C++、STL标准模板库和泛型编程 ——算法、迭代器 (侯捷)
C++、STL标准模板库和泛型编程 ——算法、迭代器 (侯捷)--- 持续更新
- 迭代器
-
- iterator_category
- 算法
-
- accumulate
- for_each
- replace
- count
- find
- sort
- binary_search
使用一个东西,却不明白它的道理,不高明!—— 林语堂
阶段学习
使用C++标准库
认识C++标准库(胸中自有丘壑!)
良好使用C++标准库
扩充C++标准库
所谓 Generic Programming (GP,泛型编程),就是使用 template (模板)为主要工具来编写程序。
-
GP是将datas和methods分开来;Containers和Algorithms可各自闭门造车﹐其间以Iterator连通即可·Algorithms通过Iterators确定操作范围﹐也通过Iterators取用Container元素。
-
OOP(Object-Oriented Programming),企图将datas和methods关联在一起。
C++标准模板库Standard Template 最重要的六大部件(Components):容器、算法、仿函数、迭代器、适配器、分配器
- 容器(
Containers)是class template - 算法(
Algorithms)是function template(其内最终涉及元素本身的操作,无非就是比大小!) - 迭代器(
Iterators)是class template - 仿函数(
Functors)是class template - 适配器(
Adapters)是class template - 分配器(
Allocators)是class template
关系图:
![]()
迭代器
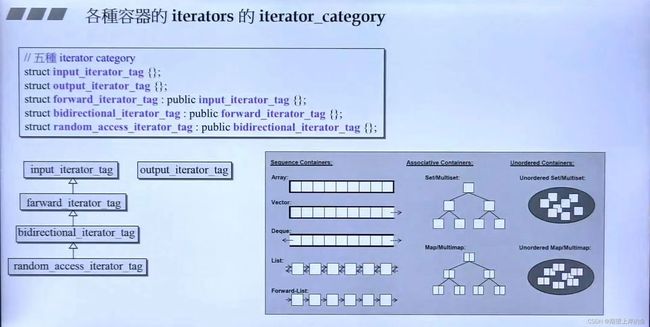
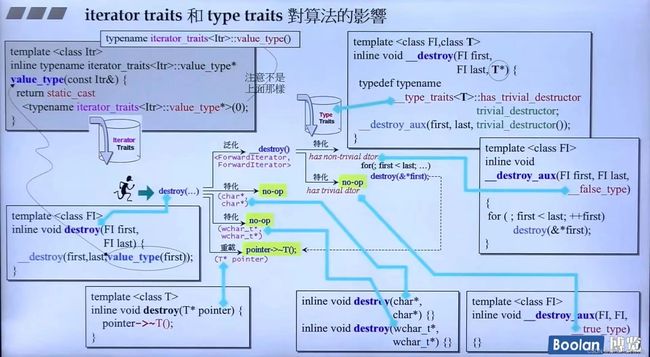
前面说到迭代器中必须要有5种关联类型:pointer、reference、iterator_category(迭代器类型,比如说随机存取)、value_type(值存放类型)、difference_type(容器两个元素之间的距离类型)。
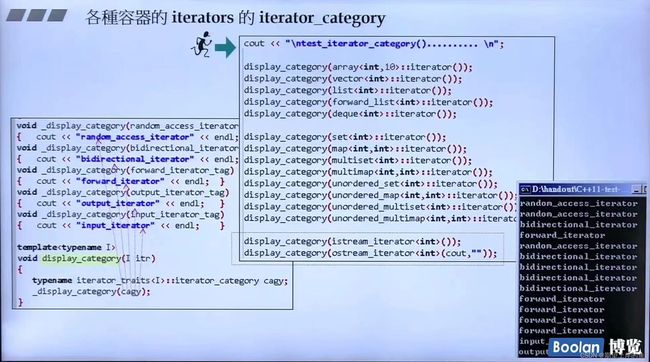
iterator_category
也有五种迭代器类型:随机存取迭代器(array、vector、deque)、双向迭代器(list、红黑树容器)、单向迭代器(forward_list,hash类容器)、输入迭代器(istream迭代器),输出迭代器(ostream迭代器)。
- 方便迭代器类型作为参数进行传递,如果是整数的是不方便的;还有一个原因,有些算法的实现没有实现特定类型的迭代器类别,就可以用继承关系去找父迭代器类别。
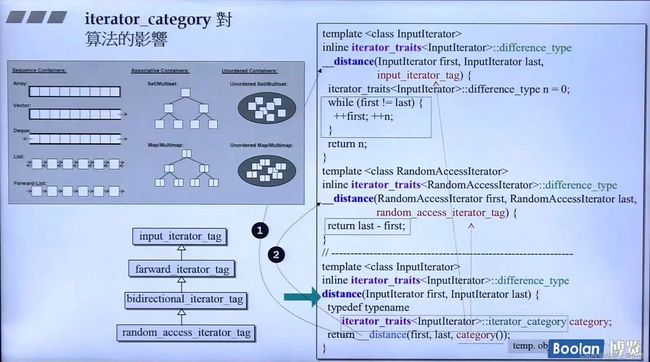
以这个distance函数为例,会根据迭代器的类别来调用不同的具体实现函数,
- 一个是只包含一个减法操作的语句,
- 一个是包含一个
