编译原理 C-Minus 语义分析(Flex / Bison)
C-Minus 源代码 语义分析
文章目录
- C-Minus 源代码 语义分析
-
- 一、实现目标
- 二、实现过程
-
- 内容综述
- 1. 语法分析树实现
- 2. 符号表实现
-
- 2.1 变量符号表
- 2.2 函数符号表实现
- 2.3 数组符号表实现
- 2.4 结构体符号表实现
- 3. Flex/Bison代码分析
-
- 3.1 错误类型1
- 3.2 错误类型2、3
- 3.3 错误类型4、5、13
- 3.4 错误类型6
- 3.5 错误类型7
- 3.6 错误类型8
- 3.7 错误类型9、10
- 3.8 错误类型11
- 3.9 错误类型12
- 三、结果分析验证
- 四、心得与体会
- 五、全部代码
-
- syntax_tree.y
- syntax_tree.l
- syntax_tree.h
- syntax_tree.c
一、实现目标
书接上文,在之前的两篇文章中,我们已经实现了词法分析、语法分析,接下来,我们需要实现的是语义分析。
具体目标:
- 在词法及语法分析程序的基础上,编写一个程序对使用类C语言书写的源代码进行语义分析及类型检查,并打印分析结果。
- 程序要能够检查源代码中是否符合以下语义要求:
(1)最低要求3.1:能够实现对整型(int)和浮点型(float)变量的类型检查,两类变量不能相互赋值及运算;仅整型及浮点型变量才能参与算术运算
(2)其他要求3.2:能判断源代码是否符合以下语义假设并给出相应错误具体位置:函数仅能定义一次、程序中所有变量均不能重名、函数不可嵌套定义
(3)其他要求3.3:能检查结构体中域是否与变量重名,不同结构体中域是否重名 - 报错信息需能定位错误位置
其他要求:
在本次实验中,我们对C-语言做如下假设,你可以认为这些就是C-语言的特性(注意,假设3、假设4、假设5可能因后面的不同选做要求而有所改变):
- 假设1:整型(int)变量不能与浮点型(float)变量相互赋值或者相互运算。
- 假设2:仅有int型变量才能进行逻辑运算或者作为if和 while语句的条件;仅有int型和 float型变量才能参与算术运算。
- 假设3:任何函数只进行一次定义,无法进行函数声明。
- 假设4:所有变量(包括函数的形参)的作用域都是全局的,即程序中所有变量均不能重名
- 假设5:结构体间的类型等价机制采用名等价( Name Equivalence)的方式
- 假设6:函数无法进行嵌套定义。
- 假设7:结构体中的域不与变量重名,并且不同结构体中的域互不重名。以上假设1~假设7也可视为要求,违反即会导致各种语 义错误,不过我们只对后面讨论的错误类型进行考查。此外你可以安全地假设输入文件中不包含注释、八进制数、十六进制数以及指数形式的浮点数,也不包含任何词法或语法错误(除了特别说明的针对选做要求的测试)
你的程序需要对输入文件进行语义分析并检查如下类型的错误,必做部分不会出现结构体和数组:
- 错误类型1:变量在使用时未经定义。
- 错误类型2:赋值号两边的表达式类型不匹配。
- 错误类型3:赋值号左边出现一个只有右值的表达式。
- 错误类型4:对普通变量使用“(…)”或“()”(函数调用)操作符。
- 错误类型5:函数在调用时未经定义。
- 错误类型6:操作数类型不匹配或操作数类型与操作符不匹配(例如整型变量与数组变量相加减,或数组(或结构体)变量与数组(或结构体)结构体变量相加减)。
除此之外,你的程序可以选择完成以下部分或全部的要求:
- 选做2.1,这部分是与定义相关的
- 错误类型7:变量出现重复定义。
- 错误类型8:函数出现重复定义(即同样的函数名出现了不止一次定义)
- 选做2.2,这部分是与结构体相关的
- 类型9:结构体中域与变量重名。
- 类型10:不同结构体中的域重名。(类型9和10不一定是错误,但需要检查是否重名并进行提示)
- 错误类型11:结构体的名字与前面定义过的结构体或变量的名字重复。
以上是根据实验要求给出的错误类型检查示例,你不一定要完全遵循这里给出的错误类型的检查,只要给出符合实验报告语义要求的错误类型检查都可以,需要你在实验报告中说明。这里给出的实验测试代码中的函数均无参数,若完成有参数的函数并进行参数检查有额外加分。此外选做部分均无测试代码,请根据自己给出的错误类型,自行给出测试样例说明。
二、实现过程
内容综述
- 本文使用线性链表实现符号表
- 实现了必做部分错误检测
- 实现了选做2.1定义相关全部类型检测
- 实现了选做2.2结构体相关全部类型检测
- 实现了函数参数以及返回值类型的检测
1. 语法分析树实现
// 抽象语法树
typedef struct treeNode
{
// 行数
int line;
// Token类型
char *name;
// 1变量 2函数 3常数 4数组 5结构体
int tag;
// 使用孩子数组表示法
struct treeNode *cld[10];
int ncld;
// 语义值
char *content;
// 数据类型 int 或 float
char *type;
// 变量的值
float value;
} * Ast, *tnode;
为了便于获取孩子节点属性,修改了实验二中语法分析树的实现方式,用数组存储子节点。
// 表示当前节点不是终结符号,还有子节点
if (num > 0)
{
father->ncld = num;
// 第一个孩子节点
temp = va_arg(list, tnode);
father->cld[0] = temp;
setChildTag(temp);
// 父节点行号为第一个孩子节点的行号
father->line = temp->line;
if (num == 1)
{
//父节点的语义值等于左孩子的语义值
father->content = temp->content;
father->tag = temp->tag;
}
else
{
for (i = 1; i < num; i++)
{
temp = va_arg(list, tnode);
(father->cld)[i] = temp;
// 该节点为其他节点的子节点
setChildTag(temp);
}
}
}
为了在语法分析的同时实现语义分析,除了在Bison代码中进行修改外,还需要修改语法分析树节点的构造函数,实现属性/类型/语义值的传递。父节点的类型、语义值可以从子节点处获得。
2. 符号表实现
我用线性链表实现了符号表,将不同种类的符号组织成不同的表,维护每张表的表头和表尾,从表尾插入,从表头开始遍历。
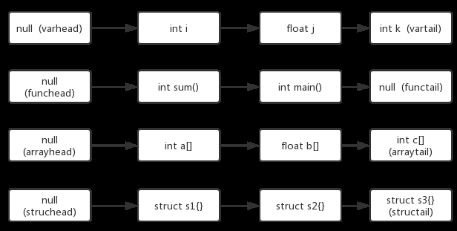
2.1 变量符号表
// 变量符号表的结点
typedef struct var_
{
char *name;
char *type;
// 是否为结构体域
int inStruc;
// 所属的结构体编号
int strucNum;
