mybatis源码运行详细流程
文章目录
- 学习链接
- 1.准备环境
-
- 1.创建项目,导入相关jar包
- 2.编写mybatis核心配置文件
- 3. EmployeeMapper.xml、EmployeeMapper
- 4.log4j.xml、Employee实体类
- 2.测试
-
- 1.测试类
- 2.测试结果
- 3.源码流程分析
-
- SqlSessionFactoryBuilder
-
- XMLConfigBuilder
- BaseBuilder
- Configuration
- parser.parse()
-
- settings标签解析
- properties标签解析
- typeAliases标签解析
- plugins标签解析
- environments标签解析
- typeHandlers标签解析
- mappers标签解析
- XMLMapperBuilder
-
- mapperParser.parse()
-
- MapperBuilderAssistant
- 解析mapper.xml
-
- cache-ref标签解析
- cache标签解析
- statement标签解析
-
- XMLStatementBuilder
- 绑定Mapper命名空间
-
- configuration.addMapper
- SqlSession
-
- sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
-
- TransactionFactory
- Transaction
- sqlSession.getMapper(class)
-
- MapperRegistry
- MapperProxyFactory
- MapperProxy
- MapperMethod
-
- ParamNameResovler
- sqlSession.selectOne
- CachingExecutor
- BaseExecutor
-
- queryFromDatabase
- SimpleExecutor
-
- StatementHandler
- ParameterHandler
- ResultSetHandler
- Plugin插件机制
-
- mybatis执行流程
- 四大对象
- InterceptorChain
- Plugin工具类
-
- 脱敏插件示例
- 打印Sql插件示例
- 打印每条SQL语句及其执行时间
学习链接
mybatis中文文档
MyBatis7:MyBatis插件及示例----打印每条SQL语句及其执行时间
Jsqlparser 学习相关链接
mybatis看这一篇就够了,简单全面一发入魂
MyBatis详解
1.准备环境
1.创建项目,导入相关jar包
2.编写mybatis核心配置文件
mybatis-config.xml
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC" />
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" />
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis" />
<property name="username" value="root" />
<property name="password" value="root" />
dataSource>
environment>
environments>
<mappers>
<mapper resource="EmployeeMapper.xml" />
mappers>
3. EmployeeMapper.xml、EmployeeMapper
EmployeeMapper.xml
DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.atguigu.mybatis.dao.EmployeeMapper">
<select id="getEmpById" resultType="com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.Employee">
select id,last_name lastName,email,gender,hire_date from tbl_employee where id = #{id,jdbcType=VARCHAR}
select>
mapper>
EmployeeMapper接口
package com.atguigu.mybatis.dao;
import com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.Employee;
public interface EmployeeMapper {
public Employee getEmpById(Integer id);
}
4.log4j.xml、Employee实体类
log4j.xml
**
**
Employee.java
public class Employee {
private Integer id;
private String lastName;
private String email;
private String gender;
private Date hireDate;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
public void setLastName(String lastName) {
this.lastName = lastName;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public String getGender() {
return gender;
}
public void setGender(String gender) {
this.gender = gender;
}
public Date getHireDate() {
return hireDate;
}
public void setHireDate(Date hireDate) {
this.hireDate = hireDate;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Employee{" +
"id=" + id +
", lastName='" + lastName + '\'' +
", email='" + email + '\'' +
", gender='" + gender + '\'' +
", hireDate=" + hireDate +
'}';
}
}
2.测试
1.测试类
package com.atguigu.mybatis.test;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.List;
import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;
import com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.Employee;
import com.atguigu.mybatis.dao.EmployeeMapper;
import org.junit.Test;
public class MyBatisTest {
/**
* 1、获取sqlSessionFactory对象:
* 解析文件的每一个信息保存在Configuration中,返回包含Configuration的DefaultSqlSession;
* 注意:【MappedStatement】:代表一个增删改查的详细信息
*
* 2、获取sqlSession对象
* 返回一个DefaultSQlSession对象,包含Executor和Configuration;
* 这一步会创建Executor对象;
*
* 3、获取接口的代理对象(MapperProxy)
* getMapper,使用MapperProxyFactory创建一个MapperProxy的代理对象
* 代理对象里面包含了,DefaultSqlSession(Executor)
* 4、执行增删改查方法
*
* 总结:
* 1、根据配置文件(全局,sql映射)初始化出Configuration对象
* 2、创建一个DefaultSqlSession对象,
* 他里面包含Configuration以及
* Executor(根据全局配置文件中的defaultExecutorType创建出对应的Executor)
* 3、DefaultSqlSession.getMapper():拿到Mapper接口对应的MapperProxy;
* 4、MapperProxy里面有(DefaultSqlSession);
* 5、执行增删改查方法:
* 1)、调用DefaultSqlSession的增删改查(Executor);
* 2)、会创建一个StatementHandler对象。
* (同时也会创建出ParameterHandler和ResultSetHandler)
* 3)、调用StatementHandler预编译参数以及设置参数值;
* 使用ParameterHandler来给sql设置参数
* 4)、调用StatementHandler的增删改查方法;
* 5)、ResultSetHandler封装结果
* 注意:
* 四大对象每个创建的时候都有一个interceptorChain.pluginAll(parameterHandler);
*
* @throws IOException
*/
@Test
public void test01() throws IOException {
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
// 1、获取sqlSessionFactory对象
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
// 2、获取sqlSession对象
SqlSession openSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
try {
// 3、获取接口的实现类对象
// 会为接口自动的创建一个代理对象,代理对象去执行增删改查方法
EmployeeMapper mapper = openSession.getMapper(EmployeeMapper.class);
Employee employee = mapper.getEmpById(1);
System.out.println(employee);
} finally {
openSession.close();
}
}
}
2.测试结果
DEBUG 06-11 11:08:17,311 ==> Preparing: select id,last_name lastName,email,gender,hire_date from tbl_employee where id = ? (BaseJdbcLogger.java:145)
DEBUG 06-11 11:08:17,337 ==> Parameters: 1(Integer) (BaseJdbcLogger.java:145)
DEBUG 06-11 11:08:17,355 <== Total: 1 (BaseJdbcLogger.java:145)
Employee{id=1, lastName='曾泽华', email='[email protected]', gender='男', hireDate=null}
Process finished with exit code 0
3.源码流程分析
通过上面的简单案例,先来大概的分析下源码的运行流程:
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder
1.上面测试类的第一步:
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
直接new一个 SqlSessionFactoryBuilder 对象,并且通过这个 SqlSessionFactoryBuilder 对象根据传过来的mybatis核心配置文件流,使用build方法创建SqlSessionFactory。而build方法的参数就是Configuration对象。
public class SqlSessionFactoryBuilder {
public SqlSessionFactory build(Configuration config) { // 参数是Configuration
// 默认创建的是DefaultSqlSessionFactory对象,它需要传进去一个Configuration对象
return new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(config);
}
}
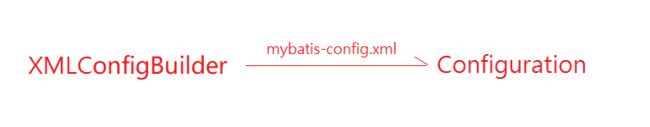
所以,mybatis核心配置文件就是用来创建Configuration对象的,那么就需要解析mybatis核心配置文件mybatis-config.xml ,mybatis里面的SqlSessionFactoryBuilder 就是借助XMLConfigBuilder对象来解析这个核心配置文件,并返回Configuration对象。
public class SqlSessionFactoryBuilder {
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties properties) {
try {
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(inputStream, environment, properties);
// parser.parse()返回Configuration对象,并将它传递给DefaultSqlSessionFactory对象
return build(parser.parse());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// Intentionally ignore. Prefer previous error.
}
}
}
}
这也就是说:SqlSessionFactory对象需要Configuration对象,而Configuration对象就是通过解析mybatis-config.xml配置文件来的。
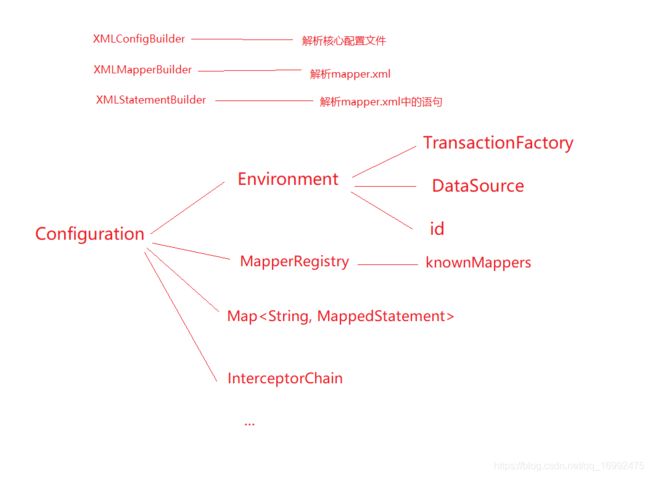
- 先混个眼熟,Configuration对象包含了mybatis运行时大部分核心配置(比如:二级缓存的开关,驼峰映射开关,log实现,默认执行器Executor类型,mapper注册中心,拦截器链,类型转换器注册中心,别名注册中心,映射的mappedStatement),所以这是一个很关键的对象,一定要留意它,特别是在spring中,我们只要能抓住这个对象,就可以通过修改它里面的属性,从而修改它
上面总结起来就是如下图:
XMLConfigBuilder
所以接下来就是具体看XMLConfigBuilder对象是怎么解析mybatis-config.xml的。
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(inputStream, environment, properties);
// parser.parse()返回Configuration对象,并将它传递给DefaultSqlSessionFactory对象
return build(parser.parse());
我们先看下上面的这个new XMLConfigBuilder的这个过程,都会调用到下面这个构造方法,这里会new 一个Configuration对象,并且设置给BaseBuilder。
private XMLConfigBuilder(XPathParser parser, String environment, Properties props) {
// 我们看到了,Configuration对象是直接new出来的,并给到了XMLConfig的父类BaseBuilder
super(new Configuration());
ErrorContext.instance().resource("SQL Mapper Configuration");
// Configuration的Properties属性赋值
this.configuration.setVariables(props);
// 标识还未开始解析
this.parsed = false;
// 如果有传递environment
this.environment = environment;
// XMLConfigBuilder使用XPathParser来解析配置文件
this.parser = parser;
}
我们可以顺便简单的看下BaseBuilder
BaseBuilder
public abstract class BaseBuilder {
protected final Configuration configuration; // 核心配置对象在这里保存
protected final TypeAliasRegistry typeAliasRegistry; // 别名注册中心
protected final TypeHandlerRegistry typeHandlerRegistry; // 类型转换器注册中心
public BaseBuilder(Configuration configuration) {
this.configuration = configuration;
// 这里直接拿configuration对象的typeAliasRegistry
this.typeAliasRegistry = this.configuration.getTypeAliasRegistry();
// 这里直接拿configuration对象的typeHandlerRegistry
this.typeHandlerRegistry = this.configuration.getTypeHandlerRegistry();
}
// 省略了一些解析的方法...
