时间复杂度:O(1)
空间复杂度:O(1)
class Solution {
public:
bool isPowerOfFour(int n) {
return n > 0 && (n & (n - 1)) == 0 && n % 3 == 1;
}
};
318. 最大单词长度乘积【中等】
思路一:双for暴力破解,写一个判断word是否有相同字母的函数
- 思路二:位运算
时间复杂度:O(n^2 + L)
空间复杂度:O(n)
class Solution {
public:
int maxProduct(vector<string>& words) {
unordered_map<int, int> map;
int res = 0;
for(const string& word : words){
int mask = 0;
int size = word.size();
for(const char& c : word){ //求到该单词对应的长度为26的二进制数字
mask |= 1 << (c - 'a');
}
map[mask] = max(map[mask], size); //max(ab, aab) 最优,避免了重复计算
for(const auto& [h_mask, h_len] : map){
if(!(mask & h_mask)){ //如果两个字符串含有重复数字,它们的二进制表示按位与不为0
res = max(res, size * h_len);
}
}
}
return res;
}
};
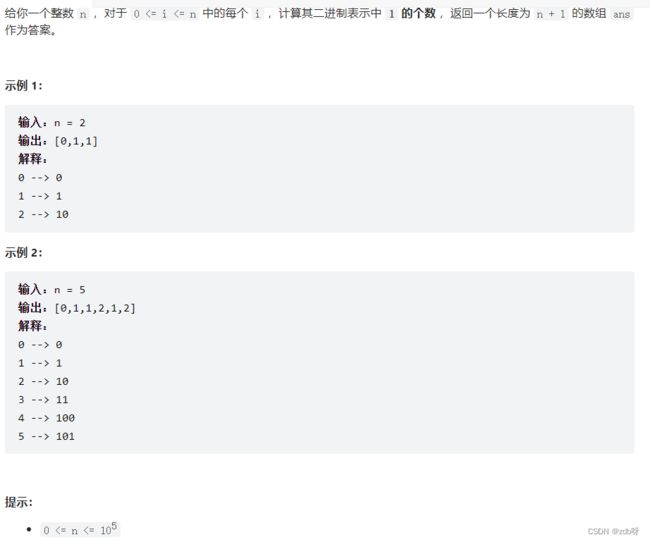
338. 比特位计数【简单】
思路一:分别计算每一个i的1比特位
时间复杂度:O(nlogn)
空间复杂度:O(n)
class Solution {
public:
int count (int i){
int res = 0;
while(i){
i &= (i - 1);
res++;
}
return res;
}
vector<int> countBits(int n) {
vector<int> res(n+1);
for(int i = 0; i <= n; i++){
res[i] = count(i);
}
return res;
}
};
- 思路二:动态规划
时间复杂度:O(n)
空间复杂度:O(n)
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> countBits(int n) {
vector<int> bits(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
bits[i] = bits[i & (i - 1)] + 1;
}
return bits;
}
};
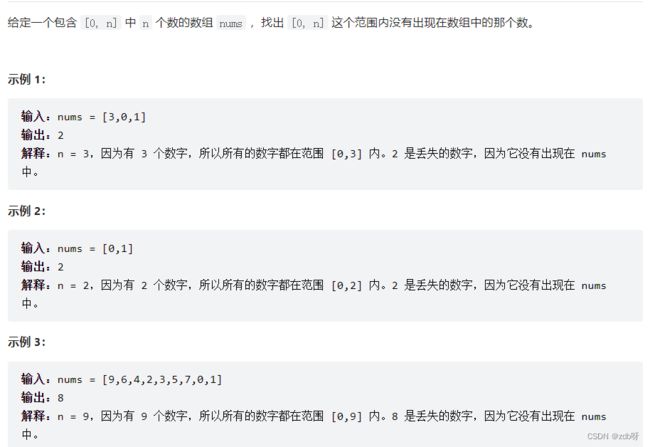
268. 丢失的数字【简单】
class Solution {
public:
int missingNumber(vector<int>& nums) {
int res = 0;
int n = nums.size();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
res ^= nums[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
res ^= i;
}
return res;
}
};
389. 找不同【简单】
思路一:哈希表
时间复杂度:O(n)
空间复杂度:O(n)
- 思路二:位运算
时间复杂度:O(n)
空间复杂度:O(1)
class Solution {
public:
char findTheDifference(string s, string t) {
int res = 0;
for(auto i : s)
res ^= i;
for(auto i : t)
res ^= i;
return res;
}
};
思路三:求和
class Solution {
public:
char findTheDifference02(string s, string t) {
int s_sum = 0;
int t_sum = 0;
for (char ch : s)
s_sum += ch;
for (char ch : t)
t_sum += ch;
return t_sum - s_sum;
}
};
693. 交替位二进制数【简单】
class Solution {
public:
bool hasAlternatingBits(int n) {
long a = n ^ (n >> 1); //如果n交替,则a的二进制全为1
return (a & (a + 1)) == 0;
}
};
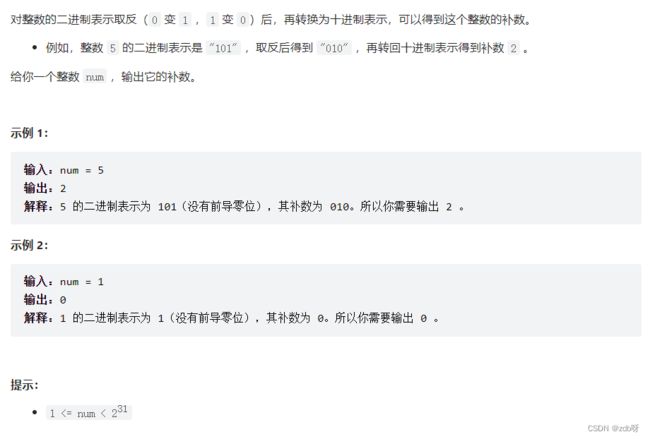
476. 数字的补数【简单】
class Solution {
public:
int findComplement(int num) {
long a = 1;
while(true){
if(num >= a){
a <<= 1; // 等价于 a *= 2;
}else{
return a - num - 1;
}
}
}
};