SpringSecurity源码解析
SpringSecurity源码解析
SpringSecurity是独立于SpringMVC的,SpringSecurity是直接与Servlet容器整合在一起的。它通过Filter整合到Servlet中。本篇分如下几个方面介绍SpringSecurity:
- 通过
DelegatingFilterProxy向应用注册BeanFilter - 通过
SecurityConfigurer配置SecurityFilterChain - 常见认证和授权过程
1. 通过DelegatingFilterProxy注册过滤器链
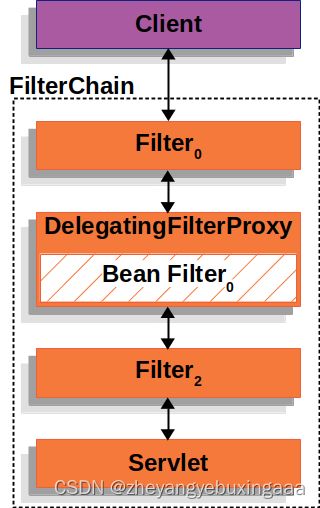
在介绍DelegatingFilterProxy前,先回顾一下Servlet容器的FilterChain。下面是Servlet容器处理Http请求的流程:
Servlet容器的请求过程如下:
- 浏览器发送
HTTPServletRequest - 容器创建
FilterChain(包含Filter和Servlet,在SpringMVC中这里的Servlet是DispatcherServlet) HTTPServletRequest依次经过Filter和Servlet处理。
下面就是FilterChain的工作代码示意:
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) {
// 在激活后续过滤器前做一些处理
chain.doFilter(request, response); // 激活后续过滤器
// 在激活后续过滤器后做一些处理
}
由于FilterChain中的Filter可以影响后续Filter,比如直接返回而不激活后续过滤器,又比如修改请求等,因此Filter的执行顺序很重要。
为了整合Spring和Servlet容器,Spring提供了DelegatingFilterProxy。它是一个Servlet容器的Filter;它的工作则是拦截请求到Spring Bean中,这样Spring容器中的Bean就无需注册成Servlet容器的Filter即可拦截请求。
下图是DelegatingFilterProxy整合到Servlet FilterChain中的示意图:
DelegatingFilterProxy拦截请求到Bean的工作示意代码如下:
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) {
// 获取 BeanFilter,例子中是 BeanFilter0
Filter delegate = getFilterBean(someBeanName);
// 代理工作到 BeanFilter
delegate.doFilter(request, response);
}
DelegatingFilterProxy 是Spring提供的,如果你要自己整合Spring和Servlet容器,则需要自己注册DelegatingFilterProxy。但如果使用SpringWeb,则它已经帮我们注册好了,我们只需要实现Filter接口。(并且可以通过DelegatingFilterProxyRegistrationBean指定Filter对应的URL或servlet)
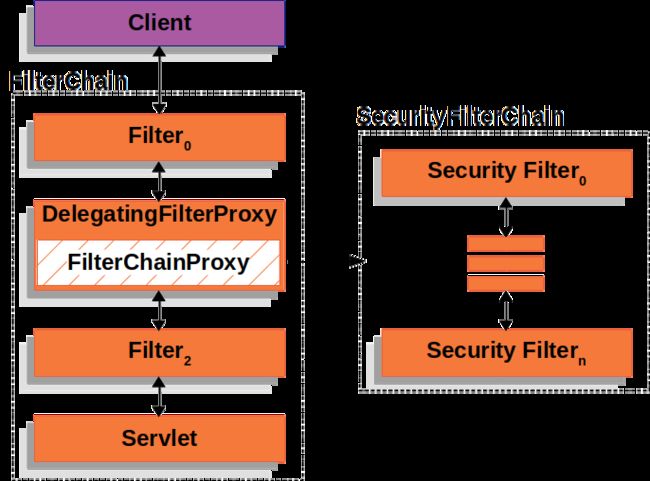
有了DelegatingFilterProxy之后,SpringSecurity就可以通过提供BeanFilter整合到Servlet容器的Filter了。SpringSecurity提供了一个叫FilterChainProxy的BeanFilter。FilterChainProxy的工作是将请求拦截到SecurityFilterChain中。而SecurityFilterChain中的一个个过滤器就是SpringSecurity用来进行认证和授权用的过滤器。
SpringSecurity提供的FilterChainProxy整合到DelegatingFilterProxy的示意图如下:
右边的SecurityFilterChain中的过滤器,即SpringSecurity实现功能的各种过滤器。
下面是SpringSecurity借助DelegatingFilterProxy注册FilterChainProxy的源码:(通过DelegatingFilterProxyRegistrationBean 来向 Servlet3.0+ 容器注册DelegatingFilterProxy)
public DelegatingFilterProxyRegistrationBean securityFilterChainRegistration(
SecurityProperties securityProperties) {
// 通过 RegistrationBean 注册 DelegatingFilterProxy
// 这个 Proxy 对应的 FilterBean 名字为 DEFAULT_FILTER_NAME 常量
// DEFAULT_FILTER_NAME 常量的值为 springSecurityFilterChain
DelegatingFilterProxyRegistrationBean registration = new DelegatingFilterProxyRegistrationBean(
DEFAULT_FILTER_NAME);
registration.setOrder(securityProperties.getFilter().getOrder());
registration.setDispatcherTypes(getDispatcherTypes(securityProperties));
return registration;
}
下面是上面被代理的 springSecurityFilterChain Bean 的定义,即SpringSecurity提供的默认SecurityFilterChain:
@Bean(name = AbstractSecurityWebApplicationInitializer.DEFAULT_FILTER_NAME)
public Filter springSecurityFilterChain() throws Exception {
// SpringSecurity 的两种配置方式
// 老版本使用 Adapter,新版本可以直接创建 SecurityFilterChain Bean
boolean hasConfigurers = this.webSecurityConfigurers != null && !this.webSecurityConfigurers.isEmpty();
boolean hasFilterChain = !this.securityFilterChains.isEmpty();
