hibernate-validator校验参数(统一异常处理)
hibernate-validator
一、概述
Bean Validation源于JSR-303 ,而JSR303是 Java EE 6 中的一项子规范。JSR349、JSR380是其升级版,添加了一些新的特性。Oracle公司传统艺能,一流公司定标准,它们只定义了一些校验注解(Constraint),如@Null@NotNull@Pattern],位于javax.validation.constraints包下,只提供规范不提供实现。
Hibernate Validator是对这个规范的实现(不要和数据库ORM框架Hibernate联系在一起),并增加了一些自定义校验注解,如@Email、@Length、@Range,位于org.hibernate.validator.constraints包下。
这里贴上常用的注解和解释
| 注解 | 释义 |
|---|---|
| @Null | 被注释的元素必须为 null |
| @NotNull | 被注释的元素必须不为 null |
| @AssertTrue | 被注释的元素必须为 true |
| @AssertFalse | 被注释的元素必须为 false |
| @Min(value) | 被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须大于等于指定的最小值 |
| @Max(value) | 被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须小于等于指定的最大值 |
| @DecimalMin(value) | 被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须大于等于指定的最小值 |
| @DecimalMax(value) | 被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须小于等于指定的最大值 |
| @Size(max, min) | 被注释的元素的大小必须在指定的范围内,元素必须为集合,代表集合个数 |
| @Digits (integer, fraction) | 被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须在可接受的范围内 |
| @Past | 被注释的元素必须是一个过去的日期 |
| @Future | 被注释的元素必须是一个将来的日期 |
| 被注释的元素必须是电子邮箱地址 | |
| @Length(min=, max=) | 被注释的字符串的大小必须在指定的范围内,必须为数组或者字符串,若微数组则表示为数组长度,字符串则表示为字符串长度 |
| @NotEmpty | 被注释的字符串的必须非空,可以为空格,空字符串,null |
| @Range(min=, max=) | 被注释的元素必须在合适的范围内 |
| @NotBlank | 被注释的字符串的必须非空,不可以为空格,可以为空字符串,null |
| @Pattern(regexp = ) | 正则表达式校验 |
二、基础使用
在实际的web项目开发中,我们无需手动引入依赖。当依赖spring-boot-starter-web这个starter时,会自动传递相应的Bean Validation依赖。但有一点需要注意,在更新版本的SpringBoot中,默认移除了Bean Validtion相关依赖。具体的对应关系可以参照如下表格:
| spring boot 版本 | validation依赖 |
|---|---|
| < 2.3.x | spring-boot-starter-web传递校验依赖 |
| > 2.3.x | 需要手动引入spring-boot-starter-validation |
注:以下的示例代码是基于spring-boot 2.3.0.RELEASE版本
工程依赖文件如下
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombokgroupId>
<artifactId>lombokartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-validationartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-testartifactId>
<scope>testscope>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.junit.vintagegroupId>
<artifactId>junit-vintage-engineartifactId>
exclusion>
exclusions>
dependency>
dependencies>
Controller层校验
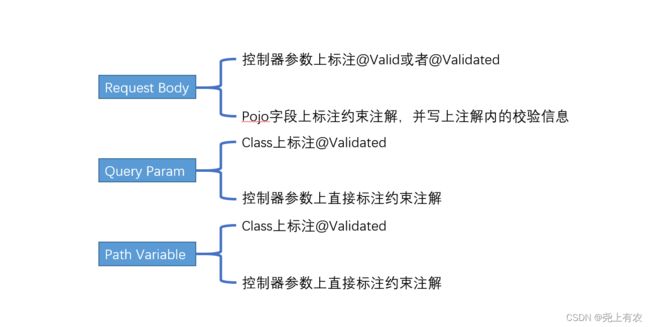
假设我们实现了一个Spring REST控制器,想要验证由客户端传入的参数。根据请求方式、携带的内容以及实际应用场景,一般有三类:
-
POST Request Body;
-
GET PathVariable (如/foos/{id});
-
GET Query Param(如url?q=param)
上面三种基本覆盖了大部分的开发场景
1.验证Request Body
接收参数的包装类
@Getter
@Setter
public class RequestParam {
@Min(1)
@Max(5)
private Integer number;
@Email
private String email;
}
接收请求的controller
@RestController
public class ValidateRequestBodyController {
@PostMapping("/validateBody")
public ResponseEntity<String> validateBody(@Valid @RequestBody RequestParam param) {
