数组,链表,哈希表
代码随想录学习笔记—数组,链表,哈希表
目录
- 代码随想录学习笔记—数组,链表,哈希表
-
- 一.数组
-
- 1.理论
- 2. 二分查找
- 3.移除元素
- 4.[ 有序数组的平方](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/squares-of-a-sorted-array/)
- 5.[长度最小的子数组](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/minimum-size-subarray-sum/)
- 6.[螺旋矩阵 II](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/spiral-matrix-ii/)
- 二.链表
-
- 1.理论
- 2.[反转链表](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-linked-list/)
- 3.[删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/remove-nth-node-from-end-of-list/)
- 4.[链表相交](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists-lcci/)
- 5.[环形链表 II](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii/)
- 三.哈希表
-
- 1.理论
- 2. [有效的字母异位词](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/valid-anagram/)
- 3.[两个数组的交集](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/intersection-of-two-arrays/)
- 4.[快乐数](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/happy-number/)
- 5.[两数之和](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/two-sum/)
- 6.[四数相加 II](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/4sum-ii/)
- 7.[赎金信](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/ransom-note/)
- 8.[三数之和](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/3sum/)
- 9.[四数之和](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/4sum/)
- 10.总结
结合自身需求,主要偏重java
学习地址
一.数组
1.理论
- 数组是存放在连续内存空间上的相同类型数据的集合。
- 数组下标都是从0开始的。
- 数组内存空间的地址是连续的。
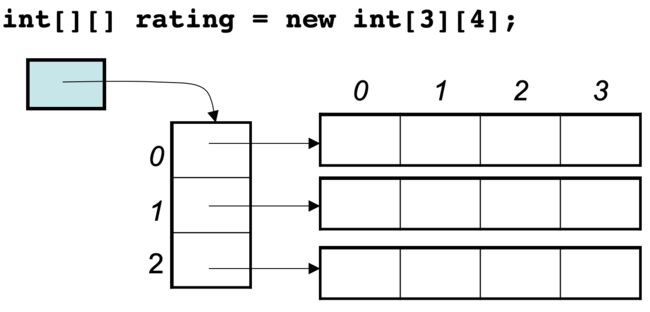
- java内存图:
2. 二分查找
二分查找也称折半查找(Binary Search),是一个高效的查找算法。
首先,假设数组中的元素是按升序排列;
将数组中间位置记录的元素值与要查找的元素值比较,如果两者相等,则查找成功;
否则利用中间位置的记录将数组分成前、后两个子数组;
如果中间位置记录的元素值大于要查找元素值,则进一步查找前一子数组,否则进一步查找后一子数组。
重复以上过程,直到找到满足条件的记录,使查找成功,或直到子表不存在为止,此时查找不成功。
在java的集合对象中也提供了二分查找的算法,如下面的java api接口:
如果返回值>=0 说明存在key,否则不存在该key(不存在返回-(low + 1)
java.util.Arrays.binarySearch(java.lang.Object,java.lang.Object,java.util.Comparator)
java.util.Arrays.binarySearch(java.lang.Object[], java.lang.Object)
重点:***折半查找要求查询的数组的元素是 1.有序排列的 2.无重复的 *。
public class t_binarySearch {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = new int[]{10,11,23,33,45,50,60,65};
int i = Arrays.binarySearch(a, 20);
System.out.println("索引下标是"+i);
//索引下标是-3
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = new int[]{10,11,23,33,45,50,60,65};
int i = Arrays.binarySearch(a, 11);
System.out.println("索引下标是"+i);
//索引下标是1
}
3.移除元素
双指针法(快慢指针法)在数组和链表的操作中是非常常见的,很多考察数组、链表、字符串等操作的面试题,都使用双指针法。
本题的理解:快指针是在前面进行预先处理的,慢指针保存我们最后需要的结果
class Solution {
public int removeElement(int[] nums, int val) {
// 快慢指针
int fastIndex = 0;
int slowIndex;
for (slowIndex = 0; fastIndex < nums.length; fastIndex++) {
if (nums[fastIndex] != val) {
nums[slowIndex] = nums[fastIndex];
slowIndex++;
}
}
return slowIndex;
}
}
例题1:283. 移动零
class Solution {
public void moveZeroes(int[] nums) {
int fastIndex;
int slowIndex=0;
int c=0;
for(fastIndex = 0; fastIndex<nums.length;fastIndex++){
if(nums[fastIndex] != 0){
nums[slowIndex]=nums[fastIndex];
slowIndex++;
c++;
}
}
for(int i=c;i<nums.length;i++){
nums[i]=0;
}
System.out.print(nums);
}
}
先移动不是0的元素在前面,后面的补零即可。
4. 有序数组的平方
给你一个按 非递减顺序 排序的整数数组 nums,返回 每个数字的平方 组成的新数组,要求也按 非递减顺序 排序。
解读:给你一个递增序列,返回每个元素平方后的递增序列。
