Heap堆的升序排序
在heap堆中,大根堆是一种特殊的堆,它满足下列性质:对于任意一个非叶子节点i,其左右子节点的值均小于等于它本身的值。
在大根堆中,堆顶元素永远是值最大的元素,所以将堆顶元素不断取出来,就相当于对数组进行了从大到小的排序操作。
相比较于其他排序算法,使用大根堆进行数组排序的优点在于:
1:时间复杂度稳定为O(nlogn),空间复杂度仅为O(1),并且算法实现简洁、易于理解。
2:由于大根堆的特殊性质,堆排序还具有良好的局部性和稳定性,能够保持元素在排序前后的相对位置关系,不会改变具有相同值的元素之间的顺序。
下面用图片来梳理我们的思路
代码注解
首先我们先创建一个数组:
1: 首先我们将数组中的值建立成大根堆
2:首尾换位,向下调整成为循环
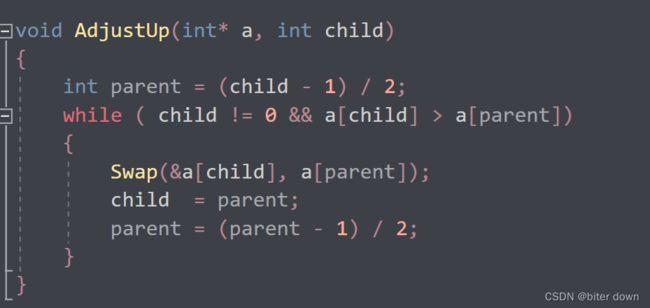
我们将数组中的值建立成大根堆的Adjustup函数的实现
Adjustup函数的实现的空间复杂度(3条消息) 堆的向下调整与向上调整的时间复杂度_biter down的博客-CSDN博客
我们将数组中的值建立成大根堆的Adjustup函数的实现
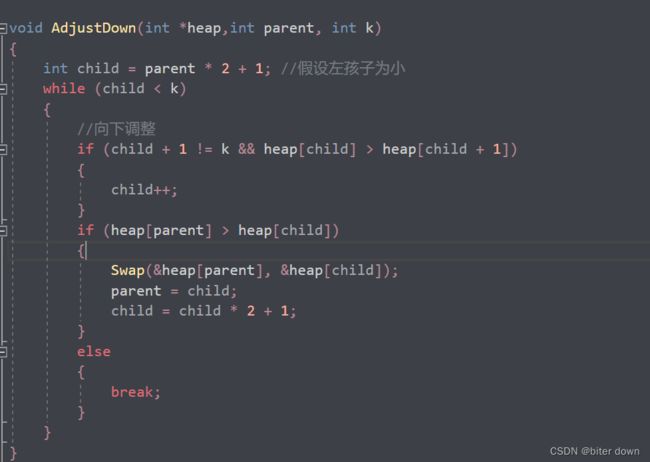
Adjustdown函数的实现的空间复杂度(3条消息) 堆的向下调整与向上调整的时间复杂度_biter down的博客-CSDN博客
源码提供参考:
#include
void Swap(int* p1, int* p2) {
int t = *p1;
*p1 = *p2;
*p2 = t;
}
void AdjustDown(int* a, int size) {
int parent = 0;
//将leftchild作为最大的孩子
int child = parent * 2 + 1;
while (child < size)
{
//当leftchild的值小于rightchlid时,child的值应该为较大值的右孩子
if (child + 1 < size && a[child + 1] > a[child])
{
child++;
}
Swap(&a[child], a[parent]);
parent = child;
child = child * 2 + 1;
}
}
void AdjustUp(int* a, int child)
{
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while ( child != 0 && a[child] > a[parent])
{
Swap(&a[child], a[parent]);
child = parent;
parent = (parent - 1) / 2;
}
}
//排升序,建大根堆
void HeapSort(int* a,int n)
{
//将数组中的值建立成大根堆
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i)
{
AdjustUp(a, i);
}
//将大根堆数组的元素升序
for(int i=n;i>0;i--)
{
Swap(&a[0], &a[i]); //首尾互换
AdjustDown(a, i); //向下调整
}
}
int main()
{
int arr[10] = { 2,1,5,7,6,8,0,9,4 }; //对数组进行大根堆排序
HeapSort(arr, sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]));
return 0;
}