return ResponseEntity.ok("valid");
}
}
注意:此时注解标注的位置,必须放在方法参数上,放在类上会导致校验不生效,行为不符合预期。此外,针对这种情形@Valid和@Validated两个注解可以混用。 使用@Validated时也需要放在参数列表中,放在类上和放在方法上都会导致没有校验。
如果校验失败,会抛出一个MethodArgumentNotValidException异常,Spring默认会把这个转为400(Bad Request)请求。

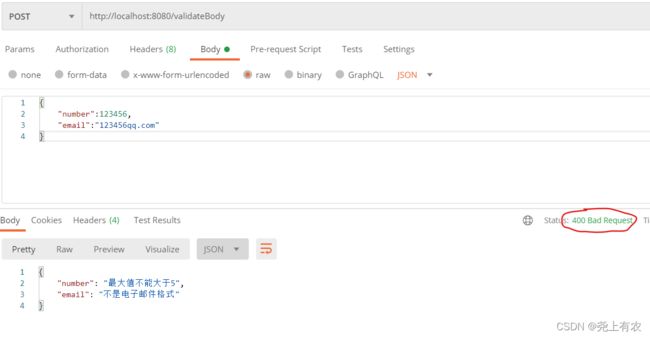
请求:
{
"number":123456,
"email":"[email protected]"
}
返回:
{
"timestamp": "2020-07-30T10:18:19.435+00:00",
"status": 400,
"error": "Bad Request",
"message": "",
"path": "/validateBody"
}
异常:
org.springframework.web.bind.MethodArgumentNotValidException: Validation failed for argument [0]...
在实际项目开发中,通常会用 ExceptionHandler处理该异常,包裹返回一个更友好的提示:
定义全局异常处理器:
@RestControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
/**
* 处理POST请求参数校验异常
* @return
*/
@ExceptionHandler(MethodArgumentNotValidException.class)
public ResponseEntity<Map<String,Object>> validExceptionHandler(MethodArgumentNotValidException e) {
List<FieldError> fieldErrors = e.getBindingResult().getFieldErrors();
Map<String, Object> errorMap = fieldErrors.stream()
.collect(Collectors.toMap(item -> item.getField(), item -> item.getDefaultMessage()));
return ResponseEntity.badRequest().body(errorMap);
}
}
再次请求
#参数
{
"number":123456,
"email":"123456qq.com"
}
#结果
{
"number": "最大值不能大于5",
"email": "不是电子邮件格式"
}
2. 校验PathVariable/RequestParam
开发中,如果参数个数小于三个,倾向于不写Java Bean来封装参数,而是平铺写到方法入参中。对于这种情况,需要在入参上直接声明约束注解(如@Min()),并在类上标注@Validated注解。
注意:在类级别上标注@Validated注解告诉Spring需要校验方法参数上的约束。
接收请求的controller
@RestController
@Validated // 告诉Spring校验方法参数上的约束
public class ValidateParametersController {
/**
* @param id
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("/validatePathVariable/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<String> validatePathVariable(
@PathVariable("id") @Min(value = 5,message = "id不能小于5") Integer id,
@RequestParam("email") @Email(message = "邮箱格式不对") String email
) {
return ResponseEntity.ok("valid");
}
}
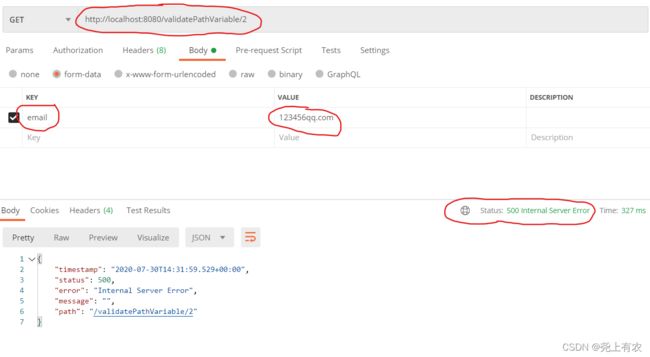
测试请求
异常信息
javax.validation.ConstraintViolationException: validatePathVariable.email: 邮箱格式不对, validatePathVariable.id: id不能小于5
这是返回的状态码是:500,抛出的是ConstraintViolationException
在全局异常处理器中捕获该异常,处理该异常
@ExceptionHandler(ConstraintViolationException.class)
public ResponseEntity<List<String>> constrainViolationHandler(ConstraintViolationException e){
Set<ConstraintViolation<?>> violationSet = e.getConstraintViolations();
List<String> errorList = violationSet.stream()
.map(item -> item.getMessage()).collect(Collectors.toList());
return ResponseEntity.badRequest().body(errorList);
}
再次请求:
注意:这种情况你要是把注解@Valid或者@Validated标注在方法或者参数列表中,都不会校验。
总结一下:
3.配置验证