Assert.state(!(hasConfigurers && hasFilterChain),
"Found WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter as well as SecurityFilterChain. Please select just one.");
if (!hasConfigurers && !hasFilterChain) {
WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter adapter = this.objectObjectPostProcessor
.postProcess(new WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter() {
});
this.webSecurity.apply(adapter);
}
// 新版使用这个过滤器链,它通过 bean 自动注入
for (SecurityFilterChain securityFilterChain : this.securityFilterChains) {
this.webSecurity.addSecurityFilterChainBuilder(() -> securityFilterChain);
for (Filter filter : securityFilterChain.getFilters()) {
if (filter instanceof FilterSecurityInterceptor) {
this.webSecurity.securityInterceptor((FilterSecurityInterceptor) filter);
break;
}
}
}
for (WebSecurityCustomizer customizer : this.webSecurityCustomizers) {
customizer.customize(this.webSecurity);
}
// 最后通过 SecurityFilterChain 构造出一个名字为 springSecurityFilterChain 的 Filter
// 这个 Filter 最终会被 DelegatingFilterProxy 代理到 Servlet 容器中
return this.webSecurity.build();
}
上面的this.webSecurity.build()方法最终会回到WebSecurity的performBuild()方法中,就是在这个方法构造了这个Filter具体如下:
protected Filter performBuild() throws Exception {
Assert.state(!this.securityFilterChainBuilders.isEmpty(),
() -> "At least one SecurityBuilder needs to be specified. "
+ "Typically this is done by exposing a SecurityFilterChain bean. "
+ "More advanced users can invoke " + WebSecurity.class.getSimpleName()
+ ".addSecurityFilterChainBuilder directly");
int chainSize = this.ignoredRequests.size() + this.securityFilterChainBuilders.size();
List<SecurityFilterChain> securityFilterChains = new ArrayList<>(chainSize);
List<RequestMatcherEntry<List<WebInvocationPrivilegeEvaluator>>> requestMatcherPrivilegeEvaluatorsEntries = new ArrayList<>();
// 添加一条由忽略url组成的 securityFilterChain
for (RequestMatcher ignoredRequest : this.ignoredRequests) {
WebSecurity.this.logger.warn("You are asking Spring Security to ignore " + ignoredRequest
+ ". This is not recommended -- please use permitAll via HttpSecurity#authorizeHttpRequests instead.");
SecurityFilterChain securityFilterChain = new DefaultSecurityFilterChain(ignoredRequest);
securityFilterChains.add(securityFilterChain);
requestMatcherPrivilegeEvaluatorsEntries
.add(getRequestMatcherPrivilegeEvaluatorsEntry(securityFilterChain));
}
// 1.添加自己配置的 SecurityFilterChain
// 2.即上面那段代码中自动注入的 SecurityFilterChain
for (SecurityBuilder<? extends SecurityFilterChain> securityFilterChainBuilder : this.securityFilterChainBuilders) {
SecurityFilterChain securityFilterChain = securityFilterChainBuilder.build();
securityFilterChains.add(securityFilterChain);
requestMatcherPrivilegeEvaluatorsEntries
.add(getRequestMatcherPrivilegeEvaluatorsEntry(securityFilterChain));
}
if (this.privilegeEvaluator == null) {
this.privilegeEvaluator = new RequestMatcherDelegatingWebInvocationPrivilegeEvaluator(
requestMatcherPrivilegeEvaluatorsEntries);
}
