回归预测 | MATLAB实现INFO-ELM向量加权算法优化极限学习机多输入单输出回归预测
回归预测 | MATLAB实现INFO-ELM向量加权算法优化极限学习机多输入单输出回归预测
目录
-
- 回归预测 | MATLAB实现INFO-ELM向量加权算法优化极限学习机多输入单输出回归预测
-
- 效果一览
- 基本介绍
- 程序设计
- 参考资料
效果一览
基本介绍
1.MATLAB实现INFO-ELM向量加权算法优化极限学习机多输入单输出回归预测;
2.输入7个特征,输出1个,即多输入单输出;
3.运行环境Matlab2018及以上,运行主程序main即可,其余为函数文件无需运行,所有程序放在一个文件夹,data为数据集;
4.INFO-ELM向量加权算法优化极限学习机权值和偏置,命令窗口输出RMSE、MAE、R2、MAPE等评价指标。
程序设计
- 完整程序和数据下载方式1(资源处直接下载):MATLAB实现INFO-ELM向量加权算法优化极限学习机多输入单输出回归预测
- 完整程序和数据下载方式2(订阅《ELM极限学习机》专栏,同时可阅读《ELM极限学习机》专栏收录的所有内容,数据订阅后私信我获取):MATLAB实现INFO-ELM向量加权算法优化极限学习机多输入单输出回归预测
- 完整程序和数据下载方式3(订阅《智能学习》专栏,同时获取《智能学习》专栏收录程序6份,数据订阅后私信我获取):MATLAB实现INFO-ELM向量加权算法优化极限学习机多输入单输出回归预测
%% 优化参数设置
Particles_no = 6; % 种群数量
Max_iter = 50; % 设定最大迭代次数
dim = hiddennum * inputnum + hiddennum; % 优化参数个数
lb = -1 * ones(1, dim); % 优化参数目标下限
ub = 1 * ones(1, dim); % 优化参数目标上限
%% 优化算法
fobj = @(x)fun(x, p_train, t_train, hiddennum);
[Best_pos,Best_score, curve] = INFO(Particles_no, Max_iter, lb, ub, dim, fobj);
%% 获取最优权值
w1 = Best_pos(1 : inputnum * hiddennum);
B1 = Best_pos(inputnum * hiddennum + 1 : inputnum * hiddennum + hiddennum);
IW = reshape(w1, hiddennum, inputnum);
B = reshape(B1, hiddennum, 1);
%% 网络训练
[IW, B, LW, TF, TYPE] = elmtrain(p_train, t_train, 'sig', 0, IW, B);
%% 网络预测
T_sim1 = elmpredict(p_train, IW, B, LW, TF, TYPE);
T_sim2 = elmpredict(p_test , IW, B, LW, TF, TYPE);
%% 均方根误差
error1 = sqrt(sum((T_sim1 - T_train).^2) ./ M);
error2 = sqrt(sum((T_sim2 - T_test ).^2) ./ N);
%% 绘图
figure
plot(1: M, T_train, 'r-*', 1: M, T_sim1, 'b-o', 'LineWidth', 1)
legend('真实值','预测值')
xlabel('预测样本')
ylabel('预测结果')
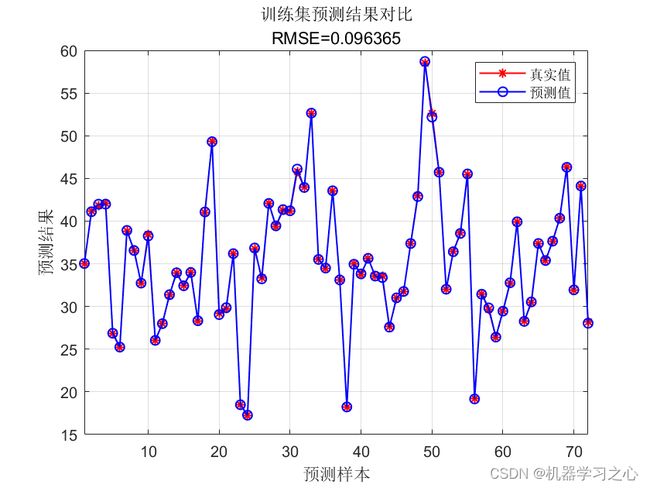
string = {'训练集预测结果对比'; ['RMSE=' num2str(error1)]};
title(string)
xlim([1, M])
grid
figure
plot(1: N, T_test, 'r-*', 1: N, T_sim2, 'b-o', 'LineWidth', 1)
legend('真实值','预测值')
xlabel('预测样本')
ylabel('预测结果')
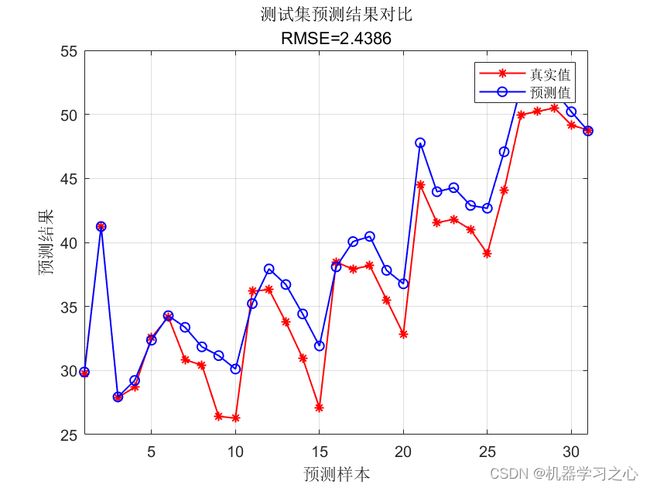
string = {'测试集预测结果对比';['RMSE=' num2str(error2)]};
title(string)
xlim([1, N])
grid
%% 适应度曲线
figure;
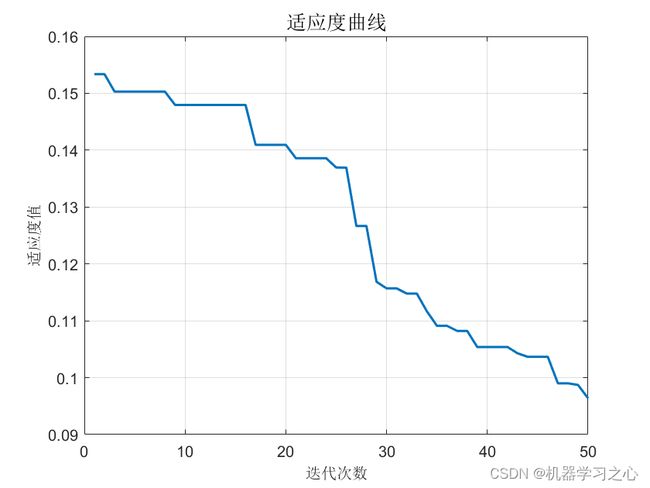
plot(1 : length(curve), curve, 'LineWidth', 1.5);
title('适应度曲线', 'FontSize', 13);