import org.hibernate.validator.HibernateValidator;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.validation.beanvalidation.MethodValidationPostProcessor;
import javax.validation.Validation;
import javax.validation.Validator;
@Configuration
public class ValidatorConfig {
@Bean
public static Validator validator() {
return Validation
.byProvider(HibernateValidator.class)
.configure()
//开启快速校验,默认校验所有参数,false校验全部
.failFast(true)
.buildValidatorFactory()
.getValidator();
}
@Bean
public MethodValidationPostProcessor methodValidationPostProcessor() {
MethodValidationPostProcessor processor = new MethodValidationPostProcessor();
//设置validator模式为快速失败返回
processor.setValidator(validator());
return processor;
}
}
三、嵌套校验
上文提到过针对Java Bean的校验,里面的字段都是非嵌套。实际的业务场景中,对象内字段类型也是对象的场景并不罕见。
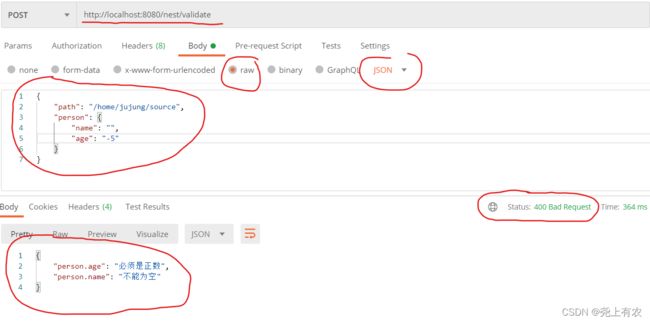
正确使用示例:
@Data
public class Input {
@NotBlank
private String path;
@Valid //这个注解不加就不会校验Person里面的约束
private Person person;
}
@Data
class Person{
@NotBlank
private String name;
@Positive // 正数
private Integer age;
}
可以看到此处的 Input有一个 person字段,该字段指向另一个Java Bean。针对这种场景,需要在person字段上标注@Valid注解,并且该字段指向的类同样需要标注约束注解。
controller
@RestController()
@RequestMapping("/nest")
public class NestValidateController {
@PostMapping("/validate")
public ResponseEntity<String> validateNestingAttr(@Valid @RequestBody Input input) {
return ResponseEntity.ok("valid");
}
}
注意:此时用@Valid和@Validated都可以,总结一下:在使用@RequestBody接收json数据时,必须在方法的参数列表里面使用@Valid或@Validated来告诉hibernate-validator需要校验参数封装实体的字段约束(被标注到字段上的校验注解),然后在需要嵌套校验的字段上标注@Valid注解,因为@Validated是不能使用在类的字段上的,所以只能使用@Valid
四、分组校验
通常,某些Java Bean在不同的请求之间共享。以典型的CRUD操作为例:Create请求和Update请求很可能都采用相同的对象类型作为输入。但是,在不同的情况下可能会触发不同的验证。
正确使用的示例:
@Data
public class User {
@NotNull(groups = OnUpdate.class)
@Null(groups = OnCreate.class)
private Long id;
@NotEmpty(groups = OnCreate.class)
private String userName;
@NotEmpty(groups = OnCreate.class)
private String mobile;
// 仅仅作为一个标记接口
public interface OnUpdate{}
public interface OnCreate{}
}
三个字段标明在创建操作时需要校验
controller
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/group")
public class GroupValidateController {
@PostMapping("/user")
public ResponseEntity<String> save(@Validated(value = {User.OnCreate.class}) @RequestBody User user) {
return ResponseEntity.ok("valid");
}
}
方法参数中标明需要校验的分组
只有@Validated才支持分组校验,所以这里必须使用@Validated,不能用@Valid替换
此时生效的是:@Null(groups = OnCreate.class),id必须为空,userName和mobile不能为空
五、自定义校验
有时官方提供的注解规则不能满足我们的需要,这时就要自定义注解来自定义校验规则,举一个典型的应用场景,只接收给定的字符,其它字符都校验不通过。比如:性别只接收 M,F;
1.定义一个注解
/**
* @Constraint: 关联解析类
* @Target: 注解作用于的位置
*/
@Constraint(validatedBy = EnumValueValidator.class)
@Target({ElementType.FIELD,ElementType.PARAMETER,ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface EnumValue {
