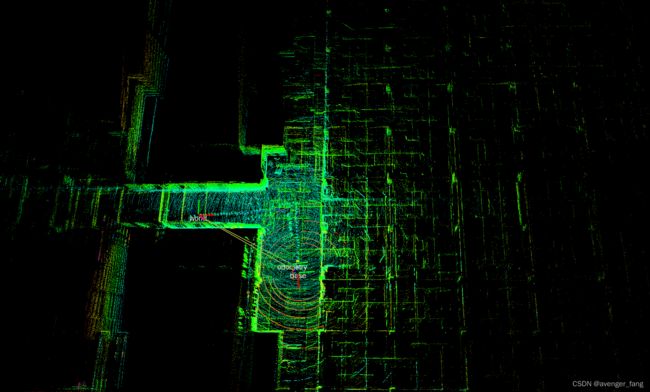
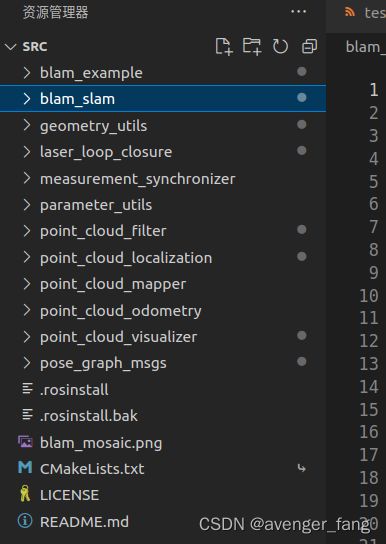
伯克利BLAM纯激光SLAM
属于只用3D激光雷达所做的SLAM,其代码地址为:
github:GitHub - erik-nelson/blam
自测效果还是比较好的
BLAM系统框架:
代码主要分为下列几个大部分
代码目录结构:
1. blam_example 没有代码,只有launch文件、rviz文件、yaml文件配置。
2. blam_slam文件夹
blam_slam.cc为系统启动节点,即main程序入口
而BlamSlam.cc为为SLAM算法接口,它封装成库, main程序通过它进入算法,包括ros的初始化、参数读取、传感器数据回调等。
3.geometry_utils文件夹是对矩阵操作、几何旋转操作的声明定义的头文件,通用的
4.MeasurementSynchronizer
封装ros的传感器测量时间同步
5.parameter_utils 参数读取的公共代码
因为整个SLAM的节点只有一个
6.point_cloud_filter
PointCloudFilter.cc是点云预处理算法,封装成库,而point_cloud_filter.cc只是提供测试的一个接口,用来 验证点云预处理,只有ros初始化和main入口。

- point_cloud_filter:对输入的点云数据进行如进行统计滤波处理,得到过滤后的点云数据
7.point_cloud_odometry 需要先初始化,给出先验位姿,通过使用默认值也可
bool PointCloudOdometry::UpdateEstimate(const PointCloud& points) {
// Store input point cloud's time stamp for publishing.
stamp_.fromNSec(points.header.stamp*1e3);
// If this is the first point cloud, store it and wait for another.
if (!initialized_) {
copyPointCloud(points, *query_);
initialized_ = true;
return false;
}
// Move current query points (acquired last iteration) to reference points.
copyPointCloud(*query_, *reference_);
// Set the incoming point cloud as the query point cloud.
copyPointCloud(points, *query_);
// Update pose estimate via ICP.
return UpdateICP();
}
bool PointCloudOdometry::UpdateICP() {
// Compute the incremental transformation.
GeneralizedIterativeClosestPoint icp;
icp.setTransformationEpsilon(params_.icp_tf_epsilon);
icp.setMaxCorrespondenceDistance(params_.icp_corr_dist);
icp.setMaximumIterations(params_.icp_iterations);
icp.setRANSACIterations(0);
icp.setInputSource(query_);
icp.setInputTarget(reference_);
PointCloud unused_result;
icp.align(unused_result);
const Eigen::Matrix4f T = icp.getFinalTransformation();
// Update pose estimates.
incremental_estimate_.translation = gu::Vec3(T(0, 3), T(1, 3), T(2, 3));
incremental_estimate_.rotation = gu::Rot3(T(0, 0), T(0, 1), T(0, 2),
T(1, 0), T(1, 1), T(1, 2),
T(2, 0), T(2, 1), T(2, 2));
// Only update if the incremental transform is small enough.
if (!transform_thresholding_ ||
(incremental_estimate_.translation.Norm() <= max_translation_ &&
incremental_estimate_.rotation.ToEulerZYX().Norm() <= max_rotation_)) {
integrated_estimate_ =
gu::PoseUpdate(integrated_estimate_, incremental_estimate_);
} else {
ROS_WARN(
"%s: Discarding incremental transformation with norm (t: %lf, r: %lf)",
name_.c_str(), incremental_estimate_.translation.Norm(),
incremental_estimate_.rotation.ToEulerZYX().Norm());
}
// Convert pose estimates to ROS format and publish.
