栈和队列oj题自测
1.LeetCode225 用队列实现栈

解题思路:
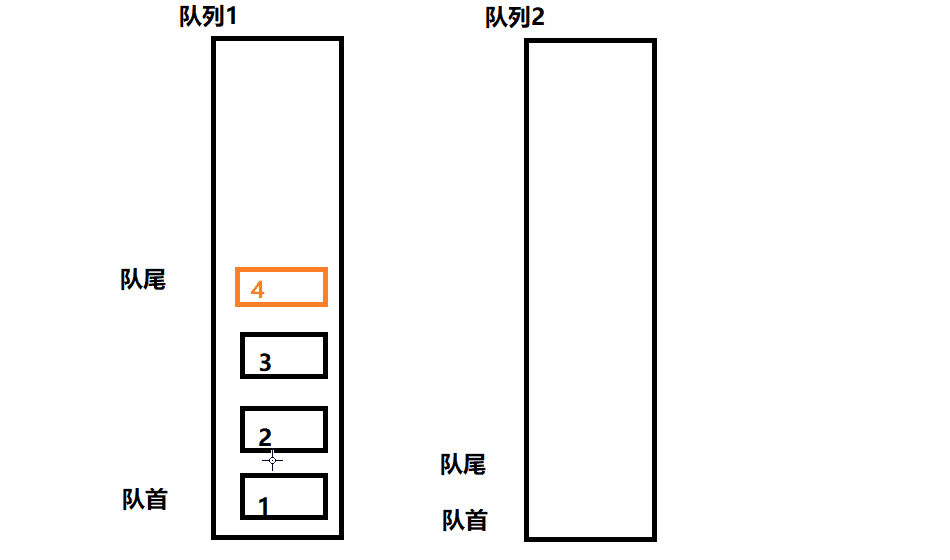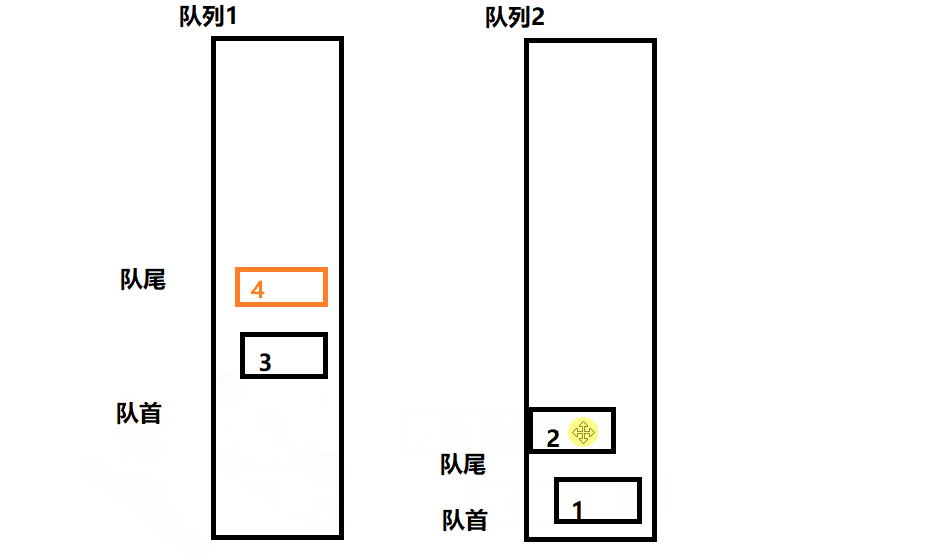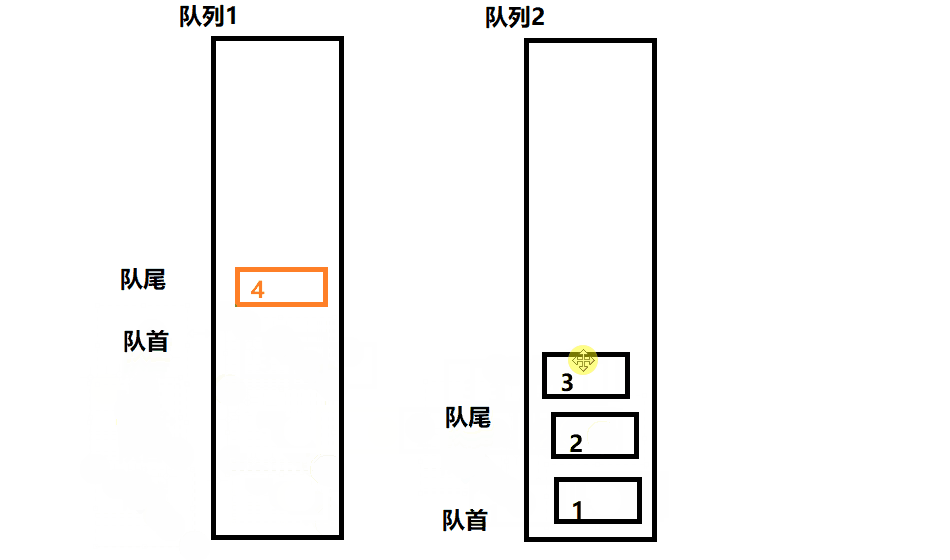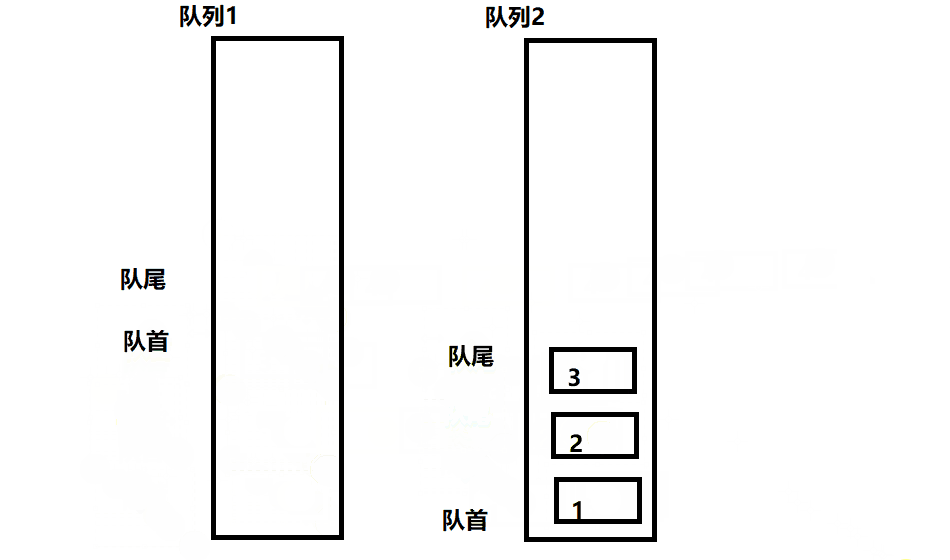
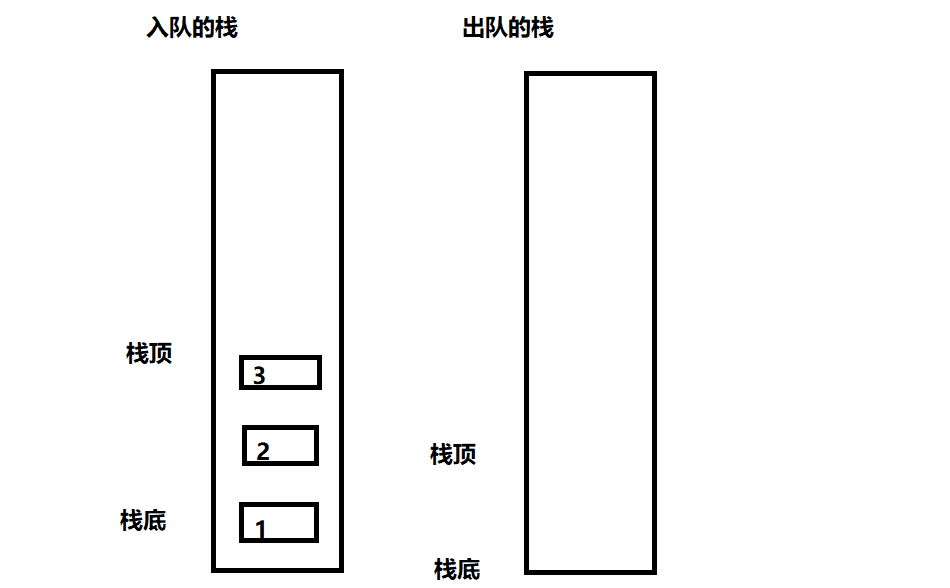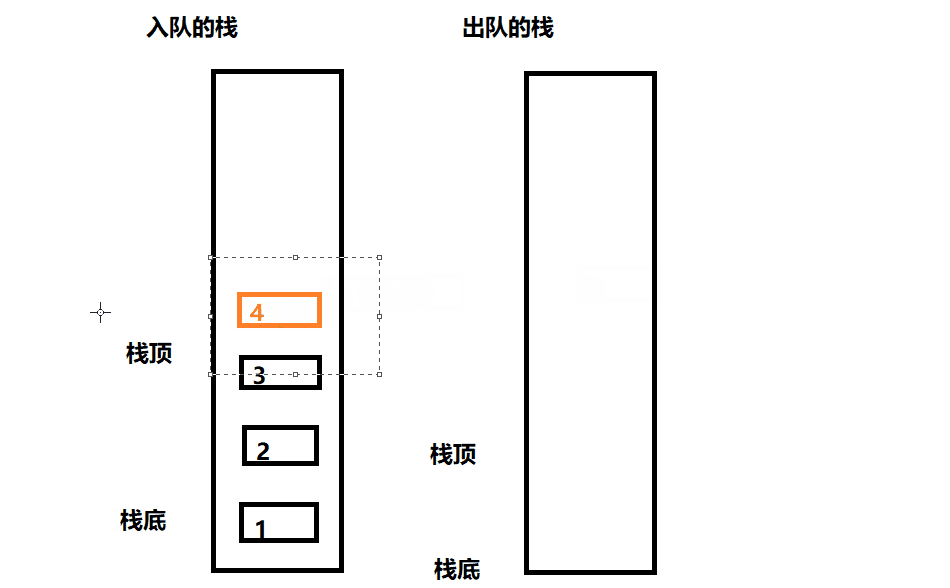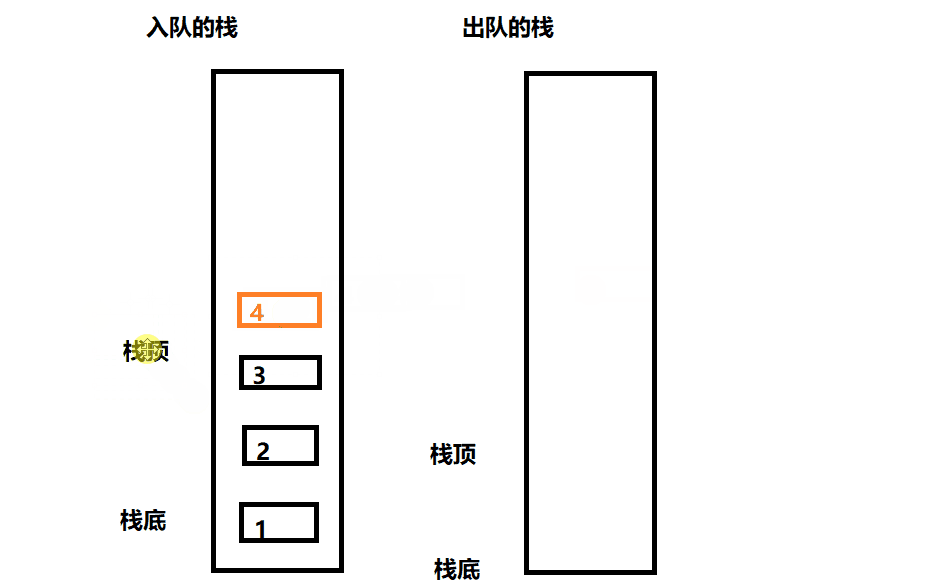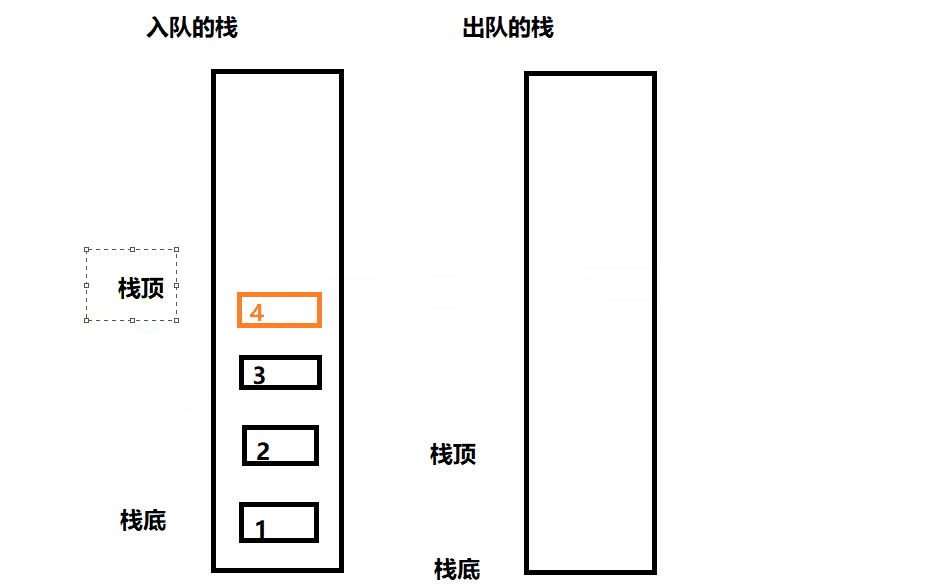
此题可以用两个队列去实现一个栈,每次始终保持一个队列为空。
- 入栈操作相当于给非空队列进行入队操作
- 出栈操作相当于非空队列的队尾元素出队,此时需要把非空队列除最后一个元素之外的其余元素入队到空队列,然后出队最后一个队尾元素
typedef int QDatatype;
typedef struct QueueNode
{
struct QNode* next;
QDatatype data;
}QNode;
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode* head;
QNode* tail;
int size;
}Queue;
void QueueInit(Queue* q);
void QueuePush(Queue* q, QDatatype x);
void QueuePop(Queue* q);
QDatatype QueueFront(Queue* q);
QDatatype QueueBack(Queue* q);
int Queuesize(Queue* q);
int QueueEmpty(Queue* q);
void QueueDestroy(Queue* q);
void QueueInit(Queue* q)
{
assert(q);
q->head = q->tail = NULL;
q->size = 0;
}
void QueuePush(Queue* q, QDatatype x)
{
QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return;
}
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
//队列为空
if (q->head == NULL)
{
assert(q->tail == NULL);
q->head = q->tail = newnode;
}
//队列不空
else
{
q->tail->next = newnode;
q->tail = newnode;
}
q->size++;
}
void QueuePop(Queue* q)
{
assert(q);
assert(q->head != NULL);
//队中只有一个元素
if (q->head->next == NULL)
{
free(q->head);
q->head = q->tail = NULL;
}
