Delphi Web Server 流程分析
通过向导 "Web Server Application" (选择 "Stand-alone GUI Application") 创建一个 WebServer Demo。
主单元代码:
......
private
FServer: TIdHTTPWebBrokerBridge;
procedure StartServer;
.............
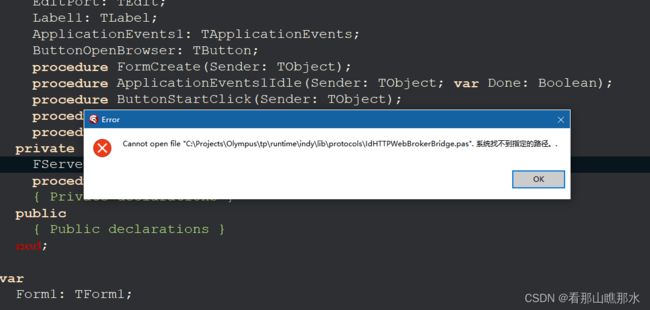
Delphi的网络组件是基于INDY的,这里的FServer是TIdHTTPWebBrokerBridge,就是WebServer了。是什么呢?
直接"Ctrl+Click"浏览代码,直接报错:
哎........
手动打开单元 "IdHTTPWebBrokerBridge.pas"(路径:"D:\Program Files (x86)\Embarcadero\Studio\22.0\source\Indy10\Protocols"):
TIdHTTPWebBrokerBridge = class(TIdCustomHTTPServer),
先看看继承:
TIdHTTPWebBrokerBridge->TIdCustomHTTPServer->TIdCustomTCPServer->TIdComponent...
是从TCPServer来的。
再看主单元的StartServer方法,是如何启动Server的:
procedure TForm1.StartServer;
begin
if not FServer.Active then
begin
FServer.Bindings.Clear;
FServer.DefaultPort := StrToInt(EditPort.Text);
FServer.Active := True;
end;
end;
设置Active=True启动,(这里可以"Ctrl+Click" "Active"属性),直接到"IdCustomTCPServer.pas"的 " TIdCustomTCPServer"类,看代码:
SetActive -> Startup():
procedure TIdCustomTCPServer.Startup;
var
LScheduler: TIdScheduler;
LIOHandler: TIdServerIOHandler;
{$IFDEF CanCreateTwoBindings}
LBinding: TIdSocketHandle;
{$ENDIF}
begin
// Set up bindings
if Bindings.Count = 0 then begin
// Binding object that supports both IPv4 and IPv6 on the same socket...
{$IFDEF CanCreateTwoBindings}LBinding := {$ENDIF}Bindings.Add; // IPv4 or IPv6 by default
{$IFDEF CanCreateTwoBindings}
case LBinding.IPVersion of
Id_IPv4: begin
if GStack.SupportsIPv6 then begin
Bindings.Add.IPVersion := Id_IPv6;
end;
end;
Id_IPv6: begin
if GStack.SupportsIPv4 then begin
Bindings.Add.IPVersion := Id_IPv4;
end;
end;
end;
{$ENDIF}
end;
// Setup IOHandler
LIOHandler := FIOHandler;
if not Assigned(LIOHandler) then begin
LIOHandler := TIdServerIOHandlerStack.Create(Self);
SetIOHandler(LIOHandler);
FImplicitIOHandler := True;
end;
LIOHandler.Init;
// Set up scheduler
LScheduler := FScheduler;
if not Assigned(FScheduler) then begin
LScheduler := TIdSchedulerOfThreadDefault.Create(Self);
SetScheduler(LScheduler);
FImplicitScheduler := True;
// Useful in debugging and for thread names
LScheduler.Name := Name + 'Scheduler'; {do not localize}
end;
LScheduler.Init;
StartListening;
end;
这里添加了ip6支持,然后设置IO句柄(用于https,加密,压缩等),然后是设置Scheduler(用于设置线程或纤程)。然后开始监听端口StartListening(),StartListening()主要是检查监听线程数量和创建监听线程,默认监听线程数量=15:
const
IdListenQueueDefault = 15;
procedure TIdCustomTCPServer.InitComponent;
..........
FListenQueue := IdListenQueueDefault;
..................
