面试被问到vue的diff算法原理,我不允许你回答不上来
一、是什么
diff 算法是一种通过同层的树节点进行比较的高效算法
其有两个特点:
- 比较只会在同层级进行, 不会跨层级比较
- 在diff比较的过程中,循环从两边向中间比较
diff 算法在很多场景下都有应用,在 vue 中,作用于虚拟 dom 渲染成真实 dom 的新旧 VNode 节点比较
二、比较方式
diff整体策略为:深度优先,同层比较
- 比较只会在同层级进行, 不会跨层级比较
- 比较的过程中,循环从两边向中间收拢
下面举个vue通过diff算法更新的例子:
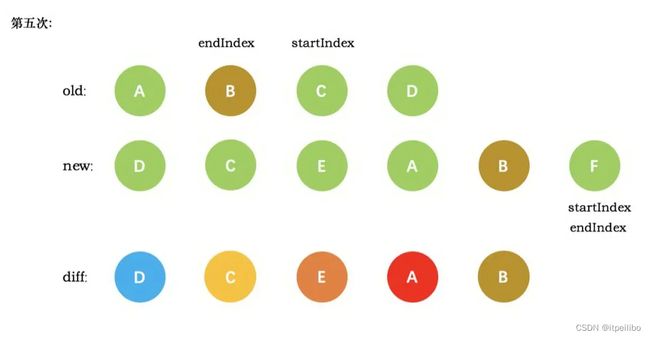
新旧VNode节点如下图所示:
第一次循环后,发现旧节点D与新节点D相同,直接复用旧节点D作为diff后的第一个真实节点,同时旧节点endIndex移动到C,新节点的 startIndex 移动到了 C
第二次循环后,同样是旧节点的末尾和新节点的开头(都是 C)相同,同理,diff 后创建了 C 的真实节点插入到第一次创建的 B 节点后面。同时旧节点的 endIndex 移动到了 B,新节点的 startIndex 移动到了 E
第三次循环中,发现E没有找到,这时候只能直接创建新的真实节点 E,插入到第二次创建的 C 节点之后。同时新节点的 startIndex 移动到了 A。旧节点的 startIndex 和 endIndex 都保持不动
第四次循环中,发现了新旧节点的开头(都是 A)相同,于是 diff 后创建了 A 的真实节点,插入到前一次创建的 E 节点后面。同时旧节点的 startIndex 移动到了 B,新节点的 startIndex 移动到了 B
第五次循环中,情形同第四次循环一样,因此 diff 后创建了 B 真实节点 插入到前一次创建的 A 节点后面。同时旧节点的 startIndex 移动到了 C,新节点的 startIndex 移动到了 F
新节点的 startIndex 已经大于 endIndex 了,需要创建 newStartIdx 和 newEndIdx 之间的所有节点,也就是节点F,直接创建 F 节点对应的真实节点放到 B 节点后面
三、原理分析
当数据发生改变时,set方法会调用Dep.notify通知所有订阅者Watcher,订阅者就会调用patch给真实的DOM打补丁,更新相应的视图
源码位置:src/core/vdom/patch.js
function patch(oldVnode, vnode, hydrating, removeOnly) {
if (isUndef(vnode)) { // 没有新节点,直接执行destory钩子函数
if (isDef(oldVnode)) invokeDestroyHook(oldVnode)
return
}
let isInitialPatch = false
const insertedVnodeQueue = []
if (isUndef(oldVnode)) {
isInitialPatch = true
createElm(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue) // 没有旧节点,直接用新节点生成dom元素
} else {
const isRealElement = isDef(oldVnode.nodeType)
if (!isRealElement && sameVnode(oldVnode, vnode)) {
// 判断旧节点和新节点自身一样,一致执行patchVnode
patchVnode(oldVnode, vnode, insertedVnodeQueue, null, null, removeOnly)
} else {
// 否则直接销毁及旧节点,根据新节点生成dom元素
if (isRealElement) {
if (oldVnode.nodeType === 1 && oldVnode.hasAttribute(SSR_ATTR)) {
oldVnode.removeAttribute(SSR_ATTR)
hydrating = true
}
if (isTrue(hydrating)) {
if (hydrate(oldVnode, vnode, insertedVnodeQueue)) {
invokeInsertHook(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue, true)
return oldVnode
}
}
oldVnode = emptyNodeAt(oldVnode)
}
return vnode.elm
}
}
}