protected TypeHandler<?> resolveTypeHandler(Class<?> javaType, Class<? extends TypeHandler<?>> typeHandlerType) {
if (typeHandlerType == null) {
return null;
}
// javaType ignored for injected handlers see issue #746 for full detail
TypeHandler<?> handler = typeHandlerRegistry.getMappingTypeHandler(typeHandlerType);
if (handler == null) {
// not in registry, create a new one
handler = typeHandlerRegistry.getInstance(javaType, typeHandlerType);
}
return handler;
}
protected Class<?> resolveClass(String alias) {
if (alias == null) {
return null;
}
try {
return resolveAlias(alias);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error resolving class. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
// 把别名解析成Class类,而解析就是通过别名注册中心来获取的
protected Class<?> resolveAlias(String alias) {
return typeAliasRegistry.resolveAlias(alias);
}
}
Configuration
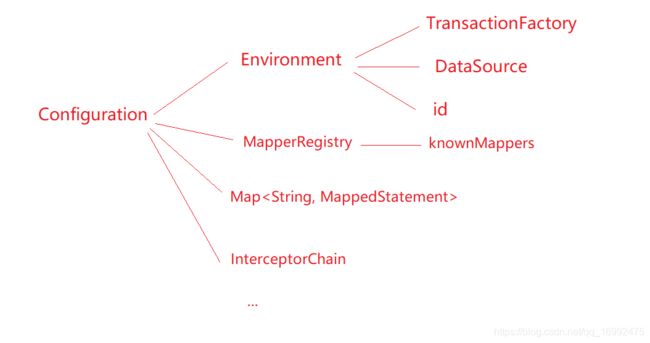
我们再来看一下Configuration的new过程,这里暂时只看下Configuration的属性和它的无参构造方法,我们可以看到构造方法里面,注册了很多的别名,并且都给到了Configuration对象的TypeAliasRegistry属性上。我们还注意一下BaseBuilder中的两个属性typeAliasRegistry、typeHandlerRegistry也是从Configuration对象中拿的。
Configuration对象是一个全局唯一的对象,整个应用要注册东西,或者要拿注册的东西,解析mapper语句的结果,注册拦截器(用来拦截四大对象),创建四大对象的方法都在这个类里面。
/**
* @author Clinton Begin
*/
public class Configuration {
protected Environment environment;
protected boolean safeRowBoundsEnabled = false;
protected boolean safeResultHandlerEnabled = true;
protected boolean mapUnderscoreToCamelCase = false;
protected boolean aggressiveLazyLoading = true;
protected boolean multipleResultSetsEnabled = true;
protected boolean useGeneratedKeys = false;
protected boolean useColumnLabel = true;
protected boolean cacheEnabled = true;
protected boolean callSettersOnNulls = false;
protected boolean useActualParamName = true;
protected String logPrefix;
protected Class <? extends Log> logImpl;
protected Class <? extends VFS> vfsImpl;
protected LocalCacheScope localCacheScope = LocalCacheScope.SESSION;
protected JdbcType jdbcTypeForNull = JdbcType.OTHER;
protected Set<String> lazyLoadTriggerMethods = new HashSet<String>(Arrays.asList(new String[] { "equals", "clone", "hashCode", "toString" }));
protected Integer defaultStatementTimeout;
protected Integer defaultFetchSize;
protected ExecutorType defaultExecutorType = ExecutorType.SIMPLE;
protected AutoMappingBehavior autoMappingBehavior = AutoMappingBehavior.PARTIAL;
protected AutoMappingUnknownColumnBehavior autoMappingUnknownColumnBehavior = AutoMappingUnknownColumnBehavior.NONE;
protected Properties variables = new Properties();
protected ReflectorFactory reflectorFactory = new DefaultReflectorFactory();
protected ObjectFactory objectFactory = new DefaultObjectFactory();
protected ObjectWrapperFactory objectWrapperFactory = new DefaultObjectWrapperFactory();
protected boolean lazyLoadingEnabled = false;
protected ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new JavassistProxyFactory(); // #224 Using internal Javassist instead of OGNL
protected String databaseId;
/**
* Configuration factory class.
* Used to create Configuration for loading deserialized unread properties.
*
* @see Issue 300 (google code)
*/
protected Class<?> configurationFactory;
// mapper.xml被解析时就放在这个mapperRegistry注册中心里面的knownMappers(key是命名空间反射的class类,value是直接new的MapperProxyFactory对象)
protected final MapperRegistry mapperRegistry = new MapperRegistry(this);
// 注册的拦截器,放到这个interceptorChain中的,通过plugins标签注入,在创建四大对象的方法中起作用
protected final InterceptorChain interceptorChain = new InterceptorChain();
// 类型处理器注册中心
protected final TypeHandlerRegistry typeHandlerRegistry = new TypeHandlerRegistry();
// 别名注册中心,还记得一new Configuration对象,就注册了一大堆别名
protected final TypeAliasRegistry typeAliasRegistry = new TypeAliasRegistry();
protected final LanguageDriverRegistry languageRegistry = new LanguageDriverRegistry();
// mapper.xml中的每一个增删改查标签被解析后,就封装成MappedStatement保存在这个里面
protected final Map<String, MappedStatement> mappedStatements = new StrictMap<MappedStatement>("Mapped Statements collection");
// 二级缓存的cache,key是命名空间,也就是说二级缓存的作用范围是namespace级别的
protected final Map<String, Cache> caches = new StrictMap<Cache>("Caches collection");
protected final Map<String, ResultMap> resultMaps = new StrictMap<ResultMap>("Result Maps collection");
protected final Map<String, ParameterMap> parameterMaps = new StrictMap<ParameterMap>("Parameter Maps collection");
protected final Map<String, KeyGenerator> keyGenerators = new StrictMap<KeyGenerator>("Key Generators collection");
protected final Set<String> loadedResources = new HashSet<String>();
protected final Map<String, XNode> sqlFragments = new StrictMap<XNode>("XML fragments parsed from previous mappers");
protected final Collection<XMLStatementBuilder> incompleteStatements = new LinkedList<XMLStatementBuilder>();
protected final Collection<CacheRefResolver> incompleteCacheRefs = new LinkedList<CacheRefResolver>();
protected final Collection<ResultMapResolver> incompleteResultMaps = new LinkedList<ResultMapResolver>();
protected final Collection<MethodResolver> incompleteMethods = new LinkedList<MethodResolver>();
/*
* A map holds cache-ref relationship. The key is the namespace that
* references a cache bound to another namespace and the value is the
* namespace which the actual cache is bound to.
*/
protected final Map<String, String> cacheRefMap = new HashMap<String, String>();
public Configuration(Environment environment) {
this();
this.environment = environment;
}
public Configuration() {
// 注册了很多的别名
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("JDBC", JdbcTransactionFactory.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("MANAGED", ManagedTransactionFactory.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("JNDI", JndiDataSourceFactory.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("POOLED", PooledDataSourceFactory.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("UNPOOLED", UnpooledDataSourceFactory.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("PERPETUAL", PerpetualCache.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("FIFO", FifoCache.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("LRU", LruCache.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("SOFT", SoftCache.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("WEAK", WeakCache.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("DB_VENDOR", VendorDatabaseIdProvider.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("XML", XMLLanguageDriver.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("RAW", RawLanguageDriver.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("SLF4J", Slf4jImpl.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("COMMONS_LOGGING", JakartaCommonsLoggingImpl.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("LOG4J", Log4jImpl.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("LOG4J2", Log4j2Impl.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("JDK_LOGGING", Jdk14LoggingImpl.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("STDOUT_LOGGING", StdOutImpl.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("NO_LOGGING", NoLoggingImpl.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("CGLIB", CglibProxyFactory.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("JAVASSIST", JavassistProxyFactory.class);
languageRegistry.setDefaultDriverClass(XMLLanguageDriver.class);
languageRegistry.register(RawLanguageDriver.class);
}
// 创建四大对象的代码
// 参数处理器
public ParameterHandler newParameterHandler(MappedStatement mappedStatement,
Object parameterObject, BoundSql boundSql) {
ParameterHandler parameterHandler =
mappedStatement.getLang().createParameterHandler(mappedStatement,
parameterObject,
boundSql);
parameterHandler = (ParameterHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(parameterHandler);
return parameterHandler;
}
// 结果集处理器
public ResultSetHandler newResultSetHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement,
RowBounds rowBounds, ParameterHandler parameterHandler,
ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
ResultSetHandler resultSetHandler = new DefaultResultSetHandler(executor, mappedStatement,
parameterHandler, resultHandler,
boundSql, rowBounds);
resultSetHandler = (ResultSetHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(resultSetHandler);
return resultSetHandler;
}
// 语句处理器
public StatementHandler newStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement,
Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds,
ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
StatementHandler statementHandler = new RoutingStatementHandler(executor, mappedStatement,
parameterObject, rowBounds,
resultHandler, boundSql);
statementHandler = (StatementHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(statementHandler);
return statementHandler;
}
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction) {
return newExecutor(transaction, defaultExecutorType);
}
// 执行器
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
Executor executor;
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
if (cacheEnabled) {
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
}
}
parser.parse()
上面也就说了XMLConfigBuilder对象的一个new的过程,它在new的时候也new 了Configuration,并且保存在父类BaseBuilder里面,接下来,就是要解析mybatis-config.xml文件,并且把解析结果设置到Configuration对象中,方便后面的使用,调用的是parser.parse(),这个parser就是XMLConfigBuilder对象,这个对象使用XPathParser对象来解析配置文件。
public class XMLConfigBuilder extends BaseBuilder {
private boolean parsed;
private XPathParser parser;
private String environment;
private ReflectorFactory localReflectorFactory = new DefaultReflectorFactory();
public Configuration parse() {
if (parsed) {
throw new BuilderException("Each XMLConfigBuilder can only be used once.");
}
parsed = true;
parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration")); // 解析Configuration节点
return configuration;
}
// 解析Configuration节点的具体解析过程
private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) {
try {
// 设置Configuration对象的属性
Properties settings = settingsAsPropertiess(root.evalNode("settings"));
// 设置Configuration对象的variables属性
//issue #117 read properties first
propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties"));
// 设置Configuration对象的vfsImpl属性
loadCustomVfs(settings);
// 注册别名
typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases"));
// 解析插件
pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins"));
// 默认new DefaultObjectFactory()
objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory"));
// 默认new DefaultObjectWrapperFactory()
objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory"));
// 默认new DefaultReflectorFactory()
reflectorFactoryElement(root.evalNode("reflectorFactory"));
// 之前解析了settings标签,现在把结果应用到Configuration对象中去
settingsElement(settings);
// read it after objectFactory and objectWrapperFactory issue #631
environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments"));
databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider"));
typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers"));
mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
}
下面只列一下,可能会用到的标签解析源码
settings标签解析
private Properties settingsAsPropertiess(XNode context) {
if (context == null) {
return new Properties();
}
Properties props = context.getChildrenAsProperties();
// 解析settings标签中的属性,然后查看Configuration类里面有没有这个属性,没有的话,将会报错
// 所以我们就明白了,settings就是用来设置Configuration对象的
// MetaClass这个是Mybatis内部的反射工具,后面再看吧
// Check that all settings are known to the configuration class
MetaClass metaConfig = MetaClass.forClass(Configuration.class, localReflectorFactory);
for (Object key : props.keySet()) {
if (!metaConfig.hasSetter(String.valueOf(key))) {
throw new BuilderException("The setting " + key + " is not known. Make sure you spelled it correctly (case sensitive).");
}
}
return props;
}
解析完settings标签后,使用解析的结果,来设置Configuration对象
private void settingsElement(Properties props) throws Exception {
configuration.setAutoMappingBehavior(AutoMappingBehavior.valueOf(props.getProperty("autoMappingBehavior", "PARTIAL")));
configuration.setAutoMappingUnknownColumnBehavior(AutoMappingUnknownColumnBehavior.valueOf(props.getProperty("autoMappingUnknownColumnBehavior", "NONE")));
// 二级缓存默认是开的
configuration.setCacheEnabled(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("cacheEnabled"), true));
configuration.setProxyFactory((ProxyFactory) createInstance(props.getProperty("proxyFactory")));
// 延迟加载默认关闭
configuration.setLazyLoadingEnabled(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("lazyLoadingEnabled"), false));
configuration.setAggressiveLazyLoading(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("aggressiveLazyLoading"), true));
configuration.setMultipleResultSetsEnabled(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("multipleResultSetsEnabled"), true));
configuration.setUseColumnLabel(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("useColumnLabel"), true));
configuration.setUseGeneratedKeys(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("useGeneratedKeys"), false));
// 默认的执行器类型是simple
configuration.setDefaultExecutorType(ExecutorType.valueOf(props.getProperty("defaultExecutorType", "SIMPLE")));
configuration.setDefaultStatementTimeout(integerValueOf(props.getProperty("defaultStatementTimeout"), null));
configuration.setDefaultFetchSize(integerValueOf(props.getProperty("defaultFetchSize"), null));
// 驼峰映射默认关闭
configuration.setMapUnderscoreToCamelCase(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("mapUnderscoreToCamelCase"), false));
configuration.setSafeRowBoundsEnabled(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("safeRowBoundsEnabled"), false));
// localCacheScope范围是SESSION
configuration.setLocalCacheScope(LocalCacheScope.valueOf(props.getProperty("localCacheScope", "SESSION")));
configuration.setJdbcTypeForNull(JdbcType.valueOf(props.getProperty("jdbcTypeForNull", "OTHER")));
configuration.setLazyLoadTriggerMethods(stringSetValueOf(props.getProperty("lazyLoadTriggerMethods"), "equals,clone,hashCode,toString"));
configuration.setSafeResultHandlerEnabled(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("safeResultHandlerEnabled"), true));
configuration.setDefaultScriptingLanguage(resolveClass(props.getProperty("defaultScriptingLanguage")));
configuration.setCallSettersOnNulls(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("callSettersOnNulls"), false));
configuration.setUseActualParamName(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("useActualParamName"), false));
configuration.setLogPrefix(props.getProperty("logPrefix"));
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Class<? extends Log> logImpl = (Class<? extends Log>)resolveClass(props.getProperty("logImpl"));
configuration.setLogImpl(logImpl);
configuration.setConfigurationFactory(resolveClass(props.getProperty("configurationFactory")));
}
properties标签解析
private void propertiesElement(XNode context) throws Exception {
if (context != null) {
// 从这里我们可以知道,properties标签里面可以嵌套标签,并且properties标签可以有resource或url属性,二者选一
