『数据结构』哈希表
什么是哈希
顺序结构以及平衡树中,元素关键码与其存储位置之间没有对应的关系,因此在查找一个元素时,必须要经过关键码的多次比较。顺序查找时间复杂度为O(N),平衡树中为树的高度,即 O ( l o g 2 N ) O(log_2N) O(log2N),搜索的效率取决于搜索过程中元素的比较次数。
理想的搜索方法:可以不经过任何比较,一次直接从表中得到要搜索的元素。如果构造一种存储结构,通过某种函数(hashFunc)使元素的存储位置与它的关键码之间能够建立一一映射的关系,那么在查找时通过该函数可以很快找到该元素。
- 向该存储结构插入元素:根据待插入元素的关键码,一次函数计算出该元素的存储位置并按此位置进行存放。
- 在该存储结构中搜索元素:对元素的关键码进行同样的计算,把求得的函数值当做元素的存储位置,在结构中按此位置取元素比较,若关键码相等,则搜索成功。
该方式即为哈希(散列)方法,哈希方法中使用的转换函数称为哈希(散列)函数,构造出来的结构称为哈希表(Hash Table)(或称散列表)。
下面我们来看一个例子:
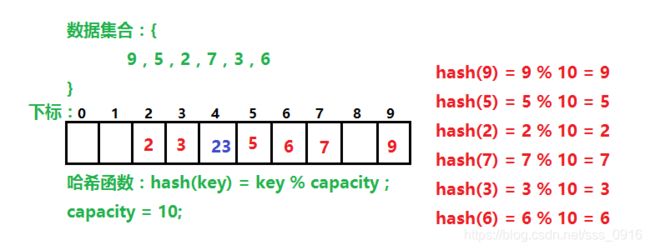
数据集合{9,5,2,7,3,6};存到一个哈希表中,哈希函数设置为:hash(key) = key % capacity;capacity为存储元素底层空间总的大小。

从上面的例子可以看出,如果我们需要对5这个数据进行搜索,只需要使用哈希函数计算出数据5所在的下标,就可以直接找到5这个数据,不必进行多次关键码的比较,因此搜索速度比较快。
但是如果我们向集合中插入23会如何呢?
我们将23带入哈希函数,得到结果为3,但是数组中下标为3的位置已经有元素了,这该怎么办呢?
哈希冲突
对于两个数据元素的关键字 k i k_i ki和 k j k_j kj ( i ≠ j ) (i \ne j) (i=j),但有: h a s h ( k i ) = = h a s h ( k j ) hash(k_i) == hash(k_j) hash(ki)==hash(kj),即:不同关键字通过相同哈希函数计算出相同的哈希地址,这种现象称为哈希冲突或哈希碰撞。
我们把具有不同关键码而具有相同哈希地址的数据元素称为“同义词”。
发生哈希冲突该如何处理呢?
哈希函数
引起哈希冲突的一个原因可能是:哈希函数设计不够合理。
哈希函数设计原则:
- 哈希函数的定义域必须包括需要存储的全部关键码,而如果散列表允许有m个地址时,其值域必须在0到m-1之间。
- 哈希函数计算出来的地址能均匀分布在整个空间中。
- 哈希函数应该比较简单。
常见哈希函数:
- 直接定址法。
取关键字的某个线性函数为哈希函数: h a s h ( k e y ) = A ∗ k e y + B hash(key) = A * key + B hash(key)=A∗key+B。
优点:简单、均匀。
缺点:需要事先知道关键字的分布情况。
使用场景:适合查找比较小且连续的情况。 - 除留余数法。
设哈希表中允许的地址数为m,取一个不大于m,但最接近或者等于m的质数p作为除数,按照哈希函数: h a s h ( k e y ) = k e y % p ( p < = m ) hash(key) = key \% p(p <= m) hash(key)=key%p(p<=m),将关键码转换成哈希地址。 - 平方取中法。
假设关键字为1234,对它平方就是1522756,抽取中间的3位277作为哈希地址;再比如关键字为4321,对它平方就是18671041,抽取中间的3位671(或710)作为哈希地址。平方取中法比较适合:不知道关键字的分布,而位数又不是很大的情况。 - 折叠法。
折叠法是将关键字从左到右分割成位数相等的几部分(最后一部分位数可以短些),然后将这几部分叠加求和,并按哈希表表长,取后几位作为哈希地址。 - 随机数法。
选择一个随机函数,取关键字的随机函数值为它的哈希地址,即 H ( k e y ) = r a n d o m ( k e y ) H(key) = random(key) H(key)=random(key),其中random为随机数函数。
注意:哈希函数设计的越精妙,产生哈希冲突的可能性就越低,但是无法避免哈希冲突。
哈希冲突解决方法
解决哈希冲突的两种常见方法是:闭散列和开散列。
闭散列
闭散列,也叫开放定址法,当发生哈希冲突的时候,如果哈希表未被装满,说明在哈希表中必然还有空位置,那么可以把key存放到冲突位置的下一个空位置去。那如何寻找下一个空位置?