// 3.使用这多条链构造 FilterChainProxy (它就是一个Filter将会被DelegatingFilterProxy代理的)
FilterChainProxy filterChainProxy = new FilterChainProxy(securityFilterChains);
if (this.httpFirewall != null) {
filterChainProxy.setFirewall(this.httpFirewall);
}
if (this.requestRejectedHandler != null) {
filterChainProxy.setRequestRejectedHandler(this.requestRejectedHandler);
}
filterChainProxy.afterPropertiesSet();
Filter result = filterChainProxy;
if (this.debugEnabled) {
this.logger.warn("\n\n" + "********************************************************************\n"
+ "********** Security debugging is enabled. *************\n"
+ "********** This may include sensitive information. *************\n"
+ "********** Do not use in a production system! *************\n"
+ "********************************************************************\n\n");
result = new DebugFilter(filterChainProxy);
}
this.postBuildAction.run();
// 返回上面含有多条 SecurityFilterChain 的 FilterChainProxy
return result;
}
这样Filter就借助DelegatingFilterProxy注册到Servlet容器中了。
2. 通过SecurityConfigurer配置过滤器链
从上面最后的代码的注释3可以看出来,SpringSecurity 的登录认证等操作都在 SecurityFilterProxy 的 SecurityFilterChain 中了。
下面是SpringSecurity默认提供的SecurityFilterChain
@Bean
@Order(SecurityProperties.BASIC_AUTH_ORDER)
SecurityFilterChain defaultSecurityFilterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
// 要求所有链接需要认证
http.authorizeRequests().anyRequest().authenticated();
// 启用表单登录
http.formLogin();
http.httpBasic();
// 构造 SecurityFilterChain
return http.build();
}
从上面代码可以看出SpringSecurity通过HttpSecurity的build()方法来构造SecurityFilterChain。它的build()方法先调用到doBuild(),然后最终调用到HttpSecurity的performBuild()方法,这两个方法如下:
@Override
protected final O doBuild() throws Exception {
synchronized (this.configurers) {
this.buildState = BuildState.INITIALIZING;
beforeInit();
init();
this.buildState = BuildState.CONFIGURING;
beforeConfigure();
configure();
this.buildState = BuildState.BUILDING;
O result = performBuild();
this.buildState = BuildState.BUILT;
return result;
}
}
这里面重要的configure()方法,它的代码如下:
private void configure() throws Exception {
Collection<SecurityConfigurer<O, B>> configurers = getConfigurers();
for (SecurityConfigurer<O, B> configurer : configurers) {
configurer.configure((B) this);
}
}
它所做的事情遍历调用 SecurityConfigurer 的configure()方法。而SecurityConfigure因为调用HttpSecurity的不同方法而配置了不同的SecurityConfigurer。比如上面http.formLogin()这个调用,就给HttpSecurity增加了一个FormLoginConfigurer如下所示:
public FormLoginConfigurer<HttpSecurity> formLogin() throws Exception {
return getOrApply(new FormLoginConfigurer<>());
}
这个FormLoginConfigure的代码如下:
public final class FormLoginConfigurer<H extends HttpSecurityBuilder<H>> extends
AbstractAuthenticationFilterConfigurer<H, FormLoginConfigurer<H>, UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter> {
// 首先是构造函数默认创建了一个 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter
public FormLoginConfigurer() {
super(new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter(), null);
usernameParameter("username");
passwordParameter("password");
}
// ...
