Householder transformation + QL to calculate eigenValue and eigenVectors of Hertian Matrix, cpu code
化Hertinan matrix eigen problem into a real symmetric matrix eigen problem:
原理:
与matlab的结果进行对比:
A=[ ...
( 3.0 + 0.0*j) (-2.0 -2.0*j) (-0.9 -0.9*j) (-0.5 -0.5*j); ...
(-2.0 + 2.0*j) ( 4.0 + 0.0*j) ( 1.0 + 1.0*j) (-0.7 -0.5*j); ...
(-0.9 + 0.9*j) ( 1.0 -1.0*j) (-1.0 + 0.0*j) ( 0.1 + 0.1*j); ...
(-0.5 + 0.5*j) (-0.7 + 0.5*j) ( 0.1 -0.1*j) ( 1.0 + 0.0*j); ...
]
[V D]=eig(A)#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
struct float2 {
float x;
float y;
};
typedef struct float2 float2;
void print_matrix(float* A, int M, int N, int lda);
void print_matrix_complex(float2* A, int M, int N, int lda);
void print_vector(float* A, int N);
/
void real_neimag_real_imag_fill(float2* A_h, int N, int lda, float* S, int n, int lds);
float max(float x, float y);
void swap(float& x, float& y);
void tred2(float* V, float* d, float* e, int n, int ldv);
void tql2(float* V, float* d, float* e, int n, int ldv);
void eigen_vector_decompose_hermitian(float2* A, int N, int lda, float2* V_cevd, float* d_cevd);
/
#define NA 4
/*
* complex A=(4x4) math topology:
( 3.0, 0.0), (-2.0, -2.0), (-0.9, -0.9), (-0.5, -0.5),
(-2.0, 2.0), ( 4.0, 0.0), ( 1.0, 1.0), (-0.7, -0.5),
(-0.9, 0.9), ( 1.0, -1.0), (-1.0, 0.0), ( 0.1, 0.1),
(-0.5, 0.5), (-0.7, 0.5), ( 0.1, -0.1), ( 1.0, 0.0)
float A_h[NA * (2*NA)] = {//complex columnMajor: mem topology
3.0, 0.0, -2.0, 2.0, -0.9, 0.9, -0.5,0.5,
-2.0,-2.0, 4.0, 0.0, 1.0,-1.0, -0.7, 0.5,
-0.9,-0.9, 1.0, 1.0, -1.0, 0.0, 0.1,-0.1,
-0.5,-0.5, -0.7,-0.5, 0.1, 0.1, 1.0, 0.0
*/
int main() {
float A_h[NA * (2 * NA)] = {//complex columnMajor:
3.0, 0.0, -2.0, 2.0, -0.9, 0.9, -0.5, 0.5,
-2.0,-2.0, 4.0, 0.0, 1.0,-1.0, -0.7, 0.5,
-0.9,-0.9, 1.0, 1.0, -1.0, 0.0, 0.1,-0.1,
-0.5,-0.5, -0.7,-0.5, 0.1, 0.1, 1.0, 0.0
};
///Parameters:
int N = NA;
int lda = N;
float2* A = nullptr;
//___________________________________________________________________
A = (float2*)malloc(lda * N * sizeof(float2));
memcpy(A, A_h, lda * N * sizeof(float2));
printf("A(ma)=\n");
print_matrix_complex(A, N, N, N);
//______________________________________________________________
// void eigen_vector_decompose(float2 * A, int N, int lda, float2 * V_cevd, float* d_cevd);
float* d_cevd = nullptr;
float2* V_cevd = nullptr;
int ldv_cevd = N;
d_cevd = (float*)malloc(N * sizeof(float));
V_cevd = (float2*)malloc(ldv_cevd * N * sizeof(float2));
eigen_vector_decompose_hermitian(A, N, lda, V_cevd, d_cevd);
#if 0
int n = 2 * N;
int lds = n;
float* S = nullptr;
S = (float*)malloc(lds * n * sizeof(float));
real_neimag_real_imag_fill((float2*)A, N, lda, S, n, lds);
printf("S(ma)=\n");