// 它们都会被封装到configuration对象的variables属性里面,并且parser里面也有这些属性的引用
Properties defaults = context.getChildrenAsProperties();
String resource = context.getStringAttribute("resource");
String url = context.getStringAttribute("url");
if (resource != null && url != null) {
throw new BuilderException("The properties element cannot specify both a URL and a resource based property file reference. Please specify one or the other.");
}
if (resource != null) {
defaults.putAll(Resources.getResourceAsProperties(resource));
} else if (url != null) {
defaults.putAll(Resources.getUrlAsProperties(url));
}
Properties vars = configuration.getVariables();
if (vars != null) {
defaults.putAll(vars);
}
parser.setVariables(defaults);
configuration.setVariables(defaults);
}
}
typeAliases标签解析
private void typeAliasesElement(XNode parent) {
if (parent != null) {
for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) {
if ("package".equals(child.getName())) {
String typeAliasPackage = child.getStringAttribute("name");
// 注册到configuration对象的类别名注册中心中去
configuration.getTypeAliasRegistry().registerAliases(typeAliasPackage);
} else {
String alias = child.getStringAttribute("alias");
String type = child.getStringAttribute("type");
try {
Class<?> clazz = Resources.classForName(type);
if (alias == null) {
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias(clazz);
} else {
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias(alias, clazz);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error registering typeAlias for '" + alias + "'. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
}
}
}
plugins标签解析
private void pluginElement(XNode parent) throws Exception {
if (parent != null) {
for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) {
// 拿plugins标签中的interceptor标签
String interceptor = child.getStringAttribute("interceptor");
Properties properties = child.getChildrenAsProperties();
// 看这里,它来解析interceptor别名了,所以现在知道为什么BaseBuilder里面有Configuration对象的别名属性了
// 并且通过反射创建实例,添加到Configuration对象的拦截器链中去
Interceptor interceptorInstance = (Interceptor) resolveClass(interceptor).newInstance();
interceptorInstance.setProperties(properties);
configuration.addInterceptor(interceptorInstance);
}
}
}
environments标签解析
private void environmentsElement(XNode context) throws Exception {
if (context != null) {
if (environment == null) {
// 说明代码里面指定环境的优先级比在xml中指定environment的优先级要搞
environment = context.getStringAttribute("default");
}
for (XNode child : context.getChildren()) {
String id = child.getStringAttribute("id");
// 判断当前的environment标签的id属性是否为指定的环境
if (isSpecifiedEnvironment(id)) {
// 解析environment标签中的transactionManager标签,
// 并且拿到该标签的type属性,创建该TransactionFactory对象(别名)
// 和该标签下的properties标签,并且设置给TransactionFactory对象
// 设置好属性之后返回。
TransactionFactory
txFactory = transactionManagerElement(child.evalNode("transactionManager"));
// 解析environment标签中的dataSource标签,
// 并且拿到该标签的type属性,创建该DataSourceFactory对象(别名)
// 和该标签下的properties标签,并且设置给DataSourceFactory对象
// 设置好属性之后返回。
DataSourceFactory dsFactory = dataSourceElement(child.evalNode("dataSource"));
// 使用上面的数据源工厂获取数据源
DataSource dataSource = dsFactory.getDataSource();
// 设置environment的【事务工厂属性】和【数据源属性】,并且环境有特定的id来标识环境
Environment.Builder environmentBuilder = new Environment.Builder(id)
.transactionFactory(txFactory)
.dataSource(dataSource);
// 把environment对象设置给Configuration
configuration.setEnvironment(environmentBuilder.build());
}
}
}
}
typeHandlers标签解析
private void typeHandlerElement(XNode parent) throws Exception {
if (parent != null) {
for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) {
// 注册整个包
if ("package".equals(child.getName())) {
String typeHandlerPackage = child.getStringAttribute("name");
typeHandlerRegistry.register(typeHandlerPackage);
} else {
// 拿到typeHandler标签的下面三个属性
String javaTypeName = child.getStringAttribute("javaType");
String jdbcTypeName = child.getStringAttribute("jdbcType");
String handlerTypeName = child.getStringAttribute("handler");
Class<?> javaTypeClass = resolveClass(javaTypeName);
JdbcType jdbcType = resolveJdbcType(jdbcTypeName);
Class<?> typeHandlerClass = resolveClass(handlerTypeName);
if (javaTypeClass != null) {
if (jdbcType == null) {
// 会解析typeHandlerClass的@MappedJdbcTypes注解
typeHandlerRegistry.register(javaTypeClass, typeHandlerClass);
} else {
typeHandlerRegistry.register(javaTypeClass, jdbcType, typeHandlerClass);
}
} else {
// 会解析该类的@MappedType注解
typeHandlerRegistry.register(typeHandlerClass);
}
}
}
}
}
mappers标签解析
private void mapperElement(XNode parent) throws Exception {
if (parent != null) {
// 获取到每个子标签,注册mapper
for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) {
if ("package".equals(child.getName())) {
String mapperPackage = child.getStringAttribute("name");
// 使用package标签直接添加整个包
configuration.addMappers(mapperPackage);
} else {
// 解析mapper标签
String resource = child.getStringAttribute("resource");
String url = child.getStringAttribute("url");
String mapperClass = child.getStringAttribute("class");
// resource、url、class三者只能选一个写
// 这也就是说,mybatis提供了3种属性方式往Configuration对象种注册mapper
// url和resource是一样的,class是一种,其实就2种
// 配置文件的形式是使用XMLMapperBuilder来解析的(我们只看这种)
// class的形式是使用MapperAnnotationBuilder来解析的
if (resource != null && url == null && mapperClass == null) {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(resource);
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser
= new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream,
configuration,
resource,
configuration.getSqlFragments());
mapperParser.parse();
} else if (resource == null && url != null && mapperClass == null) {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(url);
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getUrlAsStream(url);
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser
= new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream,
configuration,
url,
configuration.getSqlFragments());
mapperParser.parse();
} else if (resource == null && url == null && mapperClass != null) {
Class<?> mapperInterface = Resources.classForName(mapperClass);
// 直接往Configuration种注册class时,会调用mapperRegistry的addMapper方法来注册
// 并且mapperRegistry会借助MapperAnnotationBuilder把该class解析掉,在这个过程中,把
// 解析的结果给到Configuration(就是解析的每条sql封装成mappedStatement),mapperRegistry
// 存下该class,并且封装该class到new的MapperProxyFactory对象中给到knownMappers属性
configuration.addMapper(mapperInterface);
} else {
throw new BuilderException("A mapper element may only specify a url,
"resource or class, but not more than one.");
}
}
}
}
}
XMLMapperBuilder
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream,
configuration,
resource,
configuration.getSqlFragments());
mapperParser.parse();
上面我们知道了mapperParser.parse()过程的由来,那么现在就是要去解析。解析mapper.xml做的事情和上面贴的Configuration.addMapper(Class)做的事情相同。
即
1.解析mapper.xml中的各种标签添加到Configuration对象中。
2.注册class到Configuration对象的mapperRegistry注册中心中去。
mapperParser.parse()
public class XMLMapperBuilder extends BaseBuilder {
private XPathParser parser;
private MapperBuilderAssistant builderAssistant;
private Map<String, XNode> sqlFragments;
private String resource;
private XMLMapperBuilder(XPathParser parser,
Configuration configuration,
String resource,
Map<String, XNode> sqlFragments) {
super(configuration);
// 这个对象用的很多,继承自BaseBuilder,所以Configuration,typeAliasRegistry,typeHandlerRegistry它都有
// 这个对象贯穿整个mapper的解析过程,封装解析的结果
this.builderAssistant = new MapperBuilderAssistant(configuration, resource);
// Xpath去解析
this.parser = parser;
this.sqlFragments = sqlFragments;
// 解析的mapper文件
this.resource = resource;
}
public void parse() {
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {
// 解析mapper标签,进入
configurationElement(parser.evalNode("/mapper"));
// 标记这个已经载入了
configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);
bindMapperForNamespace();
}
// 解析剩余还没有解析完的元素
parsePendingResultMaps();
parsePendingChacheRefs();
parsePendingStatements();
}
}
MapperBuilderAssistant
我们先看一下这个MapperBuilderAssistant
public class MapperBuilderAssistant extends BaseBuilder {
private String currentNamespace;
private String resource;
private Cache currentCache;
private boolean unresolvedCacheRef; // issue #676
public MapperBuilderAssistant(Configuration configuration, String resource) {
super(configuration);
ErrorContext.instance().resource(resource);
this.resource = resource;
}
}
解析mapper.xml
private void configurationElement(XNode context) {
try {
// 获取命名空间
String namespace = context.getStringAttribute("namespace");
if (namespace == null || namespace.equals("")) {
throw new BuilderException("Mapper's namespace cannot be empty");
}
// 设置当前的命名空间
builderAssistant.setCurrentNamespace(namespace);
// 解析cache-ref
cacheRefElement(context.evalNode("cache-ref"));
// cache标签
cacheElement(context.evalNode("cache"));
parameterMapElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/parameterMap"));
// resultMap标签
resultMapElements(context.evalNodes("/mapper/resultMap"));
// sql标签
sqlElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/sql"));
buildStatementFromContext(context.evalNodes("select|insert|update|delete"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing Mapper XML. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
cache-ref标签解析
private void cacheRefElement(XNode context) {
if (context != null) {
// 当前的mapper的命名空间 —> 引用的缓存命名空间
configuration.addCacheRef(builderAssistant.getCurrentNamespace(),
context.getStringAttribute("namespace"));
CacheRefResolver cacheRefResolver = new CacheRefResolver(builderAssistant,
context.getStringAttribute("namespace"));
try {
// 如果是引用了别的命名空间的二级缓存,那么先看下能不能解析出来,如果能解析出来,那么就使用
cacheRefResolver.resolveCacheRef();
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
configuration.addIncompleteCacheRef(cacheRefResolver);
}
}
}
解析过程
public Cache resolveCacheRef() {
return assistant.useCacheRef(cacheRefNamespace); // 使用引用的缓存
}
public class MapperBuilderAssistant extends BaseBuilder {
private String currentNamespace;
private String resource;
private Cache currentCache; // 保存了二级缓存
public Cache useCacheRef(String namespace) {
if (namespace == null) {
throw new BuilderException("cache-ref element requires a namespace attribute.");
}
try {
unresolvedCacheRef = true;
// 从configuration中根据命名空间去拿缓存对象
Cache cache = configuration.getCache(namespace);
if (cache == null) {
throw new IncompleteElementException("No cache for namespace '"
+ namespace + "' could be found.");
}
currentCache = cache; // 将当前的缓存设置为引用的缓存
unresolvedCacheRef = false;
return cache;
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
throw new IncompleteElementException("No cache for namespace '" + namespace
+ "' could be found.", e);
}
}
}
cache标签解析
private void cacheElement(XNode context) throws Exception {
if (context != null) {
// cache标签中写的使用的缓存实现类(别名)
String type = context.getStringAttribute("type", "PERPETUAL");
Class<? extends Cache> typeClass = typeAliasRegistry.resolveAlias(type);
// 缓存实现类都实现了Cache接口,有些缓存类通过装饰者模式可以一层一层的叠加功能
// 缓存移除策略
String eviction = context.getStringAttribute("eviction", "LRU");
Class<? extends Cache> evictionClass = typeAliasRegistry.resolveAlias(eviction);
Long flushInterval = context.getLongAttribute("flushInterval");
Integer size = context.getIntAttribute("size");
// 只读
boolean readWrite = !context.getBooleanAttribute("readOnly", false);
// 阻塞
boolean blocking = context.getBooleanAttribute("blocking", false);
// 还可以设置属性
Properties props = context.getChildrenAsProperties();
builderAssistant.useNewCache(typeClass,
evictionClass, flushInterval, size, readWrite, blocking, props);
}
}
public Cache useNewCache(Class<? extends Cache> typeClass,
Class<? extends Cache> evictionClass,
Long flushInterval,
Integer size,
boolean readWrite,
boolean blocking,
Properties props) {
Cache cache = new CacheBuilder(currentNamespace) // cache的id
// 缓存默认实现是PerpetualCache,里面是hashmap的实现
.implementation(valueOrDefault(typeClass, PerpetualCache.class))
// 装饰者,使用最近最少使用的移除策略
.addDecorator(valueOrDefault(evictionClass, LruCache.class))
// 清除缓存时间间隔
.clearInterval(flushInterval)
.size(size)
.readWrite(readWrite)
.blocking(blocking)
.properties(props)
.build();
configuration.addCache(cache); // 高速configuration对象, caches.put(cache.getId(), cache);
currentCache = cache; // 设置当前的缓存
return cache;
}
statement标签解析
private void buildStatementFromContext(List<XNode> list, String requiredDatabaseId) {
// 遍历所有的select|insert|update|delete, 并解析
for (XNode context : list) {
final XMLStatementBuilder statementParser = new XMLStatementBuilder(configuration,
builderAssistant,
context,
requiredDatabaseId);
try {
statementParser.parseStatementNode();
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
configuration.addIncompleteStatement(statementParser);
}
}
}
XMLStatementBuilder
public class XMLStatementBuilder extends BaseBuilder {
private MapperBuilderAssistant builderAssistant;
private XNode context;
private String requiredDatabaseId;
public XMLStatementBuilder(Configuration configuration,
MapperBuilderAssistant builderAssistant,
XNode context, String databaseId) {
super(configuration);
this.builderAssistant = builderAssistant;
this.context = context;
this.requiredDatabaseId = databaseId;
}
public void parseStatementNode() {
// id后面会拼上的命名空间
String id = context.getStringAttribute("id");
String databaseId = context.getStringAttribute("databaseId");
if (!databaseIdMatchesCurrent(id, databaseId, this.requiredDatabaseId)) {
return;
}
Integer fetchSize = context.getIntAttribute("fetchSize");
Integer timeout = context.getIntAttribute("timeout");
String parameterMap = context.getStringAttribute("parameterMap");
String parameterType = context.getStringAttribute("parameterType");
Class<?> parameterTypeClass = resolveClass(parameterType);
String resultMap = context.getStringAttribute("resultMap");
String resultType = context.getStringAttribute("resultType");
String lang = context.getStringAttribute("lang");
LanguageDriver langDriver = getLanguageDriver(lang);
Class<?> resultTypeClass = resolveClass(resultType);
String resultSetType = context.getStringAttribute("resultSetType");
// statementType默认是预编译类型
StatementType statementType = StatementType.valueOf(context.getStringAttribute("statementType", StatementType.PREPARED.toString()));
ResultSetType resultSetTypeEnum = resolveResultSetType(resultSetType);
String nodeName = context.getNode().getNodeName();
SqlCommandType sqlCommandType = SqlCommandType.valueOf(nodeName.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH));
boolean isSelect = sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT;
// 默认 select标签的flushCache属性是false, 增删改标签的flushCache属性是true
boolean flushCache = context.getBooleanAttribute("flushCache", !isSelect);
// 默认 select标签useCache属性是true
boolean useCache = context.getBooleanAttribute("useCache", isSelect);
boolean resultOrdered = context.getBooleanAttribute("resultOrdered", false);
// Include Fragments before parsing
XMLIncludeTransformer includeParser = new XMLIncludeTransformer(configuration,
builderAssistant);
includeParser.applyIncludes(context.getNode());
// Parse selectKey after includes and remove them.