java.api暴力解答:
import java.util.Arrays;
class Solution {
public int[] sortedSquares(int[] nums) {
int n=nums.length;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
nums[i]=nums[i]*nums[i];
}
Arrays.sort(nums);
return nums;
}
}
观察最大值每次存在左右两端。
使用双指针
import java.util.Arrays;
class Solution {
public int[] sortedSquares(int[] nums) {
int right=nums.length-1;
int left=0;
//每次比较两端的值 放入数组的最后
int[] ints=new int[nums.length];
int wz=nums.length;
while(left<=right){
if(nums[left]*nums[left]>nums[right]*nums[right]){
ints[--wz]=nums[left]*nums[left];
left++;
}else{
ints[--wz]=nums[right]*nums[right];
right--;
}
}
return ints;
}
}
5.长度最小的子数组
给定一个含有 n 个正整数的数组和一个正整数 s ,找出该数组中满足其和 ≥ s 的长度最小的 连续 子数组,并返回其长度。如果不存在符合条件的子数组,返回 0。
示例:
输入:s = 7, nums = [2,3,1,2,4,3] 输出:2 解释:子数组 [4,3] 是该条件下的长度最小的子数组。
无论是暴力还是使用“滑动窗口”(双指针的方法)都是为了确定子序列的起始位置和结束位置
暴力:
class Solution {
public int minSubArrayLen(int target, int[] nums) {
int qswz=0;
int jswz=0;
int sum=0;
int jg=Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for(;qswz<nums.length;qswz++){
sum=0;
for(jswz=qswz;jswz<nums.length;jswz++){
sum+=nums[jswz];
while(sum>=target){
jg=Math.min((jswz-qswz+1),jg);
break;
}
}
}
return jg == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? 0 : jg;
}
}
就是从每一个位置开始先后计算到满足条件后跳出。
所谓滑动窗口,就是不断的调节子序列的起始位置和终止位置,从而得出我们要想的结果。
class Solution {
public int minSubArrayLen(int target, int[] nums) {
int qswz=0;
int jswz=0;
int sum=0;
int jg=Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for(jswz=0;jswz<nums.length;jswz++){
sum+=nums[jswz];
while(sum>=target){
int l=jswz-qswz+1;
jg=Math.min(l,jg);
sum-=nums[qswz];
qswz++;
}
}
return jg == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? 0 : jg;
}
}
理解:当子序列和大于等于 值 时就减去前面的,增加起始位置,子序列和小于时就加后面的元素,增加结束位置。一个循环解决问题。
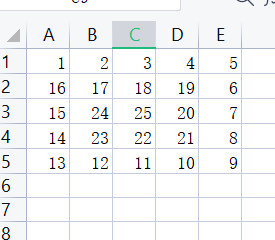
6.螺旋矩阵 II
n=3,4和5 为例.
本题在于找到合适的模拟过程;
分析:
- 一圈一圈的转 转一圈减少2行和两列;n=3,转1圈,n=4,5,转2圈;
圈数=n/2;
-
n=5,每一行一列走4个 碰到拐角停止 每次走n-1个,走4次。刚好走完一圈。
-
第二圈 改变起始位置,每次走n-3个 如果n-3=0 说明到最后一个了
-
第三圈 改变起始位置,每次走n-5个 如果n-5=0 说明到最后一个了 <0 说明走完了
class Solution {
public int[][] generateMatrix(int n) {
int[][] ints =new int[n][n];
int num=1;
int qs=n/2;
int startX=0;
int startY=0;
int zodeshu=n-1;
for(int i =0;i<qs;i++){
for(int j=0;j<zodeshu;j++){
ints[startX][startY+j]=num++;
}
for(int z=0;z<zodeshu;z++){
ints[startX+z][startY+zodeshu]=num++;
}
for(int z=0;z<zodeshu;z++){
ints[startX+zodeshu][startY+zodeshu-z]=num++;
}
for(int z=0;z<zodeshu;z++){
ints[startX+zodeshu-z][startY]=num++;
}
zodeshu=zodeshu-2;
startX++;
startY++;
}
if(n%2 == 1){
ints[n/2][n/2]=num;
}
return ints;
}
}
与教程中大致相同。
二.链表
1.理论
-
单链表
-
双链表
-
循环链表
-
虚拟头结点
链表的一大问题就是操作当前节点必须要找前一个节点才能操作。这就造成了,头结点的尴尬,因为头结点没有前一个节点了。
因为本次针对Java来学习。java中有大量的链表API 因此 有一部分略过。
2.反转链表
双指针法 与 递归法思想一致
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur!=null){
ListNode temp=cur.next;
cur.next=pre;
pre=cur;
cur =temp;
}
return pre;
}
}
temp 保存cur后面的 防止改动cur指针后丢失后面的。
3.删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode dummy =new ListNode(0,head);
ListNode cur= head;
ListNode pre = dummy;
if(head.next==null && n==1){
return null;
}
for(int i=0; i<n;i++){
cur=cur.next;
}
while(cur!=null){
cur=cur.next;
pre=pre.next;
}
pre.next=pre.next.next;