print_matrix(S, n, n, lds);
//______________________________________________________________
int ldv_evd = n;
float* V_evd = nullptr;
V_evd = (float*)malloc(lds * n * sizeof(float));
memcpy(V_evd, S, lds * n * sizeof(float));
printf("V_evd(ma)=\n");
print_matrix(V_evd, n, n, ldv_evd);
float* e = nullptr;
float* d_evd = nullptr;
e = (float*)malloc(n * sizeof(float));
d_evd = (float*)malloc(n * sizeof(float));
//______________________________________________________________
//void tred2(float* V, float* e, float* d, int n, int ldv);
tred2(V_evd, d_evd, e, n, ldv_evd);
printf("V_evd-tred2=\n");
print_matrix(V_evd, n, n, ldv_evd);
printf("\nd-tred2=\n");
print_vector(d_evd, n);
printf("\ne-tred2=\n");
print_vector(e, n);
//void tql2(float* V, float* d, float* e, int n, int ldv);
tql2(V_evd, d_evd, e, n, ldv_evd);
printf("\nV_evd-tql2=\n");
print_matrix(V_evd, n, n, ldv_evd);
printf("\nd-tql2=\n");
print_vector(d_evd, n);
printf("\ne-tql2=\n");
print_vector(e, n);
//_________________________________________________________________________________
/**float* d_cevd = nullptr;
float2* V_cevd = nullptr;
int ldv_cevd = N;
d_cevd = (float*)malloc(N * sizeof(float));
V_cevd = (float2*)malloc(ldv_cevd * N * sizeof(float2));*/
for(int i=0; i(RV[i][j2], RV[i + N][j2]);
V_cevd[i + j * ldv_cevd].y = V_evd[(i + N) + j2 * ldv_evd];
}
}
printf("\nV_cevd=\n");
print_matrix_complex(V_cevd, N, N, ldv_cevd);
#endif
return 0;
}
void real_neimag_real_imag_fill( float2 * A_h, int N, int lda, float* S, int n, int lds)//n=2*N
{
float2 *A;
A = A_h;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
S[i +j*lds] = A[i+ j*lda].x;
S[i +(j + N)*lds] = -A[i +j*lda].y;
S[(i + N)+ j*lds] = -S[i +(j + N)*lds];
S[(i + N)+ (j + N)*lds] = S[i+ j*lds];
}
}
}
//typedef float float;
void tred2(float *V, float* d, float *e, int n, int ldv)
{
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
//LL::d[j] = V[n - 1][j];
d[j] = V[(n - 1)+j*ldv];
// Householder reduction to tridiagonal form
for (int i = n - 1; i > 0; --i)
{
// scale to avoid under/overflow
float scale = 0;
float h = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < i; ++k) {
// scale += fabs(d[k]);
printf(" d[k]=%f", d[k]);
scale += fabs(d[k]);
printf(" scale=%f", scale);
}
printf("\n______________\n");
if (scale == 0)
{
e[i] = d[i - 1];
for (int j = 0; j < i; ++j)
{
d[j] = V[(i - 1)+j*ldv];
V[i+j*ldv] = 0;
V[j+i*ldv] = 0;
}
}
else
{
// generate Householder vector
for (int k = 0; k < i; ++k)
{
d[k] /= scale;
h += d[k] * d[k];
}
float f = d[i - 1];
float g = sqrt(h);
if (f > 0)
g = -g;
e[i] = scale * g;
h = h - f * g;
d[i - 1] = f - g;
for (int j = 0; j < i; ++j)
e[j] = 0;
// Apply similarity transformation to remaining columns.
