刷题日记Day2 | 构造二叉树
把题目的要求细化,搞清楚根节点应该做什么,然后剩下的事情抛给前/中/后序的遍历框架就行了,我们千万不要跳进递归的细节里,你的脑袋才能压几个栈呀。
文章目录
-
- 654.最大二叉树
- 105.根据前序和中序序列构造二叉树
- 106.根据中序和后续遍历构造二叉树
654.最大二叉树

分析:
1.根节点要做什么??
把自己构建出来。
2.具体做什么??
遍历数组把找到最大值 maxVal,把根节点 root 做出来,然后对 maxVal 左边的数组和右边的数组进行递归调用,作为 root 的左右子树。
解题思路:
TreeNode constructMaximumBinaryTree([3,2,1,6,0,5]) {
// 找到数组中的最大值
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(6);
// 递归调用构造左右子树
root.left = constructMaximumBinaryTree([3,2,1]);
root.right = constructMaximumBinaryTree([0,5]);
return root;
}
解答:
/* 主函数 */
TreeNode constructMaximumBinaryTree(int[] nums) {
return build(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
}
/* 将 nums[lo..hi] 构造成符合条件的树,返回根节点 */
TreeNode build(int[] nums, int lo, int hi) {
// base case
if (lo > hi) {
return null;
}
// 找到数组中的最大值和对应的索引
int index = -1, maxVal = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++) {
if (maxVal < nums[i]) {
index = i;
maxVal = nums[i];
}
}
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(maxVal);
// 递归调用构造左右子树
root.left = build(nums, lo, index - 1);
root.right = build(nums, index + 1, hi);
return root;
}
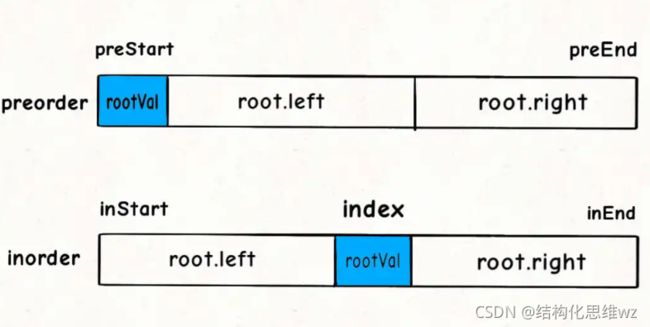
105.根据前序和中序序列构造二叉树
⭐️重点题型标注!
分析:
想办法确定根节点的值,把根节点做出来,然后递归构造左右子树即可。
如何找到根节点??

前序遍历的第一个值preorder[0]就是根节点的值,关键在于如何通过根节点的值,将preorder和postorder数组划分成两半,构造根节点的左右子树?
根据思路写出对应的代码为:
/* 主函数 */
TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
return build(preorder, 0, preorder.length - 1,
inorder, 0, inorder.length - 1);
}
/*
若前序遍历数组为 preorder[preStart..preEnd],
后续遍历数组为 postorder[postStart..postEnd],
构造二叉树,返回该二叉树的根节点
*/
TreeNode build(int[] preorder, int preStart, int preEnd,
int[] inorder, int inStart, int inEnd) {
// root 节点对应的值就是前序遍历数组的第一个元素
int rootVal = preorder[preStart];
// rootVal 在中序遍历数组中的索引
int index = 0;
for (int i = inStart; i <= inEnd; i++) {
if (inorder[i] == rootVal) {
index = i;
break;
}
}
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(rootVal);
// 递归构造左右子树
root.left = build(preorder, ?, ?,
inorder, ?, ?);
root.right = build(preorder, ?, ?,
inorder, ?, ?);
return root;
}
解答:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
return build(preorder, 0, preorder.length - 1,
inorder, 0, inorder.length - 1);
}
/*
若前序遍历数组为 preorder[preStart..preEnd],
后续遍历数组为 postorder[postStart..postEnd],
构造二叉树,返回该二叉树的根节点
*/
TreeNode build(int[] preorder, int preStart, int preEnd,
int[] inorder, int inStart, int inEnd) {
if (preStart > preEnd) {
return null;
}
// root 节点对应的值就是前序遍历数组的第一个元素
int rootVal = preorder[preStart];
// rootVal 在中序遍历数组中的索引
int index = 0;
for (int i = inStart; i <= inEnd; i++) {
if (inorder[i] == rootVal) {
index = i;
break;
}
}
int leftSize = index - inStart;
// 先构造出当前根节点
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(rootVal);
// 递归构造左右子树
root.left = build(preorder, preStart + 1, preStart + leftSize,
inorder, inStart, index - 1);
root.right = build(preorder, preStart + leftSize + 1, preEnd,
inorder, index + 1, inEnd);
return root;
}
}
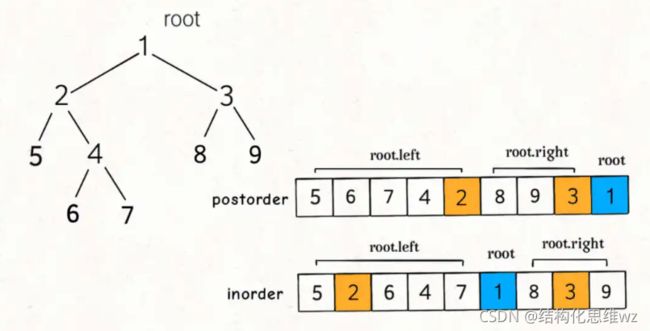
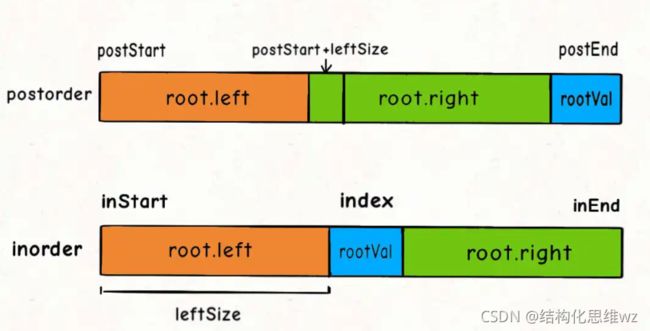
106.根据中序和后续遍历构造二叉树

分析:
有了上一题的基础,发现只要画图发现左右子树的起止点就可以了。

代码实现:
class Solution {
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) {
return build(inorder,0,inorder.length-1,
postorder,0,postorder.length-1);
}
/**构建二叉树 */
TreeNode build(int[] inorder, int inStart, int inEnd,
int[] postorder, int postStart, int postEnd) {
if (inStart > inEnd) {
return null;
}
// root 节点对应的值就是后序遍历数组的最后一个元素
int rootVal = postorder[postEnd];
// rootVal 在中序遍历数组中的索引
int index = 0;
for (int i = inStart; i <= inEnd; i++) {
if (inorder[i] == rootVal) {
index = i;
break;
}
}
// 左子树的节点个数
int leftSize = index - inStart;
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(rootVal);
// 递归构造左右子树
root.left = build(inorder, inStart, index - 1,
postorder, postStart, postStart + leftSize - 1);
root.right = build(inorder, index + 1, inEnd,
postorder, postStart + leftSize, postEnd - 1);
return root;
}
}