图论BFS(Breath First Search)Algorithm广度优先搜索遍历空间平面网格图路径选择,networkx,Python
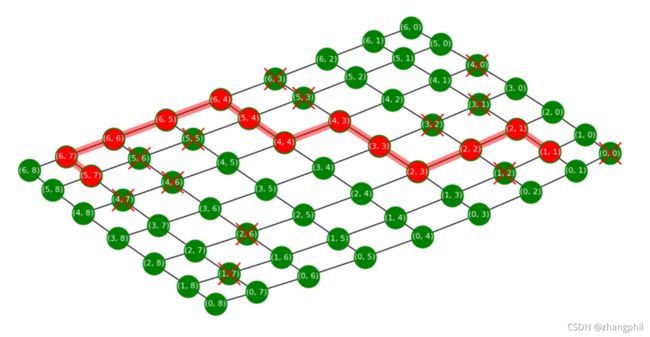
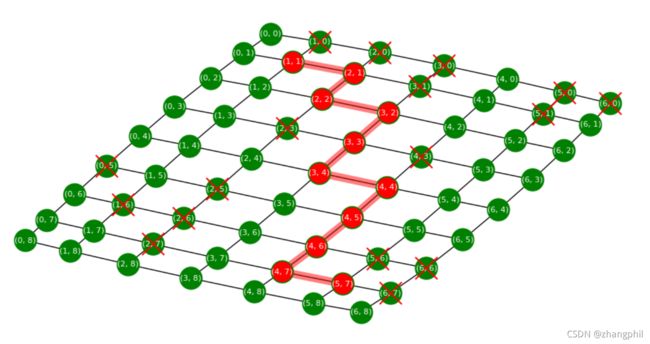
(1)在每个节点埋入一个parent指针,指向当前节点的前一个节点,通过串联起来从终点起的父节点,就构成了路径。
(2)图中打X的节点表明当前节点不可通行。
(3)网格中的节点最终被标记为红色且被淡红色粗线描出来的就是选的路。
import random
import networkx as nx
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
WALKABLE = 'walkable'
PARENT = 'parent'
VISITED = 'visited'
def my_graph():
M = 7
N = 9
G = nx.grid_2d_graph(m=M, n=N)
pos = nx.spring_layout(G, iterations=100)
nx.draw_networkx(G, pos=pos,
# labels=labels, #labels = dict(((i, j), 'Phil') for i, j in G.nodes())
font_size=8,
font_color='white',
node_color='green',
node_size=500,
width=1)
START = (1, 1) # (2, 2)
GOAL = (M - 1 - 1, N - 1 - 1)
# 0,随机生成障碍物点
# 1,精心挑选的障碍物构成陷阱
obstacle_mode = 0
road_closed_nodes = []
if obstacle_mode == 0:
obstacle = 20 # 障碍物(断点、不可达点)数量
road_closed_nodes = obstacle_nodes(G, START, GOAL, obstacle, M, N)
elif obstacle_mode == 1:
road_closed_nodes = dummy_nodes(G)
nx.draw_networkx_nodes(
G, pos,
nodelist=road_closed_nodes,
node_size=500,
node_color="red",
node_shape="x",
# alpha=0.3,
label='x'
)
bfs(G, START, GOAL)
path = find_path_by_parent(G, START, GOAL)
print('path', path)
nx.draw_networkx_nodes(
G, pos,
nodelist=path,
node_size=400,
node_color="red",
node_shape='o',
# alpha=0.3,
# label='NO'
)
# nx.draw_networkx_nodes(
# G, pos,
# nodelist=path,
# node_size=100,
# node_color="yellow",
# node_shape='*',
# # alpha=0.3,
# # label='NO'
# )
path_edges = []
for i in range(len(path)):
if (i + 1) == len(path):
break
path_edges.append((path[i], path[i + 1]))
print('path_edges', path_edges)
# 把path着色加粗重新描边
nx.draw_networkx_edges(G, pos,
edgelist=path_edges,
width=8,
alpha=0.5,
edge_color="r")
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()
# 广度优先遍历搜索路径
def bfs(G, START, GOAL):
for n in G.nodes():
G.nodes[n][VISITED] = False
print('G.nodes(data=True)', G.nodes(data=True))
# 记录搜索路径
search_path = []
open_list = [START]
while True:
if len(open_list) == 0:
break
print('-----')
print('open_list', open_list)
node = open_list[0] # 左边最头部含有上一轮父层次的节点
G.nodes[node][VISITED] = True
search_path.append(node)
print('search_path', len(search_path), search_path)
print('选择', node)
for n in nx.neighbors(G, node):
