第02天-Java数据结构和算法
目录
021_单链表新浪面试题
单链表面试题(新浪、百度、腾讯)
代码实现
022_单链表腾讯面试题
图解
代码实现
023_单链表百度面试题
图解
代码实现
024_双向链表增删改查分析图解
双向链表应用实例
图解
代码实现
026_双向链表功能测试和小结
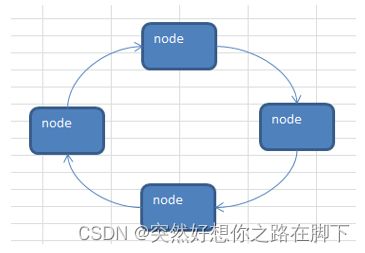
027_环形链表介绍和约瑟夫问题
单向环形链表应用场景
单向环形链表介绍
图解
编辑028_约瑟夫问题分析图解和实现(1)
图解
Josephu问题
029_约瑟夫问题分析图解和实现(2)
代码实现
030_栈的应用场景和介绍
栈的一个实际需求
栈的介绍(1)
栈的介绍(2)
栈的应用场景
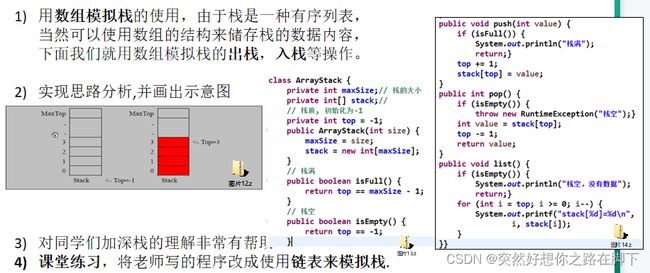
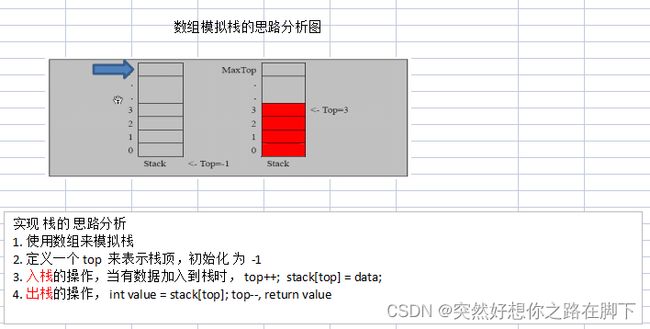
031_栈的思路分析和代码实现
栈的快速入门
图解
代码实现
032_栈的功能测试和小结
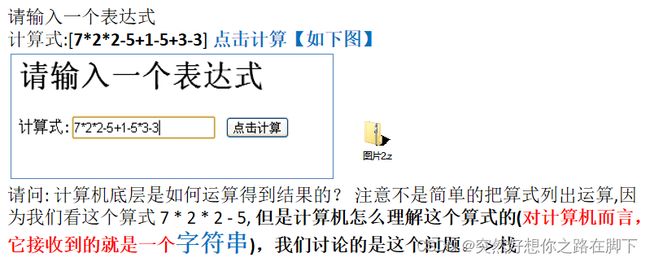
033_栈实现综合计算器-思路分析(1)
图解
034_栈实现综合计算器-代码实现(2)
035_栈实现综合计算器-代码实现(3)
036_前缀_中缀_后缀表达式规则
前缀表达式的计算机求值
中缀表达式
后缀表达式
后缀表达式的计算机求值
037_逆波兰计算器分析和实现
逆波兰计算器
代码实现
039_中缀转后缀表达式思路分析
介绍1
介绍2
图解
040_中缀转后缀表达式代码实现(1)
042_完整版逆波兰计算器和小结
代码实现
021_单链表新浪面试题
单链表面试题(新浪、百度、腾讯)
代码实现
package nanjing.linkedlist;
/**
* 单链表应用实例
*
* @author xizheng
* @date 2023-01-28 15:03:26
*/
public class SingleLinkedListDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//进行测试
//先创建节点
HeroNode hero1 = new HeroNode(1, "宋江", "及时雨");
HeroNode hero2 = new HeroNode(2, "卢俊义", "玉麒麟");
HeroNode hero3 = new HeroNode(3, "吴用", "智多星");
HeroNode hero4 = new HeroNode(4, "林冲", "豹子头");
//创建要给的链表
SingleLinkedList singleLinkedList = new SingleLinkedList();
//加入
// singleLinkedList.add(hero1);
// singleLinkedList.add(hero4);
// singleLinkedList.add(hero2);
// singleLinkedList.add(hero3);
//加入按照编号的顺序
singleLinkedList.addByOrder(hero1);
singleLinkedList.addByOrder(hero4);
singleLinkedList.addByOrder(hero2);
singleLinkedList.addByOrder(hero3);
//显示一把
singleLinkedList.list();
//测试修改节点的代码
HeroNode newHeroNode = new HeroNode(2, "小卢", "玉麒麟~~");
singleLinkedList.update(newHeroNode);
System.out.println("修改后的链表情况~~");
singleLinkedList.list();
//删除一个节点
// singleLinkedList.del(1);
// singleLinkedList.del(4);
// System.out.println("删除后的链表情况~~");
// singleLinkedList.list();
//测试一下 求单链表中有效节点的个数
System.out.println("有效的节点个数=" + getLength(singleLinkedList.getHead()));//2
//测试一下看看是否得到了倒数第K个节点
HeroNode res = findLastIndexNode(singleLinkedList.getHead(), 3);
System.out.println("res=" + res);
}
//查找单链表中的倒数第k个结点 【新浪面试题】
//思路
//1. 编写一个方法,接收head节点,同时接收一个index
//2. index 表示是倒数第index个节点
//3. 先把链表从头到尾遍历,得到链表的总的长度 getLength
//4. 得到size 后,我们从链表的第一个开始遍历 (size-index)个,就可以得到
//5. 如果找到了,则返回该节点,否则返回nulll
public static HeroNode findLastIndexNode(HeroNode head, int index) {
//判断如果链表为空,返回null
if(head.next == null) {
return null;//没有找到
}
//第一个遍历得到链表的长度(节点个数)
int size = getLength(head);
//第二次遍历 size-index 位置,就是我们倒数的第K个节点
//先做一个index的校验
if(index <=0 || index > size) {
return null;
}
//定义给辅助变量, for 循环定位到倒数的index
HeroNode cur = head.next; //3 // 3 - 1 = 2
for(int i =0; i< size - index; i++) {
cur = cur.next;
}
return cur;
}
//方法:获取到单链表的节点的个数(如果是带头节点的链表,需要不统计头节点)
/**
*
* @param head 链表的头节点
* @return 返回的就是有效节点的个数
*/
public static int getLength(HeroNode head) {
if(head.next == null) {//空链表
return 0;
}
int length = 0;
//定义一个辅助的变量,这里我们没有统计头节点
HeroNode cur = head.next;
while (cur != null) {
length++;
cur = cur.next; //遍历
}
return length;
}
}
//定义SingleLinkedList 管理我们的英雄
class SingleLinkedList {
//先初始化一个头节点,头节点不要动,不存放具体的数据