struct var_ *next;
}var;
var *varhead, *vartail;
// 建立变量符号
void newvar(int num,...);
// 变量是否已经定义
int findvar(tnode val);
// 变量类型
char* typevar(tnode val);
// 这样赋值号左边仅能出现ID、Exp LB Exp RB 以及 Exp DOT ID
int checkleft(tnode val);
实现了创建遍历符号、变量类型检查、查看变量是否已经定义、检查赋值号左边变量类型的功能函数。为了实现检查结构体域的功能,在符号表节点中设置了inStruc 和 strucNum变量,用于标注该变量属于哪一个结构体。
// 建立变量符号
void newvar(int num, ...)
{
va_list valist;
va_start(valist, num);
var *res = (var *)malloc(sizeof(var));
tnode temp = (tnode)malloc(sizeof(tnode));
if (inStruc && LCnum)
{
// 是结构体的域
res->inStruc = 1;
res->strucNum = strucNum;
}
else
{
res->inStruc = 0;
res->strucNum = 0;
}
// 变量声明 int i
temp = va_arg(valist, tnode);
res->type = temp->content;
temp = va_arg(valist, tnode);
res->name = temp->content;
vartail->next = res;
vartail = res;
}
// 查找变量
int findvar(tnode val)
{
var *temp = (var *)malloc(sizeof(var *));
temp = varhead->next;
while (temp != NULL)
{
if (!strcmp(temp->name, val->content))
{
if (inStruc && LCnum) // 当前变量是结构体域
{
if (!temp->inStruc)
{
// 结构体域与变量重名
printf("Error type 9 at Line %d:Struct Field and Variable use the same name.\n", yylineno);
}
else if (temp->inStruc && temp->strucNum != strucNum)
{
// 不同结构体中的域重名
printf("Error type 10 at Line %d:Struct Fields use the same name.\n", yylineno);
}
else
{
// 同一结构体中域名重复
return 1;
}
}
else // 当前变量是全局变量
{
if (temp->inStruc)
{
// 变量与结构体域重名
printf("Error type 9 at Line %d:Struct Field and Variable use the same name.\n", yylineno);
}
else
{
// 变量与变量重名,即重复定义
return 1;
}
}
}
temp = temp->next;
}
return 0;
}
由于设置了相关属性值,可以实现在寻找变量的同时判断错误类型9和10,这两种错误类型只做提醒,不影响变量的定义以及变量符号表的插入操作。
符号表的插入和遍历操作大致相同,这里展示变量符号表的相关操作,其他符号表只说明不同的地方。
// 赋值号左边只能出现ID、Exp LB Exp RB 以及 Exp DOT ID
int checkleft(tnode val)
{
if (val->ncld == 1 && !strcmp((val->cld)[0]->name, "ID"))
return 1;
else if (val->ncld == 4 && !strcmp((val->cld)[0]->name, "Exp") && !strcmp((val->cld)[1]->name, "LB") && !strcmp((val->cld)[2]->name, "Exp") && !strcmp((val->cld)[3]->name, "RB"))
return 1;
else if (val->ncld == 3 && !strcmp((val->cld)[0]->name, "Exp") && !strcmp((val->cld)[1]->name, "DOT") && !strcmp((val->cld)[2]->name, "ID"))
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
在赋值操作中,左值表示地址,这说明表达式“x = 3”是正确的,而“x + 2 = 3”是错误的。这样赋值号左边仅能出现ID、Exp LB Exp RB 以及 Exp DOT ID,因此需要检查赋值号左边的语法分析树节点的子节点是否符合上述三种情况,用来判断是否为对应的错误类型。
2.2 函数符号表实现
// 函数符号表的结点
typedef struct func_
{
int tag; //0表示未定义,1表示定义
char *name;
char *type;
// 是否为结构体域
int inStruc;
// 所属的结构体编号
int strucNum;
char *rtype; //声明返回值类型
int va_num; //记录函数形参个数
char *va_type[10];
struct func_ *next;
}func;
func *funchead,*functail;
// 记录函数实参
int va_num;
char* va_type[10];
void getdetype(tnode val);//定义的参数
void getretype(tnode val);//实际的参数
void getargs(tnode Args);//获取实参
int checkrtype(tnode ID,tnode Args);//检查形参与实参是否一致
// 建立函数符号
void newfunc(int num, ...);
// 函数是否已经定义
int findfunc(tnode val);
// 函数类型
char *typefunc(tnode val);
// 函数的形参个数
int numfunc(tnode val);
// 函数实际返回值类型
char *rtype[10];
int rnum;
void getrtype(tnode val);
// 创建函数符号
void newfunc(int num, ...)
