【C++】A*最优寻路算法(附加迷宫障碍自动生成)
目录
一、前言
二、关于迷宫(障碍)的生成
1.简单解释
2.代码
三、A*算法
1.简单解释
2.效果演示
3.代码
四、总代码
五、总结
一、前言
最近上了人工智能的课程,学了A*算法,就尝试使用C++来实现这个算法。
为了更方便的体现寻路过程,这里使用了easyx图像库来实时展示运动的过程。可以去easyx的官网下载这个库。easyx官网
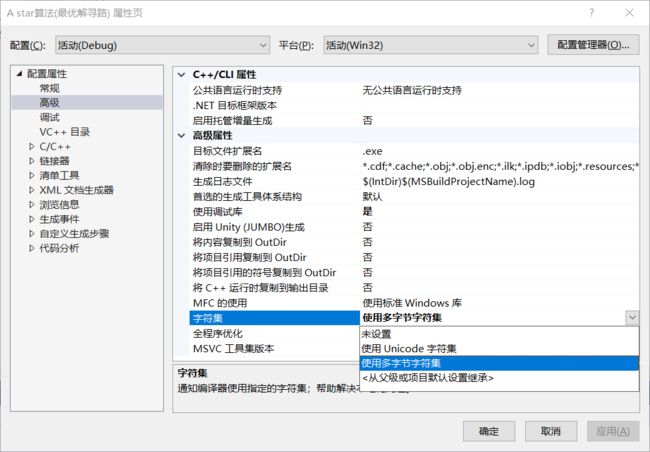
easyx库在使用中最好在:调试——调试属性——配置属性——高级——字符集 设置使用多字节字符集,否则有些函数可能会报错。
二、关于迷宫(障碍)的生成
1.简单解释
首先我们可以用一个二维数组来存放迷宫,其大小由用户输入。用1表示墙壁,0表示路。
开始初始化迷宫数组应该初始化为下面的状态。
数组(1,1)为开始点,然后开始寻找旁边是否有通路,如果有,则随机打通一路,然后记录下当前的坐标,进行递归。函数出口就是没有找到可以打通的地方,则直接return。走过的路需要标记为走过,否则可能会出现死循环导致程序不正确。这里标记走过的路为5。
进行完这一步后,需要将之前数组中所有的5改为0,即改为通路。
最后将其显示,大概就是下面这个效果,当然这种算法生成的迷宫质量不是很好,不过现在也足够使用了。
当然我们使用A*算法不需要迷宫,只需要一些障碍就行,我们再写一个函数,随机删除上面迷宫的一些墙,就完成生成障碍的这一步了。
2.代码
存放迷宫的结构体
struct AStar {
int M; //M*M map
int** maze; //map迷宫
//int* close; //close表
//int* open; //open表
int O_row; //开始的行
int O_col; //开始的列
int E_row; //终点行
int E_col; //终点列
}Astar{ 0,NULL,1,1,0,0 };初始化迷宫
int main()
{
Astar.M = 0;
cout << "请输入迷宫是几乘几的" << endl;
cin >> Astar.M;
if (Astar.M % 2 == 0)//如果输入不为奇数变为奇数
Astar.M++;
Astar.E_col = Astar.M;
Astar.E_row = Astar.M;
Astar.maze = new int* [Astar.M + 2];//动态创建二维数组
for (int i = 0; i < Astar.M + 2; i++)
Astar.maze[i] = new int[Astar.M + 2];//每一行申请一个int空间的M+2列空间
}
//初始化迷宫
void Init_Maze(AStar& Astar)
{
for (int i = 0; i < Astar.M + 2; i++)//动态创建迷宫
for (int j = 0; j < Astar.M + 2; j++)
{
if (i == 0 || i == Astar.M + 1)//1为墙壁
Astar.maze[i][j] = 1;
if ((i % 2 == 1) && (j % 2 == 1))
Astar.maze[i][j] = 0;
else Astar.maze[i][j] = 1;
}
}寻找邻居
bool findneighbor(AStar& Astar, int x_index, int y_index)
{
if ((x_index >= 3 && Astar.maze[x_index - 2][y_index] == 0) || (x_index <= Astar.M - 1 && Astar.maze[x_index + 2][y_index] == 0)
|| (y_index >= 3 && Astar.maze[x_index][y_index - 2] == 0) || (y_index <= Astar.M - 1 && Astar.maze[x_index][y_index + 2] == 0))
return 1;
else
return 0;
}创建迷宫
//随机创建迷宫
void creatMaze(AStar& Astar, int x_index, int y_index)
{
int pos, x, y, flag = 0;
x = x_index;
y = y_index;
while (1)
{
flag = 0;
flag = findneighbor(Astar, x, y);
if (!flag)
return;
else {