private HeroNode head = new HeroNode(0, "", "");
//返回头节点
public HeroNode getHead() {
return head;
}
//添加节点到单向链表
//思路,当不考虑编号顺序时
//1、找到当前链表的最后节点
//2、将最后这个节点的next 指向 新的节点
public void add(HeroNode heroNode) {
//因为head节点不能动,因此我们需要一个辅助遍历 temp
HeroNode temp = head;
while (true) {
//找到链表的最后
if(temp.next == null) {
break;
}
//如果没有找到最后,将temp后移
temp = temp.next;
}
//当退出while循环时,temp就指向了链表的最后
//将最后这个节点的next指向 新的节点
temp.next = heroNode;
}
//第二种方式在添加英雄时,根据排名将英雄插入到指定位置
//(如果有这个排名,则添加是吧,并给出提示)
public void addByOrder(HeroNode heroNode) {
//因为头节点不能动,因此我们仍然通过一个辅助指针(变量)来帮助找到添加的位置
//因为单链表,因为我们找的temp 是位于 添加位置的前一个节点,否则插入不了
HeroNode temp = head;
boolean flag = false;//false标志添加的编号是否存在,默认为false
while (true) {
if(temp.next == null) {//说明temp已经在链表的最后
break;
}
if(temp.next.no > heroNode.no) {//位置找到,就在temp的后面插入
break;
} else if(temp.next.no == heroNode.no) {//说明希望添加的heroNode的编号已然存在
flag = true; //说明编号存在
break;
}
temp = temp.next;//后移,遍历当前链表
}
//判断flag 的值
if(flag) { //不能添加,说明编号存在
System.out.printf("准备插入的英雄的编号 %d 已经存在了, 不能加入\n", heroNode.no);
} else {
//插入到链表中,temp的后面
heroNode.next = temp.next;
temp.next = heroNode;
}
}
//修改节点的信息,根据no编号来修改,即no编号不能改.
//说明
//1.根据 newHeroNode的 no 来修改即可
public void update(HeroNode newHeroNode) {
//判断是否空
if(head.next == null) {
System.out.printf("链表为空");
return;
}
//找到需要修改的节点,根据no编号
//定义一个辅助变量
HeroNode temp = head.next;
boolean flag = false;//表示是否找到该节点
while (true) {
if(temp == null) {
break;//已经遍历完链表
}
if(temp.no == newHeroNode.no) {
//找到
flag = true;
break;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
//根据flag 判断是否找到要修改的节点
if(flag) {
temp.name = newHeroNode.name;
temp.nickname = newHeroNode.nickname;
} else { //没有找到
System.out.printf("没有找到 编号 %d 的节点,不能修改\n", newHeroNode.no);
}
}
//删除节点
//思路
//1. head 不能动,因此我们需要一个temp辅助节点找到待删除节点的前一个节点
//2. 说明我们在比较时,是temp.next.no 和 需要删除的节点的no比较
public void del(int no) {
HeroNode temp = head;
boolean flag = false; // 标志是否找到待删除节点的
while(true) {
if(temp.next == null) { //已经到链表的最后
break;
}
if(temp.next.no == no) {
//找到的待删除节点的前一个节点temp
flag = true;
break;
}
temp = temp.next; //temp后移,遍历
}
//判断flag
if(flag) { //找到
//可以删除
temp.next = temp.next.next;
}else {
System.out.printf("要删除的 %d 节点不存在\n", no);
}
}
//显示链表[遍历]
public void list() {
//判断链表是否为空
if(head.next == null) {
System.out.println("链表为空");
return;
}
//因为头节点,不能动,因此我们需要一个辅助变量来遍历
HeroNode temp = head.next;
while (true) {
//判断是否到链表最后
if(temp == null) {
break;
}
//输出节点的信息
System.out.println(temp);
//将temp后移,一定小心
temp = temp.next;
}
}
}
//定义HeroNode, 每个HeroNode 对象就是一个节点
class HeroNode {
public int no;
public String name;
public String nickname;
public HeroNode next; //指向下一个节点
//构造器
public HeroNode(int no, String name, String nickname) {
this.no = no;
this.name = name;
this.nickname = nickname;
}
//为了显示方法,我们重写toString
@Override
public String toString() {
return "HeroNode{" +
"no=" + no +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", nickname='" + nickname + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
022_单链表腾讯面试题
图解
代码实现
//将单链表反转
public static void reversetList(HeroNode head) {
//如果当前链表为空,或者只有一个节点,无需反转,直接返回