{
int i;
va_list valist;
va_start(valist, num);
tnode temp = (tnode)malloc(sizeof(struct treeNode));
switch (num)
{
case 1:
if (inStruc && LCnum)
{
// 是结构体的域
functail->inStruc = 1;
functail->strucNum = strucNum;
}
else
{
functail->inStruc = 0;
functail->strucNum = 0;
}
//设置函数返回值类型
temp = va_arg(valist, tnode);
functail->rtype = temp->content;
functail->type = temp->type;
for (i = 0; i < rnum; i++)
{
if (rtype[i] == NULL || strcmp(rtype[i], functail->rtype))
printf("Error type 12 at Line %d:Func return type error.\n", yylineno);
}
functail->tag = 1; //标志为已定义
func *new = (func *)malloc(sizeof(func));
functail->next = new; //尾指针指向下一个空结点
functail = new;
break;
case 2:
//记录函数名
temp = va_arg(valist, tnode);
functail->name = temp->content;
//设置函数声明时的参数
temp = va_arg(valist, tnode);
functail->va_num = 0;
getdetype(temp);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
本次实验中,我对函数的声明和定义分别作了处理(进行FunDec和ExtDef规约时作不同处理)。在进行ExtDef规约时可以获取函数的返回值类型,并且同时判断函数的声明返回类型、实际返回值类型是否相同。在FunDec规约时检测函数是否已定义并且设置函数的形参和函数名称。
//定义的参数
void getdetype(tnode val)
{
int i;
if (val != NULL)
{
if (!strcmp(val->name, "ParamDec"))
{
functail->va_type[functail->va_num] = val->cld[0]->content;
functail->va_num++;
return;
}
for (i = 0; i < val->ncld; ++i)
{
getdetype((val->cld)[i]);
}
}
else
return;
}
//实际的参数
void getretype(tnode val)
{
int i;
if (val != NULL)
{
if (!strcmp(val->name, "Exp"))
{
va_type[va_num] = val->type;
va_num++;
return;
}
for (i = 0; i < val->ncld; ++i)
{
getretype((val->cld)[i]);
}
}
else
return;
}
//检查形参与实参是否一致,没有错误返回0
int checkrtype(tnode ID, tnode Args)
{
int i;
va_num = 0;
getretype(Args);
func *temp = (func *)malloc(sizeof(func *));
temp = funchead->next;
while (temp != NULL && temp->name != NULL && temp->tag == 1)
{
if (!strcmp(temp->name, ID->content))
break;
temp = temp->next;
}
if (va_num != temp->va_num)
return 1;
for (i = 0; i < temp->va_num; i++)
{
if (temp->va_type[i] == NULL || va_type[i] == NULL || strcmp(temp->va_type[i], va_type[i]) != 0)
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
由于在Bison代码中,对于函数形参以及实参规约的节点都是父节点,需要用先序遍历获取树结构中所有的参数节点,并进行存储,以便于检测相关类型错误。
2.3 数组符号表实现
// 数组符号表的结点
typedef struct array_
{
char *name;
char *type;
// 是否为结构体域
int inStruc;
// 所属的结构体编号
int strucNum;
struct array_ *next;
}array;
array *arrayhead,*arraytail;
// 建立数组符号
void newarray(int num, ...);
// 查找数组是否已经定义
int findarray(tnode val);
// 数组类型
char *typearray(tnode val);
本次实验中我没有对数组符号做太多处理,该符号表和变量符号表操作基本一致。
2.4 结构体符号表实现
// 结构体符号表的结点
typedef struct struc_
{
char *name;
char *type;
// 是否为结构体域
int inStruc;
// 所属的结构体编号
int strucNum;
struct struc_ *next;
}struc;
struc *struchead, *structail;
// 建立结构体符号
void newstruc(int num, ...);
// 查找结构体是否已经定义
int findstruc(tnode val);
// 当前是结构体域
int inStruc;
// 判断结构体域,{ 和 }是否抵消
int LCnum;
// 当前是第几个结构体
int strucNum;
由于错误类型11需要检测结构体定义是否和之前定义的结构体、变量名称一致,因此在检测重复定义时做一些改动:
// 结构体是否和结构体或变量的名字重复
int findstruc(tnode val)
{
struc *temp = (struc *)malloc(sizeof(struc *));
temp = struchead->next;
while (temp != NULL)
{
if (!strcmp(temp->name, val->content))
return 1;
temp = temp->next;
}
if (findvar(val) == 1)
return 1;
return 0;
}
3. Flex/Bison代码分析
需要实现在语法分析的同时进行语义分析,因此在规约时对某些类型的节点需要进行符号表插入、遍历以及错误类型的检查工作。
错误类型定义:
- 错误类型1:变量在使用时未经定义。
- 错误类型2:赋值号两边的表达式类型不匹配。
- 错误类型3:赋值号左边出现一个只有右值的表达式。
- 错误类型4:对普通变量使用“(…)”或“()”(函数调用)操作符。
- 错误类型5:函数在调用时未经定义。
- 错误类型6:操作数类型不匹配或操作数类型与操作符不匹配(例如整型变量与数组变量相加减,或数组(或结构体)变量与数 组(或结构体)结构体变量相加减)。
- 错误类型7:变量出现重复定义。
- 错误类型8:函数出现重复定义(即同样的函数名出现了不止一次定义)
- 错误类型9:结构体中域与变量重名
- 错误类型10:不同结构体中的域重名(类型9和10不一定是错误,但需要检查是否重名并进行提示)
- 错误类型11:结构体的名字与前面定义过的结构体或变量的名字重复。
- 错误类型12:函数声明的返回类型和实际返回值类型不一致
- 错误类型13:函数定义的形参与调用的实参数量或类型不一致
3.1 错误类型1
Exp:ID {
$$=newAst("Exp",1,$1);
// 错误类型1:变量在使用时未经定义
if(!findvar($1)&&!findarray($1))
printf("Error type 1 at Line %d:undefined variable %s\n",yylineno,$1->content);
else
$$->type=typevar($1);
}
操作数ID会被规约为Exp,ID就是变量的名称,因此需要在这里检测变量是否已经定义。
3.2 错误类型2、3
Exp:Exp ASSIGNOP Exp{
$$=newAst("Exp",3,$1,$2,$3);
// 当有一边变量是未定义时,不进行处理
if($1->type==NULL || $3->type==NULL){
return;
}
// 错误类型2:赋值号两边的表达式类型不匹配
if(strcmp($1->type,$3->type))
printf("Error type 2 at Line %d:Type mismatched for assignment.\n ",yylineno);
// 错误类型3:赋值号左边出现一个只有右值的表达式
if(!checkleft($1))
printf("Error type 3 at Line %d:The left-hand side of an assignment must be a variable.\n ",yylineno);
}
由于在进行语法分析树建立时修改了节点构造函数,使得子节点类型能够传递给父节点,在检测赋值号两端表达式类型时就可以直接检测表达式节点的type属性是否相同。这里判断了type属性是否为NULL(表达式是否未定义),如果不进行相关处理,碰到未定义的表达式,其type属性为NULL,直接对NULL使用strcmp函数会报出段错误。错误类型3和错误类型2都是在规约到ASSIGNOP符号时进行检测。
3.3 错误类型4、5、13
Exp:ID LP Args RP {
$$=newAst("Exp",4,$1,$2,$3,$4);
// 错误类型4:对普通变量使用“(...)”或“()”(函数调用)操作符
if(!findfunc($1) && (findvar($1)||findarray($1)))
printf("Error type 4 at Line %d:'%s' is not a function.\n ",yylineno,$1->content);
// 错误类型5:函数在调用时未经定义
else if(!findfunc($1))
printf("Error type 5 at Line %d:Undefined function %s\n ",yylineno,$1->content);
// 函数实参和形参类型不一致
else if(checkrtype($1,$3)){
printf("Error type 13 at Line %d:Function parameter type error.\n ",yylineno);
}else{}
}
|ID LP RP {
$$=newAst("Exp",3,$1,$2,$3);
// 错误类型4:对普通变量使用“(...)”或“()”(函数调用)操作符
if(!findfunc($1) && (findvar($1)||findarray($1)))
printf("Error type 4 at Line %d:'%s' is not a function.\n ",yylineno,$1->content);
// 错误类型5:函数在调用时未经定义
else if(!findfunc($1))
printf("Error type 5 at Line %d:Undefined function %s\n ",yylineno,$1->content);
else {}
}
在检测到ID LP … RP时进行函数调用错误类型的检测,我的处理方式是当函数已经定义时就不需要检测是否对普通变量进行()操作。另外对于(Args)类型的函数定义规约,需要检测实参和形参类型是否一致。
3.4 错误类型6
Exp:Exp PLUS Exp{
$$=newAst("Exp",3,$1,$2,$3);
// 错误类型6:操作数类型不匹配或操作数类型与操作符不匹配
if(strcmp($1->type,$3->type))
printf("Error type 6 at Line %d:Type mismatched for operands.\n ",yylineno);
}
|Exp MINUS Exp{
$$=newAst("Exp",3,$1,$2,$3);
// 错误类型6:操作数类型不匹配或操作数类型与操作符不匹配
if(strcmp($1->type,$3->type))
printf("Error type 6 at Line %d:Type mismatched for operands.\n ",yylineno);
}
|Exp STAR Exp{
$$=newAst("Exp",3,$1,$2,$3);
// 错误类型6:操作数类型不匹配或操作数类型与操作符不匹配
if(strcmp($1->type,$3->type))
printf("Error type 6 at Line %d:Type mismatched for operands.\n ",yylineno);
}
|Exp DIV Exp{
$$=newAst("Exp",3,$1,$2,$3);
// 错误类型6:操作数类型不匹配或操作数类型与操作符不匹配
if(strcmp($1->type,$3->type))
printf("Error type 6 at Line %d:Type mismatched for operands.\n ",yylineno);
}
在本次实验中我只对加减乘除四种运算符号进行了操作数类型是否一致的检测。
3.5 错误类型7
ParamDec:Specifire VarDec {
$$=newAst("ParamDec",2,$1,$2);
// 错误类型7:变量出现重复定义
if(findvar($2)||findarray($2))
printf("Error type 7 at Line %d:Redefined Variable '%s'\n",yylineno,$2->content);
else if($2->tag==4)
newarray(2,$1,$2);
else
newvar(2,$1,$2);
}
;
Def:Specifire DecList SEMI {
$$=newAst("Def",3,$1,$2,$3);
// 错误类型7:变量出现重复定义
if(findvar($2)||findarray($2))
printf("Error type 7 at Line %d:Redefined Variable '%s'\n",yylineno,$2->content);
else if($2->tag==4)
newarray(2,$1,$2);
else
newvar(2,$1,$2);
}
;
本次实验中假设函数形参也是全局变量,因此在对变量类型错误检测以及变量符号表插入时,需要在两个地方添加代码,分别是变量定义、函数定义时。
3.6 错误类型8
FunDec:ID LP VarList RP {
$$=newAst("FunDec",4,$1,$2,$3,$4); $$->content=$1->content;
// 错误类型8:函数出现重复定义(即同样的函数名出现了不止一次定义)
if(findfunc($1))
printf("Error type 8 at Line %d:Redefined Function '%s'\n",yylineno,$1->content);
// 设置函数名称以及参数列表
else newfunc(2,$1,$3);
}
|ID LP RP {
