二叉树遍历结果推二叉树_二叉树遍历(PreOrder,InOrder,PostOrder)
二叉树遍历结果推二叉树
In this article, we shall look into how we can perform a Binary Tree Traversal using different methods.
在本文中,我们将研究如何使用不同的方法执行二叉树遍历。
A Binary Tree is a data structure where every node has at most two children. We call the topmost node as the Root node.
二叉树是一种数据结构,其中每个节点最多具有两个子节点。 我们将最顶层的节点称为“ 根”节点。
Since it could have two children, we could move across the Binary Tree in different ways. Here, we will discuss the three most commonly used methods for traversal, namely:
由于它可以有两个孩子,因此我们可以以不同的方式在二叉树上移动。 在这里,我们将讨论三种最常用的遍历方法,即:
- PreOrder Traversal 预购遍历
- InOrder Traversal 有序遍历
- PostOrder Traversal 后订单遍历
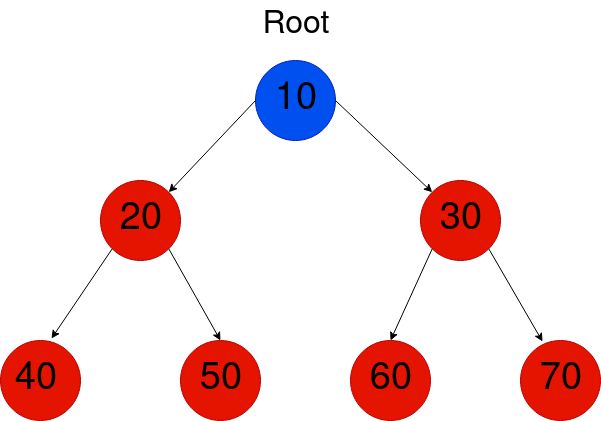
Let us consider the below Binary Tree and try to traverse it using the above methods.
让我们考虑下面的二叉树,并尝试使用上述方法遍历它。
1.二叉树预遍历 (1. Binary Tree PreOrder Traversal)
In a PreOrder traversal, the nodes are traversed according to the following sequence from any given node:
在PreOrder遍历中,将按照以下顺序从任何给定节点遍历节点:
- It will mark the current node as visited first. 它将当前节点标记为首先访问。
- Then, if a left child exists, it will go to the left sub-tree and continue the same process. 然后,如果存在左子节点,它将转到左子树并继续相同的过程。
- After visiting the left sub-tree, it will then move to its right sub-tree and continue the same process. 访问左侧子树后,它将移至右侧子树并继续相同的过程。
Since the sequence is node -> left -> right, it is referred to as a PreOrder traversal, since the node is visited before the left sub-tree.
由于序列是节点->左->右,因此被称为PreOrder遍历 ,因为该节点在左子树之前被访问。
Let’s write the C/C++ code for this:
让我们为此编写C / C ++代码:
void preorder_traversal(Node* root) {
if (root == NULL)
return;
printf("%d -> ", root->value);
preorder_traversal(root->left);
preorder_traversal(root->right);
}
PreOrder Traversal for our Binary Tree:
二叉树的预遍历:
10 -> 20 -> 40 -> 50 -> 30 -> 60 -> 70
10-> 20-> 40-> 50-> 30-> 60-> 70
2.二叉树有序遍历 (2. Binary Tree InOrder Traversal)
In an InOrder traversal, the nodes are traversed according to the following sequence from any given node:
在InOrder遍历中,将按照以下顺序从任何给定节点遍历节点:
- If a left child exists, it will always go to it first. 如果存在左孩子,则它将始终优先处理。
- After it visits the left sub-tree, it will visit the currently given node 访问左子树后,它将访问当前给定的节点
- After visiting the node, it will then move to its right sub-tree. 访问该节点后,它将移至其右子树。
As the sequence is left -> node -> right, it will refer to it as an InOrder traversal, since we will visit the nodes “in order”, from left to the right.