线性探测
使用线性探测的方法,来寻找下一个位置。
比如前面的例子,现在需要插入元素23,先通过哈希函数计算出哈希地址,hashAddr为3,因此23理论上应该插入在下标为3的位置,但是这个位置已经有了元素3,即发生了哈希冲突。
线性探测:从发生冲突的位置开始,依次向后探测,直到寻找到下一个空位置为止。
插入:
删除:
采用闭散列处理哈希冲突时,不能随便物理删除哈希表中已有的元素,若直接删除元素会影响其他元素的搜索。因此线性探测采用标记的伪删除法来删除一个元素。
线性探测的模拟实现:
#pragma once
#include 上述哈希表还存在以下缺陷:
- 只能存储key为整型的元素,其他类型怎么解决?
可以使用字符哈希算法,将字符串按照固定的算法转化为整型数据。
各种字符哈希算法 - 除留余数法,最好模一个素数,如何每次快速取一个类似两倍关系的素数?
const int PRIMECNT = 28;
const size_t PrimeList[PRIMECNT] = {
53ul, 97ul, 193ul, 389ul, 769ul,
1543ul, 3079ul, 6151ul, 12289ul, 24593ul,
49157ul, 98317ul, 196613ul, 393241ul, 786433ul,
1572869ul, 3145739ul, 6291469ul, 12582917ul, 25165843ul,
50331653ul, 100663319ul, 201326611ul, 402653189ul, 805306457ul,
1610612741ul, 3221225473ul, 4294967291ul
};
// 获取下一个素数
size_t GetNextPrime(size_t prime){
for(size_t i = 0; i < PRIMECNT; ++i){
if(PrimeList[i] > prime){
return PrimeList[i];
}
}
return PrimeList[i];
}
- 什么时机增容,如何增容?