$$=newAst("FunDec",3,$1,$2,$3); $$->content=$1->content;
// 错误类型8:函数出现重复定义(即同样的函数名出现了不止一次定义)
if(findfunc($1))
printf("Error type 8 at Line %d:Redefined Function '%s'\n",yylineno,$1->content);
// 设置函数名称以及参数列表
else newfunc(2,$1,$3);
}
;
我对函数声明和函数定义(有函数体时)分别进行了处理,函数定义时检测是否重复定义,并且设置函数名称以及参数列表。
3.7 错误类型9、10
// 当前是结构体域
int inStruc;
// 判断结构体域,{ 和 }是否抵消
int LCnum;
// 当前是第几个结构体
int strucNum;
为了实现结构体域的检测,设置了相关的全局变量。
在词法分析过程中,当遇到STRUCT TOKEN时,表示有结构体定义,这时将inStruc置1并且strucNum++。
{STRUCT} {
yylval.type_tnode=newAst("STRUCT",0,yylineno);
// 结构体数加一
strucNum++;
// 开始扫描结构体定义内容
inStruc=1;
return STRUCT;}
同时为了区分结构体域和结构体声明之外的其他全局变量,我通过两种方式来进行检测,一种是在进行StructSpecifire:STRUCT OptTag LC DefList RC规约时,将inStruc置0;
StructSpecifire:STRUCT OptTag LC DefList RC {
// 结构体定义完成,当前在结构体定义外部
inStruc = 0;
另一种是在词法分析器遇到LC TOKEN时判断inStruc,如果是在结构体声明中,则LCnum++,如果词法分析器遇到RC并且也在结构体声明中,则LCnum—
{LC} {
yylval.type_tnode=newAst("LC",0,yylineno);
if(inStruc){
// 结构体定义内部存在LC左花括号
LCnum++;
}
return LC;}
{RC} {
yylval.type_tnode=newAst("RC",0,yylineno);
if(inStruc){
// 结构体定义内部存在RC右花括号
LCnum--;
}
return RC;}
当inStruc为1且LCnum不为0时定义的变量就是结构体的域,此时会调用findvar和findarray函数进行相关错误类型的判断。
Exp:ID {
$$=newAst("Exp",1,$1);
// 错误类型1:变量在使用时未经定义
if(!findvar($1)&&!findarray($1))
printf("Error type 1 at Line %d:undefined variable %s\n",yylineno,$1->content);
else
$$->type=typevar($1);
}
// 函数是否已经定义
int findfunc(tnode val)
{
func *temp = (func *)malloc(sizeof(func *));
temp = funchead->next;
while (temp != NULL && temp->name != NULL && temp->tag == 1)
{
if (!strcmp(temp->name, val->content))
{
if (inStruc && LCnum) // 当前变量是结构体域
{
if (!temp->inStruc)
{
// 结构体域与变量重名
printf("Error type 9 at Line %d:Struct Field and Variable use the same name.\n", yylineno);
}
else if (temp->inStruc && temp->strucNum != strucNum)
{
// 不同结构体中的域重名
printf("Error type 10 at Line %d:Struct Fields use the same name.\n", yylineno);
}
else
{
// 同一结构体中域名重复
return 1;
}
}
else // 当前变量是全局变量
{
if (temp->inStruc)
{
// 变量与结构体域重名
printf("Error type 9 at Line %d:Struct Field and Variable use the same name.\n", yylineno);
}
else
{
// 变量与变量重名,即重复定义
return 1;
}
}
}
temp = temp->next;
}
return 0;
}
3.8 错误类型11
StructSpecifire:STRUCT OptTag LC DefList RC {
// 结构体定义完成,当前在结构体定义外部
inStruc = 0;
$$=newAst("StructSpecifire",5,$1,$2,$3,$4,$5);
// 错误类型11:结构体的名字与前面定义过的结构体或变量的名字重复
if(findstruc($2))
printf("Error type 11 at Line %d:Duplicated name '%s'\n",yylineno,$2->content);
else newstruc(1,$2);
}
在结构体声明时检测是否有重复定义。
3.9 错误类型12
Stmt:Exp SEMI {$$=newAst("Stmt",2,$1,$2); }
|Compst {$$=newAst("Stmt",1,$1); }
|RETURN Exp SEMI {
$$=newAst("Stmt",3,$1,$2,$3);
getrtype($2);
}
//函数实际返回值类型
void getrtype(tnode val)
{
rtype[rnum] = val->type;
rnum++;
}
在检测到return语句时将返回值类型存入到全局遍历数组中。
ExtDef:Specifire FunDec Compst {
$$=newAst("ExtDef",3,$1,$2,$3);
// 设置函数声明的返回值类型并检查返回类型错误
newfunc(1,$1);
}
;
在规约完函数声明以及函数体后可以进行返回类型错误检测,调用newfunc函数,传入参数 1:
// 创建函数符号
void newfunc(int num, ...)
{
int i;
va_list valist;
va_start(valist, num);
tnode temp = (tnode)malloc(sizeof(struct treeNode));
switch (num)
{
case 1:
if (inStruc && LCnum)
{
// 是结构体的域
functail->inStruc = 1;
functail->strucNum = strucNum;
}
else
{
functail->inStruc = 0;
functail->strucNum = 0;
}
//设置函数返回值类型
temp = va_arg(valist, tnode);
functail->rtype = temp->content;
functail->type = temp->type;
for (i = 0; i < rnum; i++)
{
if (rtype[i] == NULL || strcmp(rtype[i], functail->rtype))
printf("Error type 12 at Line %d:Func return type error.\n", yylineno);
}
functail->tag = 1; //标志为已定义
func *new = (func *)malloc(sizeof(func));
functail->next = new; //尾指针指向下一个空结点
functail = new;
break;
......