这个数量太小了,现在的一般台式机都可以轻松支持200以上,所以建议开始时设置,
procedure TForm1.FormCreate(Sender: TObject);
begin
FServer := TIdHTTPWebBrokerBridge.Create(Self);
FServer.ListenQueue := 200;
end;
StartListening():
procedure TIdCustomTCPServer.StartListening;
var
LListenerThreads: TIdListenerList;
LListenerThread: TIdListenerThread;
I: Integer;
LBinding: TIdSocketHandle;
LName: string;
begin
LListenerThreads := FListenerThreads.LockList;
try
// Set up any sockets that are not already listening
I := LListenerThreads.Count;
try
while I < Bindings.Count do begin
LBinding := Bindings[I];
LBinding.AllocateSocket;
// do not overwrite if the default. This allows ReuseSocket to be set per binding
if FReuseSocket <> rsOSDependent then begin
LBinding.ReuseSocket := FReuseSocket;
end;
DoBeforeBind(LBinding);
LBinding.Bind;
LBinding.UseNagle := FUseNagle;
Inc(I);
end;
except
Dec(I); // the one that failed doesn't need to be closed
while I >= 0 do begin
Bindings[I].CloseSocket;
Dec(I);
end;
raise;
end;
if I > LListenerThreads.Count then begin
DoAfterBind;
end;
// Set up any threads that are not already running
LName := Name;
if LName = '' then begin
LName := 'IdCustomTCPServer'; {do not localize}
end;
for I := LListenerThreads.Count to Bindings.Count - 1 do
begin
LBinding := Bindings[I];
LBinding.Listen(FListenQueue);
LListenerThread := TIdListenerThread.Create(Self, LBinding);
try
LListenerThread.Name := LName + ' Listener #' + IntToStr(I + 1); {do not localize}
LListenerThread.OnBeforeRun := DoBeforeListenerRun;
//http://www.midnightbeach.com/jon/pubs/2002/BorCon.London/Sidebar.3.html
LListenerThread.Priority := tpListener;
LListenerThreads.Add(LListenerThread);
except
LBinding.CloseSocket;
FreeAndNil(LListenerThread);
raise;
end;
LListenerThread.Start;
end;
finally
FListenerThreads.UnlockList;
end;
end;
设置完线程,然后启动线程,就开始端口监听了,工作就转到了监听线程TIdListenerThread:
TIdListenerThread = class(TIdThread)
父类TIdThread处理一般情况,子类只要实现Run()抽象方法:
procedure TIdListenerThread.Run;
var
LContext: TIdServerContext;
LIOHandler: TIdIOHandler;
LPeer: TIdTCPConnection;
LYarn: TIdYarn;
begin
Assert(Server<>nil);
Assert(Server.IOHandler<>nil);
LContext := nil;
LPeer := nil;
LYarn := nil;
try
// GetYarn can raise exceptions
LYarn := Server.Scheduler.AcquireYarn;
// the user to reject connections before they are accepted. Somehow
// expose an event here for the user to decide with...
LIOHandler := Server.IOHandler.Accept(Binding, Self, LYarn);
if LIOHandler = nil then begin
// Listening has finished
Stop;
Abort;
end else begin
// We have accepted the connection and need to handle it
LPeer := TIdTCPConnection.Create(nil);
{$IFDEF USE_OBJECT_ARC}
// under ARC, the TIdTCPConnection.IOHandler property is a weak reference.
// TIdServerIOHandler.Accept() returns an IOHandler with no Owner assigned,
// so lets make the TIdTCPConnection become the Owner in order to keep the
// IOHandler alive when this method exits.
//
//
LPeer.InsertComponent(LIOHandler);
{$ENDIF}
LPeer.IOHandler := LIOHandler;
LPeer.ManagedIOHandler := True;
end;
// LastRcvTimeStamp := Now; // Added for session timeout support
// ProcessingTimeout := False;
// Check MaxConnections
if (Server.MaxConnections > 0) and (not Server.Contexts.IsCountLessThan(Server.MaxConnections)) then begin
FServer.DoMaxConnectionsExceeded(LIOHandler);
LPeer.Disconnect;
Abort;
end;
// Create and init context
LContext := Server.FContextClass.Create(LPeer, LYarn, Server.Contexts);
LContext.FServer := Server;
// We set these instead of having the context call them directly
// because they are protected methods. Also its good to keep
// Context indepent of the server as well.