PublishPose(incremental_estimate_, incremental_estimate_pub_);
PublishPose(integrated_estimate_, integrated_estimate_pub_);
// Publish point clouds for visualization.
PublishPoints(query_, query_pub_);
PublishPoints(reference_, reference_pub_);
// Convert transform between fixed frame and odometry frame.
geometry_msgs::TransformStamped tf;
tf.transform = gr::ToRosTransform(integrated_estimate_);
tf.header.stamp = stamp_;
tf.header.frame_id = fixed_frame_id_;
tf.child_frame_id = odometry_frame_id_;
tfbr_.sendTransform(tf);
return true;
} 通过GICP算法计算两帧点云数据的位姿变换(初步计算),只有符合一定要求的里程计才会作为位姿更新,然后发布里程计和TF。
8. point_cloud_localization:通过初步计算的位姿变换来获取当前帧对应的地图中最近临点,再次执行GICP得到精确的位姿变换(第二次计算)
bool PointCloudLocalization::MeasurementUpdate(const PointCloud::Ptr& query,
const PointCloud::Ptr& reference,
PointCloud* aligned_query) {
if (aligned_query == NULL) {
ROS_ERROR("%s: Output is null.", name_.c_str());
return false;
}
// Store time stamp.
stamp_.fromNSec(query->header.stamp*1e3);
// ICP-based alignment. Generalized ICP does (roughly) plane-to-plane
// matching, and is much more robust than standard ICP.
GeneralizedIterativeClosestPoint icp;
icp.setTransformationEpsilon(params_.tf_epsilon);
icp.setMaxCorrespondenceDistance(params_.corr_dist);
icp.setMaximumIterations(params_.iterations);
icp.setRANSACIterations(0);
icp.setMaximumOptimizerIterations(50); // default 20
icp.setInputSource(query);
icp.setInputTarget(reference);
PointCloud unused;
icp.align(unused);
// Retrieve transformation and estimate and update.
const Eigen::Matrix4f T = icp.getFinalTransformation();
pcl::transformPointCloud(*query, *aligned_query, T);
gu::Transform3 pose_update;
pose_update.translation = gu::Vec3(T(0, 3), T(1, 3), T(2, 3));
pose_update.rotation = gu::Rot3(T(0, 0), T(0, 1), T(0, 2),
T(1, 0), T(1, 1), T(1, 2),
T(2, 0), T(2, 1), T(2, 2));
// Only update if the transform is small enough.
if (!transform_thresholding_ ||
(pose_update.translation.Norm() <= max_translation_ &&
pose_update.rotation.ToEulerZYX().Norm() <= max_rotation_)) {
incremental_estimate_ = gu::PoseUpdate(incremental_estimate_, pose_update);
} else {
ROS_WARN(
" %s: Discarding incremental transformation with norm (t: %lf, r: %lf)",
name_.c_str(), pose_update.translation.Norm(),
pose_update.rotation.ToEulerZYX().Norm());
}
integrated_estimate_ =
gu::PoseUpdate(integrated_estimate_, incremental_estimate_);
// Convert pose estimates to ROS format and publish.
PublishPose(incremental_estimate_, incremental_estimate_pub_);
PublishPose(integrated_estimate_, integrated_estimate_pub_);
// Publish point clouds for visualization.
PublishPoints(*query, query_pub_);
PublishPoints(*reference, reference_pub_);
PublishPoints(*aligned_query, aligned_pub_);
// Publish transform between fixed frame and localization frame.
geometry_msgs::TransformStamped tf;
tf.transform = gr::ToRosTransform(integrated_estimate_);
tf.header.stamp = stamp_;
tf.header.frame_id = fixed_frame_id_;
tf.child_frame_id = base_frame_id_;
tfbr_.sendTransform(tf);
return true;
}
9. laser_loop_closure:
通过GICP寻找两帧的回环,
bool LaserLoopClosure::PerformICP(const PointCloud::ConstPtr& scan1,
const PointCloud::ConstPtr& scan2,
const gu::Transform3& pose1,
const gu::Transform3& pose2,
gu::Transform3* delta,
LaserLoopClosure::Mat66* covariance) {
if (delta == NULL || covariance == NULL) {
ROS_ERROR("%s: Output pointers are null.", name_.c_str());
return false;
}
// Set up ICP.
pcl::GeneralizedIterativeClosestPoint icp;
icp.setTransformationEpsilon(icp_tf_epsilon_);
icp.setMaxCorrespondenceDistance(icp_corr_dist_);
icp.setMaximumIterations(icp_iterations_);
icp.setRANSACIterations(0);
// Filter the two scans. They are stored in the pose graph as dense scans for
// visualization.