else
{
QNode* next = q->head->next;
free(q->head);
q->head = next;
}
q->size--;
}
QDatatype QueueFront(Queue* q)
{
assert(q);
assert(!QueueEmpty(q));
return q->head->data;
}
QDatatype QueueBack(Queue* q)
{
assert(q);
assert(!QueueEmpty(q));
return q->tail->data;
}
int Queuesize(Queue* q)
{
assert(q);
return q->size;
}
int QueueEmpty(Queue* q)
{
assert(q);
return q->size == 0;
}
void QueueDestroy(Queue* q)
{
assert(q);
QNode* cur = q->head;
while (cur)
{
QNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
q->head = q->tail = NULL;
q->size = 0;
}
typedef struct {
Queue q1;
Queue q2;
} MyStack;
MyStack* myStackCreate() {
MyStack* tst=(MyStack*)malloc(sizeof(MyStack));
if(tst==NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return NULL;
}
QueueInit(&tst->q1);
QueueInit(&tst->q2);
return tst;
}
//往有数据的队列里插入
void myStackPush(MyStack* obj, int x) {
if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
{
QueuePush(&obj->q1,x);
}
else{
QueuePush(&obj->q2,x);
}
}
//把非空队列中的数据导入空队列中,然后弹出非空队列里的最后一个数据
int myStackPop(MyStack* obj) {
Queue* emptyQ=&obj->q1;
Queue* noneemptyQ=&obj->q2;
if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
{
emptyQ=&obj->q2;
noneemptyQ=&obj->q1;
}
while(Queuesize(noneemptyQ)>1)
{
QueuePush(emptyQ,QueueFront(noneemptyQ));
QueuePop(noneemptyQ);
}
int top=QueueFront(noneemptyQ);
QueuePop(noneemptyQ);
return top;
}
int myStackTop(MyStack* obj) {
if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