for (int j = 0; j < i; ++j)
{
f = d[j];
V[j+i*ldv] = f;
g = e[j] + V[j+j*ldv] * f;
for (int k = j + 1; k <= i - 1; ++k)
{
g += V[k+j*ldv] * d[k];
e[k] += V[k+j*ldv] * f;
}
e[j] = g;
}
f = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < i; ++j)
{
e[j] /= h;
f += e[j] * d[j];
}
float hh = f / (h + h);
for (int j = 0; j < i; ++j)
e[j] -= hh * d[j];
for (int j = 0; j < i; ++j)
{
f = d[j];
g = e[j];
for (int k = j; k <= i - 1; ++k)
V[k+j*ldv] -= (f * e[k] + g * d[k]);
d[j] = V[(i - 1)+j*ldv];
V[i+j*ldv] = 0;
}
}
d[i] = h;
}
// accumulate transformations
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
{
V[n - 1+i*ldv] = V[i+i * ldv];
V[i+i * ldv] = 1;
float h = d[i + 1];
if (h != 0)
{
for (int k = 0; k <= i; ++k)
d[k] = V[k+(i + 1) *ldv] / h;
for (int j = 0; j <= i; ++j)
{
float g = 0;
for (int k = 0; k <= i; ++k)
g += V[k+(i + 1) * ldv] * V[k+j * ldv];
for (int k = 0; k <= i; ++k)
V[k+j * ldv] -= g * d[k];
}
}
for (int k = 0; k <= i; ++k)
V[k+(i + 1) * ldv] = 0;
}
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
{
d[j] = V[(n - 1)+j * ldv];
V[(n - 1)+j * ldv] = 0;
}
V[(n - 1)+(n - 1) * ldv] = 1;
e[0] = 0;
}
float max(float x, float y) {
return (x > y) ? x : y;
}
void swap(float& x, float& y) {
float tmp;
tmp = x;
x = y;
y = tmp;
}
void tql2(float* V, float* d, float* e, int n, int ldv)
{
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i)
e[i - 1] = e[i];
e[n - 1] = 0;
float f = 0;
float tst1 = 0;
float eps = pow(2.0, -52.0);
for (int l = 0; l < n; ++l)
{
// find small subdiagonal element
tst1 = max(tst1, fabs(d[l]) + fabs(e[l]));
int m = l;
// original while-loop from Java code
while (m < n)
{
if (fabs(e[m]) <= eps * tst1)
break;
m++;
}
// if m == l, d[l] is an eigenvalue, otherwise, iterate
if (m > l)
{
int iter = 0;
do
{
iter = iter + 1;
// compute implicit shift
float g = d[l];
float p = (d[l + 1] - g) / (2.0 * e[l]);
float r = hypot(p, 1.0);
if (p < 0)
r = -r;
d[l] = e[l] / (p + r);
d[l + 1] = e[l] * (p + r);
float dl1 = d[l + 1];
float h = g - d[l];
for (int i = l + 2; i < n; ++i)
d[i] -= h;
f += h;
// implicit QL transformation.
p = d[m];
float c = 1;
float c2 = c;
float c3 = c;
float el1 = e[l + 1];
float s = 0;
float s2 = 0;
for (int i = m - 1; i >= l; --i)
{
c3 = c2;
c2 = c;
s2 = s;
g = c * e[i];
h = c * p;
r = hypot(p, e[i]);
e[i + 1] = s * r;
s = e[i] / r;
c = p / r;
p = c * d[i] - s * g;
d[i + 1] = h + s * (c * g + s * d[i]);
// accumulate transformation.
for (int k = 0; k < n; ++k)
{
h = V[k+(i + 1)*ldv];
V[k+(i + 1) * ldv] = s * V[k+i * ldv] + c * h;
V[k+i * ldv] = c * V[k+i * ldv] - s * h;
}
}
p = -s * s2 * c3 * el1 * e[l] / dl1;
e[l] = s * p;
d[l] = c * p;
} while (fabs(e[l]) > eps * tst1);
}
d[l] += f;
e[l] = 0;
}
// Sort eigenvalues and corresponding vectors.
