第八讲 数论
文章目录
-
- 等差数列(最大公约数gcdget到了)
- X的因子链
- 聪明的燕姿(约数之和,dfs,难)
- 五指山(exgcd())
- C 循环(exgcd())
- 正则问题(dfs)
等差数列(最大公约数gcdget到了)

思路:首先我们可以肯定最大值和最小值肯定是等差数列的首项和尾项,an=a1+(n-1)d,得到n=(an-a1)/d+1,为了使项数更少,显然是d越大越好,那么最大的d是什么呢,显然是排序后两项之间的差的最大公约数。
很明显,选择了一个所有的差的约数,为了更大,需要选择最大公约数。
比如样例:2 4 6 10 20
2 2 4 10的最大公约数是2所以公差是2
public class Main{
static Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
static PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
static int N = 100010;
static long ans = 0;
static int n = 0,m = 0;
static int[]a = new int[N];
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
n = sc.nextInt();
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
a[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
Arrays.sort(a,1,1 + n);
if(a[1] == a[n]) {
System.out.println(n);
}else {
int d = 0; //0和任何数的最大公约数都是本身
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
d = gcd(d,a[i + 1] - a[i]);
}
System.out.println(1 + (a[n] - a[1])/d);
}
}
private static int gcd(int a, int b) {
if(b == 0) {
return a;
}
return gcd(b,a%b);
}
}
X的因子链
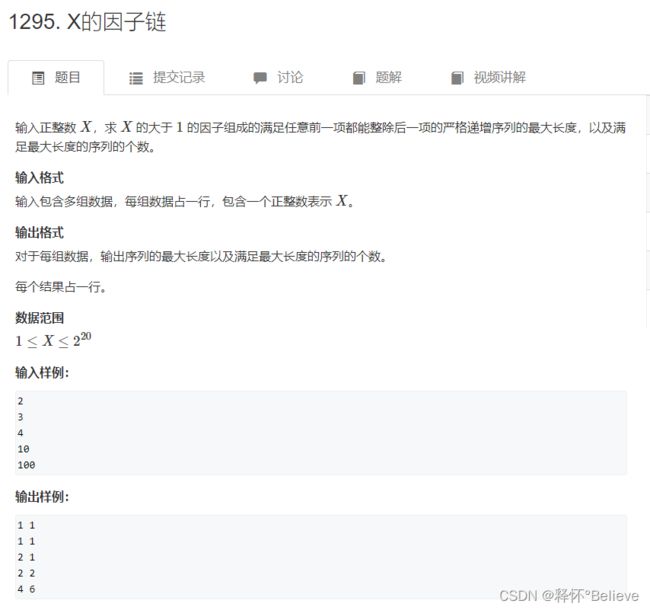
法1:dp(TLE)
dp[]记录最长条数,count[]记录有多少种方案
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
static Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
static PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
static int N = 100010;
static long ans = 0;
static int n = 0,m = 0;
static int[]dp = new int[N];
static int[]count = new int[N];
static int[]prime = new int[N];
static int[]a = new int[N];
static int x = 0,cnt = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
while(sc.hasNext()) {
x = sc.nextInt();
Arrays.fill(dp, 0);
Arrays.fill(prime, 0);
Arrays.fill(count, 0);
getpirme(x);
count[cnt] = 1;
for(int i = cnt; i >= 1; i--) {
dp[i] = 1;
for(int j = i + 1; j <= cnt; j++) {
if(prime[i] != 0 && prime[j] % prime[i] == 0) {
if(dp[i] < dp[j] + 1) {
dp[i] = dp[j] + 1;
count[i] = count[j];
} else if (dp[i] == dp[j] + 1) {
count[i] = count[i] + count[j];
}
}
}
}
int maxn = 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= cnt; i++) {
maxn = Math.max(maxn,dp[i]);
}
System.out.print(maxn + " ");
int tol = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= cnt; i++) {
if(dp[i] == maxn) {
tol += count[i];
}
