Elasticsearch(ES)简介及基本使用
ES 简介
ES是一个使用java语言编写的并且基于Lucene编写的搜索引擎, 他提供了分布式的全文搜索服务, 还提供了一个RESTful风格的web接口, 官方还对多种语言提供了相应的API
Lucene?
Lucene 本身就是一个搜索引擎的底层,
ES特点
分布式: ES主要为了横向扩展能力
全文检索: 将一段词语进行分词, 并且将分出的单个词语统一的放入一个分词库中,在搜索时,根据关键字去分词库中搜索去找到想找到的内容,(倒排索引)
RESTful风格web接口: 操作ES非常简单, 只需要发送一个Http请求并且根据请求方式不同和携带参数不同,执行相应的功能,
倒排索引
待补充
安装ES&kibana
version: "3.1"
services:
elasticsearch:
image: daocloud.io/library/elasticsearch:6.5.4
restart: always
container_name: elasticsearch
environment:
- "cluster.name=elasticsearch" #设置集群名称为elasticsearch
- "discovery.type=single-node" #以单一节点模式启动
- "ES_JAVA_OPTS=-Xms4096m -Xmx4096m" #设置使用jvm内存大小
ports:
- 9200:9200
kibana:
image: daocloud.io/library/kibana:6.5.4
restart: always
container_name: kibane
ports:
- 5601:5601
depends_on:
- elasticsearch #kibana在elasticsearch启动之后再启动
environment:
- "elasticsearch.hosts=http://127.0.0.1:9200" #设置访问elasticsearch的地址
IK 分词器
安装
下载地址: https://github.com/medcl/elasticsearch-analysis-ik/releases?after=v6.7.2
下载需要与ES版本一直否则无法启动ES,
在 elasticsearch/plugins 下新建IK文件夹, 解压 后 重启ES即可
IK 介绍
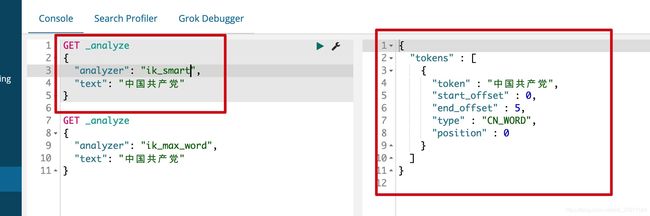
如果使用中文建议使用IK,他有两种分词模式 ik_mart(最少切分)与 ik_max_word(最细粒度划分)
ik_mart 使用介绍
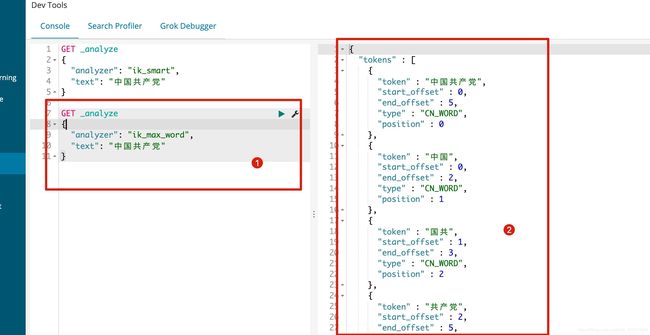
ik_max_word使用介绍
但是使用IK_MAX_WORD有一个问题, 他是根据他认识的进行分词, 比如我们想把胡雪阔当连起来他是不可以的
这个时候就需要自己加到字典中,
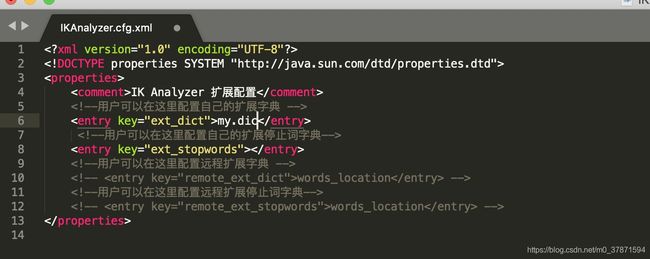
IK 分词器加入自定义词语
首先在elasticsearch/plugins/ik/config文件夹下面创建自己的字典my.dic后加入huxuekuo一行文字
然后编辑IKAnalyzer.cfg.xml配置文件,修改
然后重启ES看效果 !!