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; ++i)
{
int k = i;
float p = d[i];
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; ++j)
if (d[j] < p)
{
k = j;
p = d[j];
}
if (k != i)
{
d[k] = d[i];
d[i] = p;
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
swap(V[j+i * ldv], V[j+k * ldv]);
}
}
}
void eigen_vector_decompose_hermitian(float2* A, int N, int lda, float2* V_cevd, float* d_cevd)
{
int n = 2 * N;
int lds = n;
float* S = nullptr;
S = (float*)malloc(lds * n * sizeof(float));
real_neimag_real_imag_fill((float2*)A, N, lda, S, n, lds);
printf("S(ma)=\n");
print_matrix(S, n, n, lds);
//______________________________________________________________
int ldv_evd = n;
float* V_evd = nullptr;
V_evd = (float*)malloc(lds * n * sizeof(float));
memcpy(V_evd, S, lds * n * sizeof(float));
printf("V_evd(ma)=\n");
print_matrix(V_evd, n, n, ldv_evd);
float* e = nullptr;
float* d_evd = nullptr;
e = (float*)malloc(n * sizeof(float));
d_evd = (float*)malloc(n * sizeof(float));
//______________________________________________________________
//void tred2(float* V, float* e, float* d, int n, int ldv);
tred2(V_evd, d_evd, e, n, ldv_evd);
printf("V_evd-tred2=\n");
print_matrix(V_evd, n, n, ldv_evd);
printf("\nd-tred2=\n");
print_vector(d_evd, n);
printf("\ne-tred2=\n");
print_vector(e, n);
//void tql2(float* V, float* d, float* e, int n, int ldv);
tql2(V_evd, d_evd, e, n, ldv_evd);
printf("\nV_evd-tql2=\n");
print_matrix(V_evd, n, n, ldv_evd);
printf("\nd-tql2=\n");
print_vector(d_evd, n);
printf("\ne-tql2=\n");
print_vector(e, n);
//_________________________________________________________________________________
/**float* d_cevd = nullptr;
float2* V_cevd = nullptr;
d_cevd = (float*)malloc(N * sizeof(float));
V_cevd = (float2*)malloc(ldv_cevd * N * sizeof(float2));
*/
int ldv_cevd = N;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
d_cevd[i] = d_evd[2 * i];
printf("\nd_cevd=\n");
print_vector(d_cevd, N);
for (int j = 0; j < N; ++j)
{
int j2 = 2 * j;
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
V_cevd[i + j * ldv_cevd].x = V_evd[i + j2 * ldv_evd];//complex(RV[i][j2], RV[i + N][j2]);
V_cevd[i + j * ldv_cevd].y = V_evd[(i + N) + j2 * ldv_evd];
}
}
printf("\nV_cevd=\n");
print_matrix_complex(V_cevd, N, N, ldv_cevd);
}
void print_vector(float* A, int N) {
for (int idx = 0; idx < N; idx++) {
printf("%7.4f ", A[idx]);
}
}
void print_matrix(float* A, int M, int N, int lda)
{
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
printf("%7.4f ", A[i + j * lda]);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
void print_matrix_complex(float2* A, int M, int N, int lda) {
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {//*(sizeof(complex)/sizeof(float))
printf("(%7.4f, %7.4f)", A[i + j * lda].x, A[i + j * lda].y);
}
printf("\n");
}
} 运行:
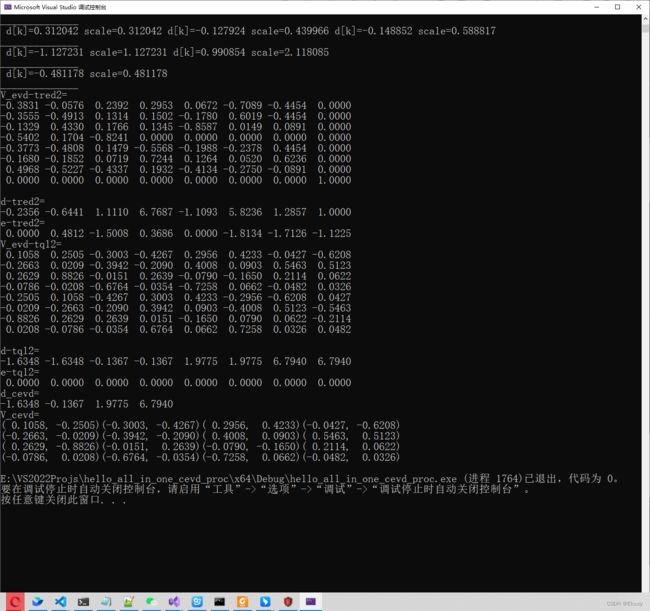
结果分析:
matlab: