图像分类:Pytorch图像分类之--ResNet模型
文章目录
-
-
- 前言
- ResNet创新点介绍
-
- BasicBlock结构
- Bottleneck结构
- Batch Normalization介绍
-
- BN计算过程
- BN作用
- ResNet介绍
- 程序的介绍
-
- model.py
- train.py
- train_tool.py
-
前言
ResNet 网络是在 2015年 由微软实验室提出,斩获当年ImageNet竞赛中分类任务第一名,目标检测第一名。获得COCO数据集中目标检测第一名,图像分割第一名。
原论文地址:Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition(作者是CV大佬何凯明团队)
ResNet创新点介绍
在ResNet网络中创新点:
- 提出 Residual 结构(残差结构),并搭建超深的网络结构(可突破1000层)
- 使用 Batch Normalization 加速训练(丢弃dropout)
1、什么是残差网络?
残差网络让非线形层满足 F ( x ) F(x) F(x) ,然后从输入直接引入一个短连接到非线形层的输出上,使得整个映射变为 y = F ( x ) + x y= F(x) + x y=F(x)+x.
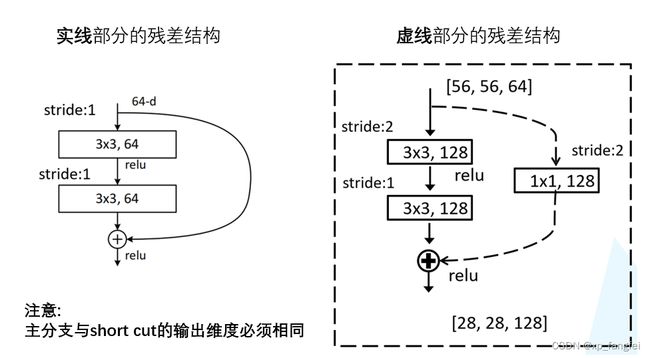
一个残差模块的定义如下图:

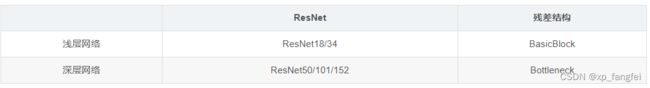
残差块分为两种:BasicBlock结构和Bottleneck结构;
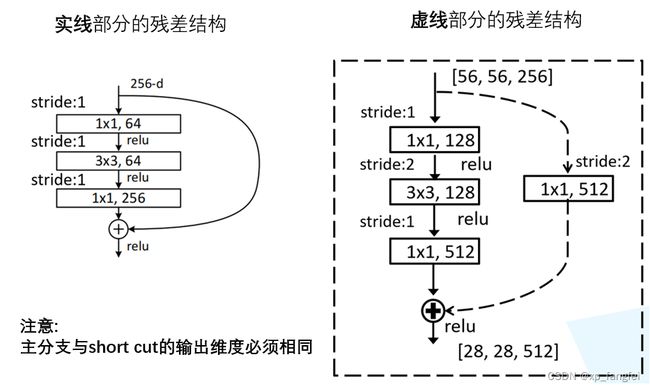
2、残差块中 shortcut 的介绍
有些残差块的 short cut 是实线的,而有些则是虚线的;这些虚线的 short cut 上通过1×1的卷积核对输入参数进行了维度处理,来保证主分支与 short cut 的输出维度相同;
3、传统神经网络相对于残差网络的问题:
在根据损失函数计算的误差通过梯度反向传播的方式对深度网络权值进行更新时,得到的梯度值接近0或特别大,也就是梯度消失或爆炸
- 梯度消失或梯度爆炸问题
- 梯度消失:若每一层的误差梯度小于1,反向传播时,网络越深,梯度越趋近于0;
- 梯度爆炸:若每一层的误差梯度大于1,反向传播时,网路越深,梯度越来越大;
解决方案:在网络中使用 BN(Batch Normalization)层来解决;
- 深层中的网络退化问题
解决方案:引入残差网络。可以人为地让神经网络某些层跳过下一层神经元的连接,隔层相连,弱化每层之间的强联系。
BasicBlock结构
1、BasicBlock结构适用于浅层网络;
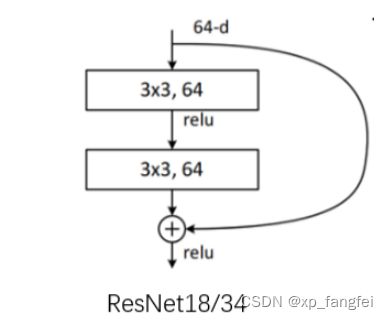
上图BasicBlock残差结构所需的参数为:
3 × 3 × 64 × 64 + 3 × 3 × 64× 64 = 73728
Bottleneck结构
1、Bottleneck结构适用于深层网络;其中1×1的卷积核起到降维和升维的作用,同时可以大大减少网络参数。
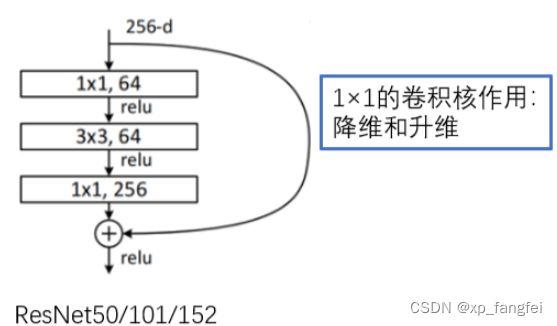
上图Bottleneck残差结构所需的参数为:
1 × 1 × 256× 64 + 3 × 3 × 64× 64 + 1×1 ×64×256= 69632
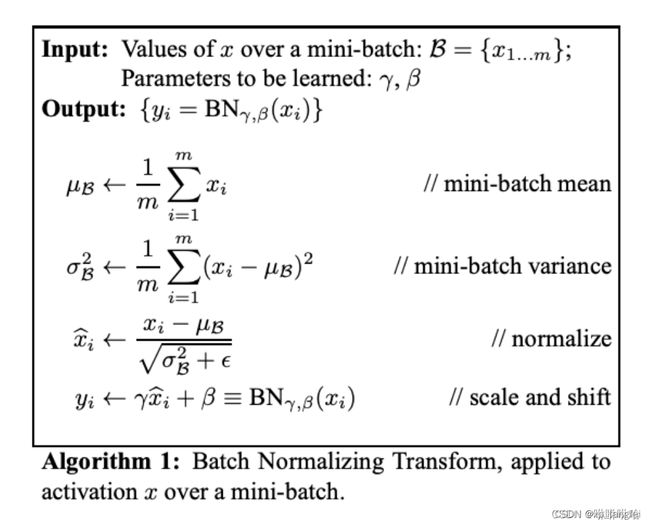
Batch Normalization介绍
BN计算过程
BN作用
- 抑制梯度消失和梯度爆炸
- 加快收敛速度
- 防止过拟合
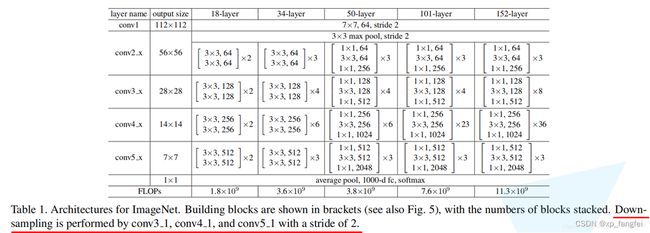
ResNet介绍
下图是原论文给出的不同深度的ResNet网络结构配置,注意表中的残差结构给出了主分支上卷积核的大小与卷积核个数,表中 残差块×N 表示将该残差结构重复N次。
程序的介绍
以下程序中model.py为为ResNet模型;train.py为训练脚本;train_tool.py为一个类,训练时用到的函数,供train.py调用;为预测脚本,应用训练出的模型进行预测。
model.py
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torchinfo import summary
class BasicBlock(nn.Module):
expansion = 1 #残差网络中,主分支的卷积核个数是否发生变化,不变为1
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, stride=1, downsample=None):
super(BasicBlock, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channels, out_channels=out_channels, kernel_size=3,
stride=stride, padding=1, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=out_channels, out_channels=out_channels,kernel_size=3,
stride=1, padding=1, bias=False)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
self.downsample = downsample
def forward(self, x):
identity = x
if self.downsample is not None: #虚线残差结构,需要下采样
identity = self.downsample(x)
x = self.bn1(self.conv1(x))
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.relu(self.conv2(x))
x = x + identity
x = self.relu(x)
return x
class Bottleneck(nn.Module):
expansion = 4 #残差结构中第三层卷积核个数是第一、二层卷积核个数的四倍
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels,stride=1, downsample=None):
super(Bottleneck, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channels, out_channels=out_channels, kernel_size=1,
stride=1, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=out_channels, out_channels=out_channels, kernel_size=3,
stride=stride, padding=1, bias=False)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=out_channels, out_channels=out_channels, kernel_size=1,
stride=1, bias=False)
self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.downsample = downsample
def forward(self, x):
identity = x
if self.downsample is not None:
identity = self.downsample(x)
x = self.bn1(self.conv1(x))
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.bn2(self.conv2(x))
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.bn2(self.conv3(x))
x = x + identity
x = self.relu(x)
return x
class ResNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, block, blocks_num, num_classes=5, include_top=True):
super(ResNet, self).__init__()
self.include_top = include_top
self.in_channel = 64
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=3, out_channels=self.in_channel, kernel_size=7, stride=2,
padding=3, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(self.in_channel)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)
self.layer1 = self._make_layer(block, 64, blocks_num[0])
self.layer2 = self._make_layer(block, 128, blocks_num[1], stride=2)
self.layer3 = self._make_layer(block, 256, blocks_num[2], stride=2)
self.layer4 = self._make_layer(block, 512, blocks_num[3], stride=2)
if self.include_top:
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1)) #output size = (1, 1)
self.fc = nn.Linear(512 * block.expansion, num_classes)
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.bn1(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.maxpool(x)
x = self.layer1(x)
x = self.layer2(x)
x = self.layer3(x)
x = self.layer4(x)
if self.include_top:
x = self.avgpool(x)
x = torch.flatten(x, 1)
x = self.fc(x)
return x
# channel为残差结构中第一层卷积核个数
def _make_layer(self, block, channel, block_num, stride=1):
"""
:param block: BasicBlock或者Bottleneck
:param channel:
:param block_num:
:param stride:
:return:
"""
downsample = None
if stride != 1 or self.in_channel != channel * block.expansion:
downsample = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(self.in_channel, channel * block.expansion, kernel_size=1,
stride=stride, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(channel * block.expansion)
)
layers = []
layers.append(block(self.in_channel, channel, downsample=downsample, stride=stride))
self.in_channel = channel * block.expansion
for _ in range(1, block_num):
layers.append(block(self.in_channel, channel))
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
#定义34层残差网络
def resnet34(num_classes=1000, include_top=True):
return ResNet(BasicBlock, [3, 4, 6, 3], num_classes=num_classes, include_top=include_top)
#定义101层残差网络
def resnet101(num_classes=1000, include_top=True):
return ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 23, 3], num_classes=num_classes, include_top=include_top)
train.py
把数据类别和对应索引写到.json文件中
#--------------------------------------------------------#
# 把类别数据写到.json文件中
#--------------------------------------------------------#
# 字典,类别:索引 {'daisy':0, 'dandelion':1, 'roses':2, 'sunflower':3, 'tulips':4}
flower_list = train_dataset.class_to_idx
# 将 flower_list 中的 key 和 val 调换位置
cla_dict = dict((val, key) for key, val in flower_list.items())
# 将 cla_dict 写入 json 文件中
json_str = json.dumps(cla_dict, indent=4)
with open('class_indices.json', 'w') as json_file:
json_file.write(json_str)
train.py
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torchvision import transforms, datasets
import json
import os
from model import ResNet, BasicBlock, Bottleneck, resnet34
import torch.optim as optim
from train_tool import TrainTool
import torchvision.models.resnet
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
#--------------------------------------------------------#
# 数据预处理
#--------------------------------------------------------#
transform = {
"train": transforms.Compose([transforms.RandomResizedCrop(224),
transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize([0.485, 0.456, 0.406],[0.229, 0.224, 0.225])]),
"test": transforms.Compose([transforms.Resize(256),
transforms.CenterCrop(224),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize([0.485, 0.456, 0.406],[0.229, 0.224, 0.225])])
}
#--------------------------------------------------------#
# 获取数据的路径
#--------------------------------------------------------#
data_root = os.getcwd()
image_path = data_root + "/data/"
print(image_path)
# 导入训练集并进行处理
train_dataset = datasets.ImageFolder(root=image_path + "/train",
transform=transform["train"])
#加载训练集
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(train_dataset, #导入的训练集
batch_size=16, #每批训练样本个数
shuffle=True, #打乱训练集
num_workers=0) #使用线程数
#导入测试集并进行处理
test_dataset = datasets.ImageFolder(root=image_path + "/test",
transform=transform["test"])
test_num = len(test_dataset)
#加载测试集
test_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(test_dataset, #导入的测试集
batch_size=16, #每批测试样本个数
shuffle=True, #打乱测试集
num_workers=0) #使用线程数
#--------------------------------------------------------#
# 网络模型实例化
#--------------------------------------------------------#
resnet = resnet34()
# load pretrain weights
model_weight_path = "./pre_model/resnet34-b627a593.pth" #记载预训练模型(比从头开始训练要快)
missing_keys, unexpected_keys = resnet.load_state_dict(torch.load(model_weight_path), strict=False)
inchannel = resnet.fc.in_features
resnet.fc = nn.Linear(inchannel, 5) #预训练模型的输出类别为1000,改为5