{
return QueueBack(&obj->q1);
}
else{
return QueueBack(&obj->q2);
}
}
bool myStackEmpty(MyStack* obj) {
return QueueEmpty(&obj->q1)&&QueueEmpty(&obj->q2);
}
void myStackFree(MyStack* obj) {
QueueDestroy(&obj->q1);
QueueDestroy(&obj->q2);
free(obj);
}
2.LeetCode232 用栈实现队列

解题思路:
此题可以用两个栈实现,一个栈进行入队操作,另一个栈进行出队操作。
- 出队操作: 当出队的栈不为空时,直接进行出栈操作,如果为空,需要把入队的栈元素全部导入到出队的栈,然后再进行出栈操作。
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* a;
int top;
int capacity;
}ST;
void STinit(ST* ps);
void STDestory(ST* ps);
void STPush(ST* ps,STDataType x);
void STPop(ST* ps);
int STSIze(ST* ps);
bool STEmpty(ST* ps);
STDataType STTop(ST* ps);
void STinit(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->a=(STDataType*)malloc(sizeof(STDataType)*4);
if(ps->a==NULL)
{
perror("mallloc fali");
return ;
}
ps->top=0;
ps->capacity=4;
}
void STDestory(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->a);
ps->a=NULL;
ps->top=0;
ps->capacity=0;
}
void STPush(ST* ps,STDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
if(ps->top==ps->capacity)
{
STDataType* tem=(STDataType*)realloc(ps->a,sizeof(STDataType)*ps->capacity*2);
if(tem==NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail");
return ;
}
ps->a=tem;
ps->capacity*=2;
}
ps->a[ps->top]=x;
ps->top++;
}
bool STEmpty(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top==0;
}
void STPop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!STEmpty(ps));
ps->top--;
}
