OpenCV中的相机标定
之前在https://blog.csdn.net/fengbingchun/article/details/130039337 中介绍了相机的内参和外参,这里通过OpenCV中的接口实现对内参和外参的求解。
估计相机参数的过程称为相机标定(camera calibration)。相机标定是使用已知的真实世界模式(例如棋盘)来估计相机镜头和传感器的外在参数(旋转和平移, Rotation(R) and Translation(t), 相机相对于某些世界坐标系的方向)和内在参数(例如镜头的焦距fx,fy、光学中心cx,cy、畸变系数k1,k2,k3,p1,p2)的过程,以减少相机缺陷引起的畸变误差。
棋盘标定是执行相机标定和估计未知参数值的常用技术。棋盘非常适合用于相机标定:
(1).它是平坦的(flat),棋盘上的所有点都在同一平面上;
(2).有清晰的corners和points,它们都出现在直线上,易于在图像中检测到,棋盘上的正方形角非常适合定位它们,便于将3D真实世界坐标系中的点映射到相机2D像素坐标系上的点。
OpenCV中相机标定步骤:
(1).使用已知大小的棋盘格定义3D点的真实世界坐标;
(2).从多幅图像捕获棋盘格的不同视点(different viewpoints);
(3).查找不同图像的棋盘格的2D坐标:
查找棋盘角:findChessboardCorners
完善棋盘角:cornerSubPix
(4).标定相机:calibrateCamera
以下是C++的实现:
int test_opencv_camera_calibration()
{
#ifdef _MSC_VER
std::string path = "../../../test_images/camera_calibration/*.jpg";
#else
std::string path = "test_images/camera_calibration/*.jpg";
#endif
std::vector images;
cv::glob(path, images, false);
if (images.size() == 0) {
std::cout << "Error: the requested images were not found: " << path << "\n";
return -1;
}
auto pos = path.find_last_of("/");
std::string path_result = path.substr(0, pos + 1);
auto get_image_name = [](const std::string& image) {
#ifdef _MSC_VER
auto pos = image.find_last_of("\\");
#else
auto pos = image.find_last_of("/");
#endif
auto name = image.substr(pos + 1, image.size());
return name.substr(0, name.size() - 4);
};
// the dimensions of checkerboard
const int CHECKERBOARD[2] = { 11, 13 }; // rows,cols
// the world coordinates for 3D points
std::vector pts_3d_world_coord;
for (auto i = 0; i < CHECKERBOARD[1]; ++i) {
for (auto j = 0; j < CHECKERBOARD[0]; ++j)
pts_3d_world_coord.push_back(cv::Point3f(j, i, 0));
}
// vector to store the pixel coordinates of detected checker board corners
std::vector pts_corners;
cv::Mat frame, gray;
bool success = false;
// store vectors of 3D points for each checkerboard image
std::vector > pts_3d;
// store vectors of 2D points for each checkerboard image
std::vector > pts_2d;
for (auto i = 0; i < images.size(); ++i) {
frame = cv::imread(images[i]);
if (frame.empty()) {
std::cout << "Error: fail to read image: " << images[i] << "\n";
return -1;
}
cv::cvtColor(frame, gray, cv::COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
// finding checker board corners
success = cv::findChessboardCorners(gray, cv::Size(CHECKERBOARD[0], CHECKERBOARD[1]), pts_corners, cv::CALIB_CB_ADAPTIVE_THRESH | cv::CALIB_CB_FAST_CHECK | cv::CALIB_CB_NORMALIZE_IMAGE);
if (!success) {
std::cout << "Error: fail to find chess board corners: " << images[i] << "\n";
return -1;
}
cv::TermCriteria criteria(cv::TermCriteria::EPS | cv::TermCriteria::MAX_ITER, 30, 0.001);
// refining pixel coordinates for given 2d points
cv::cornerSubPix(gray, pts_corners, cv::Size(11, 11), cv::Size(-1, -1), criteria);
// displaying the detected corner points on the checker board
cv::drawChessboardCorners(frame, cv::Size(CHECKERBOARD[0], CHECKERBOARD[1]), pts_corners, success);
pts_3d.push_back(pts_3d_world_coord);
pts_2d.push_back(pts_corners);
//cv::imshow("Image", frame);
//cv::waitKey(0);
cv::imwrite(path_result + "result_" + get_image_name(images[i]) + ".png", frame);
}
cv::Mat camera_matrix, dist_coeffs, R, t;
cv::calibrateCamera(pts_3d, pts_2d, cv::Size(gray.rows, gray.cols), camera_matrix, dist_coeffs, R, t);
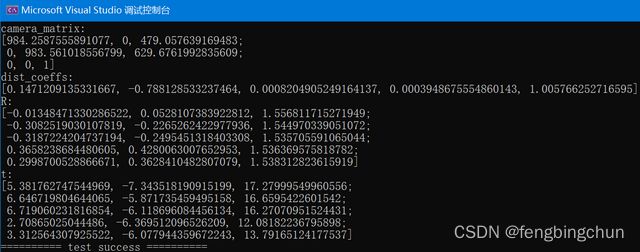
std::cout << "camera_matrix:\n" << camera_matrix << "\n"; // 3*3 matrix
std::cout << "dist_coeffs:\n" << dist_coeffs << "\n"; // 5*1 vector
std::cout << "R:\n" << R << "\n"; // each image, 3*1 vector
std::cout << "t:\n" << t << "\n"; // each image, 3*1 vector
return 0;
} 终端输出结果如下:5幅测试图像来自于手机拍摄
其中测试图像1.jpg角点检测结果如下所示:
以下是参考C++实现的Python代码:
import cv2
import numpy as np
import glob
from sys import platform
def get_image_name(path):
if platform == "win32":
pos = path.rfind("\\")
elif platform == "linux":
pos = path.rfind("/")
else:
raise Exception(f"Error: Unsupported platform: {platform}")
return path[pos+1:len(path)-4]
def camera_calibration(checkerboard_size, path):
images = glob.glob(path)
if len(images) == 0:
raise Exception(f"Error: the requested images were not found: {path}")
if platform == "win32":
pos = images[0].rfind("\\")
elif platform == "linux":
pos = images[0].rfind("/")
else:
raise Exception(f"Error: Unsupported platform: {platform}")
path_result = images[0][0:pos+1]
# the world coordinates for 3D points
pts_3d_world_coord = np.zeros((1, checkerboard_size[0] * checkerboard_size[1], 3), np.float32)
pts_3d_world_coord[0,:,:2] = np.mgrid[0:checkerboard_size[0], 0:checkerboard_size[1]].T.reshape(-1, 2)
#print(f"pts_3d_world_coord: {pts_3d_world_coord}")
# store vectors of 3D points for each checkerboard image
pts_3d = []
# store vectors of 2D points for each checkerboard image
pts_2d = []
for name in images:
frame = cv2.imread(name)
if frame is None:
raise Exception(f"Error: fail to read image: {frame}")
gray = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
ret, pts_corners = cv2.findChessboardCorners(gray, checkerboard_size, cv2.CALIB_CB_ADAPTIVE_THRESH + cv2.CALIB_CB_FAST_CHECK + cv2.CALIB_CB_NORMALIZE_IMAGE)
if ret != True:
raise Exception(f"Error: fail to find chess board corners: {name}")
criteria = (cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_EPS + cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_MAX_ITER, 30, 0.001)
# refining pixel coordinates for given 2d points
pts_corners = cv2.cornerSubPix(gray, pts_corners, (11,11), (-1,-1), criteria)
# displaying the detected corner points on the checker board
frame = cv2.drawChessboardCorners(frame, checkerboard_size, pts_corners, ret)
pts_3d.append(pts_3d_world_coord)
pts_2d.append(pts_corners)
#cv2.imshow("Image", frame)
#cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.imwrite(path_result + "result_" + get_image_name(name) + ".png", frame)
ret, camera_matrix, dist_coeffs, R, t = cv2.calibrateCamera(pts_3d, pts_2d, gray.shape[::-1], None, None)
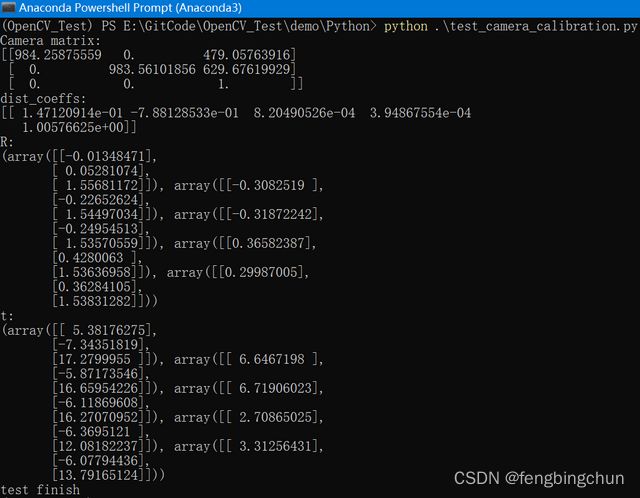
print(f"Camera matrix:\n{camera_matrix}")
print(f"dist_coeffs:\n{dist_coeffs}")
print(f"R:\n{R}")
print(f"t:\n{t}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
# the dimensions of checkerboard
CHECKERBOARD = (11, 13)
# images path
path = "../../test_images/camera_calibration/*.jpg"
camera_calibration(CHECKERBOARD, path)
print("test finish")终端输出结果如下:与C++一致
GitHub:https://github.com/fengbingchun/OpenCV_Test