if(head.next == null || head.next.next == null) {
return ;
}
//定义一个辅助的指针(变量),帮助我们遍历原来的链表
HeroNode cur = head.next;
HeroNode next = null;// 指向当前节点[cur]的下一个节点
HeroNode reverseHead = new HeroNode(0, "", "");
//遍历原来的链表,每遍历一个节点,就将其取出,并放在新的链表reverseHead 的最前端
//动脑筋
while(cur != null) {
next = cur.next;//先暂时保存当前节点的下一个节点,因为后面需要使用
cur.next = reverseHead.next;//将cur的下一个节点指向新的链表的最前端
reverseHead.next = cur; //将cur 连接到新的链表上
cur = next;//让cur后移
}
//将head.next 指向 reverseHead.next , 实现单链表的反转
head.next = reverseHead.next;
}023_单链表百度面试题
图解
代码实现
//方式2:
//可以利用栈这个数据结构,将各个节点压入到栈中,然后利用栈的先进后出的特点,就实现了逆序打印的效果
public static void reversePrint(HeroNode head) {
if(head.next == null) {
return;//空链表,不能打印
}
//创建要给一个栈,将各个节点压入栈
Stack stack = new Stack();
HeroNode cur = head.next;
//将链表的所有节点压入栈
while(cur != null) {
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.next; //cur后移,这样就可以压入下一个节点
}
//将栈中的节点进行打印,pop 出栈
while (stack.size() > 0) {
System.out.println(stack.pop()); //stack的特点是先进后出
}
} 024_双向链表增删改查分析图解
双向链表应用实例
图解
代码实现
package nanjing.linkedlist;
/**
* 双向链表演示
*
* @author xizheng
* @date 2023-01-29 10:04:43
*/
public class DoubleLinkedListDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
}
//创建一个双向链表的类
class DoubleLinkedList {
//先初始化一个头节点,头节点不要动,不存放具体的数据
private HeroNode2 head = new HeroNode2(0, "", "");
//返回头节点
public HeroNode2 getHead() {
return head;
}
//遍历双向链表的方法
//显示链表[遍历]
public void list() {
// 判断链表是否为空
if(head.next == null) {
System.out.println("链表为空");
return;
}
// 因为头节点,不能动,因此我们需要一个辅助变量来遍历
HeroNode2 temp = head.next;
while (true) {
// 判断是否到链表最后
if(temp == null) {
break;
}
// 输出节点的信息
System.out.println(temp);
temp = temp.next;
}
}
// 添加一个节点到双向链表的最后
public void add(HeroNode2 heroNode) {
// 因为head节点不能动,因此我们需要一个辅助遍历 temp
HeroNode2 temp = head;
// 遍历链表,找到最后
while (true) {
//找到链表的最后
if(temp.next == null) {
break;
}
// 如果没有找到最后,将temp后移
temp = temp.next;
}
//当退出while循环时,temp就指向了链表的最后
//形成一个双向链表
temp.next = heroNode;
heroNode.pre = temp;
}
//修改一个节点的内容,可以看到双向链表的节点内容修改和单向链表一样
//只是 节点类型改成 HeroNode2
public void update(HeroNode2 newHeroNode) {
//判断是否空
if(head.next == null) {
System.out.println("链表为空~");
return;
}
//找到需要修改的节点,根据no编号
//定义一个辅助变量
HeroNode2 temp = head.next;
boolean flag = false;//表示是否找到该节点
while (true) {
if(temp == null) {
break;//已经遍历完链表
}
if(temp.no == newHeroNode.no) {
// 找到
flag = true;
break;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
// 根据flag判断是否找到要修改的节点
if(flag) {
temp.name = newHeroNode.name;
temp.nickname = newHeroNode.nickname;
} else {//没有找到
System.out.printf("没有找到 编号 %d 的节点,不能修改\n", newHeroNode.no);
}
}
//从双向链表中删除一个节点
//说明
//1 对于双向链表,我们可以直接找到要删除的这个节点
//2 找到后,自我删除即可
public void del(int no) {
//判断当前链表是否为空
if(head.next == null) { //空链表
System.out.printf("链表为空,无法删除");
return;
}
HeroNode2 temp = head.next; //辅助变量(指针)
boolean flag = false;//标志是否找到待删除节点的
while (true) {
if(temp == null) { //已经到链表的最后
break;
}
if(temp.no == no) {
//找到的待删除节点的前一个节点temp
flag = true;
break;
}
temp = temp.next;//temp后移,遍历
}
// 判断flag
if(flag) { //找到
//可以删除
//temp.next = temp.next.next;[单向链表]
temp.pre.next = temp.next;
//这里我们的代码有问题?