// 然后是它的 configure 方法(这个方法在父类中)
@Override
public void configure(B http) throws Exception {
PortMapper portMapper = http.getSharedObject(PortMapper.class);
if (portMapper != null) {
this.authenticationEntryPoint.setPortMapper(portMapper);
}
RequestCache requestCache = http.getSharedObject(RequestCache.class);
if (requestCache != null) {
this.defaultSuccessHandler.setRequestCache(requestCache);
}
this.authFilter.setAuthenticationManager(http.getSharedObject(AuthenticationManager.class));
this.authFilter.setAuthenticationSuccessHandler(this.successHandler);
this.authFilter.setAuthenticationFailureHandler(this.failureHandler);
if (this.authenticationDetailsSource != null) {
this.authFilter.setAuthenticationDetailsSource(this.authenticationDetailsSource);
}
SessionAuthenticationStrategy sessionAuthenticationStrategy = http
.getSharedObject(SessionAuthenticationStrategy.class);
if (sessionAuthenticationStrategy != null) {
this.authFilter.setSessionAuthenticationStrategy(sessionAuthenticationStrategy);
}
RememberMeServices rememberMeServices = http.getSharedObject(RememberMeServices.class);
if (rememberMeServices != null) {
this.authFilter.setRememberMeServices(rememberMeServices);
}
SecurityContextConfigurer securityContextConfigurer = http.getConfigurer(SecurityContextConfigurer.class);
if (securityContextConfigurer != null && securityContextConfigurer.isRequireExplicitSave()) {
SecurityContextRepository securityContextRepository = securityContextConfigurer
.getSecurityContextRepository();
this.authFilter.setSecurityContextRepository(securityContextRepository);
}
// 重点是这里,前面都是配置那个 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter
// 这里将这个 Filter 添加到 HttpSecurity 的 filters 中
F filter = postProcess(this.authFilter);
http.addFilter(filter);
}
}
最后,使用HttpSecurity的filters生成SecurityFilterChain,如下所示:
protected DefaultSecurityFilterChain performBuild() {
ExpressionUrlAuthorizationConfigurer<?> expressionConfigurer = getConfigurer(
ExpressionUrlAuthorizationConfigurer.class);
AuthorizeHttpRequestsConfigurer<?> httpConfigurer = getConfigurer(AuthorizeHttpRequestsConfigurer.class);
boolean oneConfigurerPresent = expressionConfigurer == null ^ httpConfigurer == null;
Assert.state((expressionConfigurer == null && httpConfigurer == null) || oneConfigurerPresent,
"authorizeHttpRequests cannot be used in conjunction with authorizeRequests. Please select just one.");
// 1.主要代码在这里,排序 HttpSecurity 的 Filter
this.filters.sort(OrderComparator.INSTANCE);
List<Filter> sortedFilters = new ArrayList<>(this.filters.size());
for (Filter filter : this.filters) {
sortedFilters.add(((OrderedFilter) filter).filter);
}
// 2.用 filters 构造 SecurityFilterChain 返回
return new DefaultSecurityFilterChain(this.requestMatcher, sortedFilters);
}
这样,一个 SecurityFilterChain 就构造好了。
3. 常见认证和授权流程
上面最后代码配置的 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter 就是常用的认证和授权流程存在的地方。它的流程不复杂,所以都写在注释里面了。它的代码如下所示:
public class UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter extends AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter {
// ... ...