processSelectKeyNodes(id, parameterTypeClass, langDriver);
// Parse the SQL (pre: and were parsed and removed)
SqlSource sqlSource = langDriver.createSqlSource(configuration, context, parameterTypeClass);
String resultSets = context.getStringAttribute("resultSets");
String keyProperty = context.getStringAttribute("keyProperty");
String keyColumn = context.getStringAttribute("keyColumn");
KeyGenerator keyGenerator;
String keyStatementId = id + SelectKeyGenerator.SELECT_KEY_SUFFIX;
keyStatementId = builderAssistant.applyCurrentNamespace(keyStatementId, true);
if (configuration.hasKeyGenerator(keyStatementId)) {
keyGenerator = configuration.getKeyGenerator(keyStatementId);
} else {
keyGenerator = context.getBooleanAttribute("useGeneratedKeys",
configuration.isUseGeneratedKeys() &&
SqlCommandType.INSERT.equals(sqlCommandType))
? new Jdbc3KeyGenerator() : new NoKeyGenerator();
}
builderAssistant.addMappedStatement(id, sqlSource, statementType, sqlCommandType,
fetchSize, timeout, parameterMap, parameterTypeClass,
resultMap, resultTypeClass,
resultSetTypeEnum, flushCache, useCache, resultOrdered,
keyGenerator, keyProperty, keyColumn, databaseId,
langDriver, resultSets);
}
}
public class MapperBuilderAssistant extends BaseBuilder {
public MappedStatement addMappedStatement(
String id,
SqlSource sqlSource,
StatementType statementType,
SqlCommandType sqlCommandType,
Integer fetchSize,
Integer timeout,
String parameterMap,
Class<?> parameterType,
String resultMap,
Class<?> resultType,
ResultSetType resultSetType,
boolean flushCache,
boolean useCache,
boolean resultOrdered,
KeyGenerator keyGenerator,
String keyProperty,
String keyColumn,
String databaseId,
LanguageDriver lang,
String resultSets)
{
if (unresolvedCacheRef) {
throw new IncompleteElementException("Cache-ref not yet resolved");
}
id = applyCurrentNamespace(id, false); // id拼接上命名空间
boolean isSelect = sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT;
MappedStatement.Builder statementBuilder = new MappedStatement.Builder(configuration, id,
sqlSource,
sqlCommandType)
.resource(resource)
.fetchSize(fetchSize)
.timeout(timeout)
.statementType(statementType)
.keyGenerator(keyGenerator)
.keyProperty(keyProperty)
.keyColumn(keyColumn)
.databaseId(databaseId)
.lang(lang)
.resultOrdered(resultOrdered)
.resultSets(resultSets)
.resultMaps(getStatementResultMaps(resultMap, resultType, id))
.resultSetType(resultSetType)
.flushCacheRequired(valueOrDefault(flushCache, !isSelect))
.useCache(valueOrDefault(useCache, isSelect))
.cache(currentCache); // 之前解析的cache,将保存在mappedStatement中
ParameterMap statementParameterMap = getStatementParameterMap(parameterMap, parameterType, id);
if (statementParameterMap != null) {
statementBuilder.parameterMap(statementParameterMap);
}
MappedStatement statement = statementBuilder.build();
// 添加到configuration的mappedStatements属性中,key是: 命名空间+id
configuration.addMappedStatement(statement);
return statement;
}
}
绑定Mapper命名空间
在解析完mapper.xml之后,需要把命名空间(接口全类名),添加给Configuration中的MapperRegistry注册中心,这样可以方便通过这个这个接口的全类名与命名空间一致,方法名与id一致,那么就可以使用方法名映射到之前解析的mappedStatement,然后拿到mappedStatement中解析出来的各个属性,并根据方法传过来的参数设置给里面的sql,并且执行,最后封装结果集返回对象,这就是mybatis的大概的一个逻辑。
public class XMLMapperBuilder extends BaseBuilder {
private void bindMapperForNamespace() {
String namespace = builderAssistant.getCurrentNamespace();
if (namespace != null) {
Class<?> boundType = null;
try {
// 根据命名空间反射出Class类
boundType = Resources.classForName(namespace);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
//ignore, bound type is not required
}
if (boundType != null) {
if (!configuration.hasMapper(boundType)) {
// Spring may not know the real resource name so we set a flag
// to prevent loading again this resource from the mapper interface
// look at MapperAnnotationBuilder#loadXmlResource
configuration.addLoadedResource("namespace:" + namespace);
// 调用Configuration的addMapper方法
configuration.addMapper(boundType);
}
}
}
}
}
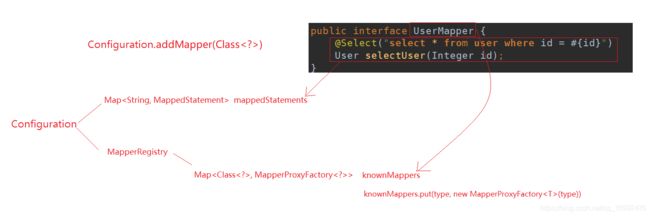
configuration.addMapper
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {
if (type.isInterface()) {
if (hasMapper(type)) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is already known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
boolean loadCompleted = false;
try {
// 这里直接new一个MapperProxyFactory工厂,传进去了接口
// 这个对象将使用jdk动态代理的方式创建接口的代理
knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory<T>(type));
// It's important that the type is added before the parser is run
// otherwise the binding may automatically be attempted by the
// mapper parser. If the type is already known, it won't try.
MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type);
// 使用MapperAnnotationBuilder来解析添加的Class,注解的更多用法看这个类就行了
// 前面已经说过这个方法大概做的事情了,就不看了
parser.parse();
loadCompleted = true;
} finally {
if (!loadCompleted) {
knownMappers.remove(type);
}
}
}
}
SqlSession
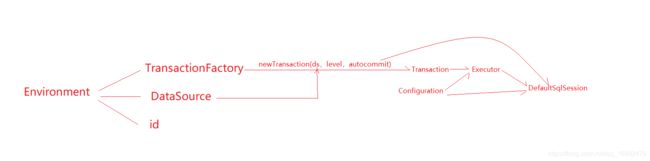
通过上面我们知道了SqlSessionBuilder借助XMLConfigBuilder,解析mybatis核心配置文件,在解析mapper.xml时候,又借助了XMLMapperBuilder,这些配置都设置给了Configuration对象。并且Configuration对象还持有Environment对象,Environment对象里面又有事务工厂和数据源。
sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
我们在获得了sqlSessionFactory,即sqlSession的工厂,那么我们可以使用这个工厂创建SqlSession对象,这也是第二步。
SqlSession openSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
因为我们之前的SqlSessionBuilder使用的是DefaultSqlSessionFactory,所以我们看下这个类
public class DefaultSqlSessionFactory implements SqlSessionFactory {
private final Configuration configuration;
public DefaultSqlSessionFactory(Configuration configuration) {
this.configuration = configuration;
}
// 默认的openSession方法
@Override
public SqlSession openSession() {
// 其实我们在获取SqlSession的时候,还可以指定执行器的类型和隔离级别,以及是否关闭自动提交事务
return openSessionFromDataSource(configuration.getDefaultExecutorType(), null, false);
}
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType,
TransactionIsolationLevel level,
boolean autoCommit) {
Transaction tx = null;
try {
// 从 configuration对象中拿到Environment
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
// 再从拿到的Environment对象中去拿TransactionFactory事务工厂
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory
= getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
// 使用transactionFactory事务工厂对象,根据environment的数据源等参数,创建事务
// TransactionFactory 是个接口,就是用来创建Transaction事务的
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
// 创建的事务对象和执行器类型将传给configuration,使用configuration的newExecutor方法创建执行器
// 为什么要让configuration去创建Executor呢?
// 1.configuration全局配置中有默认执行器类型
// 2.使用CachingExecutor包装executor(如果开启了二级缓存的话)
// 3.可以使用插件拦截executor
// 注意到事务被封装到了executor执行器中,并且Executor接口中有获取Transaction事务的方法
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
// sqlSession中封装了Configuration、executor、autoCommit
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception e) {
closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close()
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
private SqlSession openSessionFromConnection(ExecutorType execType, Connection connection) {
try {
boolean autoCommit;
try {
autoCommit = connection.getAutoCommit();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// Failover to true, as most poor drivers
// or databases won't support transactions
autoCommit = true;
}
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory
= getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
final Transaction tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(connection);
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
}
TransactionFactory
public interface TransactionFactory {
// 设置属性回调
void setProperties(Properties props);
// 都是创建事务的方法
Transaction newTransaction(Connection conn);
Transaction newTransaction(DataSource dataSource,
TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit);
}
Transaction
public interface Transaction {
Connection getConnection() throws SQLException;
void commit() throws SQLException;
void rollback() throws SQLException;
void close() throws SQLException;
Integer getTimeout() throws SQLException;
}
至此SqlSession已经可以获得了,并且里面的执行器也已经有了,那么现在其实就可以执行sql语句了。但是mybatis使用动态代理的方式,让执行sql更加简单。接下来看sqlSession是如何获取到动态代理的。
sqlSession.getMapper(class)
public class DefaultSqlSession implements SqlSession {
private Configuration configuration;
private Executor executor;
private boolean autoCommit;
private boolean dirty;
private List<Cursor<?>> cursorList;
@Override
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type) {
// 我们之前往configuration中addMapper,现在终于getMapper了
// 还有一点是关键, 当前的sqlSession对象的this引用也传过去了
return configuration.<T>getMapper(type, this);
}
}
public class Configuration {
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
// 同样是从注册中心里面去获取,
// 我们应该记得addMapper的时候,往mapperRegistry里面扔进去了一个class,和对应的MapperProxyFactory对象
// 所以这里拿的就是MapperProxyFactory对象
return mapperRegistry.getMapper(type, sqlSession);
}
}
MapperRegistry
public class MapperRegistry {
private final Configuration config;
private final Map<Class<?>, MapperProxyFactory<?>> knownMappers
= new HashMap<Class<?>, MapperProxyFactory<?>>();
public MapperRegistry(Configuration config) {
this.config = config;
}
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
// 拿到之前放进去的mapperProxyFactory对象
final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory
= (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type);
if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
try {
// sqlSession也传递进去了,并且调用mapperProxyFactory对象的newInstance方法
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {
if (type.isInterface()) {
if (hasMapper(type)) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type
+ " is already known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
boolean loadCompleted = false;
try {
knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory<T>(type));
// It's important that the type is added before the parser is run
// otherwise the binding may automatically be attempted by the
// mapper parser. If the type is already known, it won't try.
MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type);
parser.parse();
loadCompleted = true;
} finally {
if (!loadCompleted) {
knownMappers.remove(type);
}
}
}
}
}
MapperProxyFactory
public class MapperProxyFactory<T> {
private final Class<T> mapperInterface;
private final Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache
= new ConcurrentHashMap<Method, MapperMethod>();
public MapperProxyFactory(Class<T> mapperInterface) {
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
}
public Class<T> getMapperInterface() {
return mapperInterface;
}
public Map<Method, MapperMethod> getMethodCache() {
return methodCache;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(),
new Class[] { mapperInterface },
mapperProxy);
}
// 先调用这个方法
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
// 这个就是InvocationHandler, 并且sqlSession就封装在这个invocationHandler里面
final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<T>(sqlSession,
// mapper接口
mapperInterface,
// 这个直接拿的Factory对象里面的
methodCache);
return newInstance(mapperProxy);
}
}
MapperProxy
jdk动态代理的关键就是invocationHandler的invoke方法,可以看下
public class MapperProxy<T> implements InvocationHandler, Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -6424540398559729838L;
private final SqlSession sqlSession;
private final Class<T> mapperInterface;
// 已经解析的方法,就缓存起来,下次同样的方法来了,就不用解析了
private final Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache;
public MapperProxy(SqlSession sqlSession,
Class<T> mapperInterface,
Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache) {
this.sqlSession = sqlSession;
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
this.methodCache = methodCache;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
// 声明在Object中的方法,直接调用
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
try {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
}
// 非Object中的方法,也就是接口中的方法, 解析当前当前调用的方法,封装成MapperMethod,并且缓存起来
final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);
// 执行(需要传入sqlSession)
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
private MapperMethod cachedMapperMethod(Method method) {
MapperMethod mapperMethod = methodCache.get(method);
if (mapperMethod == null) {
// 进去这个new方法,可以看到
mapperMethod = new MapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration());
methodCache.put(method, mapperMethod);
}
return mapperMethod;
}
}
MapperMethod
上面看到执行使用的是MapperMethod对象,并且传入了一个sqlSession。实际上执行靠的是SqlSession。
MapperMethod封装的是当前被调用的接口方法的信息封装,并且封装在其中的SqlCommand属性和MethodSignature属性里。
public class MapperMethod {
private final SqlCommand command;
private final MethodSignature method;
public MapperMethod(Class<?> mapperInterface, Method method, Configuration config) {
this.command = new SqlCommand(config, mapperInterface, method);
this.method = new MethodSignature(config, mapperInterface, method);
}
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
// 根据sql命令的类型来
switch (command.getType()) {
case INSERT: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case UPDATE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case DELETE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case SELECT:
if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {
executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
result = null;
} else if (method.returnsMany()) {
result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsMap()) {
result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsCursor()) {
result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);
} else {
// 将传过来的args参数使用参数解析器解析
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
// 调用sqlSession的selectOne方法, SqlSession就是个门面
result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
}
break;
case FLUSH:
result = sqlSession.flushStatements();
break;
default:
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());
}
if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) {
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName()
+ " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive
"return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ").");
}
return result;
}
public static class SqlCommand {
private final String name; // mappedStatement的id
private final SqlCommandType type; // sql命令的类型
public SqlCommand(Configuration configuration, Class<?> mapperInterface, Method method) {
// 执行还是mapper接口的全类名加上方法的名字
String statementName = mapperInterface.getName() + "." + method.getName();
MappedStatement ms = null;
// 判断configuration对象中是否有该statement
if (configuration.hasStatement(statementName)) {
ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statementName);
} else if (!mapperInterface.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) { // issue #35
// 根据方法声明所在类的类名去找
String parentStatementName = method.getDeclaringClass().getName() + "."
+ method.getName();
if (configuration.hasStatement(parentStatementName)) {
ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(parentStatementName);
}
}
if (ms == null) {
// 没有找到,除非你是flush
if(method.getAnnotation(Flush.class) != null){
name = null;
type = SqlCommandType.FLUSH;
} else {
// 这个异常反正我是见过了
throw new BindingException("Invalid bound statement (not found): "
+ statementName);
}
} else {
// 设置属性
name = ms.getId();
type = ms.getSqlCommandType();
if (type == SqlCommandType.UNKNOWN) {
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + name);
}
}
}
}
// 就是拿到方法签名,然后解析
public static class MethodSignature {
private final boolean returnsMany;
private final boolean returnsMap;
private final boolean returnsVoid;
private final boolean returnsCursor;
private final Class<?> returnType;
// 可以使用@MapKey注解
private final String mapKey;
private final Integer resultHandlerIndex;
private final Integer rowBoundsIndex;
private final ParamNameResolver paramNameResolver;
public MethodSignature(Configuration configuration, Class<?> mapperInterface, Method method) {
Type resolvedReturnType = TypeParameterResolver.resolveReturnType(method, mapperInterface);
if (resolvedReturnType instanceof Class<?>) {
this.returnType = (Class<?>) resolvedReturnType;
} else if (resolvedReturnType instanceof ParameterizedType) {
this.returnType = (Class<?>) ((ParameterizedType) resolvedReturnType).getRawType();
} else {
this.returnType = method.getReturnType();
}
this.returnsVoid = void.class.equals(this.returnType);
this.returnsMany = (configuration.getObjectFactory().isCollection(this.returnType)
|| this.returnType.isArray());
this.returnsCursor = Cursor.class.equals(this.returnType);
// 获取方法上的@MapKey注解
this.mapKey = getMapKey(method);
this.returnsMap = (this.mapKey != null);
this.rowBoundsIndex = getUniqueParamIndex(method, RowBounds.class);
this.resultHandlerIndex = getUniqueParamIndex(method, ResultHandler.class);
// 参数解析器,解析@Param注解的,没有写的话就是param1,param2...
this.paramNameResolver = new ParamNameResolver(configuration, method);
}
private String getMapKey(Method method) {
String mapKey = null;
// 返回值必须是Map类型
if (Map.class.isAssignableFrom(method.getReturnType())) {
// 获取@MapKey注解
final MapKey mapKeyAnnotation = method.getAnnotation(MapKey.class);
if (mapKeyAnnotation != null) {
mapKey = mapKeyAnnotation.value();
}
}
return mapKey;
}
}
}
ParamNameResovler
public class ParamNameResolver {
private static final String GENERIC_NAME_PREFIX = "param";
private static final String PARAMETER_CLASS = "java.lang.reflect.Parameter";
private static Method GET_NAME = null;
private static Method GET_PARAMS = null;
static {
try {
Class<?> paramClass = Resources.classForName(PARAMETER_CLASS);
GET_NAME = paramClass.getMethod("getName");
GET_PARAMS = Method.class.getMethod("getParameters");
} catch (Exception e) {
// ignore
}
}
private final SortedMap<Integer, String> names;
private boolean hasParamAnnotation;
// 在构造方法里就开始解析@Param注解了
public ParamNameResolver(Configuration config, Method method) {
final Class<?>[] paramTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
final Annotation[][] paramAnnotations = method.getParameterAnnotations();
final SortedMap<Integer, String> map = new TreeMap<Integer, String>();
int paramCount = paramAnnotations.length;
// get names from @Param annotations
for (int paramIndex = 0; paramIndex < paramCount; paramIndex++) {
// RowBounds or ResultHandler 是特殊的参数,需要跳过
if (isSpecialParameter(paramTypes[paramIndex])) {
// skip special parameters
continue;
}
String name = null;
for (Annotation annotation : paramAnnotations[paramIndex]) {
if (annotation instanceof Param) {
// 有@Param注解,那么就获取它
hasParamAnnotation = true;
name = ((Param) annotation).value();
break;
}
}
// 但是@Param注解里面没有写值
if (name == null) {
// @Param was not specified.
// 根据Configuratino对象判断是否要获取实际的参数名字(一般获取不到)
if (config.isUseActualParamName()) {
name = getActualParamName(method, paramIndex);
}
if (name == null) {
// use the parameter index as the name ("0", "1", ...)
// gcode issue #71
name = String.valueOf(map.size()); // 这里就是直接拿的map的大小递增的字符串形式
}
}
map.put(paramIndex, name);
}
names = Collections.unmodifiableSortedMap(map); // 放到names里面
}
private String getActualParamName(Method method, int paramIndex) {
if (GET_PARAMS == null) {
return null;
}
try {
Object[] params = (Object[]) GET_PARAMS.invoke(method);
return (String) GET_NAME.invoke(params[paramIndex]);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new ReflectionException("Error occurred when invoking Method#getParameters().", e);
}
}
private static boolean isSpecialParameter(Class<?> clazz) {
return RowBounds.class.isAssignableFrom(clazz) || ResultHandler.class.isAssignableFrom(clazz);
}
public Object getNamedParams(Object[] args) {
final int paramCount = names.size();
if (args == null || paramCount == 0) {
return null;
} else if (!hasParamAnnotation && paramCount == 1) {
return args[names.firstKey()];
} else {
final Map<String, Object> param = new ParamMap<Object>();
int i = 0;
for (Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry : names.entrySet()) {
param.put(entry.getValue(), args[entry.getKey()]);
// add generic param names (param1, param2, ...)
// GENERIC_NAME_PREFIX就是常量param
final String genericParamName = GENERIC_NAME_PREFIX + String.valueOf(i + 1);
// ensure not to overwrite parameter named with @Param
if (!names.containsValue(genericParamName)) {
param.put(genericParamName, args[entry.getKey()]);
}
i++;
}
return param; // 多个参数将会返回map, 如果参数本身就是map的话,那么进入上面的这个分支也是返回map
}
}
}
看完上面,我们基本上就知道了mapper代理的作用,它其实就是为了方便调用方法的,实际上还是得看sqlSession的。所以前面的动态代理就是为了能够拿到调用方法对应的【mappedStatement的id】和【param】参数。
我们其实也可以这样去调用。
@Test
public void test01() throws IOException {
// 1、获取sqlSessionFactory对象
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = getSqlSessionFactory();
// 2、获取sqlSession对象
SqlSession openSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
try {
// 3、获取接口的实现类对象
//会为接口自动的创建一个代理对象,代理对象去执行增删改查方法
// EmployeeMapper mapper = openSession.getMapper(EmployeeMapper.class);
// Employee employee = mapper.getEmpById(1);
HashMap map = new HashMap();
map.put("id", 1);
Employee employee1 = openSession.selectOne("com.atguigu.mybatis.dao."+
"EmployeeMapper.getEmpById", map);
Employee employee2 = openSession.selectOne("com.atguigu.mybatis.dao."+
"EmployeeMapper.getEmpById", 1);
System.out.println(employee1);
System.out.println(employee2);
} finally {
openSession.close();
}
}
sqlSession.selectOne
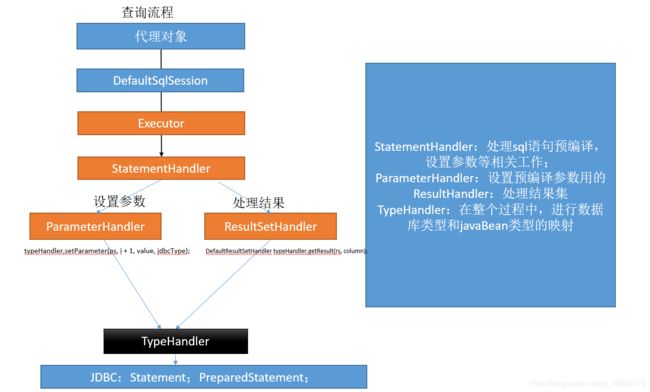
先对整个流程有个总览
接下来我们看这句
result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
查单个,其实就是查list,然后取第一个
public class DefaultSqlSession implements SqlSession {
// statement就是namespace+methodName; parameter如果是多个的话,就是Map类型的参数
@Override
public <T> T selectOne(String statement, Object parameter) {
// Popular vote was to return null on 0 results and throw exception on too many.