//如果是最后一个节点,就不需要执行下面这句话,否则出现空指针
if(temp.next != null) {
temp.next.pre = temp.pre;
}
} else {
System.out.printf("要删除的 %d 节点不存在\n", no);
}
}
}
//定义HeroNode2, 每个HeroNode 对象就是一个节点
class HeroNode2 {
public int no;
public String name;
public String nickname;
public HeroNode2 next;//指向下一个节点,默认为null
public HeroNode2 pre;//指向前一个节点,默认为null
//构造器
public HeroNode2(int no, String name, String nickname) {
this.no = no;
this.name = name;
this.nickname = nickname;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "HeroNode2{" +
"no=" + no +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", nickname='" + nickname + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
026_双向链表功能测试和小结
027_环形链表介绍和约瑟夫问题
单向环形链表应用场景
单向环形链表介绍
图解
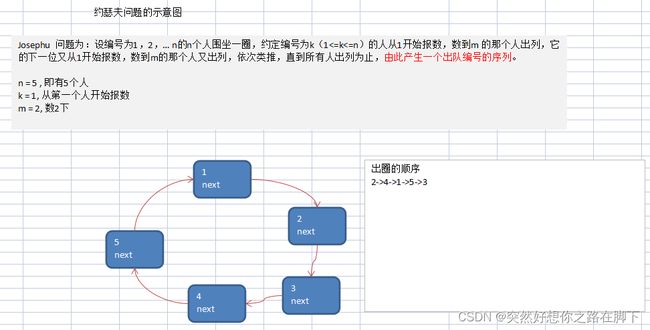 028_约瑟夫问题分析图解和实现(1)
028_约瑟夫问题分析图解和实现(1)
图解
Josephu问题
029_约瑟夫问题分析图解和实现(2)
代码实现
package nanjing.linkedlist;
/**
* 约瑟夫问题
*
* @author xizheng
* @date 2023-01-29 11:25:32
*/
public class Josepfu {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 测试一把看看构建环形链表,和遍历是否ok
CircleSingleLinkedList circleSingleLinkedList = new CircleSingleLinkedList();
circleSingleLinkedList.addBoy(125);// 加入5个小孩节点
circleSingleLinkedList.showBoy();
//测试一把小孩出圈是否正确
circleSingleLinkedList.countBoy(10, 20, 125); // 2->4->1->5->3
//String str = "7*2*2-5+1-5+3-3";
}
}
//创建一个环形的单向链表
class CircleSingleLinkedList {
//创建一个first节点,当前没有编号
private Boy first = null;
//添加小孩节点,构建成一个环形的链表
public void addBoy(int nums) {
// nums 做一个数据校验
if(nums < 1) {
System.out.println("nums的值不正确");
return;
}
Boy curBoy = null;//辅助指针,帮助构建环形链表
//使用for来创建我们的环形链表
for (int i = 1; i < nums; i++) {
//根据编号,创建小孩节点
Boy boy = new Boy(i);
//如果是第一个小孩
if(i == 1) {
first = boy;
first.setNext(first);//构成环
curBoy = first;//让curBoy指向第一个小孩
} else {
curBoy.setNext(boy);
boy.setNext(first);
curBoy = boy;
}
}
}
//遍历当前的环形链表
public void showBoy() {
//判断链表是否为空
if(first == null) {
System.out.println("没有任何小孩~~");
return;
}
//因为first不能动,因此我们仍然使用一个辅助指针完成遍历
Boy curBoy = first;
while (true) {
System.out.printf("小孩的编号 %d \n", curBoy.getNo());
if(curBoy.getNext() == first) { //说明已经遍历完毕
break;
}
curBoy = curBoy.getNext();//curBoy后移
}
}
//根据用户的输入,计算出小孩出圈的顺序
/**
*
* @param startNo 表示从第几个小孩开始数数
* @param countNum 表示数几下
* @param nums 表示最初有多少小孩在圈中
*/
public void countBoy(int startNo, int countNum, int nums) {
// 先对数据进行校验
if (first == null || startNo < 1 || startNo > nums) {
System.out.println("参数输入有误, 请重新输入");
return;
}
// 创建要给辅助指针,帮助完成小孩出圈
Boy helper = first;
// 需求创建一个辅助指针(变量) helper , 事先应该指向环形链表的最后这个节点
while (true) {
if (helper.getNext() == first) { // 说明helper指向最后小孩节点
break;
}
helper = helper.getNext();
}
//小孩报数前,先让 first 和 helper 移动 k - 1次
for(int j = 0; j < startNo - 1; j++) {
first = first.getNext();
helper = helper.getNext();
}
//当小孩报数时,让first 和 helper 指针同时 的移动 m - 1 次, 然后出圈
//这里是一个循环操作,知道圈中只有一个节点
while(true) {
if(helper == first) { //说明圈中只有一个节点
break;
}
//让 first 和 helper 指针同时 的移动 countNum - 1
for(int j = 0; j < countNum - 1; j++) {
first = first.getNext();
helper = helper.getNext();
}
//这时first指向的节点,就是要出圈的小孩节点
System.out.printf("小孩%d出圈\n", first.getNo());
//这时将first指向的小孩节点出圈
first = first.getNext();
helper.setNext(first); //
}
System.out.printf("最后留在圈中的小孩编号%d \n", first.getNo());
}
}
//创建一个Boy类,表示一个节点
class Boy {
private int no;//编号
private Boy next;//指向下一个节点,默认null
public Boy(int no) {
this.no = no;
}
public int getNo() {
return no;
}
public void setNo(int no) {
this.no = no;
}
public Boy getNext() {
return next;
}
public void setNext(Boy next) {
this.next = next;
}
}
030_栈的应用场景和介绍
栈的一个实际需求
栈的介绍(1)
栈的介绍(2)
栈的应用场景
031_栈的思路分析和代码实现
栈的快速入门
图解
代码实现
package com.nanjing.stack;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* 数组堆栈演示
*
* @author xizheng