LContext.OnBeforeRun := Server.ContextConnected;
LContext.OnRun := Server.DoExecute;
LContext.OnAfterRun := Server.ContextDisconnected;
LContext.OnException := Server.DoException;
//
Server.ContextCreated(LContext);
//
// If all ok, lets start the yarn
Server.Scheduler.StartYarn(LYarn, LContext);
except
on E: Exception do begin
// RLebeau 1/11/07: TIdContext owns the Peer by default so
// take away ownership here so the Peer is not freed twice
if LContext <> nil then begin
TIdServerContextAccess(LContext).FOwnsConnection := False;
end;
FreeAndNil(LContext);
FreeAndNil(LPeer);
// Must terminate - likely has not started yet
if LYarn <> nil then begin
Server.Scheduler.TerminateYarn(LYarn);
end;
// EAbort is used to kick out above and destroy yarns and other, but
// we dont want to show the user
// To ignore EIdConnClosedGracefully, for instance...
if not (E is EAbort) then begin
Server.DoListenException(Self, E);
end;
end;
end;
end;
.......
// Create and init context
LContext := Server.FContextClass.Create(LPeer, LYarn, Server.Contexts);
LContext.FServer := Server;
// We set these instead of having the context call them directly
// because they are protected methods. Also its good to keep
// Context indepent of the server as well.
LContext.OnBeforeRun := Server.ContextConnected;
LContext.OnRun := Server.DoExecute;
LContext.OnAfterRun := Server.ContextDisconnected;
LContext.OnException := Server.DoException;
//
Server.ContextCreated(LContext);
//
// If all ok, lets start the yarn
Server.Scheduler.StartYarn(LYarn, LContext);
通过上下文的事件关联到了Server的执行方法。主要是LContext.OnRun := Server.DoExecute;
TIdCustomTCPServer.DoExecute 没做什么事,就检查了tcpConnected,具体工作在子类。
TIdCustomHTTPServer.DoExecute,这个方法是个复杂的处理(代码太长了,不贴了),主要是循环处理各种HTTP 方法,解析请求头,判断请求类别,归类参数等等,然后调用DoCommandGet(子类通过此方法来具体处理),最后给客户端返回响应Response,直到连接断开。
我们的子类是TIdHTTPWebBrokerBridge,看看其DoCommandGet():
procedure TIdHTTPWebBrokerBridge.DoCommandGet(AThread: TIdContext;
ARequestInfo: TIdHTTPRequestInfo; AResponseInfo: TIdHTTPResponseInfo);
begin
if FWebModuleClass <> nil then begin
// FWebModuleClass, RegisterWebModuleClass supported for backward compatability
RunWebModuleClass(AThread, ARequestInfo, AResponseInfo)
end else
begin
{$IFDEF HAS_CLASSVARS}
TIdHTTPWebBrokerBridgeRequestHandler.FWebRequestHandler.Run(AThread, ARequestInfo, AResponseInfo);
{$ELSE}
IndyWebRequestHandler.Run(AThread, ARequestInfo, AResponseInfo);
{$ENDIF}
end;
end;
开始时,FWebModuleClass = nil;
所以执行的是:
TIdHTTPWebBrokerBridgeRequestHandler.FWebRequestHandler.Run(AThread, ARequestInfo, AResponseInfo);
type
TIdHTTPWebBrokerBridgeRequestHandler = class(TWebRequestHandler)
{$IFDEF HAS_CLASSVARS}
private
class var FWebRequestHandler: TIdHTTPWebBrokerBridgeRequestHandler;
{$ENDIF}
public
constructor Create(AOwner: TComponent); override;
{$IFDEF HAS_CLASSVARS}
{$IFDEF HAS_CLASSDESTRUCTOR}
class destructor Destroy;
{$ENDIF}
{$ENDIF}
destructor Destroy; override;
procedure Run(AThread: TIdContext; ARequestInfo: TIdHTTPRequestInfo; AResponseInfo: TIdHTTPResponseInfo);
end;
这个辅助类是从TWebRequestHandler继承的,其类变量FWebRequestHandler的赋值是通过独立局部函数:
function IdHTTPWebBrokerBridgeRequestHandler: TWebRequestHandler;
begin
{$IFDEF HAS_CLASSVARS}
if not Assigned(TIdHTTPWebBrokerBridgeRequestHandler.FWebRequestHandler) then
TIdHTTPWebBrokerBridgeRequestHandler.FWebRequestHandler := TIdHTTPWebBrokerBridgeRequestHandler.Create(nil);