List<T> list = this.<T>selectList(statement, parameter);
if (list.size() == 1) {
return list.get(0);
} else if (list.size() > 1) {
throw new TooManyResultsException("Expected one result (or null) to be returned
"by selectOne(), but found: " + list.size());
} else {
return null;
}
}
@Override
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) {
try {
// 从Configuration对象中拿到MappedStatement对象
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
// 使用执行器来执行sql,
// 并且前面我们看到在创建执行器的时候是根据Configuration的可配置项类型创建的
return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds,Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
}
CachingExecutor
public class CachingExecutor implements Executor {
// 被包装的执行器
private Executor delegate;
// 事务缓存管理器,里面维护了一个Map transactionalCaches
// 其中键就是ms的cache(即二级缓存),
// 值为TransactionCache封装了ms的cache
private TransactionalCacheManager tcm = new TransactionalCacheManager();
// 唯一构造方法
public CachingExecutor(Executor delegate) {
this.delegate = delegate;
delegate.setExecutorWrapper(this);
}
@Override
public Transaction getTransaction() {
return delegate.getTransaction();
}
@Override
public boolean isClosed() {
return delegate.isClosed();
}
@Override
public int update(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject) throws SQLException {
// 这里就根据ms的配置的flushCache属性来决定是否要清空二级缓存了
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
return delegate.update(ms, parameterObject);
}
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject,
RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, boundSql);
return query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject,
RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key,
BoundSql boundSql)
throws SQLException {
// 先拿二级缓存
Cache cache = ms.getCache();
if (cache != null) {
// 如果拿到了二级缓存进去
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
// 判断是否使用缓存,就是ms的useCache属性
if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) {
// 有输出参数的,不支持缓存查询
ensureNoOutParams(ms, parameterObject, boundSql);
// 从事务缓存管理器中,根据cache去拿TransactionCache(TransactionCache包装了cache),
// 然后根据key到TransactionCache中去拿
// 这个去TransactionCache中拿的过程有个控制
List<E> list = (List<E>) tcm.getObject(cache, key);
if (list == null) {
// 执行查询
list = delegate.<E> query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds,
resultHandler, key, boundSql);
// 查询过后,放入事务缓存管理器的事务缓存TransactionCache中,还未真正的放入二级缓存
// 要等到事务缓存管理器调用commit()方法时,才会把事务缓存中数据放入到二级缓存中
// 反之,如果事务缓存管理器调用rollback()方法,还未放入二级缓存中的缓存就被清理掉
// 所以,需要CachingExecutor调用commit方法或者close方法
tcm.putObject(cache, key, list); // issue #578 and #116
}
return list;
}
}
// 不使用二级缓存的查询
return delegate.<E> query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
@Override
public void commit(boolean required) throws SQLException {
delegate.commit(required);
tcm.commit();
}
@Override
public void close(boolean forceRollback) {
try {
//issues #499, #524 and #573
if (forceRollback) {
tcm.rollback();
} else {
tcm.commit();
}
} finally {
delegate.close(forceRollback);
}
}
@Override
public void rollback(boolean required) throws SQLException {
try {
delegate.rollback(required);
} finally {
if (required) {
tcm.rollback();
}
}
}
@Override
public List<BatchResult> flushStatements() throws SQLException {
return delegate.flushStatements();
}
@Override
public CacheKey createCacheKey(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject,
RowBounds rowBounds, BoundSql boundSql) {
return delegate.createCacheKey(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, boundSql);
}
@Override
public void clearLocalCache() {
delegate.clearLocalCache();
}
private void flushCacheIfRequired(MappedStatement ms) {
Cache cache = ms.getCache();
if (cache != null && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) {
tcm.clear(cache);
}
}
}
BaseExecutor
public abstract class BaseExecutor implements Executor {
private static final Log log = LogFactory.getLog(BaseExecutor.class);
protected Transaction transaction; // 事务
protected Executor wrapper;
protected ConcurrentLinkedQueue<DeferredLoad> deferredLoads;
protected PerpetualCache localCache; // 本地一级缓存
protected PerpetualCache localOutputParameterCache;
protected Configuration configuration;
protected int queryStack = 0;
private boolean closed;
protected BaseExecutor(Configuration configuration, Transaction transaction) {
this.transaction = transaction;
this.deferredLoads = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<DeferredLoad>();
// 一级缓存默认时localCache
this.localCache = new PerpetualCache("LocalCache");
this.localOutputParameterCache = new PerpetualCache("LocalOutputParameterCache");
this.closed = false;
this.configuration = configuration;
this.wrapper = this;
}
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter,
RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler,
CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource())
.activity("executing a query").object(ms.getId());
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
// ms的flushCache属性
if (queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) {
clearLocalCache();
}
List<E> list;
try {
queryStack++;
// 去本地一级缓存中去拿
list = resultHandler == null ? (List<E>) localCache.getObject(key) : null;
if (list != null) {
handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql);
} else {
// 没拿到
list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
} finally {
queryStack--;
}
if (queryStack == 0) {
for (DeferredLoad deferredLoad : deferredLoads) {
deferredLoad.load();
}
// issue #601
deferredLoads.clear();
if (configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) {
// issue #482
clearLocalCache();
}
}
return list;
}
@Override
public void close(boolean forceRollback) {
try {
try {
rollback(forceRollback);
} finally {
if (transaction != null) {
transaction.close();
}
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
// Ignore. There's nothing that can be done at this point.
log.warn("Unexpected exception on closing transaction. Cause: " + e);
} finally {
transaction = null;
deferredLoads = null;
localCache = null;
localOutputParameterCache = null;
closed = true;
}
}
@Override
public void clearLocalCache() {
if (!closed) {
localCache.clear(); // 清空缓存
localOutputParameterCache.clear();
}
}
@Override
public void commit(boolean required) throws SQLException {
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Cannot commit, transaction is already closed");
}
clearLocalCache(); // 清空缓存
flushStatements();
if (required) {
transaction.commit();
}
}
@Override
public void rollback(boolean required) throws SQLException {
if (!closed) {
try {
clearLocalCache(); // 清空缓存
flushStatements(true);
} finally {
if (required) {
transaction.rollback();
}
}
}
}
protected abstract int doUpdate(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException;
protected abstract List<BatchResult> doFlushStatements(boolean isRollback) throws SQLException;
// 实际查询,由具体的执行器类型决定
protected abstract <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter,
RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler,
BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException;
protected abstract <E> Cursor<E> doQueryCursor(MappedStatement ms,
Object parameter,
RowBounds rowBounds,
BoundSql boundSql)throws SQLException;
}
queryFromDatabase
private <E> List<E> queryFromDatabase(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter,
RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key,
BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
List<E> list;
// 占位
localCache.putObject(key, EXECUTION_PLACEHOLDER);
try {
list = doQuery(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
} finally {
localCache.removeObject(key);
}
// 放入一级缓存
localCache.putObject(key, list);
// 调用存储过程,才放入localOutputParameterCache缓存中
if (ms.getStatementType() == StatementType.CALLABLE) {
localOutputParameterCache.putObject(key, parameter);
}
return list;
}
SimpleExecutor
一共有3种执行器,ReuseExecutor(存储预编译好的sql)、BatchExecutor(批量操作)、SimpleExecutor,那么就看下SimpleExecutor的实现
StatementHandler
@Override
public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
try {
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
// 使用Configuration去创建第二大对象StatementHandler
// 这里会根据ms的statementType类型判断,去创建
// SimpleStatementHandler、
// PreparedStatementHandler、(默认时预编译的statement)
// CallableStatementHandler
// 并且由RoutingStatementHandler包装。
//
// 除此之外, StatemntHandler创建的同时,还会创建【DefaultParameterHandler】对象
// 和【DefaultResultSetHandler】对象
// 并且把它们设置给DefaultStatementHandler中的属性
//
// 然后还会继续走拦截器,插件模式
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter,
rowBounds, resultHandler,
boundSql);
// 使用StatementHandler对象预编译Statement,并且借助ParameterHandler设置参数
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
// 设置完参数之后,执行stmt, 并且借助ResultSetHandler处理结果集,
// 下面我们继续以PreparedStatementHandler种的实现为例
return handler.<E>query(stmt, resultHandler);
} finally {
closeStatement(stmt);
}
private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler,
Log statementLog) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt;
// 看是否要将connection包装成动态代理
Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog);
// statementHandler使用connection预编译statement(connection.preparedStatement)
stmt = handler.prepare(connection, transaction.getTimeout());
// 使用StatementHandler给stmt设置参数,其中借助的就是ParameterHandler做的
handler.parameterize(stmt);
return stmt;
}
protected Connection getConnection(Log statementLog) throws SQLException {
Connection connection = transaction.getConnection();
// 如果statementLog开启了,那么使用动态代理把connection包一层
// ,invocationHandler是ConnectionLogger,预编译打印的Preparing:就是在这个类里面打印的
if (statementLog.isDebugEnabled()) {
return ConnectionLogger.newInstance(connection, statementLog, queryStack);
} else {
return connection;
}
}
}
ParameterHandler
public class DefaultParameterHandler implements ParameterHandler {
private final TypeHandlerRegistry typeHandlerRegistry;
private final MappedStatement mappedStatement;
private final Object parameterObject;
private BoundSql boundSql;
private Configuration configuration;
public DefaultParameterHandler(MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject,
BoundSql boundSql) {
this.mappedStatement = mappedStatement;
this.configuration = mappedStatement.getConfiguration();
this.typeHandlerRegistry = mappedStatement.getConfiguration().getTypeHandlerRegistry();
this.parameterObject = parameterObject;
this.boundSql = boundSql;
}
@Override
public void setParameters(PreparedStatement ps) {
ErrorContext.instance().activity("setting parameters")
.object(mappedStatement.getParameterMap()
.getId());
List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings();
if (parameterMappings != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < parameterMappings.size(); i++) {
// 拿到sql中需要设置的每个参数的信息,就是#{..}里面填的信息的封装
ParameterMapping parameterMapping = parameterMappings.get(i);
if (parameterMapping.getMode() != ParameterMode.OUT) {
Object value;
String propertyName = parameterMapping.getProperty();
if (boundSql.hasAdditionalParameter(propertyName)) {
value = boundSql.getAdditionalParameter(propertyName);
} else if (parameterObject == null) {
value = null;
} else if (typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(parameterObject.getClass())) {
// 查看类型转换器中是否有参数类型相关的类型转换器
// 既然有相关类型的转换器, 那么就不慌了, 直接就拿parameterObject当value
// 因为mybatis知道这种参数类型可以转换了
value = parameterObject;
} else {
// 如果没有对应的类型转换器,那么mybatis就会使用自己的反射工具直接从参数对象中
// 根据属性名字拿到value值
MetaObject metaObject = configuration.newMetaObject(parameterObject);
value = metaObject.getValue(propertyName);
}
// 先去看下用户有没有指定类型转化器typeHandler,
// 如果有, 那么就拿用户指定的;
// 如果没有,那就是默认的UnknowTypeHandler,它里面封装了去类型转换中心去拿转换器的逻辑
TypeHandler typeHandler = parameterMapping.getTypeHandler();
JdbcType jdbcType = parameterMapping.getJdbcType();
if (value == null && jdbcType == null) {
jdbcType = configuration.getJdbcTypeForNull();
}
try {
// 使用typeHandler设置参数, 这里我们可以配置给mybatis
typeHandler.setParameter(ps, i + 1, value, jdbcType);
} catch (TypeException e) {
throw new TypeException("Could not set parameters for mapping: "
+ parameterMapping + ". Cause: " + e, e);
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new TypeException("Could not set parameters for mapping: "
+ parameterMapping + ". Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
}
}
}
}
ResultSetHandler
public class PreparedStatementHandler{
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(Statement statement, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
PreparedStatement ps = (PreparedStatement) statement;
ps.execute();
// 执行完预编译的statement,使用StatementHandler中的resultSetHandler属性处理结果集
return resultSetHandler.<E> handleResultSets(ps);
}
}
public class DefaultResultSetHandler implements ResultSetHandler {
@Override
public List<Object> handleResultSets(Statement stmt) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().activity("handling results").object(mappedStatement.getId());
// 这里是直接new了一个list出来,所以返回的list不可能是null
final List<Object> multipleResults = new ArrayList<Object>();
int resultSetCount = 0;
ResultSetWrapper rsw = getFirstResultSet(stmt);
List<ResultMap> resultMaps = mappedStatement.getResultMaps();
