PyTorch使用一维卷积对时间序列数据分类
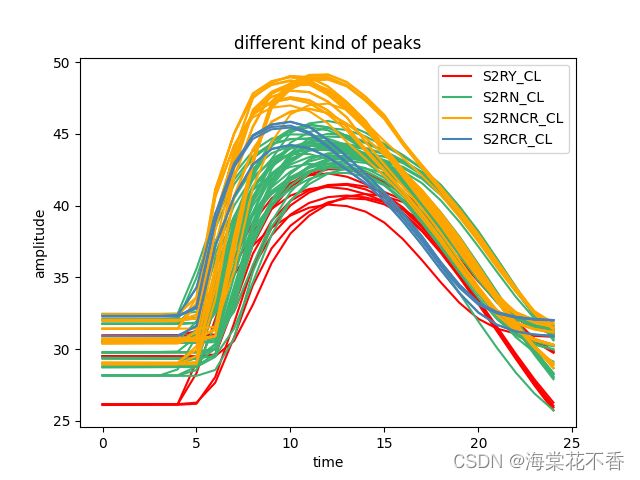
数据展示
时间序列数据也就是自变量是时间的一维数据,平时接触到的y= x, y = sinx等都是可以认为是时间序列数据。本次实验使用的是波形数据,可以认为不同形态的反射波形代表不同的类别。以下分别是两种类别的数据集,和四种类别的数据集,同一种颜色代表同一种类别。
模型搭建
采用PyTorch搭建网络模型,两层卷积层,卷积核大小为64,32。模型结构如下
由于pytorch的网络模型画网络结构不像tensorflow那么方便,需要转化为onnx模型,在用netron画出来,参考后面的源码。
源码
网络模型
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torch.utils.data import Dataset
class CNNnet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, *, inputLength = 80, kernelSize = 3, kindsOutput = 4):
super().__init__()
filterNum1 = 64
filterNum2 = 32
self.layer1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv1d(1, filterNum1, kernelSize), # inputLength - kernelSize + 1 = 80 - 3 + 1 = 78
nn.BatchNorm1d(filterNum1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool1d(kernelSize, stride = 1) # 78 - 3 + 1 = 76
)
self.layer2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv1d(filterNum1, filterNum2, kernelSize), # 76 - 3 + 1 = 74
nn.BatchNorm1d(filterNum2),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool1d(kernelSize, stride = 1) # 74 - 3 + 1 = 72
)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(0.2)
self.fc = nn.Linear(filterNum2 * (inputLength - 8), kindsOutput)
def forward(self,x):
x = x.to(torch.float32)
x = self.layer1(x)
x = self.layer2(x)
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
x = self.fc(x)
x = self.dropout(x)
return x
class DatasetOfDiv(Dataset):
def __init__(self, data_features, data_target):
self.len = len(data_features)
self.features = torch.from_numpy(data_features)
self.target = torch.from_numpy(data_target)
def __getitem__(self, index):
return self.features[index], self.target[index]
def __len__(self):
return self.len
请注意,这里的DatasetOfDiv是需要为自己的数据集,继承Dataset这个类来实现。
模型训练
def train(trainData, trainLabel, *, savePath='..\models\pytorch', modelName = 'model.pt', epochs = 100, batchSize = 4, classNum = 4):
trainFeatures, trainTarget, testFeatures, testTarget = datasetSplit(trainData, trainLabel)
print('trainFeatures shape:', trainFeatures.shape, '\ttestFeatures shape:', testFeatures.shape)
trainSet = DatasetOfDiv(trainFeatures, trainTarget)
trainLoader = DataLoader(dataset=trainSet, batch_size=batchSize, shuffle=True, drop_last=True)
model = CNNnet(inputLength=trainFeatures.shape[1], kindsOutput = classNum)
# criterion = nn.MSELoss()
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.001)
model.train()
start_time = time.time()
for epoch in range(epochs):
for seq, y_train in trainLoader:
# 每次更新参数前都梯度归零和初始化
# sampleSize = seq.shape[0]
optimizer.zero_grad()
# 注意这里要对样本进行reshape,转换成conv1d的(batch size, channel, series length)
# y_pred = model(seq.reshape(sampleSize, 1, -1))
y_pred = model(seq.reshape(batchSize, 1, -1))
y_train = y_train.long()
loss = criterion(y_pred, y_train)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
# compute test accuracy
_y_pred = model(torch.from_numpy(testFeatures).reshape(testFeatures.shape[0], 1, -1))
y_pred = torch.max(_y_pred, 1)[1]
numCorrect = (y_pred.data.numpy() == testTarget).astype(int).sum()
numOfTestSample = testTarget.size
accuracy = float(numCorrect)/numOfTestSample
print(f'Epoch: \t{epoch+1} \t Accuracy: {accuracy:.2f} \t Loss: {loss.item():.5f} \
\t NumOfTestSample:{numOfTestSample} \t numOfPredictCorrect:{numCorrect}'.replace(" ",""))
print(f'\nDuration: {time.time() - start_time:.0f} seconds')
# torch.save(model.state_dict(), savePath + '\\' + modelName)
# torch.save(model, savePath + '\\' + modelName)
torch.onnx.export(
model,
torch.randn(5, 1, trainFeatures.shape[1]),
savePath + '\\' + 'model.onnx',
export_params=True,
# opset_version=8,
)
return model
模型测试
def testModelEval(self, modelPath, trainData, trainLabel, *, classNum = 4):
model = CNNnet(inputLength = trainData.shape[1], kindsOutput = classNum)
model.load_state_dict(torch.load(modelPath))
model.eval()
testData = trainData
_eval_result = model(torch.from_numpy(testData).reshape(testData.shape[0], 1, -1))
eval_result = torch.max(_eval_result, 1)[1]
result = eval_result.data.numpy()
predErrNum = result.size - result[trainLabel==result].size
print('sum:', result.size, '\tpredErrNum:', predErrNum)
使用演示
def main():
filePath = '\your\data\path'
trainData, trainLabel = getYourData(filePath) #getYourData是你自己的数据解析函数
train(trainData,trainLabel)
...
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
enjoy~
有疑问评论区交流
参考文档
[深度应用]·使用一维卷积神经网络处理时间序列数据
CNN实现时间序列预测(PyTorch版)
积神经网络处理时间序列数据
PyTorch搭建CNN实现时间序列预测(风速预测)