patch函数前两个参数位为oldVnode 和 Vnode ,分别代表新的节点和之前的旧节点,主要做了四个判断:
- 没有新节点,直接触发旧节点的
destory钩子 - 没有旧节点,说明是页面刚开始初始化的时候,此时,根本不需要比较了,直接全是新建,所以只调用
createElm - 旧节点和新节点自身一样,通过
sameVnode判断节点是否一样,一样时,直接调用patchVnode去处理这两个节点 - 旧节点和新节点自身不一样,当两个节点不一样的时候,直接创建新节点,删除旧节点
下面主要讲的是patchVnode部分
function patchVnode (oldVnode, vnode, insertedVnodeQueue, removeOnly) {
// 如果新旧节点一致,什么都不做
if (oldVnode === vnode) {
return
}
// 让vnode.el引用到现在的真实dom,当el修改时,vnode.el会同步变化
const elm = vnode.elm = oldVnode.elm
// 异步占位符
if (isTrue(oldVnode.isAsyncPlaceholder)) {
if (isDef(vnode.asyncFactory.resolved)) {
hydrate(oldVnode.elm, vnode, insertedVnodeQueue)
} else {
vnode.isAsyncPlaceholder = true
}
return
}
// 如果新旧都是静态节点,并且具有相同的key
// 当vnode是克隆节点或是v-once指令控制的节点时,只需要把oldVnode.elm和oldVnode.child都复制到vnode上
// 也不用再有其他操作
if (isTrue(vnode.isStatic) &&
isTrue(oldVnode.isStatic) &&
vnode.key === oldVnode.key &&
(isTrue(vnode.isCloned) || isTrue(vnode.isOnce))
) {
vnode.componentInstance = oldVnode.componentInstance
return
}
let i
const data = vnode.data
if (isDef(data) && isDef(i = data.hook) && isDef(i = i.prepatch)) {
i(oldVnode, vnode)
}
const oldCh = oldVnode.children
const ch = vnode.children
if (isDef(data) && isPatchable(vnode)) {
for (i = 0; i < cbs.update.length; ++i) cbs.update[i](oldVnode, vnode)
if (isDef(i = data.hook) && isDef(i = i.update)) i(oldVnode, vnode)
}
// 如果vnode不是文本节点或者注释节点
if (isUndef(vnode.text)) {
// 并且都有子节点
if (isDef(oldCh) && isDef(ch)) {
// 并且子节点不完全一致,则调用updateChildren
if (oldCh !== ch) updateChildren(elm, oldCh, ch, insertedVnodeQueue, removeOnly)
// 如果只有新的vnode有子节点
} else if (isDef(ch)) {
if (isDef(oldVnode.text)) nodeOps.setTextContent(elm, '')
// elm已经引用了老的dom节点,在老的dom节点上添加子节点
addVnodes(elm, null, ch, 0, ch.length - 1, insertedVnodeQueue)
// 如果新vnode没有子节点,而vnode有子节点,直接删除老的oldCh
} else if (isDef(oldCh)) {
removeVnodes(elm, oldCh, 0, oldCh.length - 1)
// 如果老节点是文本节点
} else if (isDef(oldVnode.text)) {
nodeOps.setTextContent(elm, '')
}
// 如果新vnode和老vnode是文本节点或注释节点
// 但是vnode.text != oldVnode.text时,只需要更新vnode.elm的文本内容就可以
} else if (oldVnode.text !== vnode.text) {