Astar.maze[x_index][y_index] = 5;
x = x_index;
y = y_index;
while (1)
{
pos = rand() % (4 - 1 + 1) + 1;
if (pos == 1 && x_index >= 3 && Astar.maze[x_index - 2][y_index] == 0)//上
{
x_index -= 2;
}
else if (pos == 2 && x_index <= Astar.M - 1 && Astar.maze[x_index + 2][y_index] == 0)//下
{
x_index += 2;
}
else if (pos == 3 && y_index <= Astar.M - 1 && Astar.maze[x_index][y_index + 2] == 0)
{
y_index += 2;
}
else if (pos == 4 && y_index >= 3 && Astar.maze[x_index][y_index - 2] == 0)
{
y_index -= 2;
}
Astar.maze[(x + x_index) / 2][(y + y_index) / 2] = 5;
Astar.maze[x_index][y_index] = 5;
// showmaze(maze, M);
creatMaze(Astar, x_index, y_index);
break;
}
}
}
}改变数组中的通路,标识入口和出口
//给创建的迷宫创建标识
void makeMaze(AStar& Astar)
{
for (int i = 0; i < Astar.M + 2; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < Astar.M + 2; j++)
{
if (Astar.maze[i][j] == 5)
{
Astar.maze[i][j] = 0;
}
}
Astar.maze[1][1] = 8;
Astar.maze[Astar.M][Astar.M] = 2;
}
改变地形
//改变地形,出现更多通路
void MakeDifficult(AStar& Astar)
{
if (Astar.M > 5)
{
int half = (int)((0.4 * Astar.M) * (0.5 * Astar.M));
int x_c, y_c = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < half;)
{
x_c = rand() % (Astar.M - 1 + 1) + 1;
y_c = rand() % (Astar.M - 1 + 1) + 1;
if (Astar.maze[x_c][y_c] == 1)
{
Astar.maze[x_c][y_c] = 0;
i++;
}
}
}
}
显示迷宫
//图像显示迷宫
//3为路,4为搜寻的路,1为墙,2为终点,8为开始
void show(AStar& Astar)
{
IMAGE star, wall, ball ,ly;
loadimage(&star, "./五角星.png", SIZE, SIZE);
loadimage(&wall, "./墙.png", SIZE, SIZE);
loadimage(&ball, "./球.png", SIZE, SIZE);
loadimage(&ly, "./兰音.png", SIZE, SIZE);
for (int i = 0; i < Astar.M + 2; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < Astar.M + 2; j++)
{
if (Astar.maze[i][j] == 1)
{
putimage((j + Astar.M + 2 + 1) * SIZE, (i)*SIZE, &wall);
putimage(j * SIZE, i * SIZE, &wall);
}
else if (Astar.maze[i][j] == 4)
{
putimage((j + Astar.M + 2 + 1) * SIZE, (i)*SIZE, &ball);
}
else if (Astar.maze[i][j] == 3)
{
putimage(j * SIZE, (i)*SIZE, &ly);
}
}
}
putimage((Astar.M + 2 + 1 + 1) * SIZE, (SIZE), &star);