根据当前函数符号表中存储的返回类型值和返回值类型全局数组存储的类型值做对比,检测返回值类型不匹配的错误。
三、结果分析验证
目标完成情况:
- 完成了基础要求1-6
- 完成了选做2.1的7、8
- 完成了选做2.2的9、10、11
- 完成了识别函数返回类型(错误类型12)、参数类型(错误类型13)
程序代码编译过程:
bision -d syntax_tree.y
flex syntax_tree.l
gcc syntax_tree.tab.c syntax_tree.c lex.yy.c -lfl -ly -o parser
测试代码:
// Type1.cmm
int main()
{
int i = 0;
j = i +1;
}
![]()
// Type2.cmm
int main()
{
int i;
i = 3.7;
}
![]()
// Type3.cmm
int main()
{
int i;
10 = i;
}
![]()
// Type4.cmm
int main()
{
int i;
i();
}
![]()
// Type5.cmm
int main()
{
int i;
inc();
return 0;
}
![]()
// Type6.cmm
int main()
{
float j;
10 + j;
}
![]()
// Type7.cmm
int main()
{
int i;
float i;
int j;
float j;
}
// Type8.cmm
int func(int i)
{
return i;
}
int func()
{
return 0;
}
int main()
{
}
![]()
// Type9.cmm
struct Position
{
float x;
};
int main()
{
float x;
}
![]()
// Type10.cmm
struct Position
{
float x;
};
struct Number
{
float x;
};
int main()
{
}
![]()
// Type11.cmm
struct Position
{
float x;
};
struct Position
{
float y;
};
int main()
{
}
![]()
// Type12.cmm
int main(){
float j;
return j;
}
![]()
// Type13.cmm
int sum(int a,int b)
{
}
int main(){
int i;
float j;
sum(i,j);
}
![]()
四、心得与体会
- 刚开始想从两种语义分析实现方法中选择一种,分别是分析语法分析树结构、在语法分析的同时进行语义分析,经过仔细研究后发现采用分析语法树的方法工程量太大,需要将各种规约情况(子节点类型)考虑到,最终选择了在bison代码中添加新的内容,实现在语法分析的同时进行语义分析,减少工作量。
- 在选择采用第二种实现方式后,由于是自底向上的分析方法,子节点无法得到父节点的继承属性,因此采用了属性传递(生成式左边的属性、类型等于右边的属性、类型),并在规约时进行各种错误类型的判断,而在进行错误类型的判断时只需要进行较少次数的子节点类型判断即可。同时为了方便进行子节点类型的读取,我将上篇文章中的语法分析树节点的孩子兄弟表示法修改为了孩子数组表示。
- 采用自底向上的语义分析时也可以结合词法分析器实现层级符号表,在本文中我只实现了识别结构体域,实际上可以通过检测词法分析器中遇到LC Token的情况(表示进入到新的作用域),通过设置一些全局变量来实现层级符号表。
- 在实现判断函数参数类型错误时,由于进行判断的是Args和VarList节点,需要提取出树结构中真正的参数信息,我将之前的先序遍历函数做了一些改动,实现了提取树结构中有效节点信息的功能
五、全部代码
syntax_tree.y
/*
*bison语法分析,对每条规则 按照孩子兄弟表示法建立语法结点
*/
%{
#includesyntax_tree.l
/*
按照C-Tokens文件中要求定义
对终结符建立叶子结点,返回Token
*/
/*第一部分 头文件和变量*/
%{
#include syntax_tree.h
#include syntax_tree.c
#include "syntax_tree.h"
// 用于遍历
int i;
Ast newAst(char *name, int num, ...)
{
// 生成父节点
tnode father = (tnode)malloc(sizeof(struct treeNode));
// 添加子节点
tnode temp = (tnode)malloc(sizeof(struct treeNode));
if (!father)
{
yyerror("create treenode error");
exit(0);
}
father->name = name;
// 参数列表,详见 stdarg.h 用法
va_list list;
// 初始化参数列表
va_start(list, num);
// 表示当前节点不是终结符号,还有子节点
if (num > 0)
{
father->ncld = num;
// 第一个孩子节点
temp = va_arg(list, tnode);
father->cld[0] = temp;
setChildTag(temp);
// 父节点行号为第一个孩子节点的行号
father->line = temp->line;
if (num == 1)
{
//父节点的语义值等于左孩子的语义值
father->content = temp->content;
father->tag = temp->tag;
}
else
{
for (i = 1; i < num; i++)
{
temp = va_arg(list, tnode);
(father->cld)[i] = temp;
// 该节点为其他节点的子节点
setChildTag(temp);
}
}
}
else //表示当前节点是终结符(叶节点)或者空的语法单元,此时num表示行号(空单元为-1)
{
father->ncld = 0;
father->line = va_arg(list, int);
// strcmp()==0 表示相同
if (!strcmp(name, "INT"))
{
father->type = "int";
father->value = atoi(yytext);
}
else if (!strcmp(name, "FLOAT"))
{
father->type = "float";
father->value = atof(yytext);
}
else
{
// 存储词法单元语义值
char *str;
str = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char) * 40);
strcpy(str, yytext);
father->content = str;
}
}
nodeList[nodeNum] = father;
nodeNum++;
return father;
}
// 父节点->左子节点->右子节点....
