SpringBoot 启动时执行:CommandLineRunner、ApplicationRunner 和 ApplicationListener
SpringBoot 启动时执行:CommandLineRunner、ApplicationRunner 和 ApplicationListener
零、前置知识:SpringBoot run() 源码解析
SpringApplication.run 方法源码
/**
* Run the Spring application, creating and refreshing a new
* {@link ApplicationContext}.
* @param args the application arguments (usually passed from a Java main method)
* @return a running {@link ApplicationContext}
*/
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
// 计时器
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>();
// 配置系统属性:默认缺失外部显示屏等允许启动
configureHeadlessProperty();
// 获取并启动事件监听器,如果项目中没有其他监听器,则默认只有 EventPublishingRunListener
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
// 将事件广播给 listeners
listeners.starting();
try {
// application 启动参数列表
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(
args);
// 配置运行环境:例如激活应用***.yml配置文件
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners,
applicationArguments);
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
// 加载配置的banner(gif,txt...),即控制台图样
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
// 创建上下文对象,并实例化
context = createApplicationContext();
exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(
SpringBootExceptionReporter.class,
new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context);
// 配置 Spring 容器:准备上下文,装配 bean
prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments,
printedBanner);
// 刷新 Spring 上下文,创建 bean 过程中
refreshContext(context);
// 刷新上下文后的动作:空方法,子类实现
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
// 停止计时器:计算线程启动共用时间
stopWatch.stop();
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass)
.logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
// 启动事件监听器
listeners.started(context);
// 开始加载资源
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, listeners, exceptionReporters, ex);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
// 监听器正式运行
listeners.running(context);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
return context;
}
callRunners 源码分析
private void callRunners(ApplicationContext context, ApplicationArguments args) {
// 将实现 ApplicationRunner 和 CommandLineRunner 接口的类,存储到集合中
List<Object> runners = new ArrayList<>();
runners.addAll(context.getBeansOfType(ApplicationRunner.class).values());
runners.addAll(context.getBeansOfType(CommandLineRunner.class).values());
// 按照加载先后顺序排序
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(runners);
for (Object runner : new LinkedHashSet<>(runners)) {
if (runner instanceof ApplicationRunner) {
callRunner((ApplicationRunner) runner, args);
}
if (runner instanceof CommandLineRunner) {
callRunner((CommandLineRunner) runner, args);
}
}
}
一、CommandLineRunner 接口 和 ApplicationRunner 接口
1. 执行时机
springboot 完全初始化完毕后
2. 使用
@Component
public class ServerDispatcher implements CommandLineRunner {
@Override
public void run(String... args){
// 逻辑代码
}
}
@Component
public class ServerDispatcher implements ApplicationRunner {
@Override
public void run(ApplicationArguments args){
// 逻辑代码
}
}
3. 区别
参数不同
4. 特点
可以添加 @Order 注解等注解:指定执行的顺序 (数字小的优先)
@Priority 或其他排序的接口也可
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.FIELD})
@Documented
public @interface Order {
/**
* The order value.
* Default is {@link Ordered#LOWEST_PRECEDENCE}.
* @see Ordered#getOrder()
*/
int value() default Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE;
}
public interface Ordered {
int HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int LOWEST_PRECEDENCE = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int getOrder();
}
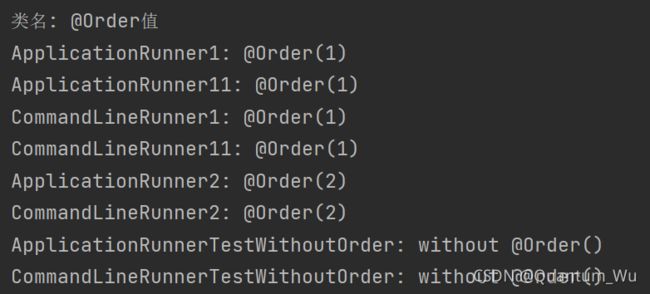
执行顺序
- 先根据 @Order 注解的值,@Order 的 value 值越小,则优先,没有该注解则默认最后执行。
- @Order 值相同时,ApplicationRunner 优先于 CommandLineRunner。
- @Order 值和继承的接口类型都相同时,按照注入容器的顺序(应该是按照类的名称)。
二、ApplicationListener 接口
1. 实现原理
监听机制
2. 使用示例:监听 ContextRefreshedEvent
@Component
public class ServerDispatcher implements ApplicationListener<ContextRefreshedEvent> {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ContextRefreshedEvent contextRefreshedEvent) {
// 逻辑代码
}
}
2.1 执行时机
在 IOC 容器的启动过程,当所有的 bean 都已经处理完成之后,spring 的 ioc 容器会有一个发布 ContextRefreshedEvent 事件的动作。
2.2 注意事项
系统会存在两个容器,一个是 root application context , 另一个就是我们自己的 projectName-servlet context(作为root application context的子容器)
这种情况下,就会造成 onApplicationEvent 方法被执行两次。为了避免上面提到的问题,我们可以只在 root application context 初始化完成后调用逻辑代码,其他的容器的初始化完成,则不做任何处理
加入判断即可:if (event.getApplicationContext().getParent() == null)
@Component
public class ServerDispatcher implements ApplicationListener<ContextRefreshedEvent> {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ContextRefreshedEvent contextRefreshedEvent) {
// 当 spring 容器初始化完成后就会执行该方法
if (event.getApplicationContext().getParent() == null) {
//逻辑代码
}
}
}
3. 拓展:监听事件的类型
- ContextRefreshedEvent:ApplicationContext 被初始化或刷新时,该事件被发布。这也可以在 ConfigurableApplicationContext 接口中使用 refresh() 方法来发生。此处的初始化是指:所有的 Bean 被成功装载,后处理 Bean 被检测并激活,所有 Singleton Bean 被预实例化,ApplicationContext 容器已就绪可用。
- ContextStartedEvent:当使用 ConfigurableApplicationContext (ApplicationContext子接口)接口中的 start() 方法启动 ApplicationContext 时,该事件被发布。你可以调查你的数据库,或者你可以在接受到这个事件后重启任何停止的应用程序。
- ContextStoppedEvent:当使用 ConfigurableApplicationContext 接口中的 stop() 停止 ApplicationContext 时,发布这个事件。你可以在接受到这个事件后做必要的清理的工作。
- ContextClosedEvent:当使用 ConfigurableApplicationContext 接口中的 close() 方法关闭 ApplicationContext 时,该事件被发布。一个已关闭的上下文到达生命周期末端;它不能被刷新或重启。
- RequestHandledEvent:这是一个 web-specific 事件,告诉所有 bean HTTP 请求已经被服务。只能应用于使用DispatcherServlet的Web应用。在使用Spring作为前端的MVC控制器时,当Spring处理用户请求结束后,系统会自动触发该事件。
小技巧
如果刚好可以在一个方法内执行 Spring 启动后的动作,可以让 SpringBoot 的启动类继承上述的某个接口,然后重写相应的方法即可。