* @date 2023-01-29 13:51:59
*/
public class ArrayStackDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//测试一下ArrayStack 是否正确
//先创建一个ArrayStack对象->表示栈
ArrayStack stack = new ArrayStack(4);
String key = "";
boolean loop = true; //控制是否退出菜单
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while(loop) {
System.out.println("show: 表示显示栈");
System.out.println("exit: 退出程序");
System.out.println("push: 表示添加数据到栈(入栈)");
System.out.println("pop: 表示从栈取出数据(出栈)");
System.out.println("请输入你的选择");
key = scanner.next();
switch (key) {
case "show":
stack.list();
break;
case "push":
System.out.println("请输入一个数");
int value = scanner.nextInt();
stack.push(value);
break;
case "pop":
try {
int res = stack.pop();
System.out.printf("出栈的数据是 %d\n", res);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
break;
case "exit":
scanner.close();
loop = false;
break;
default:
break;
}
}
System.out.println("程序退出~~~");
}
}
//定义一个 ArrayStack 表示栈
class ArrayStack {
private int maxSize; //栈的大小
private int[] stack; //数组,数组模拟栈,数据就放在该数组
private int top = -1; //top表示栈顶,初始化为-1
//构造器
public ArrayStack(int maxSize) {
this.maxSize = maxSize;
stack = new int[this.maxSize];
}
//栈满
public boolean isFull() {
return top == maxSize - 1;
}
//栈空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return top == -1;
}
//入栈-push
public void push(int value) {
//先判断栈是否满
if(isFull()) {
System.out.println("栈满");
return;
}
top++;
stack[top] = value;
}
//出栈-pop, 将栈顶的数据返回
public int pop() {
//先判断栈是否空
if(isEmpty()) {
//抛出异常
throw new RuntimeException("栈空,没有数据~");
}
int value = stack[top];
top--;
return value;
}
//显示栈的情况[遍历栈], 遍历时,需要从栈顶开始显示数据
public void list() {
if(isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("栈空,没有数据~~");
return;
}
//需要从栈顶开始显示数据
for(int i = top; i >= 0 ; i--) {
System.out.printf("stack[%d]=%d\n", i, stack[i]);
}
}
}
032_栈的功能测试和小结
033_栈实现综合计算器-思路分析(1)
图解
034_栈实现综合计算器-代码实现(2)
package com.nanjing.stack;
/**
* 计算器
*
* @author xizheng
* @date 2023-01-29 16:34:45
*/
public class Calculator {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//根据前面老师思路,完成表达式的运算
String expression = "7*2*2-5+1-5+3-4"; // 15//如何处理多位数的问题?
//创建两个栈,数栈,一个符号栈
ArrayStack2 numStack = new ArrayStack2(10);
ArrayStack2 operStack = new ArrayStack2(10);
//定义需要的相关变量
int index = 0;//用于扫描
int num1 = 0;
int num2 = 0;
int oper = 0;
int res = 0;
char ch = ' '; //将每次扫描得到char保存到ch
String keepNum = ""; //用于拼接 多位数
//开始while循环的扫描expression
while(true) {
//依次得到expression 的每一个字符
ch = expression.substring(index, index+1).charAt(0);
//判断ch是什么,然后做相应的处理
if(operStack.isOper(ch)) {//如果是运算符
//判断当前的符号栈是否为空
if(!operStack.isEmpty()) {
//如果符号栈有操作符,就进行比较,如果当前的操作符的优先级小于或者等于栈中的操作符,就需要从数栈中pop出两个数,
//在从符号栈中pop出一个符号,进行运算,将得到结果,入数栈,然后将当前的操作符入符号栈
if(operStack.priority(ch) <= operStack.priority(operStack.peek())) {
num1 = numStack.pop();
num2 = numStack.pop();
oper = operStack.pop();
res = numStack.cal(num1, num2, oper);
//把运算的结果如数栈
numStack.push(res);
//然后将当前的操作符入符号栈
operStack.push(ch);
} else {
//如果当前的操作符的优先级大于栈中的操作符, 就直接入符号栈.
operStack.push(ch);
}
}else {
//如果为空直接入符号栈..
operStack.push(ch); // 1 + 3
}
} else { //如果是数,则直接入数栈
//numStack.push(ch - 48); //? "1+3" '1' => 1
//分析思路
//1. 当处理多位数时,不能发现是一个数就立即入栈,因为他可能是多位数
//2. 在处理数,需要向expression的表达式的index 后再看一位,如果是数就进行扫描,如果是符号才入栈
//3. 因此我们需要定义一个变量 字符串,用于拼接
//处理多位数
keepNum += ch;
//如果ch已经是expression的最后一位,就直接入栈
if (index == expression.length() - 1) {
numStack.push(Integer.parseInt(keepNum));
}else{
//判断下一个字符是不是数字,如果是数字,就继续扫描,如果是运算符,则入栈
//注意是看后一位,不是index++
if (operStack.isOper(expression.substring(index+1,index+2).charAt(0))) {
//如果后一位是运算符,则入栈 keepNum = "1" 或者 "123"
numStack.push(Integer.parseInt(keepNum));
//重要的!!!!!!, keepNum清空
keepNum = "";
}
}
}
//让index + 1, 并判断是否扫描到expression最后.
