TreeMap 红黑树实现
TreeMap 是一个有序的key-value集合,它是通过 红黑树 实现的。
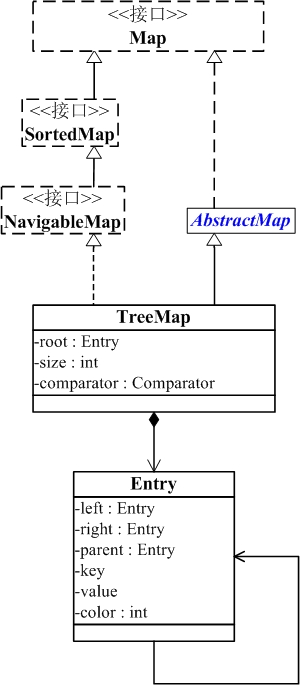
TreeMap 继承于AbstractMap,所以它是一个Map,即一个key-value集合。
TreeMap 实现了NavigableMap,Cloneable和Serializable接口。
TreeMap的基本操作 containsKey、get、put 和 remove 的时间复杂度是 log(n) 。
首先是TreeMap的构造方法:
public TreeMap() { comparator = null; }
/** * Constructs a new, empty tree map, ordered according to the given comparator. */ public TreeMap(Comparator<? super K> comparator) { this.comparator = comparator; } /** * Constructs a new tree map containing the same mappings as the given * map, ordered according to the <em>natural ordering</em> of its keys. */ public TreeMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) { comparator = null; putAll(m); } /** * Constructs a new tree map containing the same mappings and * using the same ordering as the specified sorted map. This * method runs in linear time. */ public TreeMap(SortedMap<K, ? extends V> m) { comparator = m.comparator(); try { buildFromSorted(m.size(), m.entrySet().iterator(), null, null); } catch (java.io.IOException cannotHappen) { } catch (ClassNotFoundException cannotHappen) { } }
TreeMap是基于红黑树实现的,以下是树结点的定义,主要key(键)、value(值)、left(左孩子)、right(右孩子)、parent(父节点)、color(颜色)六个字段,根据key的值进行排序。该内部类比较简单,不做分析。
static final class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> { K key; V value; Entry<K,V> left = null; Entry<K,V> right = null; Entry<K,V> parent; boolean color = BLACK; /** * Make a new cell with given key, value, and parent, and with * {@code null} child links, and BLACK color. */ Entry(K key, V value, Entry<K,V> parent) { this.key = key; this.value = value; this.parent = parent; } ...... }
以下是红黑树的插入put和删除deleteEntry操作,以及执行插入删除时需要用到的操作:左旋rotateLeft、右旋rotateRight、插入修正fixAfterInsertion和删除修正fixAfterDeletion。
插入操作,先找到要插入的位置,插入新结点,调用fixAfterInsertion对插入结果进行修正:
public V put(K key, V value) { Entry<K,V> t = root; if (t == null) { compare(key, key); // type (and possibly null) check root = new Entry<>(key, value, null); size = 1; modCount++; return null; } int cmp; Entry<K,V> parent; // split comparator and comparable paths Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator; if (cpr != null) { do { parent = t; cmp = cpr.compare(key, t.key); if (cmp < 0) t = t.left; else if (cmp > 0) t = t.right; else return t.setValue(value); } while (t != null); } else { if (key == null) throw new NullPointerException(); Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key; do { parent = t; cmp = k.compareTo(t.key); if (cmp < 0) t = t.left; else if (cmp > 0) t = t.right; else return t.setValue(value); } while (t != null); } Entry<K,V> e = new Entry<>(key, value, parent); if (cmp < 0) parent.left = e; else parent.right = e; fixAfterInsertion(e); size++; modCount++; return null; }
fixAfterInsertion操作,保证插入节点之后,仍然是一棵红黑树:
private void fixAfterInsertion(Entry<K, V> x) { x.color = RED; while (x != null && x != root && x.parent.color == RED) { if (parentOf(x) == leftOf(parentOf(parentOf(x)))) { Entry<K, V> y = rightOf(parentOf(parentOf(x))); if (colorOf(y) == RED) { setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK); setColor(y, BLACK); setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED); x = parentOf(parentOf(x); } else { if (x == rightOf(parentOf(x))) { x = parentOf(x) rotateLeft(x); } setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK); setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED); rotateRight(parentOf(parentOf(x))); } } else { Entry<K, V> y = leftOf(parentOf(parentOf(x))); if (colorOf(y) == RED) { setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK); setColor(y, BLACK); setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED); x = parentOf(parentOf(x); } else { if (x == leftOf(parentOf(x))) { x = parentOf(x) rotateRight(x); } setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK); setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED); rotateLeft(parentOf(parentOf(x))); } } } root.COLOR = BLACK; }
之中用到了leftRotate和rightRotate操作,这里先介绍这两个操作,在fixAfterDeletion中也会用到:
private void rotateLeft(Entry<K,V> p) { if (p != null) { Entry<K,V> r = p.right; p.right = r.left; if (r.left != null) r.left.parent = p; r.parent = p.parent; if (p.parent == null) root = r; else if (p.parent.left == p) p.parent.left = r; else p.parent.right = r; r.left = p; p.parent = r; } } private void rotateRight(Entry<K,V> p) { if (p != null) { Entry<K,V> l = p.left; p.left = l.right; if (l.right != null) l.right.parent = p; l.parent = p.parent; if (p.parent == null) root = l; else if (p.parent.right == p) p.parent.right = l; else p.parent.left = l; l.right = p; p.parent = l; } }
删除操作,先按二叉查找树的方法删除节点,然后调用fixAfterDeletion使得树保持红黑树性质:
private void deleteEntry(Entry<K, V> p) { modCount++; size--; if (p.left != null && p.right != null) { Entry<K, V> s = successor(p); p.key = s.key; p.value = s.value; p = s; } Entry<K,V> replacement = p.left != null ? p.left : p.right; if (replacement != null) { replacement.parent = p.parent; if (p.parent == null) root = replacement; else if (p == p.parent.left) p.parent.left = replacement; else p.parent.right = replacement; p.left = p.right = p.parent = null; if (p.COLOR == BLACK) fixAfterDeletion(replacement); } else if (p.parent == NULL) { root = null; } else { if (p.color == BLACK) fixAfterDeletion(p); if (p.parent != null) { if (p ==p.parent.left) p.parent.left = null; else p.parent.right = null; p.parent = null; } } }