while循环的语句,可想而知,当真实距离很大时,有while循环的具体实现函数效率会非常低下。
使用萃取机iterator_traits,虽然只有两种,但是这几种类型都是继承关系is a 父类input_iterator_tag,如果没有重载,最终都会落到input_iterator_tag。
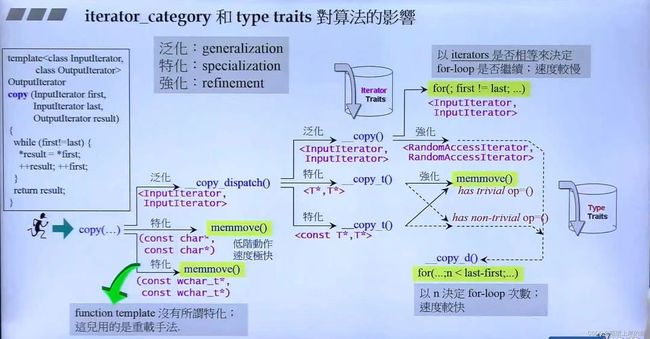
看一个特别能体现C++注重效率的体现:
copy实现,到最终的实现细节,经过了很多判断,这些判断是为了找到最高效率的实现,就是判断迭代器的分类。
算法
Algorithms看不见Containers,对其一无所知;所以,它所需要的一切信息都必须从Iterators取得,而Iterators(由Containers供应)必须能够回答Algorithm的所有提问,才能搭配该Algorithm的所有操作。
template<typename Iterator>
Algorithm(Iterator it1, Iterator it2){
...
}
template<typename Iterator, typename Cmp>//Cmp为传入的一个准则,比如比大小准则
Algorithm(Iterator it1, Iterator it2, Cmp comp){
...
}
accumulate
template<class InputInterator, class T>
T accumulate(InputIterator first, InputIterator last, T init){...}
//另外一个版本为:
template<class InputInterator, class T, class BinaryOperation>
T accumulate(InputIterator first, InputIterator last, T init, BinaryOperation binary_op){...}
上面这个binary_op指明是一个二元操作数的函数,可以是仿函数(实质上是一个类),也可以是函数,只要是能够在该算法的函数体内通过小括号调用就行!!!!
- 也就是能够这么用:
binary_op(a, b); - 就算是在算法(函数)里面,也能够使用仿函数,但是传入的是仿函数的对象实例,而如果要传入函数的话,就传函数名就可以了。
int init = 100;
int nums[] = {10,20,30};
accumulate(nums, nums+3, init);//不指定具体怎么操作,默认为加法,输出160
accumulate(nums, nums+3, init, minus<int>()); //这minus时减法的意思,所以输出为40
for_each
- 对容器区间内的元素做同样的事情。
template<class InputIterator, class Function>
Function for_each(InputIterator first, InputIterator last, Function f){...}
replace
1、 replace
- 将容器区间内的元素进行替换,如果元素值等于
old_value就把它替换为new_value.