resnet.to(device)
#--------------------------------------------------------#
# 设置损失函数和优化器
#--------------------------------------------------------#
loss_function = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.Adam(resnet.parameters(), lr=0.0001)
#--------------------------------------------------------#
# 开始训练
#--------------------------------------------------------#
#正式训练
train_acc = []
train_loss = []
test_acc = []
test_loss = []
epoch = 0
#for epoch in range(epochs):
while True:
epoch = epoch + 1;
resnet.train()
epoch_train_acc, epoch_train_loss = TrainTool.train(train_loader, resnet, optimizer, loss_function, device)
resnet.eval()
epoch_test_acc, epoch_test_loss = TrainTool.test(test_loader,resnet, loss_function,device)
if epoch_train_acc < 0.93 and epoch_test_acc < 0.94:
template = ('Epoch:{:2d}, train_acc:{:.1f}%, train_loss:{:.2f}, test_acc:{:.1f}%, test_loss:{:.2f}')
print(template.format(epoch, epoch_train_acc * 100, epoch_train_loss, epoch_test_acc * 100, epoch_test_loss))
continue
else:
torch.save(resnet.state_dict(),'./model/resnet34_params.pth')
print('Done')
break
train_tool.py
import torch
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
class TrainTool:
def image_show(images):
print(images.shape)
images = images.numpy() #将图片有tensor转换成array
print(images.shape)
images = images.transpose((1, 2, 0)) # 将【3,224,256】-->【224,256,3】
# std = [0.5, 0.5, 0.5]
# mean = [0.5, 0.5, 0.5]
# images = images * std + mean
print(images.shape)
plt.imshow(images)
plt.show()
def train(train_loader, model, optimizer, loss_function, device):
train_size = len(train_loader.dataset) # 训练集的大小
num_batches = len(train_loader) # 批次数目
train_acc, train_loss = 0, 0 # 初始化正确率和损失
# 获取图片及标签
for images, labels in train_loader:
images, labels = images.to(device), labels.to(device)
# 计算预测误差
pred_labels = model(images)
loss = loss_function(pred_labels, labels)
# 反向传播
optimizer.zero_grad() # grad属性归零
loss.backward() # 反向传播
optimizer.step() # 每一步自动更新
# 记录acc和loss
train_acc += (pred_labels.argmax(1) == labels).type(torch.float).sum().item()
train_loss += loss.item()
train_acc /= train_size
train_loss /= num_batches
return train_acc, train_loss
def test(test_loader, model, loss_function, device):
test_size = len(test_loader.dataset) # 测试集的大小,一共10000张图片
num_batches = len(test_loader) # 批次数目,313(10000/32=312.5,向上取整)
test_loss, test_acc = 0, 0
# 当不进行训练时,停止梯度更新,节省计算内存消耗
with torch.no_grad():
for images, labels in test_loader:
images, labels = images.to(device), labels.to(device)
# 计算loss
pred_labels = model(images)
loss = loss_function(pred_labels, labels)
test_acc += (pred_labels.argmax(1) == labels).type(torch.float).sum().item()
test_loss += loss.item()
test_acc /= test_size
test_loss /= num_batches
return test_acc, test_loss
predict.py预测脚本参照:图像分类:Pytorch图像分类之–VGG模型文章中预测脚本
如有错误欢迎指正,如果帮到您请点赞加关注哦!