int resultMapCount = resultMaps.size();
validateResultMapsCount(rsw, resultMapCount);
while (rsw != null && resultMapCount > resultSetCount) {
ResultMap resultMap = resultMaps.get(resultSetCount);
// 处理结果集
handleResultSet(rsw, resultMap, multipleResults, null);
rsw = getNextResultSet(stmt);
cleanUpAfterHandlingResultSet();
resultSetCount++;
}
String[] resultSets = mappedStatement.getResultSets();
if (resultSets != null) {
while (rsw != null && resultSetCount < resultSets.length) {
ResultMapping parentMapping = nextResultMaps.get(resultSets[resultSetCount]);
if (parentMapping != null) {
String nestedResultMapId = parentMapping.getNestedResultMapId();
ResultMap resultMap = configuration.getResultMap(nestedResultMapId);
handleResultSet(rsw, resultMap, null, parentMapping);
}
rsw = getNextResultSet(stmt);
cleanUpAfterHandlingResultSet();
resultSetCount++;
}
}
return collapseSingleResultList(multipleResults);
}
private void handleResultSet(ResultSetWrapper rsw, ResultMap resultMap,
List<Object> multipleResults,
ResultMapping parentMapping) throws SQLException {
try {
if (parentMapping != null) {
handleRowValues(rsw, resultMap, null, RowBounds.DEFAULT, parentMapping);
} else {
if (resultHandler == null) {
// 结果会被封装在这个对象里面
DefaultResultHandler defaultResultHandler
= new DefaultResultHandler(objectFactory);
// 处理每行数据
handleRowValues(rsw, resultMap, defaultResultHandler, rowBounds, null);
// 将resultHandler中的对象给到multipleResults中去
multipleResults.add(defaultResultHandler.getResultList());
} else {
handleRowValues(rsw, resultMap, resultHandler, rowBounds, null);
}
}
} finally {
// issue #228 (close resultsets)
closeResultSet(rsw.getResultSet());
}
}
public void handleRowValues(ResultSetWrapper rsw, ResultMap resultMap,
ResultHandler<?> resultHandler, RowBounds rowBounds,
ResultMapping parentMapping) throws SQLException {
if (resultMap.hasNestedResultMaps()) {
ensureNoRowBounds();
checkResultHandler();
handleRowValuesForNestedResultMap(rsw, resultMap, resultHandler, rowBounds, parentMapping);
} else {
// 处理数据,数据到了resultHanlder中
handleRowValuesForSimpleResultMap(rsw, resultMap, resultHandler, rowBounds, parentMapping);
}
}
private void handleRowValuesForSimpleResultMap(ResultSetWrapper rsw, ResultMap resultMap,
ResultHandler<?> resultHandler, RowBounds rowBounds,
ResultMapping parentMapping) throws SQLException {
DefaultResultContext<Object> resultContext = new DefaultResultContext<Object>();
skipRows(rsw.getResultSet(), rowBounds);
// 逐行解析
while (shouldProcessMoreRows(resultContext, rowBounds) && rsw.getResultSet().next()) {
ResultMap discriminatedResultMap = resolveDiscriminatedResultMap(rsw.getResultSet(),
resultMap, null);
// 获取单行的结果
Object rowValue = getRowValue(rsw, discriminatedResultMap);
// rowValue保存了结果对象,先放到resultContext,然后resultHandler从resultContext中获取到
storeObject(resultHandler, resultContext, rowValue, parentMapping, rsw.getResultSet());
}
}
private Object getRowValue(ResultSetWrapper rsw, ResultMap resultMap) throws SQLException {
final ResultLoaderMap lazyLoader = new ResultLoaderMap();
// 创建一个属性都为空的对象, 但是如果这里有懒加载的情况,就会创建一个代理出来
Object resultObject = createResultObject(rsw, resultMap, lazyLoader, null);
if (resultObject != null && !hasTypeHandlerForResultObject(rsw, resultMap.getType())) {
final MetaObject metaObject = configuration.newMetaObject(resultObject);
boolean foundValues = !resultMap.getConstructorResultMappings().isEmpty();
if (shouldApplyAutomaticMappings(resultMap, false)) {
// 给属性都为空的对象设置值
foundValues = applyAutomaticMappings(rsw, resultMap, metaObject, null) || foundValues;
}
foundValues = applyPropertyMappings(rsw, resultMap, metaObject, lazyLoader, null)
|| foundValues;
foundValues = lazyLoader.size() > 0 || foundValues;
resultObject = foundValues ? resultObject : null;
return resultObject;
}
return resultObject;
}
private Object createResultObject(ResultSetWrapper rsw, ResultMap resultMap,
ResultLoaderMap lazyLoader,
String columnPrefix) throws SQLException {
final List<Class<?>> constructorArgTypes = new ArrayList<Class<?>>();
final List<Object> constructorArgs = new ArrayList<Object>();
// 创建目标对象
final Object resultObject = createResultObject(rsw, resultMap, constructorArgTypes,
constructorArgs, columnPrefix);
if (resultObject != null && !hasTypeHandlerForResultObject(rsw, resultMap.getType())) {
final List<ResultMapping> propertyMappings = resultMap.getPropertyResultMappings();
for (ResultMapping propertyMapping : propertyMappings) {
// issue gcode #109 && issue #149
// 如果有延迟加载, 就创建代理并返回
if (propertyMapping.getNestedQueryId() != null && propertyMapping.isLazy()) {
return configuration.getProxyFactory().createProxy(resultObject, lazyLoader,
configuration, objectFactory,
constructorArgTypes,
constructorArgs);
}
}
}
return resultObject;
}
private boolean applyAutomaticMappings(ResultSetWrapper rsw, ResultMap resultMap,
MetaObject metaObject,
String columnPrefix) throws SQLException {
List<UnMappedColumnAutoMapping> autoMapping = createAutomaticMappings(rsw, resultMap,
metaObject,columnPrefix);
boolean foundValues = false;
if (autoMapping.size() > 0) {
for (UnMappedColumnAutoMapping mapping : autoMapping) {
// 使用typeHandler类型转换器将数据库中的数据值转为java属性值
final Object value = mapping.typeHandler.getResult(rsw.getResultSet(), mapping.column);
if (value != null) {
foundValues = true;
}
if (value != null || (configuration.isCallSettersOnNulls() && !mapping.primitive)) {
// gcode issue #377, call setter on nulls (value is not 'found')
// mybatis的反射工具, 设置值
metaObject.setValue(mapping.property, value);
}
}
}
return foundValues;
}
}
Plugin插件机制
mybatis执行流程
在说mybatis的插件机制前,先大概回顾下mybatis的运行过程。mybatis使用sqlSession作为门面,封装各大对象的功能暴露接口给外界调用。而且这几个重要对象的创建过程都是在Configuration类中。
执行sql语句,靠的就是Executor执行器对象。执行器又分3种ReuseExecutor、BatchExecutor、BaseExecutor(默认),由Configuration对象的defaultExecutorType属性指定。
执行器单独不能完成功能,它执行的流程中会使用configuration对象去创建StatementHandler对象,StatementHandler对象又分为SimpleStatementHandler、PreparedStatementHandler(默认),CallableStatementHandler,由ms的statementType决定,默认是PREPARED。
在创建statementHandler对象的构造方法里,又会同时创建DefaultParameterHandler对象和DefaultResultSetHandler对象(这两个对象的也都是使用configuration对象创建的),并且设置到statementHandler对象中。Executor执行器在创建完这些对象之后,使用statementHandler对象预编译sql语句。预编译sql需要Connection对象,Executor执行器从事务对象Transaction中拿到连接。执行器还是借助statementHandler完成预编译stmt和设置参数,而设置参数这件事则是statementHandler借助parameterHandler来完成的。
接着Executor执行器继续借助statementHandler对象执行statement并返回执行结果,而statementHandler则是自己使用resultSetHandler处理结果集来完成功能的。
四大对象
上面说到了四大对象的创建,而且这四大对象的创建都是在Configuration类中创建的,而且同时它们的创建过程都有类似的代码,可以植入插件。
public class Configuration{
// 这个拦截器链中封装了List interceptors, 那么我们得看一下这个Interceptor接口了
protected final InterceptorChain interceptorChain = new InterceptorChain();
// ParameterHandler
public ParameterHandler newParameterHandler(MappedStatement mappedStatement,
Object parameterObject, BoundSql boundSql) {
ParameterHandler parameterHandler = mappedStatement.getLang()
.createParameterHandler(mappedStatement,
parameterObject,
boundSql);
// 拦截
parameterHandler = (ParameterHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(parameterHandler);
return parameterHandler;
}
// ResultSetHandler
public ResultSetHandler newResultSetHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement,
RowBounds rowBounds, ParameterHandler parameterHandler,
ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
ResultSetHandler resultSetHandler = new DefaultResultSetHandler(executor, mappedStatement,
parameterHandler,
resultHandler, boundSql,
rowBounds);
// 拦截
resultSetHandler = (ResultSetHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(resultSetHandler);
return resultSetHandler;
}
// StatementHandler
public StatementHandler newStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement,
Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds,
ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
StatementHandler statementHandler = new RoutingStatementHandler(executor,
mappedStatement,
parameterObject, rowBounds,
resultHandler, boundSql);
// 拦截
statementHandler = (StatementHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(statementHandler);
return statementHandler;
}
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction) {
return newExecutor(transaction, defaultExecutorType);
}
// Executor
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
Executor executor;
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
if (cacheEnabled) {
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
// 拦截
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
}
}
InterceptorChain
public class InterceptorChain {
private final List<Interceptor> interceptors = new ArrayList<Interceptor>();
public Object pluginAll(Object target) {
// 挨个去包装
for (Interceptor interceptor : interceptors) {
target = interceptor.plugin(target);
}
return target;
}
public void addInterceptor(Interceptor interceptor) {
interceptors.add(interceptor);
}
public List<Interceptor> getInterceptors() {
return Collections.unmodifiableList(interceptors);
}
}
public interface Interceptor {
Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable;
// 传进去一个对象,返回一个对象。很像spring的BeanPostProcessor的接口。
// 那么就可以就可以在这里返回的时候搞事情了
Object plugin(Object target);
void setProperties(Properties properties);
}
public class Invocation {
// 我们只要知道method.invoke(target),那么这个类就知道是干嘛的了
private Object target;
private Method method;
private Object[] args;
public Invocation(Object target, Method method, Object[] args) {
this.target = target;
this.method = method;
this.args = args;
}
// ...
}
Plugin工具类
也就是说在mybatis里面,它提供了这样的Interceptor接口让外界能够介入它的执行流程,比如说改改参数,设置分页啥的。那么我们就需要写自己的Interceptor,然后配置给mybatis就可以了(使用plugins标签配置)。
mybatis为了能够更方便的使用插件机制,还写了个工具给我们使用,让我们可以使用@Intercepts注解就可以轻松的完成植入。所以先看看Plugin这个类。
public class Plugin implements InvocationHandler {
// 目标对象
private Object target;
// 拦截器, 由它完成拦截的逻辑
private Interceptor interceptor;
// 需要被拦截的方法
private Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap;
// 全参构造
private Plugin(Object target, Interceptor interceptor, Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap) {
this.target = target;
this.interceptor = interceptor;
this.signatureMap = signatureMap;
}
// 这是个静态方法
// 整体的逻辑就是获取Interceptor实现类上的@Intercepts注解,那么就知道应该拦截那些类的哪些方法
// target是: 当目标对象来了, 获取目标对象类的所有接口, 看这些接口是不是在上面的拦截范围中,
// 如果在,就拦截,返回个jdk代理回去,注意一下这个invocationHandler就是当前的Plugin
// 并且把target、interceptor、signatureMap都封装进去了
// 如果不在,就返回原来的target
public static Object wrap(Object target, Interceptor interceptor) {
// 获取interceptor需要拦截的方法
Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap = getSignatureMap(interceptor);
// 目标类
Class<?> type = target.getClass();
Class<?>[] interfaces = getAllInterfaces(type, signatureMap);
if (interfaces.length > 0) {
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(
type.getClassLoader(),
interfaces,
new Plugin(target, interceptor, signatureMap));
}
return target;
}
// 当调用jdk动态代理对象的方法时,都会调用到该方法
// 特别注意: 我们这个invocationHandler对象是被动态代理对象持有的,并且已经知道了invocationHandler的实现就是
// 当前的这个Plugin对象,而且这个对象里面保留了之前被拦截时封装的真实对象target、
// 拦截器interceptor、拦截的类方法集合signatureMap
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
// 需要拦截的方法集合
Set<Method> methods = signatureMap.get(method.getDeclaringClass());
if (methods != null && methods.contains(method)) {
// 在拦截范围内,执行拦截器方法
// 从这里可以看出我们的拦截器返回什么,那么动态代理调用就会返回什么
return interceptor.intercept(new Invocation(target, method, args));
}
// 不在拦截器范围内,直接调用真实对象的方法
return method.invoke(target, args);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(e);
}
}
// 解析拦截器上的@Intercepts注解
private static Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> getSignatureMap(Interceptor interceptor) {
Intercepts interceptsAnnotation = interceptor.getClass().getAnnotation(Intercepts.class);
// issue #251
if (interceptsAnnotation == null) {
throw new PluginException("No @Intercepts annotation was found in interceptor "
+ interceptor.getClass().getName());
}
Signature[] sigs = interceptsAnnotation.value();
Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap = new HashMap<Class<?>, Set<Method>>();
for (Signature sig : sigs) {
Set<Method> methods = signatureMap.get(sig.type());
if (methods == null) {
methods = new HashSet<Method>();
signatureMap.put(sig.type(), methods);
}
try {
Method method = sig.type().getMethod(sig.method(), sig.args());
methods.add(method);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new PluginException("Could not find method on " + sig.type() + " named "
+ sig.method() + ". Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
return signatureMap;
}
// 获取到目标类的所有接口
private static Class<?>[] getAllInterfaces(Class<?> type, Map<Class<?>,
Set<Method>> signatureMap) {
Set<Class<?>> interfaces = new HashSet<Class<?>>();
while (type != null) {
for (Class<?> c : type.getInterfaces()) {
if (signatureMap.containsKey(c)) {
interfaces.add(c);
}
}
type = type.getSuperclass();
}
return interfaces.toArray(new Class<?>[interfaces.size()]);
}
}
脱敏插件示例
插件
@Target({ElementType.FIELD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Desensitive {
boolean value() default true;
Class<? extends Strategy> strategy() ;
}
public interface Strategy<T> {
Object desense(T t);
}