String[] value() default "";
String message() default "参数必须为指定的值";
Class<?>[] groups() default {};
Class<? extends javax.validation.Payload>[] payload() default {};
}
2.定义校验的规则
public class EnumValueValidator implements ConstraintValidator<EnumValue,String> {
private String[] enumValue;
/**
* 初始化时把注解中的值传过来
* @param constraintAnnotation
*/
@Override
public void initialize(EnumValue constraintAnnotation) {
this.enumValue = constraintAnnotation.value();
}
/**
*
* @param source 是要被校验的值
* @param context
* @return
*/
@Override
public boolean isValid(String source, ConstraintValidatorContext context) {
if(source instanceof String) {
for (String val : enumValue) {
if(val.equals(source)) {
return true;
}
}
}else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("参数类型非法");
}
return false;
}
}
3.controller中使用
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/def")
@Validated // 这个注解一定不能忘
public class DefinationValidator {
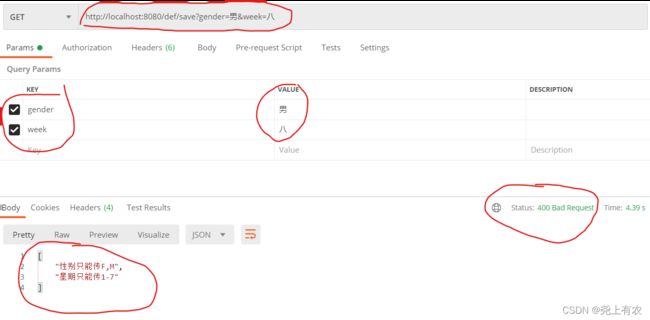
@GetMapping("/save")
public ResponseEntity<String> save(
@EnumValue(value = {"F","M"},message = "性别只能传F,M")
@RequestParam("gender") String gender,
@EnumValue(value = {"1","2","3","4","5","6","7"},message = "星期只能传1-7")
@RequestParam("week") String week
) {
return ResponseEntity.ok("valid");
}
}
4.测试
六、统一异常处理
1.定义一个异常信息描述基础信息接口类
public interface ResultCodeInterface {
/*错误描述*/
String getMsg();
/*错误码*/
int getCode();
}
2.定义一个枚举类实现上面的异常信息描述接口
public enum CommonEnum implements ResultCodeInterface {
// 数据操作错误定义
SUCCESS(200, "成功!"),
UNSUCCESS(400, "失败"),
SIGNATURE_NOT_MATCH(401, "请求的数字签名不匹配!"),
BODY_NOT_MATCH(402, "请求的数据格式不符!"),
REQUEST_NOT_MATCH(403,"请求不合法"),
NOT_FOUND(404, "未找到该资源!"),
INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR(500, "服务器内部错误!"),
SERVER_BUSY(503, "服务器正忙,请稍后再试!");
/**
* 错误码
*/
private int code;
/**
* 错误描述
*/
private String msg;
CommonEnum(int code, String resultMsg) {
this.code = code;
this.msg = resultMsg;
}
@Override
public String getMsg() {
return msg;
}
@Override
public int getCode() {
return code;
}
}
3.定义一个自定义异常类,标识业务系统出现的异常信息
public class BaseException extends RuntimeException {
private int code;
private String msg;
private Object data;
public BaseException(String msg) {
super(msg);
}
public BaseException(Exception e) {
this(e.getMessage());
}
public BaseException(String message, Throwable cause) {
super(message, cause);
}
public BaseException(int code, String msg, Throwable cause) {
super(msg, cause);
this.code = code;
this.msg = msg;
}
public BaseException(int code, String msg) {
this.code = code;
this.msg = msg;
}
public BaseException(int code, String msg, Object data) {
this.code = code;
this.msg = msg;