putimage((Astar.M + Astar.M + 2 + 1) * SIZE, (Astar.M) * SIZE, &star);
putimage(SIZE, SIZE, &star);
putimage(Astar.M * SIZE, Astar.M * SIZE, &star);
}至此,迷宫或者障碍的创建就完成了,此时的迷宫保存在maze这个二维数组中。
三、A*算法
1.简单解释
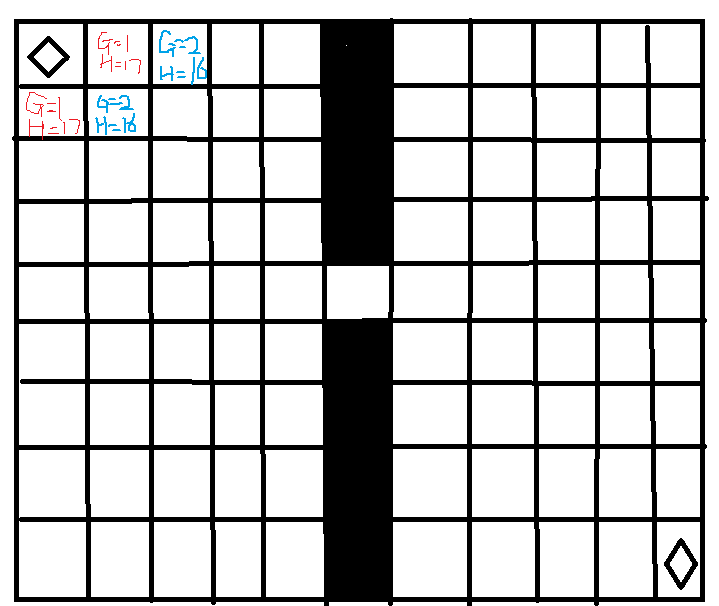
我们假设一开始是下面这幅图,起点为左上角,终点为右下角。A*算法的重点就是我们设置估价函数F的过程。
F=G+H。其中G是起始节点到当前节点的代价,H是当前节点到目标节点的代价。A*算法就是在A算法上的改进,也就是要求G必须大于0,H必须不大于实际代价这两个条件。
我们假设G为从开始移动到现在这个节点的步数,H为曼哈顿距离(即|xe-xi|+|ye-yi|,其中xe,ye是终点坐标,xi,yi是当前点坐标),为了方便起见,我们假设只能左右上下行走,不能斜着走,那么上面的F就为下面这样。起点的F值要给最大。
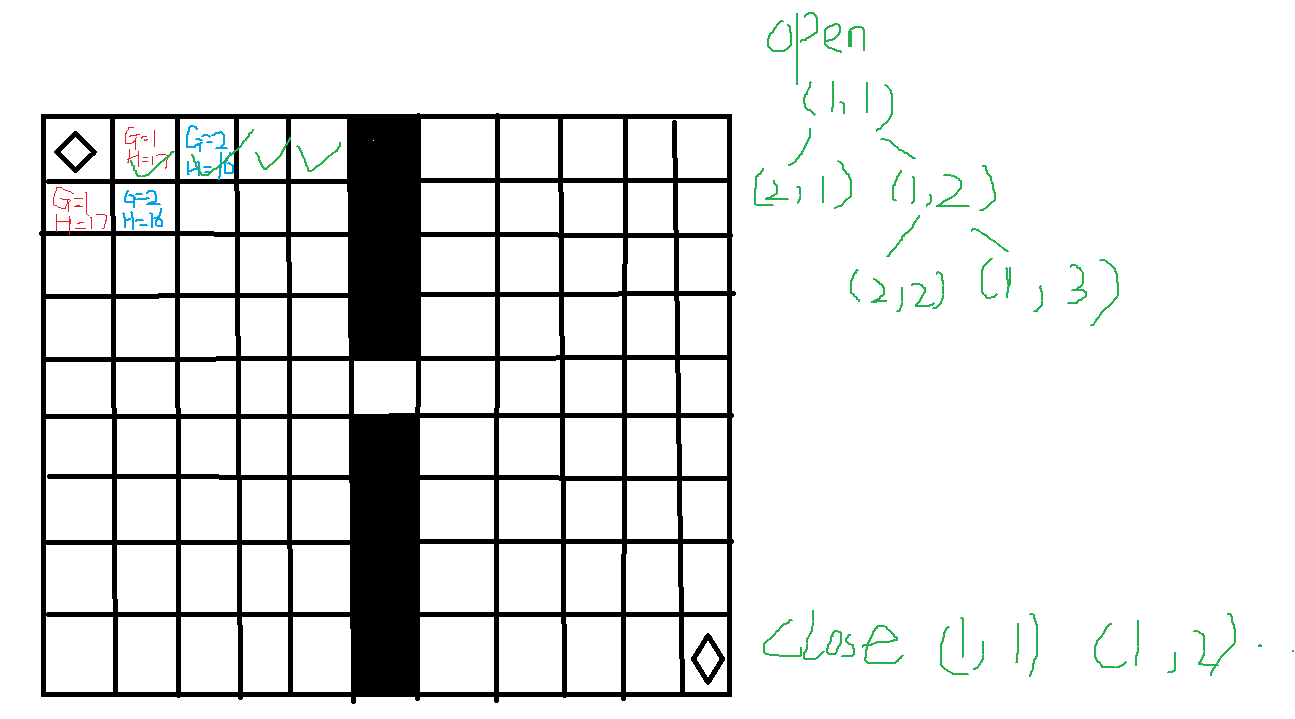
那么A*算法就是会找到最小的那个F然后走上去,并且记录下父节点。专业的来讲就是把当前节点所有可以走的节点的F值算出来,把节点放入open表中,然后找到最小的F值的节点,放入close表中。这里我们可以将open表化为一个树,close表化为一个数组。
当然我们前提是行走的四个方向都要提前做好确定,然后每次都寻找最后入树且代价最小的那一个节点,走上去,继续寻找后续节点。人工智能书上也给出了相应的参考框图。
2.效果演示
3.代码
int main()
{
treeNode* pRoot = NULL; //准备一棵树
vector open; //准备一个数组
vector::iterator it; //迭代器
vector::iterator itmin; //迭代器
pRoot = creatTreeNode(Astar.O_row, Astar.O_col); //起点入树
treeNode* Now = pRoot;
pRoot->pos.F = Astar.M * Astar.M;
open.push_back(pRoot);
while (1)
{
//1.把当前能走的点找出来
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
treeNode* pChild = creatTreeNode(Now->pos.row, Now->pos.col);
switch (i)
{
case Up:
pChild->pos.row--;
pChild->pos.g = Now->pos.g + 1;
break;
case Down:
pChild->pos.row++;
pChild->pos.g = Now->pos.g + 1;
break;
case Left:
pChild->pos.col--;
pChild->pos.g = Now->pos.g + 1;
break;
case Right:
pChild->pos.col++;
pChild->pos.g = Now->pos.g + 1;
break;
default:
break;
}
//2.判断能不能走
if (Astar.maze[pChild->pos.row][pChild->pos.col] == 0 || Astar.maze[pChild->pos.row][pChild->pos.col] == 8
|| Astar.maze[pChild->pos.row][pChild->pos.col] == 2) //如果是路则计算F
{
//标记走过
Astar.maze[pChild->pos.row][pChild->pos.col] = 4;
pChild->pos.h = getH(pChild->pos, Astar);//计算H
pChild->pos.F = pChild->pos.g + pChild->pos.h;//计算F
//入树
Now->child.push_back(pChild);
pChild->parent = Now;
//存入数组
open.push_back(pChild);
}
else {
delete pChild;
}
}
//3.找出数组最小的点,走上去
//cout << open.size() << endl;