xlabel('迭代次数', 'FontSize', 10);
ylabel('适应度值', 'FontSize', 10);
grid
%% 相关指标计算
% R2
R1 = 1 - norm(T_train - T_sim1)^2 / norm(T_train - mean(T_train))^2;
R2 = 1 - norm(T_test - T_sim2)^2 / norm(T_test - mean(T_test ))^2;
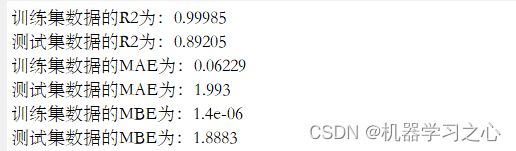
disp(['训练集数据的R2为:', num2str(R1)])
disp(['测试集数据的R2为:', num2str(R2)])
% MAE
mae1 = sum(abs(T_sim1 - T_train)) ./ M ;
mae2 = sum(abs(T_sim2 - T_test )) ./ N ;
disp(['训练集数据的MAE为:', num2str(mae1)])
disp(['测试集数据的MAE为:', num2str(mae2)])
% MBE
mbe1 = sum(T_sim1 - T_train) ./ M ;
mbe2 = sum(T_sim2 - T_test ) ./ N ;
disp(['训练集数据的MBE为:', num2str(mbe1)])
disp(['测试集数据的MBE为:', num2str(mbe2)])
%-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
function [Best_pos,Best_Cost,curve,avcurve]=INFO(pop,Max_iter,lb,ub,dim,fobj)
%% Initialization
Cost=zeros(pop,1);
M=zeros(pop,1);
X=initialization(pop,dim,ub,lb);
for i=1:pop
Cost(i) = fobj(X(i,:));
M(i)=Cost(i);
end
[~, ind]=sort(Cost);
Best_pos = X(ind(1),:);
Best_Cost = Cost(ind(1));
Worst_Cost = Cost(ind(end));
Worst_X = X(ind(end),:);
I=randi([2 5]);
Better_X=X(ind(I),:);
Better_Cost=Cost(ind(I));
%% Main Loop of INFO
for it=1:Max_iter
alpha=2*exp(-4*(it/Max_iter)); % Eqs. (5.1) & % Eq. (9.1)
M_Best=Best_Cost;
M_Better=Better_Cost;
M_Worst=Worst_Cost;
for i=1:pop
% Updating rule stage
del=2*rand*alpha-alpha; % Eq. (5)
sigm=2*rand*alpha-alpha; % Eq. (9)
% Select three random solution
A1=randperm(pop);
A1(A1==i)=[];
a=A1(1);b=A1(2);c=A1(3);
e=1e-25;
epsi=e*rand;
omg = max([M(a) M(b) M(c)]);
MM = [(M(a)-M(b)) (M(a)-M(c)) (M(b)-M(c))];
W(1) = cos(MM(1)+pi)*exp(-(MM(1))/omg); % Eq. (4.2)
W(2) = cos(MM(2)+pi)*exp(-(MM(2))/omg); % Eq. (4.3)
W(3)= cos(MM(3)+pi)*exp(-(MM(3))/omg); % Eq. (4.4)
Wt = sum(W);
WM1 = del.*(W(1).*(X(a,:)-X(b,:))+W(2).*(X(a,:)-X(c,:))+ ... % Eq. (4.1)
W(3).*(X(b,:)-X(c,:)))/(Wt+1)+epsi;
omg = max([M_Best M_Better M_Worst]);
MM = [(M_Best-M_Better) (M_Best-M_Better) (M_Better-M_Worst)];
W(1) = cos(MM(1)+pi)*exp(-MM(1)/omg); % Eq. (4.7)
W(2) = cos(MM(2)+pi)*exp(-MM(2)/omg); % Eq. (4.8)
W(3) = cos(MM(3)+pi)*exp(-MM(3)/omg); % Eq. (4.9)
Wt = sum(W);