template<class ForwardIterator, class T>
void replace(ForwardIterator first, ForwardIterator last, const T& old_value, const T& new_value){...}
2、replace_if
- 在算法中看到
if,就代表你要给他一个条件。 Predicate为一个条件,判断式子(传回真或假),如果符合条件就进行替换
template<class ForwardIterator, class Predicate, class T>
void replace_copy(ForwardIterator first, ForwardIterator last, Predicate pred, const T& new_value){...}
3、replace_copy
- 范围内所有等同于
old_value的都以new_value放置新的区间中,不符合原值的也放入新的区间
template<class InputIterator, class OutputIterator, class T>
OutputIterator replace_copy(InputIterator first, InputIterator last, OutputIterator result, const T& old_value, const T& new_value)
{...}
count
容器不带成员函数count():
array, vector, list, forward_list, deque
容器带有成员函数count()(红黑树、hash容器中有自己的count):
set /multiset
map / multimap
unordered_set / unordered_multiset
unordered_map / unordered_multimap
1、count
- 区间内有和
value相等的元素count+1。
template<class InputIterator, class T>
typename iterator_traits<InputIterator>::difference_type
count(InputIterator first, InputIterator last, const T& value){...}
2、count_if
- 区间内有符合
pred条件的count+1
template<class InputIterator, class Predicate>
typename iterator_traits<InputIterator>::difference_type
count_if(InputIterator first, InputIterator last, Predicate pred){...}
find
容器不带成员函数find():
array, vector, list, forward_list, deque
容器带有成员函数find()(红黑树、hash容器中有自己的find):
set /multiset
map / multimap
unordered_set / unordered_multiset
unordered_map / unordered_multimap
1、find
- 循序查找,返回第一个和
value相等的迭代器
template<class InputIterator, class T>
InputIterator find(InputIterator first, InputIterator last, const T& value){...}
1、find_if
- 循序查找,查找符合条件的第一个元素的迭代器
template<class InputIterator, class Predicate>
InputIterator find_if(InputIterator first, InputIterator last, Predicate pred){...}
sort
sort要求RandomAccessIterator
容器不带成员函数sort():
array, vector, deque
//已经排序,遍历自然形成sorted状态
set /multiset
map / multimap
unordered_set / unordered_multiset
unordered_map / unordered_multimap
容器带有成员函数sort():下面这两种容器都不能 " 跳 "
list, forward_list
sort
- 默认从小到大排序,也可以指定自己的比较函数,可以是仿函数,可以是函数,仿函数必须传入该仿函数的实例。
sort(InputIterator first, InputIterator last, Function f)
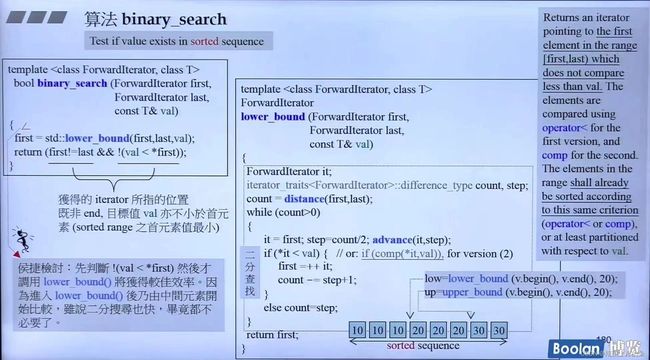
binary_search
- 一定是在已排序状态下
- 源码中就是调用
lower_bound
template<class ForwardIterator, class T>
bool binary_search(ForwardIterator first, ForwardIterator last, const T& value){...}
lower_bound(ForwardIterator first, ForwardIterator last, T target)
lower_bound二分查找的一个版本,如果找到对应的值,则返回指向其中第一个元素的迭代器,如果不存在,则返回最适合安插这个target的点的迭代器 ,也就是说它返回迭代器指向第一个不小于target的元素,返回的是不破坏排序得以安插target的第一个适当位置。