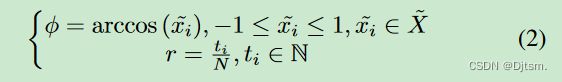格拉姆角场
格拉姆角场学习GAF官方文档
格拉姆角场能够将时间序列数据转换为图像数据,既能保留信号完整的信息,也保持着信号对于时间的依赖性。信号数据转换为图像数据后就可以充分利用CNN在图像分类识别上的优势,进行建模 。
Document:
为每个(x_i, x_j)创建一个时间相关性矩阵。首先,它以-1
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-mIHtqGZ3-1678874178580)(null)]
格拉姆矩阵:假设有一个向量V,Gram矩阵就是来自V的每一对向量的内积矩阵。
![]()
- 通过取每个 M 点的平均值来聚合时间序列以减小大小。此步骤使用分段聚合近似PAA ( Piecewise Aggregation Approximation / PAA)。
- 区间[0,1]中的缩放值。
- 通过将时间戳作为半径和缩放值的反余弦(arccosine)来生成极坐标。这杨可以提供角度的值。
- 生成GASF / GADF。在这一步中,将每对值相加(相减),然后取余弦值后进行求和汇总

- 通过取时间序列值的余弦倒数来计算 A 和 B(实际上是在 PAA 和缩放之后的值上)
代码实例
- 分段聚合近似PAA
# Author: Johann Faouzi Gramian Angular Field(时间序列转图像的过程)
# python 示例
# 导入需要的包
from pyts.approximation import PiecewiseAggregateApproximation
from pyts.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 生成一些demo数据
X = [[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8],[23,56,52,46,34,67,70,60]]
plt.plot(X[0],X[1])
plt.title(‘Time series’)
plt.xlabel(‘timestamp’)
plt.ylabel(‘value’)
plt.show()
# 分段聚合逼近和缩放
# PAA
transformer = PiecewiseAggregateApproximation(window_size=2)
result = transformer.transform(X)
# Scaling in interval [0,1]
scaler = MinMaxScaler()
scaled_X = scaler.transform(result)
plt.plot(scaled_X[0,:],scaled_X[1,:])
plt.title(‘After scaling’)
plt.xlabel(‘timestamp’)
plt.ylabel(‘value’)
plt.show()
# 转换成极坐标
arccos_X = np.arccos(scaled_X[1,:])
fig, ax = plt.subplots(subplot_kw={‘projection’: ‘polar’})
ax.plot(result[0,:], arccos_X)
ax.set_rmax(2)
ax.set_rticks([0.5, 1, 1.5, 2]) # Less radial ticks
ax.set_rlabel_position(-22.5) # Move radial labels away from plotted line
ax.grid(True)
ax.set_title(“Polar coordinates”, va=’bottom’)
plt.show()
# Gramina angular summation fields
field = [a+b for a in arccos_X for b in arccos_X]
gram = np.cos(field).reshape(-1,4)
plt.imshow(gram)
参考文献:
《Encoding Time Series as Images for Visual Inspection and Classification Using Tiled Convolutional Neural Networks》 janurary,2015
Gramian Angular Field
给定一个时间序列X,将其缩放到[-1,1],
然后再在极坐标系中表示该时间序列(通过将value编码为angular cosine,将时间戳编码为radius,
ti是时间戳,N是正则化极坐标系统跨度的常数因子。这种基于极坐标的表示方法是理解时间序列的一种新方法。随着时间的增加,相应的值在跨越圆上的不同角度点之间扭曲,就像水荡漾一样。

- 等式2的编码映射有两个重要的性质。首先,当φ∈[0,π]时,当cos(φ)单调时,它是双射的。给定一个时间序列,所提出的映射在极坐标系中产生且仅一个具有唯一反函数的结果。
- 它提供了一种保持时间依赖性的方法,因为随着位置从左上角移动到右下角,时间会增加。GAF包含时间相关性,因为G(i,ji j=k)通过相对于时间间隔k的方向叠加来表示相对相关性
Question:当编码为反函数值时,-1和1怎么确定呢?value都是正的时,对应两个角度(在 0 0 0到 2 π 2\pi 2π上)。。。怎么选