// 这个方法在父类,是过滤器执行的地方
private void doFilter(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
// 1. 判断请求是否要求认证
if (!requiresAuthentication(request, response)) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
return;
}
try {
// 2. attempAUthentication 是真正尝试认证的地方
Authentication authenticationResult = attemptAuthentication(request, response);
if (authenticationResult == null) {
// return immediately as subclass has indicated that it hasn't completed
return;
}
this.sessionStrategy.onAuthentication(authenticationResult, request, response);
// 3. 认证成功处理
if (this.continueChainBeforeSuccessfulAuthentication) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
successfulAuthentication(request, response, chain, authenticationResult);
}
catch (InternalAuthenticationServiceException failed) {
this.logger.error("An internal error occurred while trying to authenticate the user.", failed);
// 4. 认证失败处理
unsuccessfulAuthentication(request, response, failed);
}
catch (AuthenticationException ex) {
// Authentication failed
unsuccessfulAuthentication(request, response, ex);
}
}
// 2.真正实现认证的地方
@Override
public Authentication attemptAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws AuthenticationException {
// 2.1 不是POST请求直接失败
if (this.postOnly && !request.getMethod().equals("POST")) {
throw new AuthenticationServiceException("Authentication method not supported: " + request.getMethod());
}
// 2.2 获取请求用户名
String username = obtainUsername(request);
username = (username != null) ? username.trim() : "";
// 2.3 获取请求密码
String password = obtainPassword(request);
password = (password != null) ? password : "";
// 2.4 计算待认证token
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authRequest = UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken.unauthenticated(username,
password);
// Allow subclasses to set the "details" property
setDetails(request, authRequest);
// 2.5 这里是真正校验用户名和密码
return this.getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(authRequest);
}
真正进行用户名和密码校验的地方在 this.getAuthenticationManager().authentication()这个方法中,这里的AuthenticationManager从上一节UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter配置中可以看出默认是AuthenticationManager是来自HttpSecurity中的,而HttpSecurity 中默认配置 ProviderManager (这个在构造HttpSecurity bean时默认初始化的)。
综上所示:真正校验用户名和密码的地方在 ProviderManager 中。其代码如下:
@Override
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
Class<? extends Authentication> toTest = authentication.getClass();
AuthenticationException lastException = null;
AuthenticationException parentException = null;
Authentication result = null;
Authentication parentResult = null;
int currentPosition = 0;
int size = this.providers.size();
for (AuthenticationProvider provider : getProviders()) {
if (!provider.supports(toTest)) {
continue;
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(LogMessage.format("Authenticating request with %s (%d/%d)",
provider.getClass().getSimpleName(), ++currentPosition, size));
}
try {
// 主要的认证地方就在这里,其他的都是验证成功或失败的一些处理
// 主要的认证地方就在这里,其他的都是验证成功或失败的一些处理
// 主要的认证地方就在这里,其他的都是验证成功或失败的一些处理
result = provider.authenticate(authentication);
if (result != null) {
copyDetails(authentication, result);
break;
}
}
catch (AccountStatusException | InternalAuthenticationServiceException ex) {
prepareException(ex, authentication);
// SEC-546: Avoid polling additional providers if auth failure is due to
// invalid account status
throw ex;
}
catch (AuthenticationException ex) {
lastException = ex;
}
}
if (result == null && this.parent != null) {
// Allow the parent to try.