itmin = open.begin();//假设第一个F最小 时间复杂度O(n)
for (it = open.begin(); it != open.end(); it++)
{
itmin = ((*it)->pos.F <= (*itmin)->pos.F) ? it : itmin; //细节 加上等于
}
//sort(open.begin(), open.end(),cmp);
//itmin = open.begin();
Now = *itmin;
//标记走过
//Astar.maze[Now->pos.row][Now->pos.col] = -1;
show(Astar);
//删除
open.erase(itmin);
//4.判断是否找到终点
if (Now->pos.row == Astar.E_row && Now->pos.col == Astar.E_col)
{
flag = 1;
break;
}
//5.如果为数组为空也退出
if (0 == open.size()) break;
}
//成功则打印
if (flag)
{
cout << "success" << endl;
while (Now)
{
cout << "(" << Now->pos.row << "," << Now->pos.col << ")";
printf("(g:%d,h:%d,f:%d)\n", Now->pos.g, Now->pos.h, Now->pos.F);
Astar.maze[Now->pos.row][Now->pos.col] = 3;
Now = Now->parent;
}
}
else
{
cout << "not found" << endl;
}
while (1)
{
BeginBatchDraw();
show(Astar);
FlushBatchDraw();
}//循环绘图防止BUG
closegraph();
} 四、总代码
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
//1为墙壁,0为路
#define SIZE 10
bool flag = 0;
enum dirct {
Up,
Down,
Left,
Right,
};
struct AStar {
int M; //M*M map
int** maze; //map迷宫
//int* close; //close表
//int* open; //open表
int O_row; //开始的行
int O_col; //开始的列
int E_row; //终点行
int E_col; //终点列
}Astar{ 0,NULL,1,1,0,0 };
struct position {
int row, col;
int g; //路径代价 行走的步数
int h; //启发函数 曼哈顿距离
int F = h + g; //估价函数
};
struct treeNode { //close类似
position pos;
vector child;
treeNode* parent;
};
treeNode* creatTreeNode(int row, int col); //创建树节点
int getH(position pos, AStar a); //计算H
void Init_Maze(AStar& Astar); //初始化迷宫
void show(AStar& Astar); //图像显示迷宫
void creatMaze(AStar& Astar, int x_index, int y_index); //随机创建迷宫
void makeMaze(AStar& Astar); //给创建的迷宫创建标识
bool findneighbor(AStar& Astar, int x_index, int y_index); //寻找邻居
void MakeDifficult(AStar& Astar); //改变地形,出现更多通路
void ConsoleShow(AStar& Astar); //控制台显示迷宫
///*排序方式*/
//bool cmp(treeNode* m1, treeNode* m2)
//{
// return m1->pos.F < m2->pos.F;
//}
int main()
{
treeNode* pRoot = NULL; //准备一棵树
vector open; //准备一个数组
vector::iterator it; //迭代器
vector::iterator itmin; //迭代器
Astar.M = 0;