this.data = data;
}
public BaseException(ResultCodeInterface e) {
this.code = e.getCode();
this.msg = e.getMsg();
}
public int getCode() {
return code;
}
public String getMsg() {
return msg;
}
public Object getData() {
return data;
}
public void setCode(int code) {
this.code = code;
}
public void setMsg(String msg) {
this.msg = msg;
}
public void setData(Object data) {
this.data = data;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "BaseException{" +
"code='" + code + '\'' +
", msg='" + msg + '\'' +
", data=" + data +
'}';
}
}
public class RemoteException extends BaseException{
public RemoteException(ResultCodeInterface codeInterface, String message) {
super(codeInterface.getCode(), codeInterface.getMsg() + ":" + message);
}
public RemoteException(String msg) {
super(msg);
}
public RemoteException(Exception e) {
super(e);
}
public RemoteException(String message, Throwable cause) {
super(message, cause);
}
public RemoteException(int code, String msg, Throwable cause) {
super(code, msg, cause);
}
public RemoteException(ResultCodeInterface codeInterface) {
super(codeInterface.getCode(), codeInterface.getMsg());
}
public RemoteException(int code, String msg, Object data) {
super(code, msg, data);
}
}
4.定义一个统一结果返回数据封装类
@JsonInclude(value= JsonInclude.Include.NON_NULL)
public class Result<T> implements Serializable {
private int code;
private String msg;
private T data;
public Result() {
}
public void setCode(int code) {
this.code = code;
}
public void setMsg(String msg) {
this.msg = msg;
}
public void setData(T data) {
this.data = data;
}
public int getCode() {
return code;
}
public String getMsg() {
return msg;
}
public T getData() {
return data;
}
public Result(int code, String msg, T data) {
this.code = code;
this.msg = msg;
this.data = data;
}
public Result(int code, String msg) {
this.code = code;
this.msg = msg;
}
public static Result success(Object data) {
return new Result(CommonEnum.SUCCESS.getCode(), CommonEnum.SUCCESS.getMsg(), data);
}
public static Result error(String msg) {
return new Result(CommonEnum.UNSUCCESS.getCode(), CommonEnum.UNSUCCESS.getMsg(), msg);
}
public static Result error(int code, String msg) {
return new Result(code, msg);
}
public static Result error(ResultCodeInterface errorInfo) {
Result rs = new Result();
rs.setCode(errorInfo.getCode());
rs.setMsg(errorInfo.getMsg());
return rs;
}
}
5.定义一个全局异常处理类
定义全局异常处理类后,会对程序运行过程中出现的异常进行统一处理。
@RestControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
/**
* 参数不合法异常
*/
@ExceptionHandler(MethodArgumentNotValidException.class)
public Result validExceptionHandler(MethodArgumentNotValidException e) {