index++;
if (index >= expression.length()) {
break;
}
}
//当表达式扫描完毕,就顺序的从 数栈和符号栈中pop出相应的数和符号,并运行.
while(true) {
//如果符号栈为空,则计算到最后的结果, 数栈中只有一个数字【结果】
if(operStack.isEmpty()) {
break;
}
num1 = numStack.pop();
num2 = numStack.pop();
oper = operStack.pop();
res = numStack.cal(num1, num2, oper);
numStack.push(res);//入栈
}
//将数栈的最后数,pop出,就是结果
int res2 = numStack.pop();
System.out.printf("表达式 %s = %d", expression, res2);
}
}
//先创建一个栈,直接使用前面创建好
//定义一个 ArrayStack2 表示栈, 需要扩展功能
class ArrayStack2 {
private int maxSize; // 栈的大小
private int[] stack; // 数组,数组模拟栈,数据就放在该数组
private int top = -1;// top表示栈顶,初始化为-1
//构造器
public ArrayStack2(int maxSize) {
this.maxSize = maxSize;
stack = new int[this.maxSize];
}
//增加一个方法,可以返回当前栈顶的值, 但是不是真正的pop
public int peek() {
return stack[top];
}
//栈满
public boolean isFull() {
return top == maxSize - 1;
}
//栈空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return top == -1;
}
//入栈-push
public void push(int value) {
//先判断栈是否满
if(isFull()) {
System.out.println("栈满");
return;
}
top++;
stack[top] = value;
}
//出栈-pop, 将栈顶的数据返回
public int pop() {
//先判断栈是否空
if(isEmpty()) {
//抛出异常
throw new RuntimeException("栈空,没有数据~");
}
int value = stack[top];
top--;
return value;
}
//显示栈的情况[遍历栈], 遍历时,需要从栈顶开始显示数据
public void list() {
if(isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("栈空,没有数据~~");
return;
}
//需要从栈顶开始显示数据
for(int i = top; i >= 0 ; i--) {
System.out.printf("stack[%d]=%d\n", i, stack[i]);
}
}
//返回运算符的优先级,优先级是程序员来确定, 优先级使用数字表示
//数字越大,则优先级就越高.
public int priority(int oper) {
if(oper == '*' || oper == '/'){
return 1;
} else if (oper == '+' || oper == '-') {
return 0;
} else {
return -1; // 假定目前的表达式只有 +, - , * , /
}
}
//判断是不是一个运算符
public boolean isOper(char val) {
return val == '+' || val == '-' || val == '*' || val == '/';
}
//计算方法
public int cal(int num1, int num2, int oper) {
int res = 0; // res 用于存放计算的结果
switch (oper) {
case '+':
res = num1 + num2;
break;
case '-':
res = num2 - num1;// 注意顺序
break;
case '*':
res = num1 * num2;
break;
case '/':
res = num2 / num1;
break;
default:
break;
}
return res;
}
}
035_栈实现综合计算器-代码实现(3)
036_前缀_中缀_后缀表达式规则
前缀表达式的计算机求值
中缀表达式
后缀表达式
后缀表达式的计算机求值
037_逆波兰计算器分析和实现
逆波兰计算器
代码实现
package com.nanjing.stack;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Stack;
/**
* 逆波兰计算器
*
* @author xizheng
* @date 2023-01-29 16:41:28
*/
public class PolandNotation {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//完成将一个中缀表达式转成后缀表达式的功能
//说明
//1. 1+((2+3)×4)-5 => 转成 1 2 3 + 4 × + 5 –
//2. 因为直接对str 进行操作,不方便,因此 先将 "1+((2+3)×4)-5" =》 中缀的表达式对应的List
// 即 "1+((2+3)×4)-5" => ArrayList [1,+,(,(,2,+,3,),*,4,),-,5]
//3. 将得到的中缀表达式对应的List => 后缀表达式对应的List
// 即 ArrayList [1,+,(,(,2,+,3,),*,4,),-,5] =》 ArrayList [1,2,3,+,4,*,+,5,–]
String expression = "1+((2+3)*4)-5";//注意表达式
List infixExpressionList = toInfixExpressionList(expression);
System.out.println("中缀表达式对应的List=" + infixExpressionList); // ArrayList [1,+,(,(,2,+,3,),*,4,),-,5]
List suffixExpreesionList = parseSuffixExpreesionList(infixExpressionList);
System.out.println("后缀表达式对应的List" + suffixExpreesionList); //ArrayList [1,2,3,+,4,*,+,5,–]
System.out.printf("expression=%d", calculate(suffixExpreesionList)); // ?