return dummy.next;
}
}
双指针的经典应用,如果要删除倒数第n个节点,让fast移动n步,然后让fast和slow同时移动,直到fast指向链表末尾。删掉slow所指向的节点就可以了。
梳理:
-
控制好 pre 和 cur 保持的距离和n的关系,确保能删除倒是第n的
-
考虑 使用虚拟头结点 可能会删除真头结点
-
考虑 只有一个结点并要删除
4.链表相交
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
int la=0;
int lb=0;
ListNode re=null;
ListNode pa=headA;
ListNode pb=headB;
while(pa!=null){
pa=pa.next;
la++;
}
while(pb!=null){
pb=pb.next;
lb++;
}
if(la>lb){
int cha=la-lb;
pa=headA;
pb=headB;
while(cha-->0){
pa=pa.next;
}
while(pb!=pa){
pb=pb.next;
pa=pa.next;
}
re=pa;
}
if(la<=lb){
int cha=lb-la;
pa=headA;
pb=headB;
while(cha-->0){
pb=pb.next;
}
while(pb!=pa){
pb=pb.next;
pa=pa.next;
}
re=pa;
}
return re;
}
}
梳理:
-
主要可以想到后面的如果想交个数总是相同的;
根据个数的差值来来跳过一部分, 寻找后面可能相交的
5.环形链表 II
先使用快慢指针来确定是不是有环,和确定相遇的位置。再使用相遇位置和起始位置确定环的入口。
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
if (slow == fast) {// 有环
ListNode index1 = fast;
ListNode index2 = head;
// 两个指针,从头结点和相遇结点,各走一步,直到相遇,相遇点即为环入口
while (index1 != index2) {
index1 = index1.next;
index2 = index2.next;
}
return index1;
}
}
return null;
}
}
三.哈希表
1.理论
2. 有效的字母异位词
class Solution {
public boolean isAnagram(String s, String t) {
boolean bool=true;
int[] r =new int[26];
char[] ss=s.toCharArray();
char[] tt=t.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < tt.length; i++) {
char c = tt[i];
r[c-'a']++;
}
for (int i = 0; i < ss.length; i++) {
char c = ss[i];
r[c-'a']--;
}
for (int i = 0; i < r.length; i++) {
if (r[i]!=0) {
bool=false;
}
}
return bool;
}
}
哈希的应用:把 每一个字母 对应 数组中每一个位置。位置是数是字母的个数。
时间复杂度降到了O(n)。
3.两个数组的交集
计算数组的交集 数组里有重复的元素, 放入hashset 去除重复元素 然后遍历第二个数组 是否包含在set里 如果包含就加入结果数组中;
实际写代码调试的时候发现 两个数组都要去除重复元素,因为在确定返回数组的个数时,遍历第二个数组 是否包含在set里时会重复计算相同元素
class Solution {
public int[] intersection(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
int[] re =null;
int count=0;
Set<Integer> set1 = new HashSet<Integer>();
Set<Integer> set2 = new HashSet<Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < nums1.length; i++) {
set1.add(nums1[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums2.length; i++) {
set2.add(nums2[i]);
}
for (Integer i:set2) {
if (set1.contains(i)) {
count++;
}
}
re=new int[count];
count=0;
for (Integer i:set2) {
if (set1.contains(i)) {
re[count]=i;
count++;
}
}
return re;
}
}
我的题解属于暴力算法 两个数组去重后 遍历两次,一次确定重复的个数,一个添加进放回的数组。
4.快乐数
重点:题目中说了会 无限循环,那么也就是说求和的过程中,sum会重复出现
判断重复出现要使用set
class Solution {
public boolean isHappy(int n) {
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<Integer>();
while(!set.contains(n)) {
set.add(n);
n= nextN(n);
if (n==1) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
public int nextN(int n) {
int re=0;
while(n > 0) {
int a = n%10;
n=n/10;
re+=a*a;
}
return re;
}
}
5.两数之和
242. 有效的字母异位词 (opens new window)这道题目是用数组作为哈希表来解决哈希问题,349. 两个数组的交集 (opens new window)这道题目是通过set作为哈希表来解决哈希问题。
本题呢,则要使用map,那么来看一下使用数组和set来做哈希法的局限。
- 数组的大小是受限制的,而且如果元素很少,而哈希值太大会造成内存空间的浪费。
- set是一个集合,里面放的元素只能是一个key,而两数之和这道题目,不仅要判断y是否存在而且还要记录y的下标位置,因为要返回x 和 y的下标。所以set 也不能用。
此时就要选择另一种数据结构:map ,map是一种key value的存储结构,可以用key保存数值,用value在保存数值所在的下标。
class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
int[] ints = new int[]{-1,-1};
HashMap<Integer, Integer> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