nodeOps.setTextContent(elm, vnode.text)
}
if (isDef(data)) {
if (isDef(i = data.hook) && isDef(i = i.postpatch)) i(oldVnode, vnode)
}
}
patchVnode主要做了几个判断:
- 新节点是否是文本节点,如果是,则直接更新
dom的文本内容为新节点的文本内容 - 新节点和旧节点如果都有子节点,则处理比较更新子节点
- 只有新节点有子节点,旧节点没有,那么不用比较了,所有节点都是全新的,所以直接全部新建就好了,新建是指创建出所有新
DOM,并且添加进父节点 - 只有旧节点有子节点而新节点没有,说明更新后的页面,旧节点全部都不见了,那么要做的,就是把所有的旧节点删除,也就是直接把
DOM删除
子节点不完全一致,则调用updateChildren
function updateChildren (parentElm, oldCh, newCh, insertedVnodeQueue, removeOnly) {
let oldStartIdx = 0 // 旧头索引
let newStartIdx = 0 // 新头索引
let oldEndIdx = oldCh.length - 1 // 旧尾索引
let newEndIdx = newCh.length - 1 // 新尾索引
let oldStartVnode = oldCh[0] // oldVnode的第一个child
let oldEndVnode = oldCh[oldEndIdx] // oldVnode的最后一个child
let newStartVnode = newCh[0] // newVnode的第一个child
let newEndVnode = newCh[newEndIdx] // newVnode的最后一个child
let oldKeyToIdx, idxInOld, vnodeToMove, refElm
// removeOnly is a special flag used only by while循环主要处理了以下五种情景:
- 当新老
VNode节点的start相同时,直接patchVnode,同时新老VNode节点的开始索引都加 1 - 当新老
VNode节点的end相同时,同样直接patchVnode,同时新老VNode节点的结束索引都减 1 - 当老
VNode节点的start和新VNode节点的end相同时,这时候在patchVnode后,还需要将当前真实dom节点移动到oldEndVnode的后面,同时老VNode节点开始索引加 1,新VNode节点的结束索引减 1 - 当老
VNode节点的end和新VNode节点的start相同时,这时候在patchVnode后,还需要将当前真实dom节点移动到oldStartVnode的前面,同时老VNode节点结束索引减 1,新VNode节点的开始索引加 1 - 如果都不满足以上四种情形,那说明没有相同的节点可以复用,则会分为以下两种情况:
- 从旧的
VNode为key值,对应index序列为value值的哈希表中找到与newStartVnode一致key的旧的VNode节点,再进行patchVnode,同时将这个真实dom移动到oldStartVnode对应的真实dom的前面 - 调用
createElm创建一个新的dom节点放到当前newStartIdx的位置
- 从旧的
小结
-
当数据发生改变时,订阅者
watcher就会调用patch给真实的DOM打补丁 -
通过
isSameVnode进行判断,相同则调用patchVnode方法 -
patchVnode做了以下操作:
- 找到对应的真实
dom,称为el - 如果都有都有文本节点且不相等,将
el文本节点设置为Vnode的文本节点 - 如果
oldVnode有子节点而VNode没有,则删除el子节点 - 如果
oldVnode没有子节点而VNode有,则将VNode的子节点真实化后添加到el - 如果两者都有子节点,则执行
updateChildren函数比较子节点
- 找到对应的真实
-
updateChildren主要做了以下操作:
- 设置新旧
VNode的头尾指针 - 新旧头尾指针进行比较,循环向中间靠拢,根据情况调用
patchVnode进行patch重复流程、调用createElem创建一个新节点,从哈希表寻找key一致的VNode节点再分情况操作
- 设置新旧
参考文章
- https://juejin.cn/post/6881907432541552648#heading-1
- https://www.infoq.cn/article/udlcpkh4iqb0cr5wgy7f