/*
//先定义给逆波兰表达式
//(30+4)×5-6 => 30 4 + 5 × 6 - => 164
// 4 * 5 - 8 + 60 + 8 / 2 => 4 5 * 8 - 60 + 8 2 / +
//测试
//说明为了方便,逆波兰表达式 的数字和符号使用空格隔开
//String suffixExpression = "30 4 + 5 * 6 -";
String suffixExpression = "4 5 * 8 - 60 + 8 2 / +"; // 76
//思路
//1. 先将 "3 4 + 5 × 6 - " => 放到ArrayList中
//2. 将 ArrayList 传递给一个方法,遍历 ArrayList 配合栈 完成计算
List list = getListString(suffixExpression);
System.out.println("rpnList=" + list);
int res = calculate(list);
System.out.println("计算的结果是=" + res);
*/
}
//即 ArrayList [1,+,(,(,2,+,3,),*,4,),-,5] =》 ArrayList [1,2,3,+,4,*,+,5,–]
//方法:将得到的中缀表达式对应的List => 后缀表达式对应的List
public static List parseSuffixExpreesionList(List ls) {
//定义两个栈
Stack s1 = new Stack(); // 符号栈
//说明:因为s2 这个栈,在整个转换过程中,没有pop操作,而且后面我们还需要逆序输出
//因此比较麻烦,这里我们就不用 Stack 直接使用 List s2
//Stack s2 = new Stack(); // 储存中间结果的栈s2
List s2 = new ArrayList(); // 储存中间结果的Lists2
//遍历ls
for(String item: ls) {
//如果是一个数,加入s2
if(item.matches("\\d+")) {
s2.add(item);
} else if (item.equals("(")) {
s1.push(item);
} else if (item.equals(")")) {
//如果是右括号“)”,则依次弹出s1栈顶的运算符,并压入s2,直到遇到左括号为止,此时将这一对括号丢弃
while(!s1.peek().equals("(")) {
s2.add(s1.pop());
}
s1.pop();//!!! 将 ( 弹出 s1栈, 消除小括号
} else {
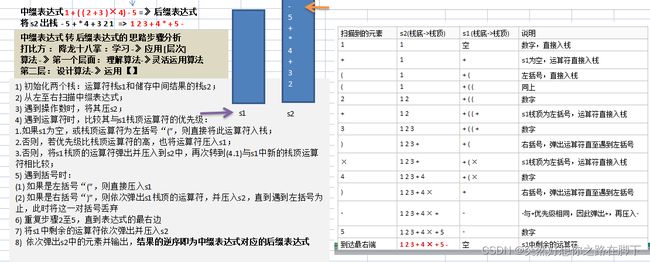
//当item的优先级小于等于s1栈顶运算符, 将s1栈顶的运算符弹出并加入到s2中,再次转到(4.1)与s1中新的栈顶运算符相比较
//问题:我们缺少一个比较优先级高低的方法
while(s1.size() != 0 && Operation.getValue(s1.peek()) >= Operation.getValue(item) ) {
s2.add(s1.pop());
}
//还需要将item压入栈
s1.push(item);
}
}
//将s1中剩余的运算符依次弹出并加入s2
while(s1.size() != 0) {
s2.add(s1.pop());
}
return s2; //注意因为是存放到List, 因此按顺序输出就是对应的后缀表达式对应的List
}
//方法:将 中缀表达式转成对应的List
// s="1+((2+3)×4)-5";
public static List toInfixExpressionList(String s) {
//定义一个List,存放中缀表达式 对应的内容
List ls = new ArrayList();
int i = 0; //这时是一个指针,用于遍历 中缀表达式字符串
String str; // 对多位数的拼接
char c; // 每遍历到一个字符,就放入到c
do {
//如果c是一个非数字,我需要加入到ls
if((c=s.charAt(i)) < 48 || (c=s.charAt(i)) > 57) {
ls.add("" + c);
i++; //i需要后移
} else { //如果是一个数,需要考虑多位数
str = ""; //先将str 置成"" '0'[48]->'9'[57]
while(i < s.length() && (c=s.charAt(i)) >= 48 && (c=s.charAt(i)) <= 57) {
str += c;//拼接
i++;
}
ls.add(str);
}
}while(i < s.length());
return ls;//返回
}
//将一个逆波兰表达式, 依次将数据和运算符 放入到 ArrayList中
public static List getListString(String suffixExpression) {
//将 suffixExpression 分割
String[] split = suffixExpression.split(" ");
List list = new ArrayList();
for(String ele: split) {
list.add(ele);
}
return list;
}
//完成对逆波兰表达式的运算
/*
* 1)从左至右扫描,将3和4压入堆栈;
2)遇到+运算符,因此弹出4和3(4为栈顶元素,3为次顶元素),计算出3+4的值,得7,再将7入栈;
3)将5入栈;
4)接下来是×运算符,因此弹出5和7,计算出7×5=35,将35入栈;
5)将6入栈;
6)最后是-运算符,计算出35-6的值,即29,由此得出最终结果
*/
public static int calculate(List ls) {
// 创建给栈, 只需要一个栈即可
Stack stack = new Stack();
// 遍历 ls
for (String item : ls) {
// 这里使用正则表达式来取出数
if (item.matches("\\d+")) { // 匹配的是多位数
// 入栈
stack.push(item);
} else {
// pop出两个数,并运算, 再入栈
int num2 = Integer.parseInt(stack.pop());
int num1 = Integer.parseInt(stack.pop());
int res = 0;
if (item.equals("+")) {
res = num1 + num2;
} else if (item.equals("-")) {
res = num1 - num2;
} else if (item.equals("*")) {
res = num1 * num2;
} else if (item.equals("/")) {
res = num1 / num2;
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("运算符有误");
}
//把res 入栈
stack.push("" + res);
}
}
//最后留在stack中的数据是运算结果
return Integer.parseInt(stack.pop());
}
}
//编写一个类 Operation 可以返回一个运算符 对应的优先级
class Operation {
private static int ADD = 1;
private static int SUB = 1;
private static int MUL = 2;
private static int DIV = 2;
//写一个方法,返回对应的优先级数字
public static int getValue(String operation) {
int result = 0;
switch (operation) {
case "+":
result = ADD;
break;
case "-":
result = SUB;
break;
case "*":
result = MUL;
break;
case "/":
result = DIV;
break;
default:
System.out.println("不存在该运算符" + operation);
break;
}
return result;
}
}
039_中缀转后缀表达式思路分析
介绍1
介绍2
图解
040_中缀转后缀表达式代码实现(1)
042_完整版逆波兰计算器和小结
代码实现
package com.nanjing.reversepolishcal;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Stack;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
/**
* 逆波兰计算器完整版
*
* @author xizheng
* @date 2023-01-30 10:02:09
*/
public class ReversePolishMultiCalc {
/**
* 匹配 + - * / ( ) 运算符
*/
static final String SYMBOL = "\\+|-|\\*|/|\\(|\\)";