int STSIze(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top;
}
STDataType STTop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!STEmpty(ps));
return ps->a[ps->top-1];
}
typedef struct {
ST pushst;
ST popst;
} MyQueue;
MyQueue* myQueueCreate() {
MyQueue* obj=(MyQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyQueue));
if(obj==NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return NULL;
}
STinit(&obj->pushst);
STinit(&obj->popst);
return obj;
}
void myQueuePush(MyQueue* obj, int x) {
STPush(&obj->pushst,x);
}
int myQueuePeek(MyQueue* obj) {
if(STEmpty(&obj->popst))
{
while(!STEmpty(&obj->pushst))
{
STPush(&obj->popst,STTop(&obj->pushst));
STPop(&obj->pushst);
}
}
return STTop(&obj->popst);
}
int myQueuePop(MyQueue* obj) {
int front=myQueuePeek(obj);
STPop(&obj->popst);
return front;
}
bool myQueueEmpty(MyQueue* obj) {
return STEmpty(&obj->pushst)&&STEmpty(&obj->popst);
}
void myQueueFree(MyQueue* obj) {
STDestory(&obj->pushst);
STDestory(&obj->popst);
free(obj);
}
3.LeetCode20 有效的括号
解题思路:
当遇到一个左括号时,先将这个左括号放入栈顶,当遇到一个右括号时,取出栈顶的左括号并判断它们是否是相同类型的括号。如果不是相同的类型,或者栈中并没有左括号,那么该字符串无效,如果是相同类型,则继续匹配,直到该字符串末尾。
代码实现:
typedef char STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* a;
int top;
int capacity;
}ST;
//先声明
void STInit(ST* ps);
void STDestroy(ST* ps);
void STPush(ST* ps, STDataType x);
void STPop(ST* ps);
int STSize(ST* ps);
bool STEmpty(ST* ps);
STDataType STTop(ST* ps);
//再定义