Result := TIdHTTPWebBrokerBridgeRequestHandler.FWebRequestHandler;
{$ELSE}
if not Assigned(IndyWebRequestHandler) then
IndyWebRequestHandler := TIdHTTPWebBrokerBridgeRequestHandler.Create(nil);
Result := IndyWebRequestHandler;
{$ENDIF}
end;
一般的运用都有编译开关HAS_CLASSVARS,所以执行的是:
if not Assigned(TIdHTTPWebBrokerBridgeRequestHandler.FWebRequestHandler) then
TIdHTTPWebBrokerBridgeRequestHandler.FWebRequestHandler := TIdHTTPWebBrokerBridgeRequestHandler.Create(nil);
Result := TIdHTTPWebBrokerBridgeRequestHandler.FWebRequestHandler;
此函数是在单元的初始化调用,并赋值给了WebReq单元的全局变量WebRequestHandlerProc。
initialization
WebReq.WebRequestHandlerProc := IdHTTPWebBrokerBridgeRequestHandler;
所以TIdHTTPWebBrokerBridgeRequestHandler.FWebRequestHandler.Run()就相当于
TIdHTTPWebBrokerBridgeRequestHandler.Run()
这里的类变量FWebRequestHandler是为了实现单例模式。
通过如此处理,就把TIdHTTPWebBrokerBridge.DoCommandGet()转到了TIdHTTPWebBrokerBridgeRequestHandler.Run()来处理,这里用了桥接模式。
也就是从TIdCustomHTTPServer转接到了TWebRequestHandler。
注:
TIdHTTPWebBrokerBridge->TIdCustomHTTPServer
TIdHTTPWebBrokerBridgeRequestHandler->TWebRequestHandler
具体看看TIdHTTPWebBrokerBridgeRequestHandler.Run():
procedure TIdHTTPWebBrokerBridgeRequestHandler.Run(AThread: TIdContext; ARequestInfo: TIdHTTPRequestInfo; AResponseInfo: TIdHTTPResponseInfo);
var
LRequest: TIdHTTPAppRequest;
LResponse: TIdHTTPAppResponse;
begin
try
LRequest := TIdHTTPAppRequest.Create(AThread, ARequestInfo, AResponseInfo);
try
LResponse := TIdHTTPAppResponse.Create(LRequest, AThread, ARequestInfo, AResponseInfo);
try
// WebBroker will free it and we cannot change this behaviour
AResponseInfo.FreeContentStream := False;
HandleRequest(LRequest, LResponse);
finally
FreeAndNil(LResponse);
end;
finally
FreeAndNil(LRequest);
end;
except
// Let Indy handle this exception
raise;
end;
end;
这里通过监听线程获得的XXXInfo参数构造了Request和Response,并调用了父类的HandleRequest(Web.WebReq.pas):
function TWebRequestHandler.HandleRequest(Request: TWebRequest;
Response: TWebResponse): Boolean;
var
I: Integer;
LWebModule: TComponent;
LWebAppServices: IWebAppServices;
LGetWebAppServices: IGetWebAppServices;
LComponent: TComponent;
begin
Result := False;
LWebModule := ActivateWebModules;
if Assigned(LWebModule) then
try
try
if Supports(IInterface(LWebModule), IGetWebAppServices, LGetWebAppServices) then
LWebAppServices := LGetWebAppServices.GetWebAppServices;
if LWebAppServices = nil then
for I := 0 to LWebModule.ComponentCount - 1 do
begin
LComponent := LWebModule.Components[I];
if Supports(LComponent, IWebAppServices, LWebAppServices) then
if LWebAppServices.Active then
break
else
LWebAppServices := nil;
end;
if LWebAppServices = nil then
LWebAppServices := TDefaultWebAppServices.Create;
LWebAppServices.InitContext(LWebModule, Request, Response);
try
try
Result := LWebAppServices.HandleRequest;
except
ApplicationHandleException(LWebAppServices.ExceptionHandler);
end;
finally
LWebAppServices.FinishContext;
end;
if Result and not Response.Sent then
Response.SendResponse;
except
ApplicationHandleException(LWebAppServices.ExceptionHandler);
end;
finally
DeactivateWebModules(LWebModule);
end;
end;
第一步:
LWebModule := ActivateWebModules;
这个是获取当前活动的Modules。
题外话:Delphi的WebBroker技术经过了多年的发展,随着大环境的发展和变化,其实现方式也不断扩展和进步。系统维护一个Module Pools,单有一个新的客户端请求Request时,就分配一个Modules。
文档:
TWebRequestHandler maintains the Web modules in an application and creates request and response objects when the application receives HTTP request messages.