WM2 = del.*(W(1).*(Best_pos-Better_X)+W(2).*(Best_pos-Worst_X)+ ... % Eq. (4.6)
W(3).*(Better_X-Worst_X))/(Wt+1)+epsi;
% Determine MeanRule
r = unifrnd(0.1,0.5);
MeanRule = r.*WM1+(1-r).*WM2; % Eq. (4)
if rand<0.5
z1 = X(i,:)+sigm.*(rand.*MeanRule)+randn.*(Best_pos-X(a,:))/(M_Best-M(a)+1);
z2 = Best_pos+sigm.*(rand.*MeanRule)+randn.*(X(a,:)-X(b,:))/(M(a)-M(b)+1);
else % Eq. (8)
z1 = X(a,:)+sigm.*(rand.*MeanRule)+randn.*(X(b,:)-X(c,:))/(M(b)-M(c)+1);
z2 = Better_X+sigm.*(rand.*MeanRule)+randn.*(X(a,:)-X(b,:))/(M(a)-M(b)+1);
end
% Vector combining stage
u=zeros(1,dim);
for j=1:dim
mu = 0.05*randn;
if rand <0.5
if rand<0.5
u(j) = z1(j) + mu*abs(z1(j)-z2(j)); % Eq. (10.1)
else
u(j) = z2(j) + mu*abs(z1(j)-z2(j)); % Eq. (10.2)
end
else
u(j) = X(i,j); % Eq. (10.3)
end
end
% Local search stage
if rand<0.5
L=rand<0.5;v1=(1-L)*2*(rand)+L;v2=rand.*L+(1-L); % Eqs. (11.5) & % Eq. (11.6)
Xavg=(X(a,:)+X(b,:)+X(c,:))/3; % Eq. (11.4)
phi=rand;
Xrnd = phi.*(Xavg)+(1-phi)*(phi.*Better_X+(1-phi).*Best_pos); % Eq. (11.3)
Randn = L.*randn(1,dim)+(1-L).*randn;
if rand<0.5
u = Best_pos + Randn.*(MeanRule+randn.*(Best_pos-X(a,:))); % Eq. (11.1)
else
u = Xrnd + Randn.*(MeanRule+randn.*(v1*Best_pos-v2*Xrnd)); % Eq. (11.2)
end
end
% Check if new solution go outside the search space and bring them back
New_X= BC(u,lb,ub);
New_Cost = fobj(New_X);
if New_Cost<Cost(i)
X(i,:)=New_X;
Cost(i)=New_Cost;
M(i)=Cost(i);
if Cost(i)<Best_Cost
Best_pos=X(i,:);
Best_Cost = Cost(i);
end
end
end
% Determine the worst solution
[~, ind]=sort(Cost);
Worst_X=X(ind(end),:);
Worst_Cost=Cost(ind(end));
% Determine the better solution
I=randi([2 5]);
Better_X=X(ind(I),:);
Better_Cost=Cost(ind(I));
% Update Convergence_curve
curve(it)=Best_Cost;
avcurve(it)=sum(curve)/length(curve);
% Show Iteration Information
%disp(['Iteration ' num2str(it) ',: Best Cost = ' num2str(Best_Cost)]);
end
end
function X = BC(X,lb,ub)
Flag4ub=X>ub;
Flag4lb=X<lb;
X=(X.*(~(Flag4ub+Flag4lb)))+ub.*Flag4ub+lb.*Flag4lb;
end
参考资料
[1] https://blog.csdn.net/kjm13182345320/article/details/129215161
[2] https://blog.csdn.net/kjm13182345320/article/details/128105718