void STInit(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->a = (STDataType*)malloc(sizeof(STDataType) * 4);
if (ps->a == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return;
}
ps->capacity = 4;
ps->top = 0; // top是栈顶元素的下一个位置
//ps->top = -1; // top是栈顶元素位置
}
void STDestroy(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->top = 0;
ps->capacity = 0;
}
void STPush(ST* ps, STDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->top == ps->capacity)
{
STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->a,
sizeof(STDataType) * ps->capacity*2);
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail");
return;
}
ps->a = tmp;
ps->capacity *= 2;
}
ps->a[ps->top] = x;
ps->top++;
}
void STPop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!STEmpty(ps));
ps->top--;
}
int STSize(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top;
}
bool STEmpty(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top == 0;
}
STDataType STTop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!STEmpty(ps));
return ps->a[ps->top - 1];
}
bool isValid(char * s){
ST st;
STInit(&st);
while(*s)
{
if(*s=='('||*s=='['||*s=='{')
{
STPush(&st,*s);
}
else
{
if(STEmpty(&st))
{
STDestroy(&st);
return false;
}
char top=STTop(&st);
STPop(&st);
if(*s==')'&&top!='('||
*s==']'&&top!='['||
*s=='}'&&top!='{')
{
STDestroy(&st);
return false;
}
}
++s;
}
bool res=STEmpty(&st);
STDestroy(&st);
return res;
}
4.LeetCode622 设计循环队列
解题思路:
通过一个定长数组实现循环队列