TWebRequestHandler keeps a pool of active Web modules. In response to a request from the application, TWebRequestHandler creates a request object and assigns it to one of the active Web modules
ActivateWebModules()代码:
function TWebRequestHandler.ActivateWebModules: TComponent;
begin
if (FMaxConnections > 0) and (FAddingActiveModules >= FMaxConnections) then
raise EWebBrokerException.CreateRes(@sTooManyActiveConnections);
FCriticalSection.Enter;
try
FAddingActiveModules := FActiveWebModules.Count + 1;
try
if (FMaxConnections > 0) and (FActiveWebModules.Count >= FMaxConnections) then
raise EWebBrokerException.CreateRes(@sTooManyActiveConnections);
if FInactiveWebModules.Count > 0 then
begin
Result := FInactiveWebModules[0];
FInactiveWebModules.Extract(Result);
FActiveWebModules.Add(Result);
end
else
begin
if WebModuleClass <> nil then
begin
Result := WebModuleClass.Create(nil);
FActiveWebModules.Add(Result);
end
else
raise EWebBrokerException.CreateRes(@sNoDataModulesRegistered);
end;
finally
FAddingActiveModules := 0;
end;
finally
FCriticalSection.Leave;
end;
end;
Module的最大数量=MaxConnections。
这里的WebModuleClass,可以是TWebModule类,如果是旧项目升级,也可以是TDataMudule+TWebDispatcher, DEMO里WebModule单元的全局变量:
var
WebModuleClass: TComponentClass = TWebModule1;
确定了这个WebModuleClass的类型,所以这里是传类别,不是实例。
WebModuleClass,("if WebModuleClass <> nil then"),这个属性的赋值,我们没有明显的看到在哪里对FWebModuleClass进行赋值,实际这个属性是在外部进行赋值的,查看Demo的项目代码:
program WebServerTest;
{$APPTYPE GUI}
uses
Vcl.Forms,
Web.WebReq,
IdHTTPWebBrokerBridge,
FormUnit1 in 'FormUnit1.pas' {Form1},
WebModuleUnit1 in 'WebModuleUnit1.pas' {WebModule1: TWebModule};
{$R *.res}
begin
if WebRequestHandler <> nil then
WebRequestHandler.WebModuleClass := WebModuleClass;
Application.Initialize;
Application.CreateForm(TForm1, Form1);
Application.Run;
end. if WebRequestHandler <> nil then
WebRequestHandler.WebModuleClass := WebModuleClass;
这里的WebRequestHandler是个“变量型函数”,定义在Web.WebReq.pas:
function WebRequestHandler: TWebRequestHandler;
..............
function WebRequestHandler: TWebRequestHandler;
begin
if Assigned(WebRequestHandlerProc) then
Result := WebRequestHandlerProc
else
Result := nil;
end;
梳理下:
首先IdHTTPWebBrokerBridge.pas的初始化部分:
initialization
WebReq.WebRequestHandlerProc := IdHTTPWebBrokerBridgeRequestHandler;
WebReq.pas声明函数指针WebRequestHandlerProc:
var
WebRequestHandlerProc: function: TWebRequestHandler = nil;
使得WebReq单元的WebRequestHandlerProc函数指针指向IdHTTPWebBrokerBridgeRequestHandler(),
执行 if WebRequestHandler <> nil then,调用了function WebRequestHandler: TWebRequestHandler,然后调用IdHTTPWebBrokerBridgeRequestHandler(),获得了TWebRequestHandler的实例,然后设置此实例的WebModuleClasss属性值:
WebRequestHandler.WebModuleClass := WebModuleClass;
此实例间接保存在全局函数指针WebRequestHandlerProc。
第二步:
判断WebModuleClass本身是否支持IGetWebAppServices,如果不支持,就检查WebModuleClass里的组件是否支持IWebAppServices,比如前面说的TDataMudule+TWebDispatcher,就通过TWebDispatcher获得。
没有组件支持IWebAppServices,就进行下一步,直接创建了默认的WebServices:
LWebAppServices := TDefaultWebAppServices.Create;
注: 我们可以试试,如果拖一个TWebDispatcher到TWebModule界面,就提示错误信息:“TWebDispatcher”组件只能添加到TDataModule或TForm,服务器只能有一个WebDispatcher,文档里也强调了,服务器只能有一个TWebModule类,这个是强制要求。
获取LWebAppServices后,初始化LWebAppServices的上下文:
LWebAppServices.InitContext(LWebModule, Request, Response);
然后调用LWebAppServices.HandleRequest,这样就到了真正处理Service的地方了。
这里我们看看TDefaultWebAppServices.HandleRequest(Web.HTTPApp.pas):
function TDefaultWebAppServices.HandleRequest: Boolean;
begin
Result := InvokeDispatcher;
end;