Restful请求详解
通过Http请求进行操作
| Method | URL | remarks |
|---|---|---|
| PUT | 127.0.0.1:9200/索引名称/类型名称/文档ID | 添加文档(自动创建索引) |
| POST | 127.0.0.1:9200/索引名称/类型名称 | 创建文档(随机索引ID) |
| POST | 127.0.0.1:9200/索引名称/类型名称/文档ID/_update | 修改文档 |
| DELETE | 127.0.0.1:9200/索引名称/类型名称/文档ID | 删除文档 |
| GET | 127.0.0.1:9200/索引名称/类型名称/文档ID | 根据文档ID获取文档 |
| POST | 127.0.0.1:9200/索引名称/类型名称/_search | 查询索引下所有文档 |
PUT 语法
创建文档案例
PUT /test1/type1/1
{
"name":"huxuekuo",
"age" : 12
}
返回 结果:
{
"_index" : "test1",
"_type" : "type1",
"_id" : "1",
"_version" : 1,
"result" : "created",
"_shards" : {
"total" : 2,
"successful" : 1,
"failed" : 0
},
"_seq_no" : 0,
"_primary_term" : 1
}
有一个问题是, 当前数据的类型是ES自动识别的,
PUT /test1/type1/1 语句中的type1 可以没有默认为_doc, PUT /test1/__doc/1 或者doc也不用加
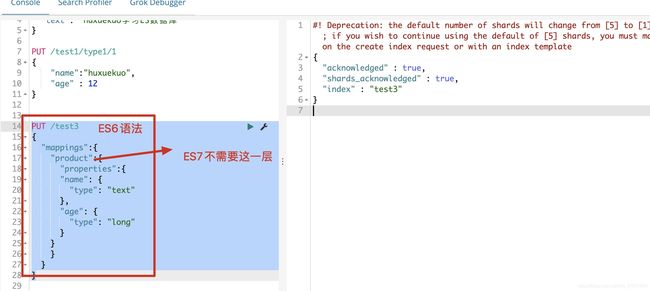
创建索引(指定属性的数据类型)
### ES7 语法
PUT /test2
{
"mappings":{
"properties":{
"name":{
"type":"text"
},
"age":{
"type":"long"
}
}
}
}
### ES6 语法
PUT /test3
{
"mappings":{
"product":{
"properties":{
"name": {
"type": "text"
},
"age": {
"type": "long"
}
}
}
}
}
返回结果
{
"acknowledged" : true,
"shards_acknowledged" : true,
"index" : "test3"
}
GET语法
获取索引信息
GET /test3
返回数据
{
"test3" : {
"aliases" : { },
"mappings" : {
"product" : {
"properties" : {
"age" : {
"type" : "long"
},
"name" : {
"type" : "text"
}
}
}
},
"settings" : {
"index" : {
"creation_date" : "1604564111952",
"number_of_shards" : "5",
"number_of_replicas" : "1",
"uuid" : "UHXqcMJnSWKQE4The-_mcQ",
"version" : {
"created" : "6050499"
},
"provided_name" : "test3"
}
}
}
}
获取文档信息
GET /test1/type1/1
{
"_index" : "test1",
"_type" : "type1",
"_id" : "1",
"_version" : 1,
"found" : true,
"_source" : {
"name" : "huxuekuo",
"age" : 12
}
}
简单条件查询
GET /test1/type1/_search?q=name:1
### 返回结果
{
"_index" : "test1",
"_type" : "type1",
"_id" : "1",
"_score" : 0.2876821,
"_source" : {
"name" : "1",
"age" : "1"
}
}
注意在简单查询中返回了
"_score" : 0.2876821,这是什么? 如果存在多条数据,匹配度越高则分数越高
POST 语法
post可以用作修改文档, put 也可以修改文档, 我们先看一下put 修改文档的方式
PUT /test1/type1/1
{
"name":"huxuekuo1",
"age" : 12
}
当文档ID已经创建, 一下语句就是修改语句, 有一个问题是, 如果修改时丢字段了
丢字段以后的文档数据:
{
"_index" : "test1",
"_type" : "type1",
"_id" : "1",
"_version" : 2,
"found" : true,
"_source" : {
"name" : "huxuekuo1"
}
}
_version 发生改变, name值确实改了,但是丢失的age字段也没有了
看一下正常的修改方式
POST /test1/type1/1/_update
{
"doc":{
"name":"1"
}
}
这样就算没有age字段他就不会更新age字段
当前的
age类型为long类型, 我们尝试看看修改为text是否可以成功
POST /test1/type1/1/_update
{
"doc":{
"age":"1爱我的"
}
}
### 返回结果
{
"type": "mapper_parsing_exception",
"reason": "failed to parse field [age] of type [long]"
}
一旦数据类型确认下来将不可以通过修改数据的方式去修改