void Preorder(Ast ast, int level)
{
int i;
if (ast != NULL)
{
// 层级结构缩进
for (i = 0; i < level; ++i)
{
printf(" ");
}
if (ast->line != -1)
{
// 打印节点类型
printf("%s", ast->name);
// 根据不同类型打印节点数据
if ((!strcmp(ast->name, "ID")) || (!strcmp(ast->name, "TYPE")))
{
printf(": %s", ast->content);
}
else if (!strcmp(ast->name, "INT"))
{
printf(": %d", (int)ast->value);
}
else if (!strcmp(ast->name, "FLOAT"))
{
printf(": %f", ast->value);
}
else
{
// 非叶节点打印行号
printf("(%d)", ast->line);
}
}
printf("\n");
for (i = 0; i < ast->ncld; ++i)
{
Preorder((ast->cld)[i], level + 1);
}
}
else
{
return;
}
}
// 错误处理
void yyerror(char *msg)
{
hasFault = 1;
fprintf(stderr, "Error type B at Line %d: %s before %s\n", yylineno, msg, yytext);
}
// 设置节点打印状态 该节点为子节点
void setChildTag(tnode node)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < nodeNum; i++)
{
if (nodeList[i] == node)
{
nodeIsChild[i] = 1;
}
}
}
// 先序遍历分析
void analysis(Ast ast)
{
int i;
if (ast != NULL)
{
for (i = 0; i < ast->ncld; ++i)
{
analysis((ast->cld)[i]);
}
}
else
return;
}
// 建立变量符号
void newvar(int num, ...)
{
va_list valist;
va_start(valist, num);
var *res = (var *)malloc(sizeof(var));
tnode temp = (tnode)malloc(sizeof(tnode));
if (inStruc && LCnum)
{
// 是结构体的域
res->inStruc = 1;
res->strucNum = strucNum;
}
else
{
res->inStruc = 0;
res->strucNum = 0;
}
// 变量声明 int i
temp = va_arg(valist, tnode);
res->type = temp->content;
temp = va_arg(valist, tnode);
res->name = temp->content;
vartail->next = res;
vartail = res;
}
// 查找变量
int findvar(tnode val)
{
var *temp = (var *)malloc(sizeof(var *));
temp = varhead->next;
while (temp != NULL)
{
if (!strcmp(temp->name, val->content))
{
if (inStruc && LCnum) // 当前变量是结构体域
{
if (!temp->inStruc)
{
// 结构体域与变量重名
printf("Error type 9 at Line %d:Struct Field and Variable use the same name.\n", yylineno);
}
else if (temp->inStruc && temp->strucNum != strucNum)
{
// 不同结构体中的域重名
printf("Error type 10 at Line %d:Struct Fields use the same name.\n", yylineno);
}
else
{
// 同一结构体中域名重复
return 1;
}
}
else // 当前变量是全局变量
{
if (temp->inStruc)
{
// 变量与结构体域重名
printf("Error type 9 at Line %d:Struct Field and Variable use the same name.\n", yylineno);
}
else
{
// 变量与变量重名,即重复定义
return 1;
}
}
}
temp = temp->next;
}
return 0;
}
// 变量类型
char *typevar(tnode val)
{
var *temp = (var *)malloc(sizeof(var *));
temp = varhead->next;
while (temp != NULL)
{
if (!strcmp(temp->name, val->content))
return temp->type; //返回变量类型
temp = temp->next;
}
return NULL;
}
// 赋值号左边只能出现ID、Exp LB Exp RB 以及 Exp DOT ID
int checkleft(tnode val)
{
if (val->ncld == 1 && !strcmp((val->cld)[0]->name, "ID"))
return 1;
else if (val->ncld == 4 && !strcmp((val->cld)[0]->name, "Exp") && !strcmp((val->cld)[1]->name, "LB") && !strcmp((val->cld)[2]->name, "Exp") && !strcmp((val->cld)[3]->name, "RB"))
return 1;
else if (val->ncld == 3 && !strcmp((val->cld)[0]->name, "Exp") && !strcmp((val->cld)[1]->name, "DOT") && !strcmp((val->cld)[2]->name, "ID"))
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
// 创建函数符号
void newfunc(int num, ...)
{
int i;
va_list valist;
va_start(valist, num);
tnode temp = (tnode)malloc(sizeof(struct treeNode));
switch (num)
{
case 1:
if (inStruc && LCnum)
{
// 是结构体的域
functail->inStruc = 1;
functail->strucNum = strucNum;
}
else
{
functail->inStruc = 0;
functail->strucNum = 0;
}
//设置函数返回值类型
temp = va_arg(valist, tnode);
functail->rtype = temp->content;
functail->type = temp->type;
for (i = 0; i < rnum; i++)
{
if (rtype[i] == NULL || strcmp(rtype[i], functail->rtype))
printf("Error type 12 at Line %d:Func return type error.\n", yylineno);
}
functail->tag = 1; //标志为已定义
func *new = (func *)malloc(sizeof(func));
functail->next = new; //尾指针指向下一个空结点
functail = new;
break;
case 2:
//记录函数名
temp = va_arg(valist, tnode);
functail->name = temp->content;
//设置函数声明时的参数
temp = va_arg(valist, tnode);
functail->va_num = 0;
getdetype(temp);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
//定义的参数
void getdetype(tnode val)
{
int i;
if (val != NULL)
{
if (!strcmp(val->name, "ParamDec"))
{
functail->va_type[functail->va_num] = val->cld[0]->content;
functail->va_num++;
return;
}
for (i = 0; i < val->ncld; ++i)
{
getdetype((val->cld)[i]);
}
}
else
return;
}
//实际的参数
void getretype(tnode val)
{
int i;
if (val != NULL)
{
if (!strcmp(val->name, "Exp"))
{
va_type[va_num] = val->type;
va_num++;
return;
}
for (i = 0; i < val->ncld; ++i)
{