}
System.out.println(tol);
}
}
private static void getpirme(int x) {
for(int i = 2; i <= x; i++) {
if(x % i == 0) {
prime[++cnt] = i;
// System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
}
聪明的燕姿(约数之和,dfs,难)
//import
#include五指山(exgcd())


前置知识:exgcd()
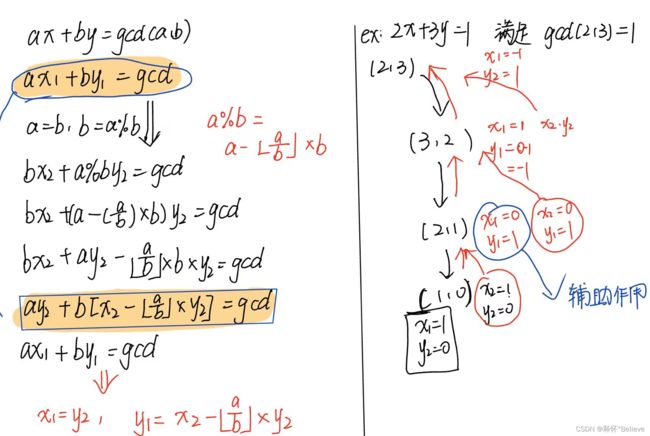
通解为x=x0+kb(gcd(a,b))(k∈Z)
其实就是x0+k(y的系数/gcd(a,b))
y的通解就是y=y0+k(x的系数/gcd(a,b))
本题让我们求x+bd = y+an =》-an+bd = y-x
让我们求x+bd = y+an ,整理得:-an+bd = y-x,只有为整数倍才会有解
如果有解可以利用扩展欧几里得求得-an+bd = gcd(n,d)中的a和b,然后将a和b扩大 (y-x)/gcd(n,d)倍
又因为他必须是逆时针,所以我们需要求得最小的x正整数解![]() ,
,![]()
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
static long x2;
static long y2;
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int T = input.nextInt();
while(T-- > 0){
int n = input.nextInt();
int d = input.nextInt();
int x = input.nextInt();
int y = input.nextInt();
int gcd = extGcd(n,d);
//x2 * n + y2 * d = gcd
if((y - x) % gcd != 0){
System.out.println("Impossible");
}else{
y2 *= (y-x) / gcd;
n /= gcd;
System.out.println((long)y2 + (long)Math.ceil(-1.0*y2/n)*(long)n);//求最小正整数解
// (x%k+k)%k k为b(gcd(a,b)
//System.out.println((y2 % n + n ) %n); 等价的作用
}
}
}
public static int extGcd(int a,int b){
if(b == 0){
x2 = 1;y2 = 0;
return a;
}else{
int gcd = extGcd(b,a%b);
long x1 = y2;
long y1 = x2 - y2 * (a / b);
x2 = x1;
y2 = y1;
return gcd;
}
}
}
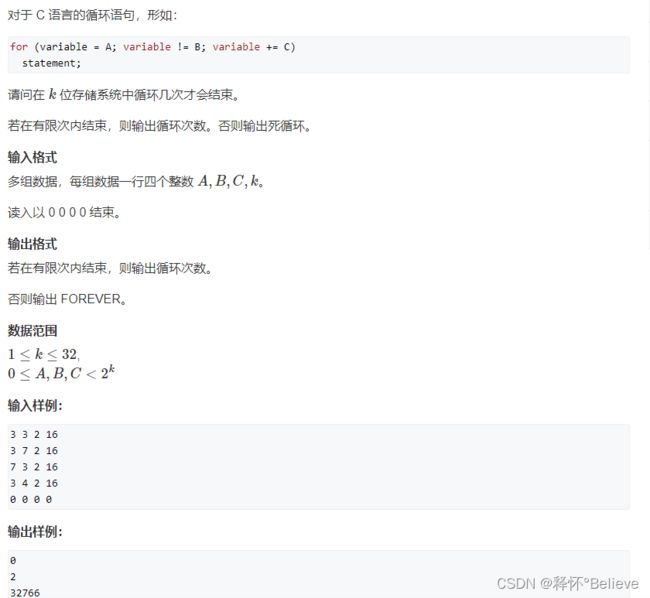
C 循环(exgcd())
思路:
比如1110111我们想要取出后3位,我们只需要mod2的2,因为3位最大是111位7,和十进制取出后几位原理差不多
k为存储的意思是保留最后k位
(A+XC)mod 2k=B时,循环结束
转换为A+XC-y倍的2的k次幂=B
xC - y2^k = B - A
此种形式可以用exgcd()求解,
当b-a不是gcd(c,2^k)的倍数时,无解
其他
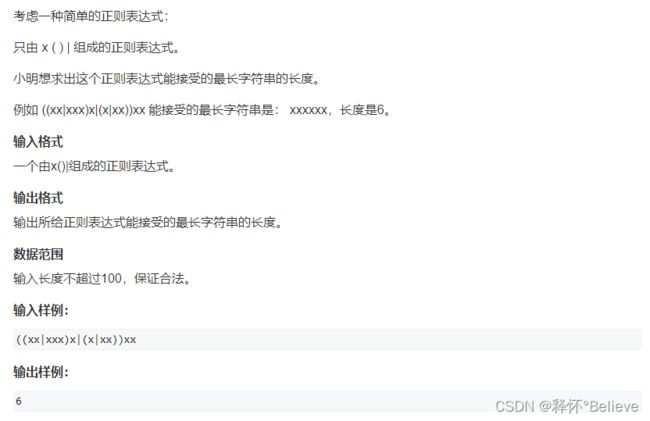
#include 正则问题(dfs)
正则表达式:
(1)|是或的意思,两个中选一个
(2)()优先算括号里面的
本题,对于(和|会影响字符串的拼接
每次碰到(和|就进行递归下一层,
时间复杂度:O(n),每个
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
static Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
static String str = "";
static int k = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
str = sc.nextLine().trim();
System.out.println(dfs());
}
private static int dfs() {
int ans = 0;
while(k < str.length()) {
char ch = str.charAt(k);
if(ch == '(') {
k++;
ans += dfs();
k++;
}else if(ch == '|') {
k++;
ans = Math.max(ans,dfs());
}else if(ch == ')') {
break;
}else {
k++;
ans++;
}
}
return ans;
}
}