DELETE语法
删除索引
DELETE test1
删除文档
DELETE /test1/type1/1
复杂查询
精准查询
GET /vms/product/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"title": "iphone11"
}
}
}
### 返回结果
{
"took" : 16,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 5,
"successful" : 5,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 1,
"max_score" : 0.2876821,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "vms",
"_type" : "product",
"_id" : "3",
"_score" : 0.2876821,
"_source" : {
"title" : "iphone11",
"date" : "2020-11-04",
"remarks" : "苹果手机无敌啊"
}
}
]
}
}
略部分字段显示(_source)
GET /vms/product/_search
{
"query": {
"match_phrase_prefix": {
"title": "iphone"
}
}
, "_source": ["title","date"]
}
### 返回结果
{
"_index" : "vms",
"_type" : "product",
"_id" : "4",
"_score" : 0.6931472,
"_source" : {
"date" : "2018-11-04",
"title" : "iphonex"
}
},
_source标记了只显示title - date在返回结果中就只有这两样
排序(sort)
简单排序
GET /vms/product/_search
{
"query": {
"match_phrase_prefix": {
"title": "iphone"
}
},
"sort": [
{
"date": {
"order": "asc"
}
}
]
}
### 返回结果
{
"took" : 12,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 5,
"successful" : 5,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 3,
"max_score" : null,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "vms",
"_type" : "product",
"_id" : "4",
"_score" : null,
"_source" : {
"date" : "2018-11-04",
"title" : "iphonex"
},
"sort" : [
1541289600000
]
},
{
"_index" : "vms",
"_type" : "product",
"_id" : "1",
"_score" : null,
"_source" : {
"date" : "2020-11-04",
"title" : "iphone12"
},
"sort" : [
1604448000000
]
},
{
"_index" : "vms",
"_type" : "product",
"_id" : "3",
"_score" : null,
"_source" : {
"date" : "2020-11-04",
"title" : "iphone11"
},
"sort" : [
1604448000000
]
}
]
}
}
asc: 升序
desc: 降序在使用
sort以后_score就没有了为null
分页查询
GET /vms/product/_search
{
"query": {
"match_phrase_prefix": {
"title": "iphone"
}
},
"sort": [
{
"date": {
"order": "asc"
}
}
],
"from": 0,
"size": 1
}
关键词
from(从第几个开始)与size(返回多少条数据), 数据的下标还是从0开始的
布尔值查询
must (并且)
GET /vms_test/_doc/_search
{
"query":{
"bool":{
"must":[
{
"match":{
"name":"胡"
}
},
{
"match":{
"age":"20"
}
}
]
}
}
}
获取同时满足两个条件的数据
should (或)
GET /vms_test/_doc/_search
{
"query":{
"bool":{
"should":[
{
"match":{
"name":"胡"
}
},
{
"match":{
"age":"20"
}
}
]
}
}
}
must_not(不等于)
GET /vms_test/_doc/_search
{
"query":{
"bool":{
"must_not":[
{
"match":{
"name":"胡"
}
},
{
"match":{
"age":"20"
}
}
]
}
}
}
filter(过滤器)
range(范围过滤)
GET vms_test/_doc/_search
{
"query":{
"bool":{
"filter":{
"range":{
"age":{
"gt":10
}
}
}
}
}
}
gt大于
lt小于
gte大于等于
lte小于等于是可以联合使用的