public class CommonStrategy implements Strategy<String> {
@Override
public Object desense(String s) {
if (s == null) {
return s;
} else if (s.length() > 0) {
s = s.charAt(0) + "某某";
return s;
}
return s;
}
}
@Intercepts({
@Signature(type = ResultSetHandler.class, method = "handleResultSets", args = {Statement.class})
})
public class DesensitiveInterceptor implements Interceptor {
private boolean active = false;
@Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
List<?> list = (List<?>) invocation.proceed();
if (active && list != null && list.size() > 0) {
Object o = list.get(0);
Class<?> clazz = o.getClass();
Field[] fields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();
if (fields != null) {
for (Field field : fields) {
if (field.getAnnotation(Desensitive.class) != null) {
Desensitive anno = field.getAnnotation(Desensitive.class);
Class<? extends Strategy> strategyClass = anno.strategy();
Strategy strategy = strategyClass.newInstance();
for (Object r : list) {
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(r, strategy.desense(field.get(r)));
}
}
}
}
}
return list;
}
@Override
public Object plugin(Object o) {
return Plugin.wrap(o, this);
}
@Override
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
String property = properties.getProperty("active", "true");
boolean isActive = Boolean.parseBoolean(property);
this.active = isActive;
}
}
DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<settings>
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
settings>
<plugins>
<plugin interceptor="com.atguigu.mybatis.interceptor.DesensitiveInterceptor">
<property name="active" value="false"/>
plugin>
plugins>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC" />
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" />
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis" />
<property name="username" value="root" />
<property name="password" value="root" />
dataSource>
environment>
environments>
<mappers>
<mapper resource="EmployeeMapper.xml" />
mappers>
configuration>
打印Sql插件示例
import org.apache.ibatis.executor.statement.StatementHandler;
import org.apache.ibatis.mapping.BoundSql;
import org.apache.ibatis.mapping.MappedStatement;
import org.apache.ibatis.mapping.ParameterMapping;
import org.apache.ibatis.plugin.*;
import org.apache.ibatis.reflection.MetaObject;
import org.apache.ibatis.reflection.SystemMetaObject;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.Configuration;
import org.apache.ibatis.type.TypeHandlerRegistry;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.text.DateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Locale;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
/**
* 类说明: @Intercepts 拦截器
* @Signature 拦截器签名
* type 拦截的类型 四大对象之一( Executor , ResultSetHandler , ParameterHandler , StatementHandler )
*/
@Intercepts({
@Signature(type = StatementHandler.class,
method = "prepare",
args = {Connection.class, Integer.class})}
)
public class MybatisSqlInterceptor implements Interceptor {
@Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
// 耗时开始时间
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 获取 StatementHandler ,默认是 RoutingStatementHandler
StatementHandler statementHandler = (StatementHandler) invocation.getTarget();
// 获取 StatementHandler 包装类
MetaObject metaObjectHandler = SystemMetaObject.forObject(statementHandler);
// 获取查询接口映射的相关信息
MappedStatement mappedStatement = (MappedStatement) metaObjectHandler
.getValue("delegate.mappedStatement");
// 获取请求时的参数
Object parameterObject = statementHandler.getParameterHandler().getParameterObject();
// 获取sql
String sql = showSql(mappedStatement.getConfiguration(),
mappedStatement.getBoundSql(parameterObject));
// 获取执行sql方法
String sqlId = mappedStatement.getId();
// 执行sql
Object result = invocation.proceed();
// 计算总耗时
long cost = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
System.out.println(" ======> SQL方法 : " + sqlId + " , 总耗时 : "
+ cost + "毫秒, SQL语句 : " + sql);
return result;
}
/**
* 拦截器对应的封装原始对象的方法,获取代理对象
*/
@Override
public Object plugin(Object target) {
return (target instanceof StatementHandler) ? Plugin.wrap(target, this) : target;
}
/**
* 设置注册拦截器时设定的属性,设置代理对象的参数
*/
@Override
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
}
private static String showSql(Configuration configuration, BoundSql boundSql) {
// 获取参数
Object parameterObject = boundSql.getParameterObject();
List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings();
// sql语句中多个空格都用一个空格代替
String sql = boundSql.getSql().replaceAll("[\\s]+", " ");
if (parameterMappings !=null && parameterMappings.size()>0 && parameterObject != null) {
// 获取类型处理器注册器,类型处理器的功能是进行java类型和数据库类型的转换
TypeHandlerRegistry typeHandlerRegistry = configuration.getTypeHandlerRegistry();
// 如果根据parameterObject.getClass()可以找到对应的类型,则替换
if (typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(parameterObject.getClass())) {
sql = sql.replaceFirst("\\?",
Matcher.quoteReplacement(getParameterValue(parameterObject)));
} else {
// MetaObject主要是封装了originalObject对象
//,提供了get和set的方法用于获取和设置originalObject的属性值,
// 主要支持对JavaBean、Collection、Map三种类型对象的操作
MetaObject metaObject = configuration.newMetaObject(parameterObject);
for (ParameterMapping parameterMapping : parameterMappings) {
String propertyName = parameterMapping.getProperty();
if (metaObject.hasGetter(propertyName)) {
Object obj = metaObject.getValue(propertyName);
sql = sql.replaceFirst("\\?",
Matcher.quoteReplacement(getParameterValue(obj)));
} else if (boundSql.hasAdditionalParameter(propertyName)) {
// 该分支是动态sql
Object obj = boundSql.getAdditionalParameter(propertyName);
sql = sql.replaceFirst("\\?",
Matcher.quoteReplacement(getParameterValue(obj)));
} else {
// 打印出缺失,提醒该参数缺失并防止错位
sql = sql.replaceFirst("\\?", "缺失");
}
}
}
}
return sql;
}
private static String getParameterValue(Object obj) {
String value;
if (obj instanceof String) {
value = "'" + obj.toString() + "'";
} else if (obj instanceof Date) {
DateFormat formatter = DateFormat.getDateTimeInstance(DateFormat.DEFAULT,
DateFormat.DEFAULT,
Locale.CHINA);
value = "'" + formatter.format(new Date()) + "'";
} else {
if (obj != null) {
value = obj.toString();
} else {
value = "";
}
}
return value;
}
}
打印每条SQL语句及其执行时间
摘录自:打印每条SQL语句及其执行时间
package org.xrq.mybatis.plugin;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Properties;
import org.apache.ibatis.executor.statement.StatementHandler;
import org.apache.ibatis.mapping.BoundSql;
import org.apache.ibatis.mapping.ParameterMapping;
import org.apache.ibatis.plugin.Interceptor;
import org.apache.ibatis.plugin.Intercepts;
import org.apache.ibatis.plugin.Invocation;
import org.apache.ibatis.plugin.Plugin;
import org.apache.ibatis.plugin.Signature;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.ResultHandler;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.defaults.DefaultSqlSession.StrictMap;
/**
* Sql执行时间记录拦截器
*/
@Intercepts({@Signature(type = StatementHandler.class, method = "query", args = {Statement.class, ResultHandler.class}),
@Signature(type = StatementHandler.class, method = "update", args = {Statement.class}),
@Signature(type = StatementHandler.class, method = "batch", args = { Statement.class })})
public class SqlCostInterceptor implements Interceptor {
@Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
Object target = invocation.getTarget();
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
StatementHandler statementHandler = (StatementHandler)target;
try {
return invocation.proceed();
} finally {
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
long sqlCost = endTime - startTime;
BoundSql boundSql = statementHandler.getBoundSql();
String sql = boundSql.getSql();
Object parameterObject = boundSql.getParameterObject();
List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappingList = boundSql.getParameterMappings();
// 格式化Sql语句,去除换行符,替换参数
sql = formatSql(sql, parameterObject, parameterMappingList);
System.out.println("SQL:[" + sql + "]执行耗时[" + sqlCost + "ms]");
}
}
@Override
public Object plugin(Object target) {
return Plugin.wrap(target, this);
}
@Override
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private String formatSql(String sql, Object parameterObject, List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappingList) {
// 输入sql字符串空判断
if (sql == null || sql.length() == 0) {
return "";
}
// 美化sql
sql = beautifySql(sql);
// 不传参数的场景,直接把Sql美化一下返回出去
if (parameterObject == null || parameterMappingList == null || parameterMappingList.size() == 0) {
return sql;
}
// 定义一个没有替换过占位符的sql,用于出异常时返回
String sqlWithoutReplacePlaceholder = sql;
try {
if (parameterMappingList != null) {
Class<?> parameterObjectClass = parameterObject.getClass();
// 如果参数是StrictMap且Value类型为Collection,获取key="list"的属性,这里主要是为了处理循环时传入List这种参数的占位符替换
// 例如select * from xxx where id in ...
if (isStrictMap(parameterObjectClass)) {
StrictMap<Collection<?>> strictMap = (StrictMap<Collection<?>>)parameterObject;
if (isList(strictMap.get("list").getClass())) {
sql = handleListParameter(sql, strictMap.get("list"));
}
} else if (isMap(parameterObjectClass)) {
// 如果参数是Map则直接强转,通过map.get(key)方法获取真正的属性值
// 这里主要是为了处理、、、
Map<?, ?> paramMap = (Map<?, ?>) parameterObject;
sql = handleMapParameter(sql, paramMap, parameterMappingList);
} else {
// 通用场景,比如传的是一个自定义的对象或者八种基本数据类型之一或者String
sql = handleCommonParameter(sql, parameterMappingList, parameterObjectClass, parameterObject);
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
// 占位符替换过程中出现异常,则返回没有替换过占位符但是格式美化过的sql,这样至少保证sql语句比BoundSql中的sql更好看
return sqlWithoutReplacePlaceholder;
}
return sql;
}
/**
* 美化Sql
*/
private String beautifySql(String sql) {
// sql = sql.replace("\n", "").replace("\t", "").replace(" ", " ").replace("( ", "(").replace(" )", ")").replace(" ,", ",");
sql = sql.replaceAll("[\\s\n ]+"," ");
return sql;
}
/**
* 处理参数为List的场景
*/
private String handleListParameter(String sql, Collection<?> col) {
if (col != null && col.size() != 0) {
for (Object obj : col) {
String value = null;
Class<?> objClass = obj.getClass();
// 只处理基本数据类型、基本数据类型的包装类、String这三种
// 如果是复合类型也是可以的,不过复杂点且这种场景较少,写代码的时候要判断一下要拿到的是复合类型中的哪个属性
if (isPrimitiveOrPrimitiveWrapper(objClass)) {
value = obj.toString();
} else if (objClass.isAssignableFrom(String.class)) {
value = "\"" + obj.toString() + "\"";
}
sql = sql.replaceFirst("\\?", value);
}
}
return sql;
}
/**
* 处理参数为Map的场景
*/
private String handleMapParameter(String sql, Map<?, ?> paramMap, List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappingList) {
for (ParameterMapping parameterMapping : parameterMappingList) {
Object propertyName = parameterMapping.getProperty();
Object propertyValue = paramMap.get(propertyName);
if (propertyValue != null) {
if (propertyValue.getClass().isAssignableFrom(String.class)) {
propertyValue = "\"" + propertyValue + "\"";
}
sql = sql.replaceFirst("\\?", propertyValue.toString());
}
}
return sql;
}
/**
* 处理通用的场景
*/
private String handleCommonParameter(String sql, List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappingList, Class<?> parameterObjectClass,
Object parameterObject) throws Exception {
for (ParameterMapping parameterMapping : parameterMappingList) {
String propertyValue = null;
// 基本数据类型或者基本数据类型的包装类,直接toString即可获取其真正的参数值,其余直接取paramterMapping中的property属性即可
if (isPrimitiveOrPrimitiveWrapper(parameterObjectClass)) {
propertyValue = parameterObject.toString();
} else {
String propertyName = parameterMapping.getProperty();
Field field = parameterObjectClass.getDeclaredField(propertyName);
// 要获取Field中的属性值,这里必须将私有属性的accessible设置为true
field.setAccessible(true);
propertyValue = String.valueOf(field.get(parameterObject));
if (parameterMapping.getJavaType().isAssignableFrom(String.class)) {
propertyValue = "\"" + propertyValue + "\"";
}
}
sql = sql.replaceFirst("\\?", propertyValue);
}
return sql;
}
/**
* 是否基本数据类型或者基本数据类型的包装类
*/
private boolean isPrimitiveOrPrimitiveWrapper(Class<?> parameterObjectClass) {
return parameterObjectClass.isPrimitive() ||
(parameterObjectClass.isAssignableFrom(Byte.class) || parameterObjectClass.isAssignableFrom(Short.class) ||
parameterObjectClass.isAssignableFrom(Integer.class) || parameterObjectClass.isAssignableFrom(Long.class) ||
parameterObjectClass.isAssignableFrom(Double.class) || parameterObjectClass.isAssignableFrom(Float.class) ||
parameterObjectClass.isAssignableFrom(Character.class) || parameterObjectClass.isAssignableFrom(Boolean.class));
}
/**
* 是否DefaultSqlSession的内部类StrictMap
*/
private boolean isStrictMap(Class<?> parameterObjectClass) {
return parameterObjectClass.isAssignableFrom(StrictMap.class);
}
/**
* 是否List的实现类
*/
private boolean isList(Class<?> clazz) {
Class<?>[] interfaceClasses = clazz.getInterfaces();
for (Class<?> interfaceClass : interfaceClasses) {
if (interfaceClass.isAssignableFrom(List.class)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
/**
* 是否Map的实现类
*/
private boolean isMap(Class<?> parameterObjectClass) {
Class<?>[] interfaceClasses = parameterObjectClass.getInterfaces();
for (Class<?> interfaceClass : interfaceClasses) {
if (interfaceClass.isAssignableFrom(Map.class)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}