static final String LEFT = "(";
static final String RIGHT = ")";
static final String ADD = "+";
static final String MINUS= "-";
static final String TIMES = "*";
static final String DIVISION = "/";
/**
* 加減 + -
*/
static final int LEVEL_01 = 1;
/**
* 乘除 * /
*/
static final int LEVEL_02 = 2;
/**
* 括号
*/
static final int LEVEL_HIGH = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
static Stack stack = new Stack<>();
static List data = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList());
/**
* 去除所有空白符
* @param s
* @return
*/
public static String replaceAllBlank(String s ){
// \\s+ 匹配任何空白字符,包括空格、制表符、换页符等等, 等价于[ \f\n\r\t\v]
return s.replaceAll("\\s+","");
}
/**
* 判断是不是数字 int double long float
* @param s
* @return
*/
public static boolean isNumber(String s){
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile("^[-\\+]?[.\\d]*$");
return pattern.matcher(s).matches();
}
/**
* 判断是不是运算符
* @param s
* @return
*/
public static boolean isSymbol(String s){
return s.matches(SYMBOL);
}
/**
* 匹配运算等级
* @param s
* @return
*/
public static int calcLevel(String s){
if("+".equals(s) || "-".equals(s)){
return LEVEL_01;
} else if("*".equals(s) || "/".equals(s)){
return LEVEL_02;
}
return LEVEL_HIGH;
}
/**
* 匹配
* @param s
* @throws Exception
*/
public static List doMatch (String s) throws Exception{
if(s == null || "".equals(s.trim())) throw new RuntimeException("data is empty");
if(!isNumber(s.charAt(0)+"")) throw new RuntimeException("data illeagle,start not with a number");
s = replaceAllBlank(s);
String each;
int start = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
if(isSymbol(s.charAt(i)+"")){
each = s.charAt(i)+"";
//栈为空,(操作符,或者 操作符优先级大于栈顶优先级 && 操作符优先级不是( )的优先级 及是 ) 不能直接入栈
if(stack.isEmpty() || LEFT.equals(each)
|| ((calcLevel(each) > calcLevel(stack.peek())) && calcLevel(each) < LEVEL_HIGH)){
stack.push(each);
}else if( !stack.isEmpty() && calcLevel(each) <= calcLevel(stack.peek())){
//栈非空,操作符优先级小于等于栈顶优先级时出栈入列,直到栈为空,或者遇到了(,最后操作符入栈
while (!stack.isEmpty() && calcLevel(each) <= calcLevel(stack.peek()) ){
if(calcLevel(stack.peek()) == LEVEL_HIGH){
break;
}
data.add(stack.pop());
}
stack.push(each);
}else if(RIGHT.equals(each)){
// ) 操作符,依次出栈入列直到空栈或者遇到了第一个)操作符,此时)出栈
while (!stack.isEmpty() && LEVEL_HIGH >= calcLevel(stack.peek())){
if(LEVEL_HIGH == calcLevel(stack.peek())){
stack.pop();
break;
}
data.add(stack.pop());
}
}
start = i ; //前一个运算符的位置
}else if( i == s.length()-1 || isSymbol(s.charAt(i+1)+"") ){
each = start == 0 ? s.substring(start,i+1) : s.substring(start+1,i+1);
if(isNumber(each)) {
data.add(each);
continue;
}
throw new RuntimeException("data not match number");
}
}
//如果栈里还有元素,此时元素需要依次出栈入列,可以想象栈里剩下栈顶为/,栈底为+,应该依次出栈入列,可以直接翻转整个stack 添加到队列
Collections.reverse(stack);
data.addAll(new ArrayList<>(stack));
System.out.println(data);
return data;
}
/**
* 算出结果
* @param list
* @return
*/
public static Double doCalc(List list){
Double d = 0d;
if(list == null || list.isEmpty()){
return null;
}
if (list.size() == 1){
System.out.println(list);
d = Double.valueOf(list.get(0));
return d;
}
ArrayList list1 = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
list1.add(list.get(i));
if(isSymbol(list.get(i))){
Double d1 = doTheMath(list.get(i - 2), list.get(i - 1), list.get(i));
list1.remove(i);
list1.remove(i-1);
list1.set(i-2,d1+"");
list1.addAll(list.subList(i+1,list.size()));
break;
}
}
doCalc(list1);
return d;
}
/**
* 运算
* @param s1
* @param s2
* @param symbol
* @return
*/
public static Double doTheMath(String s1,String s2,String symbol){
Double result ;
switch (symbol){
case ADD : result = Double.valueOf(s1) + Double.valueOf(s2); break;
case MINUS : result = Double.valueOf(s1) - Double.valueOf(s2); break;
case TIMES : result = Double.valueOf(s1) * Double.valueOf(s2); break;
case DIVISION : result = Double.valueOf(s1) / Double.valueOf(s2); break;
default : result = null;
}
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//String math = "9+(3-1)*3+10/2";
String math = "12.8 + (2 - 3.55)*4+10/5.0";
try {
doCalc(doMatch(math));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}