cout << "请输入迷宫是几乘几的" << endl;
cin >> Astar.M;
if (Astar.M % 2 == 0)//如果输入不为奇数变为奇数
Astar.M++;
Astar.E_col = Astar.M;
Astar.E_row = Astar.M;
pRoot = creatTreeNode(Astar.O_row, Astar.O_col); //起点入树
srand((unsigned)time(0));//随机播种
initgraph(((Astar.M + 2) * 2 + 1) * SIZE, (Astar.M + 2) * SIZE, SHOWCONSOLE);//打开绘图
Astar.maze = new int* [Astar.M + 2];//动态创建二维数组
for (int i = 0; i < Astar.M + 2; i++)
Astar.maze[i] = new int[Astar.M + 2];//每一行申请一个int空间的M+2列空间
Init_Maze(Astar);
creatMaze(Astar, 1, 1);
makeMaze(Astar);
MakeDifficult(Astar);
//show(Astar);
treeNode* Now = pRoot;
pRoot->pos.F = Astar.M * Astar.M;
open.push_back(pRoot);
while (1)
{
//1.把当前能走的点找出来
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
treeNode* pChild = creatTreeNode(Now->pos.row, Now->pos.col);
switch (i)
{
case Up:
pChild->pos.row--;
pChild->pos.g = Now->pos.g + 1;
break;
case Down:
pChild->pos.row++;
pChild->pos.g = Now->pos.g + 1;
break;
case Left:
pChild->pos.col--;
pChild->pos.g = Now->pos.g + 1;
break;
case Right:
pChild->pos.col++;
pChild->pos.g = Now->pos.g + 1;
break;
default:
break;
}
//2.判断能不能走
if (Astar.maze[pChild->pos.row][pChild->pos.col] == 0 || Astar.maze[pChild->pos.row][pChild->pos.col] == 8
|| Astar.maze[pChild->pos.row][pChild->pos.col] == 2) //如果是路则计算F
{
//标记走过
Astar.maze[pChild->pos.row][pChild->pos.col] = 4;
pChild->pos.h = getH(pChild->pos, Astar);//计算H
pChild->pos.F = pChild->pos.g + pChild->pos.h;//计算F
//入树
Now->child.push_back(pChild);
pChild->parent = Now;
//存入数组
open.push_back(pChild);
}
else {
delete pChild;
}
}
//3.找出数组最小的点,走上去
//cout << open.size() << endl;
itmin = open.begin();//假设第一个F最小 时间复杂度O(n)
for (it = open.begin(); it != open.end(); it++)
{
itmin = ((*it)->pos.F <= (*itmin)->pos.F) ? it : itmin; //细节 加上等于
}
//sort(open.begin(), open.end(),cmp);
//itmin = open.begin();
Now = *itmin;
//标记走过
//Astar.maze[Now->pos.row][Now->pos.col] = -1;
show(Astar);
//删除
open.erase(itmin);
//4.判断是否找到终点
if (Now->pos.row == Astar.E_row && Now->pos.col == Astar.E_col)
{
flag = 1;