function TDefaultWebAppServices.InvokeDispatcher: Boolean;
begin
if RequestHandler <> nil then
begin
Result := RequestHandler.HandleRequest(Request, Response);
end
else
raise EWebBrokerException.CreateRes(@sNoDispatcherComponent);
end;
function TDefaultWebAppServices.GetRequestHandler: IWebRequestHandler;
begin
if FRequestHandler = nil then
FRequestHandler := FindRequestHandler;
Result := FRequestHandler;
end;
function TDefaultWebAppServices.FindRequestHandler: IWebRequestHandler;
var
Component: TComponent;
begin
Result := nil;
Component := FindWebDispatcher;
if Component <> nil then
if not Supports(Component, IWebRequestHandler, Result) then
Assert(False, 'Expect support for IWebRequestHandler'); { do not localize }
end;
function TDefaultWebAppServices.FindWebDispatcher: TComponent;
var
J: Integer;
begin
Result := nil;
if WebModule is TCustomWebDispatcher then
Result := WebModule
else
for J := 0 to WebModule.ComponentCount - 1 do
if WebModule.Components[J] is TCustomWebDispatcher then
begin
Result := WebModule.Components[J];
break;
end;
end;
在InvokeDispatcher()方法里,接口RequestHandler(类型为IWebRequestHandler)是通过GetRequestHandler()获得,注意GetRequestHandler()的实现,FRequestHandler是个单例变量。
通过FindWebDispatcher()方法,最终找到实现了IWebRequestHandler接口的组件,也就是TWebModule或者TDataModule里的组件TWebDispatcher。
TWebModule和TWebDispatcher都是TCustomWebDispatcher的子类。
通过RequestHandler.HandleRequest(Request, Response)转到TCustomWebDispatcher.HandleRequest():
function TCustomWebDispatcher.HandleRequest(
Request: TWebRequest; Response: TWebResponse): Boolean;
begin
FRequest := Request;
FResponse := Response;
Result := DispatchAction(Request, Response);
end;
到这里,我们看到了"Action"字眼,爬山涉水的,露出了曙光。。。
瞧瞧DispatchAction():
function TCustomWebDispatcher.DispatchAction(Request: TWebRequest;
Response: TWebResponse): Boolean;
var
I: Integer;
Action, Default: TWebActionItem;
Dispatch: IWebDispatch;
begin
FRequest := Request;
FResponse := Response;
I := 0;
Default := nil;
if Response.Sent then
begin
Result := True;
{ Note that WebSnapSvr enabled apps have no way to mark response as sent }
Exit;
end;
Result := DoBeforeDispatch(Request, Response) or Response.Sent;
while not Result and (I < FActions.Count) do
begin
Action := FActions[I];
Result := Action.DispatchAction(Request, Response, False);
if Action.Default then Default := Action;
Inc(I);
end;
// Dispatch to self registering components
I := 0;
while not Result and (I < FDispatchList.Count) do
begin
if Supports(IInterface(FDispatchList.Items[I]), IWebDispatch, Dispatch) then
begin
Result := DispatchHandler(Self, Dispatch,
Request, Response, False);
end;
Inc(I);
end;
if not Result and Assigned(Default) then
Result := Default.DispatchAction(Request, Response, True);
if Result and not Response.Sent then
Result := DoAfterDispatch(Request, Response);
end;
用户可以在TWebModule里添加动作,就是熟悉的Route->Action的那个"Action"。
首先判断本次会话是否已经完成,如代码:
if Response.Sent then
begin
Result := True;
{ Note that WebSnapSvr enabled apps have no way to mark response as sent }
Exit;
end;
是否已经发送完Response;
Result := DoBeforeDispatch(Request, Response) or Response.Sent;
注意这一行代码!!!这里可以让我们有机会插入请求处理过程及结果。嗯,我们可以在这里"截胡"。
DoBeforeDispatch()调用OnBeforeDispatch
procedure TWebModule1.WebModuleBeforeDispatch(Sender: TObject; Request: TWebRequest;
Response: TWebResponse; var Handled: Boolean);
begin
//可以预处理或者完全处理,
//Handled := True会中段后续的处理
//调用Response.Send(),会中段后续的处理
end;
如果前面没有中断处理,则会继续处理后续的"Action",如果有的话。
到这里流程就基本明白了,如何从获取用户的请求,到我们在Server定制的功能。