由于序列在左侧->节点->右侧,因此将其称为InOrder遍历 ,因为我们将“按顺序”从左到右访问节点。
The C/C++ code is given below
C / C ++代码如下
void inorder_traversal(Node* root) {
if (root == NULL)
return;
inorder_traversal(root->left);
printf("%d\n", root->value);
inorder_traversal(root->right);
}
InOrder Traversal for our Binary Tree:
二叉树的有序遍历:
40 -> 20 -> 50 -> 10 -> 60 -> 30 -> 70
40-> 20-> 50-> 10-> 60-> 30-> 70
3.二叉树后置遍历 (3. Binary Tree PostOrder Traversal)
In a PostOrder traversal, the nodes are traversed according to the following sequence from any given node:
在PostOrder遍历中,将按照以下顺序从任何给定节点遍历节点:
- If a left child exists, it will always go to it first. 如果存在左孩子,则它将始终优先处理。
- After visiting the left sub-tree, it will then move to its right sub-tree. 访问左子树后,它将移至其右子树。
- After it visits the right sub-tree, it will finally visit the currently given node 访问正确的子树后,它将最终访问当前给定的节点
Since the sequence is left -> right -> node, it is referred to as a PostOrder traversal, since the nodes are visited at the last.
由于序列是从左->右->节点开始的,因此称为PostOrder遍历 ,因为最后一次访问了节点。
The C/C++ code is given below
C / C ++代码如下
void postorder_traversal(Node* root) {
if (root == NULL)
return;
postorder_traversal(root->left);
postorder_traversal(root->right);
printf("%d\n", root->value);
}
PostOrder Traversal for our Binary Tree:
二叉树的PostOrder遍历:
40 -> 50 -> 20 -> 60 -> 70 -> 30 -> 10
40-> 50-> 20-> 60-> 70-> 30-> 10
4.用C / C ++完全实现二叉树遍历 (4. Complete Implementation of Binary Tree Traversal in C/C++)
To put it all together, I have put together the C/C++ code for all three traversals.
综上所述,我将所有三个遍历的C / C ++代码放在一起。
/**
Code for https://journaldev.com article
Purpose: Performs common Traversals on a Binary Tree
@author: Vijay Ramachandran
@date: 28-01-2020
*/
#include
#include
// Define the types of Traversals here
enum Traversal {PREORDER, INORDER, POSTORDER};
typedef enum Traversal Traversal;
typedef struct Node Node;
// Define the Tree Node here
struct Node {
int value;
// Pointers to the left and right children
Node* left, *right;
};
Node* init_tree(int data) {
// Creates the tree and returns the
// root node
Node* root = (Node*) malloc (sizeof(Node));
root->left = root->right = NULL;
root->value = data;
return root;
}
Node* create_node(int data) {
// Creates a new node
Node* node = (Node*) malloc (sizeof(Node));
node->value = data;
node->left = node->right = NULL;
return node;
}
void free_tree(Node* root) {
// Deallocates memory corresponding
// to every node in the tree.
Node* temp = root;
if (!temp)
return;
free_tree(temp->left);
free_tree(temp->right);
if (!temp->left && !temp->right) {
free(temp);
return;
}
}
void print_tree(Traversal traversal, Node* root) {
// Prints the tree according to
// various types of traversals
if (!root)
return;
switch(traversal) {
case (PREORDER):
// Do a Preorder Traversal
printf("%d -> ", root->value);
print_tree(traversal, root->left);
print_tree(traversal, root->right);
break;
case (INORDER):
// Do an Inorder Traversal
print_tree(traversal, root->left);
printf("%d -> ", root->value);
print_tree(traversal, root->right);
break;
case (POSTORDER):
// Do a postorder Traversal
print_tree(traversal, root->left);
print_tree(traversal, root->right);
printf("%d -> ", root->value);
break;
}
}
int main() {
// Program to demonstrate finding the height of a Binary Tree
// Create the root node having a value of 10
Node* root = init_tree(10);
// Insert nodes onto the tree
root->left = create_node(20);
root->right = create_node(30);
root->left->left = create_node(40);
root->left->right = create_node(50);
root->right->left = create_node(60);
root->right->right = create_node(70);
printf("----Preorder Traversal:----\n");
print_tree(PREORDER, root);
printf("\n\n");
printf("----Inorder Traversal:----\n");
print_tree(INORDER, root);
printf("\n\n");
printf("----Postorder Traversal:----\n");
print_tree(POSTORDER, root);
printf("\n\n");
// Free the tree!
free_tree(root);
return 0;
}
Output
输出量
----Preorder Traversal:----
10 -> 20 -> 40 -> 50 -> 30 -> 60 -> 70 ->
----Inorder Traversal:----
40 -> 20 -> 50 -> 10 -> 60 -> 30 -> 70 ->
----Postorder Traversal:----
40 -> 50 -> 20 -> 60 -> 70 -> 30 -> 10 ->
翻译自: https://www.journaldev.com/35001/binary-tree-traversal-preorder-inorder-postorder
二叉树遍历结果推二叉树