for (int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){
int a=target-nums[i];
if (hashMap.containsKey(a)){
ints=new int[]{hashMap.get(a),i};
}
hashMap.put(nums[i],i);
}
return ints;
}
}
两个数相加 符合条件的 一定是一个在前 一个在后,并且同一个元素不能使用两遍。所有要先判断前面是不是有需要的,没有的话再把它加进去,
我们想要的这两个数 在循环中会都会经过。前面的是加进去的,后面的确认。 两个数一前一后 后面的肯定很找到前面的。
6.四数相加 II
class Solution {
public int fourSumCount(int[] nums1, int[] nums2, int[] nums3, int[] nums4) {
int re=0;
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map1=new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < nums1.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < nums2.length; j++) {
if (map1.containsKey(nums1[i]+nums2[j])) {
map1.put(nums1[i]+nums2[j],map1.get(nums1[i]+nums2[j])+1);
}else {
map1.put(nums1[i]+nums2[j],1);
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums3.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < nums4.length; j++) {
if (map1.containsKey(0-(nums3[i]+nums4[j]))) {
re+=map1.get(0-(nums3[i]+nums4[j]));
}
}
}
return re;
}
}
两重循环把两个数组 和 的所有可能值和个数 统计一遍。
再来两重循环 把剩余两个数组 和的所有可能的值 匹配一次
7.赎金信
class Solution {
public boolean canConstruct(String ransomNote, String magazine) {
int[] arr =new int[26];
for(char c :magazine.toCharArray()) {
arr[c-'a']++;
}
for(char c :ransomNote.toCharArray()) {
arr[c-'a']--;
}
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i]<0) {
return false;
}
}
return true ;
}
}
与 2. [有效的字母异位词] 相似 利用数组作为哈希表来解决问题
arr[i]<0 时说明ransomnote里的字母在magazine没有或不够。
8.三数之和
双指针法,使用的是map的包含方法。
如果使用双指针一定是可以排序的数组,排序后不影响结果的题目
两数之和 如果使用双指针,排序后索引改变,影响返回结果;
public class LK015 {
public List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
Arrays.sort(nums);
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] > 0) {
//满足条件,说明后面的都是大于0的,相加不可能是0
//这个if 可以省略
return result;
}
if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1]) {
//如果它和前面的数一样。那么最后放回的值一样 可以跳过。主要是达到去重,完成题目要求;
continue;
}
int left = i + 1;
int right = nums.length - 1;
while (right > left) {
int sum = nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right];
if (sum > 0) {
right--;
} else if (sum < 0) {
left++;
} else {
result.add(Arrays.asList(nums[i], nums[left], nums[right]));
//去除重复
while (right > left && nums[right] == nums[right - 1]) right--;
while (right > left && nums[left] == nums[left + 1]) left++;
right--;
left++;
}
}
}
return result;
}
}
9.四数之和
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> fourSum(int[] nums, int target) {
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
Arrays.sort(nums);
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (i>0 && nums[i]== nums[i-1]) {
continue;
}
for (int j = i+1; j < nums.length; j++) {
//j>i+1 第一个是需要的 如果后面还有是重复的
if (j>i+1 && nums[j]==nums[j-1]) {
continue;
}
int left=j+1;
int rigth=nums.length-1;
while(left<rigth) {
int sum=nums[i]+nums[j]+nums[left]+nums[rigth];
if (sum>target) {
rigth--;
}else if (sum<target) {
left++;
}else{
list.add(Arrays.asList(nums[i],nums[j],nums[left],nums[rigth]));
//这里记得写:left
while (left<rigth &&nums[left]==nums[left+1]) {
left++;
}
while (left<rigth && nums[rigth]==nums[rigth-1] ) {
rigth--;
}
left++;
rigth--;
}
}
}
}
return list;
}
}
10.总结
- 数组:2,7
- set:3,4
- map:5,6
- 双指针:8,9