try {
parentResult = this.parent.authenticate(authentication);
result = parentResult;
}
catch (ProviderNotFoundException ex) {
// ignore as we will throw below if no other exception occurred prior to
// calling parent and the parent
// may throw ProviderNotFound even though a provider in the child already
// handled the request
}
catch (AuthenticationException ex) {
parentException = ex;
lastException = ex;
}
}
if (result != null) {
if (this.eraseCredentialsAfterAuthentication && (result instanceof CredentialsContainer)) {
// Authentication is complete. Remove credentials and other secret data
// from authentication
((CredentialsContainer) result).eraseCredentials();
}
// If the parent AuthenticationManager was attempted and successful then it
// will publish an AuthenticationSuccessEvent
// This check prevents a duplicate AuthenticationSuccessEvent if the parent
// AuthenticationManager already published it
if (parentResult == null) {
this.eventPublisher.publishAuthenticationSuccess(result);
}
return result;
}
// Parent was null, or didn't authenticate (or throw an exception).
if (lastException == null) {
lastException = new ProviderNotFoundException(this.messages.getMessage("ProviderManager.providerNotFound",
new Object[] { toTest.getName() }, "No AuthenticationProvider found for {0}"));
}
// If the parent AuthenticationManager was attempted and failed then it will
// publish an AbstractAuthenticationFailureEvent
// This check prevents a duplicate AbstractAuthenticationFailureEvent if the
// parent AuthenticationManager already published it
if (parentException == null) {
prepareException(lastException, authentication);
}
throw lastException;
}
默认情况下,在InitializeUserDetailsBeanManagerConfigurer类中配置了Provider,它默认使用DaoAuthenticationProvider 来完成认证,其代码如下:
// 这个方法在父类中
@Override
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
Assert.isInstanceOf(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken.class, authentication,
() -> this.messages.getMessage("AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider.onlySupports",
"Only UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken is supported"));
// 1. 获取待验证用户名
String username = determineUsername(authentication);
boolean cacheWasUsed = true;
UserDetails user = this.userCache.getUserFromCache(username);
if (user == null) {
cacheWasUsed = false;
try {
// 2. 获取用户信息
user = retrieveUser(username, (UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken) authentication);
}
catch (UsernameNotFoundException ex) {
this.logger.debug("Failed to find user '" + username + "'");
if (!this.hideUserNotFoundExceptions) {
throw ex;
}
throw new BadCredentialsException(this.messages
.getMessage("AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider.badCredentials", "Bad credentials"));
}
Assert.notNull(user, "retrieveUser returned null - a violation of the interface contract");
}
try {
this.preAuthenticationChecks.check(user);
// 3. 验证用户名和密码
additionalAuthenticationChecks(user, (UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken) authentication);
}
catch (AuthenticationException ex) {
if (!cacheWasUsed) {
throw ex;
}
// There was a problem, so try again after checking
// we're using latest data (i.e. not from the cache)
cacheWasUsed = false;
// 4. 若验证出错,则从数据源重新获取用户信息进行认证,以免缓存失效。
user = retrieveUser(username, (UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken) authentication);
this.preAuthenticationChecks.check(user);
additionalAuthenticationChecks(user, (UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken) authentication);
}
this.postAuthenticationChecks.check(user);
if (!cacheWasUsed) {
this.userCache.putUserInCache(user);
}
Object principalToReturn = user;
if (this.forcePrincipalAsString) {
principalToReturn = user.getUsername();
}
return createSuccessAuthentication(principalToReturn, authentication, user);
}
// 3. DaoAuthenticationProvider 真正校验用户名和密码的地方
protected void additionalAuthenticationChecks(UserDetails userDetails,
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
if (authentication.getCredentials() == null) {
this.logger.debug("Failed to authenticate since no credentials provided");
throw new BadCredentialsException(this.messages
.getMessage("AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider.badCredentials", "Bad credentials"));
}
// 3.1 获取请求中的密码
String presentedPassword = authentication.getCredentials().toString();
// 3.2 验证和后端保存的密码一致
if (!this.passwordEncoder.matches(presentedPassword, userDetails.getPassword())) {
this.logger.debug("Failed to authenticate since password does not match stored value");
throw new BadCredentialsException(this.messages
.getMessage("AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider.badCredentials", "Bad credentials"));
}
}
这样用户身份认证就完成了。用户的授权过程类似,这里就不展开了。