PointCloud::Ptr scan1_filtered(new PointCloud);
PointCloud::Ptr scan2_filtered(new PointCloud);
filter_.Filter(scan1, scan1_filtered);
filter_.Filter(scan2, scan2_filtered);
// Set source point cloud. Transform it to pose 2 frame to get a delta.
const Eigen::Matrix R1 = pose1.rotation.Eigen();
const Eigen::Matrix t1 = pose1.translation.Eigen();
Eigen::Matrix4d body1_to_world;
body1_to_world.block(0, 0, 3, 3) = R1;
body1_to_world.block(0, 3, 3, 1) = t1;
const Eigen::Matrix R2 = pose2.rotation.Eigen();
const Eigen::Matrix t2 = pose2.translation.Eigen();
Eigen::Matrix4d body2_to_world;
body2_to_world.block(0, 0, 3, 3) = R2;
body2_to_world.block(0, 3, 3, 1) = t2;
PointCloud::Ptr source(new PointCloud);
pcl::transformPointCloud(*scan1_filtered, *source, body1_to_world);
icp.setInputSource(source);
// Set target point cloud in its own frame.
PointCloud::Ptr target(new PointCloud);
pcl::transformPointCloud(*scan2_filtered, *target, body2_to_world);
icp.setInputTarget(target);
// Perform ICP.
PointCloud unused_result;
icp.align(unused_result);
// Get resulting transform.
const Eigen::Matrix4f T = icp.getFinalTransformation();
gu::Transform3 delta_icp;
delta_icp.translation = gu::Vec3(T(0, 3), T(1, 3), T(2, 3));
delta_icp.rotation = gu::Rot3(T(0, 0), T(0, 1), T(0, 2),
T(1, 0), T(1, 1), T(1, 2),
T(2, 0), T(2, 1), T(2, 2));
// Is the transform good?
if (!icp.hasConverged())
return false;
if (icp.getFitnessScore() > max_tolerable_fitness_) {
return false;
}
// Update the pose-to-pose odometry estimate using the output of ICP.
const gu::Transform3 update =
gu::PoseUpdate(gu::PoseInverse(pose1),
gu::PoseUpdate(gu::PoseInverse(delta_icp), pose1));
*delta = gu::PoseUpdate(update, gu::PoseDelta(pose1, pose2));
// TODO: Use real ICP covariance.
covariance->Zeros();
for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i)
(*covariance)(i, i) = 0.01;
for (int i = 3; i < 6; ++i)
(*covariance)(i, i) = 0.04;
// If the loop closure was a success, publish the two scans.
source->header.frame_id = fixed_frame_id_;
target->header.frame_id = fixed_frame_id_;
scan1_pub_.publish(*source);
scan2_pub_.publish(*target);
return true;
} 通过isam构建的因子图,若出现回环则加入到因子图中进行优化
bool LaserLoopClosure::AddBetweenFactor(
const gu::Transform3& delta, const LaserLoopClosure::Mat66& covariance,
const ros::Time& stamp, unsigned int* key) {
if (key == NULL) {
ROS_ERROR("%s: Output key is null.", name_.c_str());
return false;
}
// Append the new odometry.
Pose3 new_odometry = ToGtsam(delta);
NonlinearFactorGraph new_factor;
Values new_value;
new_factor.add(MakeBetweenFactor(new_odometry, ToGtsam(covariance)));
Pose3 last_pose = values_.at(key_-1);
new_value.insert(key_, last_pose.compose(new_odometry));
// Store this timestamp so that we can publish the pose graph later.
keyed_stamps_.insert(std::pair(key_, stamp));
// Update ISAM2.
isam_->update(new_factor, new_value);
values_ = isam_->calculateEstimate();
// Assign output and get ready to go again!
*key = key_++;
// We always add new poses, but only return true if the pose is far enough
// away from the last one (keyframes). This lets the caller know when they
// can add a laser scan.
// Is the odometry translation large enough to add a new keyframe to the graph?
odometry_ = odometry_.compose(new_odometry);
if (odometry_.translation().norm() > translation_threshold_) {
odometry_ = Pose3::identity();
return true;
}
return false;
} 对当前帧的点云数据与历史点云数据对比判断回环是否发生,发布位姿数据
10.point_cloud_mapper:构建点云地图,发布地图数据,通过插入点的形式增加地图点云,代码精简
11.pose_graph_msgs为了RVIZ显示位姿图,新建的自定义的消息,从而能够在rviz上进行显示