try:
walkable = G.nodes[n][WALKABLE]
except:
walkable = True
visited = G.nodes[n][VISITED]
# 如果节点已经在队列里面,则不予重复添加。
if (not visited) and walkable and (n not in open_list):
open_list.append(n)
G.nodes[n][PARENT] = node
print('弹出', node)
del (open_list[0])
print('open_list', open_list)
print('nodes', G.nodes(data=True))
if node == GOAL:
print('到达->', GOAL)
break
def find_path_by_parent(G, START, GOAL):
t = GOAL
path = [t]
is_find = False
while not is_find:
for n in G.nodes(data=True):
if n[0] == t:
print('parent', n)
parent = n[1][PARENT]
path.append(parent)
if parent == START:
is_find = True
break
t = parent
list.reverse(path)
return path
# 障碍物点
def obstacle_nodes(G, START, GOAL, obstacle, M, N):
road_closed_nodes = []
for i in range(obstacle):
n = (random.randint(0, M - 1), random.randint(0, N - 1))
if n == START or n == GOAL:
continue
if n in road_closed_nodes:
continue
G.nodes[n][WALKABLE] = False
road_closed_nodes.append(n)
return road_closed_nodes
def dummy_nodes(G):
fun_nodes = []
n0 = (1, 2)
G.nodes[n0][WALKABLE] = False
fun_nodes.append(n0)
n1 = (1, 3)
G.nodes[n1][WALKABLE] = False
fun_nodes.append(n1)
n2 = (1, 4)
G.nodes[n2][WALKABLE] = False
fun_nodes.append(n2)
n3 = (1, 5)
G.nodes[n3][WALKABLE] = False
fun_nodes.append(n3)
n4 = (1, 6)
G.nodes[n4][WALKABLE] = False
fun_nodes.append(n4)
n5 = (2, 6)
G.nodes[n5][WALKABLE] = False
fun_nodes.append(n5)
n6 = (3, 6)
G.nodes[n6][WALKABLE] = False
fun_nodes.append(n6)
n7 = (4, 6)
G.nodes[n7][WALKABLE] = False
fun_nodes.append(n7)
n8 = (5, 6)
G.nodes[n8][WALKABLE] = False
fun_nodes.append(n8)
n9 = (5, 5)
G.nodes[n9][WALKABLE] = False
fun_nodes.append(n9)
n10 = (5, 4)
G.nodes[n10][WALKABLE] = False
fun_nodes.append(n10)
n11 = (5, 3)
G.nodes[n11][WALKABLE] = False
fun_nodes.append(n11)
n12 = (5, 2)
G.nodes[n12][WALKABLE] = False
fun_nodes.append(n12)
return fun_nodes
if __name__ == '__main__':
my_graph()
程序运运行几轮后的选路截图,红色X的点是随机生成的障碍物点,红色X点是说当前这个点不能行走通过:
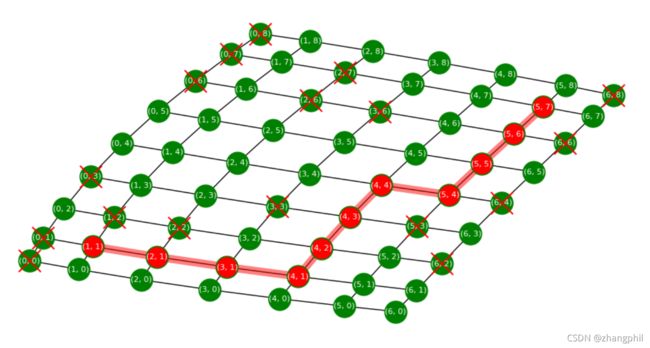
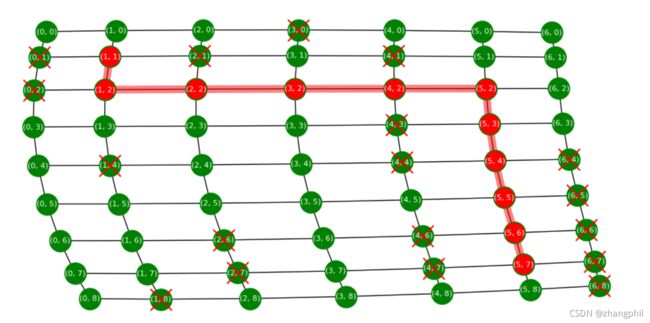
现在特别的为了挑战算法的智商水平,故意为算法制造一些陷阱出来。具体的实验方法,是做一个凹形的墙,把这个凹形的墙正对着出发点,看看算法的表现,重点考察算法是否能机智的绕过这堵墙, 找到终点。
把程序中的起点修改为(2,2)
START = (2, 2)修改障碍物模式为1:
obstacle_mode = 1算法的智商表现:
算法聪明的绕过墙、没有掉进陷阱。
networkx图论贝尔曼-福特Bellman Ford Algorithm最短路径,Python_Zhang Phil-CSDN博客