String msg = e.getBindingResult().getAllErrors().stream().map(item -> item.getDefaultMessage()).collect(Collectors.joining());
return Result.error(msg);
}
/**
* POST缺少body参数
**/
@ExceptionHandler(HttpMessageNotReadableException.class)
public Result httpMessageNotReadableHandler(HttpMessageNotReadableException e) {
return Result.error(CommonEnum.BODY_NOT_MATCH);
}
/**
* 处理url参数异常
**/
@ExceptionHandler(ConstraintViolationException.class)
public Result constrainViolationHandler(ConstraintViolationException e) {
String msg = e.getConstraintViolations().stream().map(item -> item.getMessage()).collect(Collectors.joining());
return Result.error(msg);
}
/**
* 未传入参数异常 @NotBlank
**/
@ExceptionHandler(MissingServletRequestParameterException.class)
public Result missingServletRequestParameterHandler(MissingServletRequestParameterException e) {
return Result.error(CommonEnum.BODY_NOT_MATCH);
}
/**
* 请求方式不正确
**/
@ExceptionHandler(HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException.class)
public Result httpRequestMethodNotSupportedHandler(HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException e) {
return Result.error(CommonEnum.REQUEST_NOT_MATCH);
}
/**
* 缺少请求参数
**/
@ExceptionHandler(BindException.class)
public Result bindExceptionHandler(BindException e) {
return Result.error(CommonEnum.REQUEST_NOT_MATCH);
}
/**
* 业务异常
**/
@ExceptionHandler(RemoteException.class)
public Result remoteExceptionHandler(RemoteException e) {
return Result.error(e.getCode(),e.getMsg());
}
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
public Result exceptionHandler(Exception e) {
return Result.error(CommonEnum.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR);
}
}
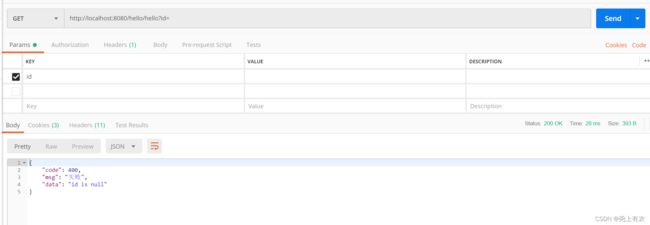
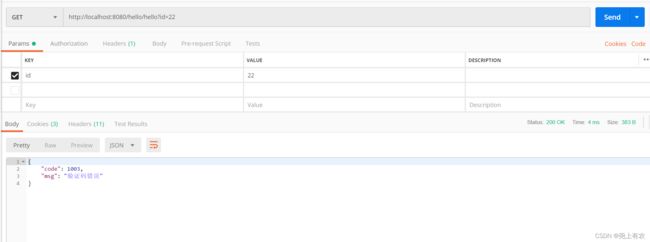
6.统一异常处理测试
定义业务枚举异常
public enum UserCodeEnum implements ResultCodeInterface {
//
USER_ADD_EXISTS(1001, "账号已存在,请重新输入"),
VERIFY_EXISTS(1002, "刷新过于频繁,请稍后再试"),
SIGN_CACHE_NOT_FOUND(1002, "验证码不存在"),
SIGN_CACHE_NO_EQUAL(1003, "验证码错误");
/**
* 处理结果码
*/
public int code;
/**
* 结果描述
*/
public String msg;
UserCodeEnum(int code, String msg) {
this.code = code;
this.msg = msg;
}
@Override
public String getMsg() {
return msg;
}
@Override
public int getCode() {
return code;
}
}
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/hello")
@Validated
public class HelloController {
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello(
@NotBlank(message = "id is null")
@RequestParam("id") String id) {
if(true){
throw new RemoteException(UserCodeEnum.SIGN_CACHE_NO_EQUAL);
}
return "hello";
}
}

参考:https://www.ddmit.com/2021/08/13/springboot-handle-exception-with-controlleradvice-exceptionhandler/
https://gitee.com/jujungfoxmail/hibernate-validator