哈希表的负载因子定义为: α = 填 入 表 中 的 元 素 个 数 / 哈 希 表 的 长 度 \alpha = 填入表中的元素个数 / 哈希表的长度 α=填入表中的元素个数/哈希表的长度。
α \alpha α是哈希表装满程度的标志因子。由于表长是定值, α \alpha α与“填入表中的元素个数”成正比,所以 α \alpha α越大,表明填入表中的元素越多,产生冲突的可能性就越大;反之, α \alpha α越小,表明填入表中的元素越少,产生冲突的可能性就越小。实际上,哈希表的平均查找长度是负载因子 α \alpha α的函数,只是不同处理冲突的方法有不同的函数。
对于开放定址法,负载因子是特别重要的因素,应严格限制在0.7-0.8以下。超过0.8,查表时的CPU缓存不命中(cache missing)按照指数曲线上升。因此,一些采用开放定址法的hash库,如Java的系统库限制了负载因子为0.75,超过这个值将增容。
void CheckCapacity(){
if(_size * 10 / _ht.Capacity() >= 7){
// 新建一个哈希表,将旧表中的元素全部插入到新表中
HashTable<T> _new_ht(GetNextPrime(_ht.Capacity());
for(size_t i = 0; i < _ht.Capacity(); ++i){
if(_ht[i]._state == EXIST){
_new_ht.Insert(_ht[i]._value);
}
}
// 交换两个哈希表
Swap(_new_ht);
}
}
线性探测优缺点:
- 优点:实现非常简单。
- 缺点:一旦发生哈希冲突,所有的冲突连在一起,容易产生数据堆积,即:不同关键码占据了可利用的空位置,使得寻找某关键码的位置需要许多次比较,导致搜索效率降低。
二次探测
线性探测的缺点是产生冲突的数据堆积在一起,这与其找下一个空位置有关系,因为找空位置的方式就是挨个往后去找,因此二次探测避免了该问题,找下一个空位置的方法为: H i = ( H 0 + i 2 ) % m H_i = (H_0 + i^2) \% m Hi=(H0+i2)%m,或者 H i = ( H 0 − i 2 ) % m H_i = (H_0 - i^2) \%m Hi=(H0−i2)%m。其中: i = 1 , 2 , 3... , H 0 i = 1,2,3...,H_0 i=1,2,3...,H0是通过哈希函数 H a s h F u n c ( k e y ) HashFunc(key) HashFunc(key)对元素的关键码key进行计算得到的位置,m是表的大小。
对于前面的例子,插入元素23结果如下:
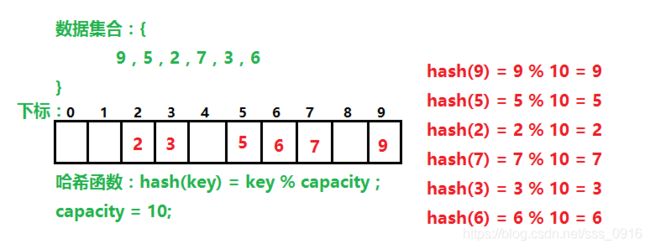
插入元素为23, H 0 = 23 % 10 = 3 H_0=23 \%10=3 H0=23%10=3,由于下标为3的空间已经有元素,所以计算 H 1 = ( H 0 + 1 2 ) % 10 = 4 H_1 = (H_0 + 1^2)\%10 = 4 H1=(H0+12)%10=4,发现4处没有元素,进行插入,如果4处有元素,继续向后计算。
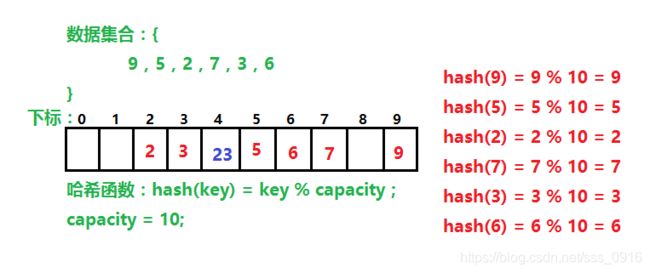
研究表明:当表的长度为质数且表的负载因子 α \alpha α不超过0.5时,新的表项一定能够插入,而且任何一个位置都不会被探查两次。因此只要表中有一半的空位置,就不会存在表满的问题。在搜索时可以不考虑表装满的情况,但在插入时必须确保表的负载因子 α \alpha α不超过0.5,如果超出,必须扩容。
总结:闭散列最大的缺陷就是空间利用率比较低,这也是哈希的缺陷。
开散列
开散列法又叫链地址法(开链法),首先对关键码集合用散列函数计算散列地址,具有相同地址的关键码归于同一子集合,每一个子集合称为一个桶,桶中的元素通过一个单链表链接起来,各链表的头结点存储在哈希表中。
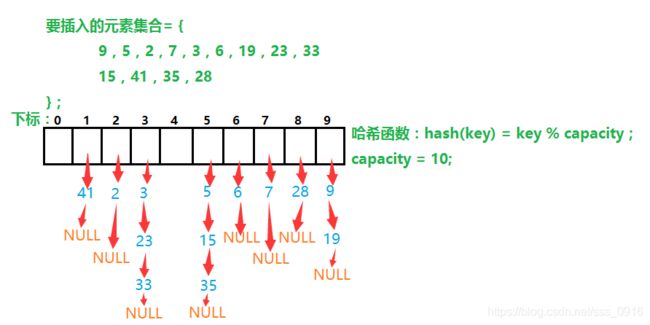
从上图可以看出,开散列的每个桶中放的都是发生哈希冲突的元素。
开散列的模拟实现
C++版:
#pragma once
#include 开散列增容:
桶的个数是一定的,随着元素的不断插入,每个桶中元素的个数不断增多,极端情况下,可能会导致一个桶中链表结点非常多,会影响哈希表的性能,因此在一定条件下需要对哈希表进行增容,那该条件怎么确认呢?开散列最好的情况是:每个哈希桶中刚好挂一个结点,再继续插入元素时,每一次都会发生哈希冲突,因此,在元素个数刚好等于桶的个数时,可以给哈希表增容。
void CheckCapacity(){
// 统计元素的数量
size_t bucketCnt = BucketCnt();
// 元素的数量等于桶的数量,扩容
if(_size == bucketCnt){
// 创建新表