break;
}
//5.如果为数组为空也退出
if (0 == open.size()) break;
}
//成功则打印
if (flag)
{
cout << "success" << endl;
while (Now)
{
cout << "(" << Now->pos.row << "," << Now->pos.col << ")";
printf("(g:%d,h:%d,f:%d)\n", Now->pos.g, Now->pos.h, Now->pos.F);
Astar.maze[Now->pos.row][Now->pos.col] = 3;
Now = Now->parent;
}
}
else
{
cout << "not found" << endl;
}
while (1)
{
BeginBatchDraw();
show(Astar);
FlushBatchDraw();
}//循环绘图防止BUG
closegraph();
}
//初始化迷宫
void Init_Maze(AStar& Astar)
{
for (int i = 0; i < Astar.M + 2; i++)//动态创建迷宫
for (int j = 0; j < Astar.M + 2; j++)
{
if (i == 0 || i == Astar.M + 1)//1为墙壁
Astar.maze[i][j] = 1;
if ((i % 2 == 1) && (j % 2 == 1))
Astar.maze[i][j] = 0;
else Astar.maze[i][j] = 1;
}
}
//图像显示迷宫
//3为路,4为搜寻的路,1为墙,2为终点,8为开始
void show(AStar& Astar)
{
IMAGE star, wall, ball ,ly;
loadimage(&star, "./五角星.png", SIZE, SIZE);
loadimage(&wall, "./墙.png", SIZE, SIZE);
loadimage(&ball, "./球.png", SIZE, SIZE);
loadimage(&ly, "./兰音.png", SIZE, SIZE);
for (int i = 0; i < Astar.M + 2; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < Astar.M + 2; j++)
{
if (Astar.maze[i][j] == 1)
{
putimage((j + Astar.M + 2 + 1) * SIZE, (i)*SIZE, &wall);
putimage(j * SIZE, i * SIZE, &wall);
}
else if (Astar.maze[i][j] == 4)
{
putimage((j + Astar.M + 2 + 1) * SIZE, (i)*SIZE, &ball);
}
else if (Astar.maze[i][j] == 3)
{
putimage(j * SIZE, (i)*SIZE, &ly);
}
}
}
putimage((Astar.M + 2 + 1 + 1) * SIZE, (SIZE), &star);
putimage((Astar.M + Astar.M + 2 + 1) * SIZE, (Astar.M) * SIZE, &star);
putimage(SIZE, SIZE, &star);
putimage(Astar.M * SIZE, Astar.M * SIZE, &star);
}
//寻找邻居
bool findneighbor(AStar& Astar, int x_index, int y_index)
{
if ((x_index >= 3 && Astar.maze[x_index - 2][y_index] == 0) || (x_index <= Astar.M - 1 && Astar.maze[x_index + 2][y_index] == 0)
|| (y_index >= 3 && Astar.maze[x_index][y_index - 2] == 0) || (y_index <= Astar.M - 1 && Astar.maze[x_index][y_index + 2] == 0))
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
//随机创建迷宫
void creatMaze(AStar& Astar, int x_index, int y_index)