- 入队:首先要判断队列是否已满,再进行入队的操作,入队操作需要考虑索引循环的问题,当索引越界,需要让它变成最小值
- 出队:首先要判断队列是否为空,再进行出队操作,出队也需要考虑索引循环的问题
typedef struct {
int *a;
int front;
int rear;
int k;
} MyCircularQueue;
MyCircularQueue* myCircularQueueCreate(int k) {
MyCircularQueue* obj=(MyCircularQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyCircularQueue));
obj->a=(int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*(k+1));
obj->front=obj->rear=0;
obj->k=k;
return obj;
}
bool myCircularQueueIsEmpty(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
return obj->front==obj->rear;
}
bool myCircularQueueIsFull(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
return obj->front==(obj->rear+1)%(obj->k+1);
}
bool myCircularQueueEnQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj, int value) {
if(myCircularQueueIsFull(obj))
{
return false;
}
obj->a[obj->rear++]=value;
obj->rear%=(obj->k+1);
return true;
}
bool myCircularQueueDeQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))
{
return false;
}
++obj->front;
obj->front%=(obj->k+1);
return true;
}
int myCircularQueueFront(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))return -1;
else return obj->a[obj->front];
}
int myCircularQueueRear(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))return -1;
else return obj->a[(obj->rear-1+obj->k+1)%(obj->k+1)];
}
void myCircularQueueFree(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
free(obj->a);
free(obj);
}
本篇到此结束,码文不易,还请多多支持哦!