HashBucket<T, HashFunc> _newht(bucketCnt);
// 遍历旧表,将其中每一个结点挂入新表
for(size_t bucket_idx = 0; bucket_idx < bucketCnt; ++bucket_idx){
Node* cur = _ht[bucket_idx];
while(cur){
// 将该结点从原表中拆出来
_ht[bucket_idx] = cur->_next;
// 计算在新表中的桶号
size_t bucketNo = _newht.HashFunc(cur->_data);
// 将该节点插入到新表中
cur->_next = _newht._ht[bucketNo];
_newht._ht[bucketNo] = cur;
cur = _ht[bucket_idx];
}
}
_newht._size = _size;
// 新表旧表交换
this->Swap(_newht);
}
}
开散列处理溢出,需要增设链接指针,似乎增加了存储开销。事实上:由于闭散列必须保持大量的空间以确保搜索效率,如二次探测要求负载因子 α < 0.7 \alpha<0.7 α<0.7,而表项所占空间又比指针大的多,所以开散列相对于闭散列更加节省空间。
Java版:
public class MyHashMap {
public static class Node {
public int key;
public int value;
public Node next = null;
public Node(int key, int value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return String.format("{%d, %d}", this.key, this.value);
}
}
private Node[] arr = new Node[101];
private int size = 0;
private static final double FACTOR = 0.75;
// 插入
public void put(int key, int value) {
int index = key % this.arr.length;
Node newNode = new Node(key, value);
newNode.next = this.arr[index];
this.arr[index] = newNode;
++this.size;
if ((double)this.size / this.arr.length > FACTOR) {
realloc();
}
}
// 查找
public Integer get(int key) {
int index = key % this.arr.length;
for (Node curNode = this.arr[index]; curNode != null; curNode = curNode.next) {
if (curNode.key == key) {
return curNode.value;
}
}
return null;
}
// 删除
public Integer remove(int key) {
int index = key % this.arr.length;
Node curNode = this.arr[index];
if (curNode == null) {
return null;
}
--this.size;
if (curNode.key == key) {
return curNode.value;
}
while (curNode.next != null) {
if (curNode.next.key == key) {
curNode.next = curNode.next.next;
break;
}
}
return curNode.value;
}
private void realloc() {
Node[] newArr = new Node[this.arr.length * 2 + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < this.arr.length; ++i) {
Node curNode = this.arr[i];
while (curNode != null) {
int index = curNode.key % newArr.length;
Node newNode = new Node(curNode.key, curNode.value);
newNode.next = newArr[index];
newArr[index] = newNode;
curNode = curNode.next;
}
}
this.arr = newArr;
}
}