getretype((val->cld)[i]);
}
}
else
return;
}
//函数实际返回值类型
void getrtype(tnode val)
{
rtype[rnum] = val->type;
rnum++;
}
//检查形参与实参是否一致,没有错误返回0
int checkrtype(tnode ID, tnode Args)
{
int i;
va_num = 0;
getretype(Args);
func *temp = (func *)malloc(sizeof(func *));
temp = funchead->next;
while (temp != NULL && temp->name != NULL && temp->tag == 1)
{
if (!strcmp(temp->name, ID->content))
break;
temp = temp->next;
}
if (va_num != temp->va_num)
return 1;
for (i = 0; i < temp->va_num; i++)
{
if (temp->va_type[i] == NULL || va_type[i] == NULL || strcmp(temp->va_type[i], va_type[i]) != 0)
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
// 函数是否已经定义
int findfunc(tnode val)
{
func *temp = (func *)malloc(sizeof(func *));
temp = funchead->next;
while (temp != NULL && temp->name != NULL && temp->tag == 1)
{
if (!strcmp(temp->name, val->content))
{
if (inStruc && LCnum) // 当前变量是结构体域
{
if (!temp->inStruc)
{
// 结构体域与变量重名
printf("Error type 9 at Line %d:Struct Field and Variable use the same name.\n", yylineno);
}
else if (temp->inStruc && temp->strucNum != strucNum)
{
// 不同结构体中的域重名
printf("Error type 10 at Line %d:Struct Fields use the same name.\n", yylineno);
}
else
{
// 同一结构体中域名重复
return 1;
}
}
else // 当前变量是全局变量
{
if (temp->inStruc)
{
// 变量与结构体域重名
printf("Error type 9 at Line %d:Struct Field and Variable use the same name.\n", yylineno);
}
else
{
// 变量与变量重名,即重复定义
return 1;
}
}
}
temp = temp->next;
}
return 0;
}
// 函数类型
char *typefunc(tnode val)
{
func *temp = (func *)malloc(sizeof(func *));
temp = funchead->next;
while (temp != NULL)
{
if (!strcmp(temp->name, val->content))
return temp->type; //返回函数类型
temp = temp->next;
}
return NULL;
}
// 形参个数
int numfunc(tnode val)
{
func *temp = (func *)malloc(sizeof(func *));
temp = funchead->next;
while (temp != NULL)
{
if (!strcmp(temp->name, val->content))
return temp->va_num; //返回形参个数
temp = temp->next;
}
}
// 创建数组符号表
void newarray(int num, ...)
{
va_list valist;
va_start(valist, num);
array *res = (array *)malloc(sizeof(array));
tnode temp = (tnode)malloc(sizeof(struct treeNode));
if (inStruc && LCnum)
{
// 是结构体的域
res->inStruc = 1;
res->strucNum = strucNum;
}
else
{
res->inStruc = 0;
res->strucNum = 0;
}
// int a[10]
temp = va_arg(valist, tnode);
res->type = temp->content;
temp = va_arg(valist, tnode);
res->name = temp->content;
arraytail->next = res;
arraytail = res;
}
// 数组是否已经定义
int findarray(tnode val)
{
array *temp = (array *)malloc(sizeof(array *));
temp = arrayhead->next;
while (temp != NULL)
{
if (!strcmp(temp->name, val->content))
return 1;
temp = temp->next;
}
return 0;
}
// 数组类型
char *typearray(tnode val)
{
array *temp = (array *)malloc(sizeof(array *));
temp = arrayhead->next;
while (temp != NULL)
{
if (!strcmp(temp->name, val->content))
return temp->type; //返回数组类型
temp = temp->next;
}
return NULL;
}
// 创建结构体符号表
void newstruc(int num, ...)
{
va_list valist;
va_start(valist, num);
struc *res = (struc *)malloc(sizeof(struc));
tnode temp = (tnode)malloc(sizeof(struct treeNode));
// struct name{}
temp = va_arg(valist, tnode);
res->name = temp->content;
structail->next = res;
structail = res;
}
// 结构体是否和结构体或变量的名字重复
int findstruc(tnode val)
{
struc *temp = (struc *)malloc(sizeof(struc *));
temp = struchead->next;
while (temp != NULL)
{
if (!strcmp(temp->name, val->content))
return 1;
temp = temp->next;
}
if (findvar(val) == 1)
return 1;
return 0;
}
// 主函数 扫描文件并且分析
// 为bison会自己调用yylex(),所以在main函数中不需要再调用它了
// bison使用yyparse()进行语法分析,所以需要我们在main函数中调用yyparse()和yyrestart()
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int j, tem;
if (argc < 2)
{
return 1;
}
for (i = 1; i < argc; i++)
{
// 初始化,用于记录结构体域
inStruc = 0;
LCnum = 0;
strucNum = 0;
// 初始化符号表
varhead = (var *)malloc(sizeof(var));
vartail = varhead;
funchead = (func *)malloc(sizeof(func));
functail = (func *)malloc(sizeof(func));
funchead->next = functail;
functail->va_num = 0;
arrayhead = (array *)malloc(sizeof(array));
arraytail = arrayhead;
struchead = (struc *)malloc(sizeof(struc));
structail = struchead;
rnum = 0;
// 初始化节点记录列表
nodeNum = 0;
memset(nodeList, 0, sizeof(tnode) * 5000);
memset(nodeIsChild, 0, sizeof(int) * 5000);
hasFault = 0;
FILE *f = fopen(argv[i], "r");
if (!f)
{
perror(argv[i]);
return 1;
}
yyrestart(f);
yyparse();
fclose(f);
// 遍历所有非子节点的节点
if (hasFault)
continue;
for (j = 0; j < nodeNum; j++)
{
if (nodeIsChild[j] != 1)
{
// Preorder(nodeList[j], 0);
}
}
}
}