{
int pos, x, y, flag = 0;
x = x_index;
y = y_index;
while (1)
{
flag = 0;
flag = findneighbor(Astar, x, y);
if (!flag)
return;
else {
Astar.maze[x_index][y_index] = 5;
x = x_index;
y = y_index;
while (1)
{
pos = rand() % (4 - 1 + 1) + 1;
if (pos == 1 && x_index >= 3 && Astar.maze[x_index - 2][y_index] == 0)//上
{
x_index -= 2;
}
else if (pos == 2 && x_index <= Astar.M - 1 && Astar.maze[x_index + 2][y_index] == 0)//下
{
x_index += 2;
}
else if (pos == 3 && y_index <= Astar.M - 1 && Astar.maze[x_index][y_index + 2] == 0)
{
y_index += 2;
}
else if (pos == 4 && y_index >= 3 && Astar.maze[x_index][y_index - 2] == 0)
{
y_index -= 2;
}
Astar.maze[(x + x_index) / 2][(y + y_index) / 2] = 5;
Astar.maze[x_index][y_index] = 5;
// showmaze(maze, M);
creatMaze(Astar, x_index, y_index);
break;
}
}
}
}
//给创建的迷宫创建标识
void makeMaze(AStar& Astar)
{
for (int i = 0; i < Astar.M + 2; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < Astar.M + 2; j++)
{
if (Astar.maze[i][j] == 5)
{
Astar.maze[i][j] = 0;
}
}
Astar.maze[1][1] = 8;
Astar.maze[Astar.M][Astar.M] = 2;
}
//改变地形,出现更多通路
void MakeDifficult(AStar& Astar)
{
if (Astar.M > 5)
{
int half = (int)((0.4 * Astar.M) * (0.5 * Astar.M));
int x_c, y_c = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < half;)
{
x_c = rand() % (Astar.M - 1 + 1) + 1;
y_c = rand() % (Astar.M - 1 + 1) + 1;
if (Astar.maze[x_c][y_c] == 1)
{
Astar.maze[x_c][y_c] = 0;
i++;
}
}
}
}
//计算H
int getH(position pos, AStar a) {
return (a.E_row - pos.row) + (a.E_col - pos.col);
}
//创建树节点
treeNode* creatTreeNode(int row, int col)
{
treeNode* pNew = new treeNode;//开内存
memset(pNew, 0, sizeof(treeNode)); //全部赋值为0
pNew->pos.col = col;
pNew->pos.row = row;
return pNew;
}
//控制台显示迷宫
void ConsoleShow(AStar& Astar)
{
cout << endl << "3为走出迷宫的路,1为墙壁,2为出口" << endl;;
for (int i = 0; i < Astar.M + 2; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < Astar.M + 2; j++)
{
cout << setw(3) << Astar.maze[i][j];
}
cout << endl;
}
}
五、总结
这份代码还有一些莫名其妙的bug,但已经改不动了。希望可以帮助到大家。