【SpringBoot知识点预备】| Xml 和 JavaConfig
目录
一:Xml 和 JavaConfig
1. JavaConfig
2. @ImportResource注解
3. @PropertyResource注解
一:Xml 和 JavaConfig
1. JavaConfig
(1)为什么要使用 Spring Boot?
①因为Spring、SpringMVC 的使用需要大量的配置文件 (xml文件),还需要配置各种对象,把使用的对象放入到spring容器中才能使用对象,需要了解其他框架配置规则;在未编写真正的业务代码时,就已经编写了大量的配置文件!
②SpringBoot 就相当于不需要配置文件的Spring+SpringMVC,常用的框架和第三方库都已经配置好了,拿来就可以使用了,所以使用SpringBoot开发效率高。
(2)Xml 和 JavaConfig
Spring 使用 Xml 作为容器配置文件, 在 3.0 版本以后加入了 JavaConfig,使用 java 类做配置文件使用。
(3)什么是 JavaConfig?
JavaConfig: 使用Java类作为Xml配置文件的替代, 是配置spring容器的纯java的方式。 在这个java类这可以创建java对象,把对象放入spring容器中(注入到容器)。
优点:
①可以使用面向对象的方式, 一个配置类可以继承配置类,可以重写方法;
②避免繁琐的 xml 配置;
使用JavaConfig需要两个注解的支持:
①@Configuration : 放在一个类的上面,表示这个类是作为配置文件使用的。
②@Bean:声明对象,把对象注入到容器中。
pom.xml配置
4.0.0
com.zl
study-springboot-001
1.0.0
jar
org.springframework
spring-context
5.3.1
junit
junit
4.12
test
maven-compiler-plugin
3.5.1
1.8
1.8
UTF-8
8
8
Student类
package com.zl.springboot.pojo;
public class Student {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String sex;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, Integer age, String sex) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.sex = sex;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", sex='" + sex + '\'' +
'}';
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
}
第一种:使用传统的XML配置文件的方式管理Bean
spring.xml核心配置
单元测试:
package com.zl.springboot.test;
import com.zl.springboot.pojo.Student;
import javafx.application.Application;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class SpringBootTest {
@Test
public void test01(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
Student studentBean = applicationContext.getBean("studentBean", Student.class);
System.out.println(studentBean);
}
}
第二种:使用JavaConfig来管理Bean对象
创建一个Java类,在类上引入@Configuration注解,在方法上引入@Bean注解
①@Configuration:表示当前类是作为配置文件使用的,就是用来配置容器的;位置:在类的上面;SpringConfig这个类就相当于spring.xml配置。
②@Bean: 创建方法,方法的返回值是对象。 在方法的上面加入@Bean,把方法的返回值对象就注入到容器中;位置:在方法的上面;把对象注入到spring容器中, 作用相当于标签;若@Bean不指定对象的名称,默认是方法名就是id。
package com.zl.springboot.config;
import com.zl.springboot.pojo.Student;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration // 当前类作为配置文件使用
public class SpringConfig {
@Bean // 不指定默认id是方法名
// @Bean("myStudent") // 也可以自己指定id
public Student createStudent(){
Student student = new Student();
student.setName("李四");
student.setAge(19);
student.setSex("女");
return student; // 返回这个对象
}
}
单元测试:
①创建AnnotationConfigApplicationContext对象,参数就是我们的SpringConfig类的.class。
②还是调用getBean方法,方法参数默认就是上面的方法名,或者使用自己指定的。
@Test
public void test02(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
// 使用默认的,id就是方法名
Student student = applicationContext.getBean("createStudent", Student.class);
// 使用自己指定的id
Student student = applicationContext.getBean("myStudent", Student.class); /
System.out.println(student);
}2. @ImportResource注解
@ImportResource作用:导入其他的xml配置文件, 例如:把前面的spring.xml核心配置导入SpringConfig类(配置spring容器的纯java方式)当中。等同于在XML中:
@ImportResource源码:有两个数组参数,value和locations,互为别名,效果是等价的
package org.springframework.context.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionReader;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.AliasFor;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Documented
public @interface ImportResource {
@AliasFor("locations")
String[] value() default {};
@AliasFor("value")
String[] locations() default {};
Class reader() default BeanDefinitionReader.class;
}
Cat类
package com.zl.springboot.pojo;
/**
* @Author:朗朗乾坤
* @Package:com.zl.springboot.pojo
* @Project:spring-boot
* @Date:2023/3/2 18:54
*/
public class Cat {
private String cardId;
private String name;
private Integer age;
public Cat() {
}
public Cat(String cardId, String name, Integer age) {
this.cardId = cardId;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Cat{" +
"cardId='" + cardId + '\'' +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
public String getCardId() {
return cardId;
}
public void setCardId(String cardId) {
this.cardId = cardId;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
catbean.xml配置
把catbean.xml核心配置,通过@ImportResource注解引入到SpringConfig类当中
单元测试:
通过new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class),调用getBean方法,id是Cat的id,也能成功创建Bean,说明成功把spring.xml文件引入到SpringConfig当中了。
@Test
public void test03(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
Cat catBean = applicationContext.getBean("catBean", Cat.class);
System.out.println(catBean);
}3. @PropertyResource注解
@PropertyResource作用: 读取xxx.properties属性配置文件。使用属性配置文件可以实现外部化配置 ,在程序代码之外提供数据。等同于在xml中:
步骤:
①在resources目录下,创建properties文件, 使用k=v的格式提供数据
②在PropertyResource 指定properties文件的位置
③使用@Value(value="${key}")
config.properties属性配置文件
tiger.name=东北虎
tiger.age=3Tiger类:使用注解式开发
package com.bjpowernode.vo;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component("tiger") // 交给Spring容器管理
public class Tiger {
@Value("${tiger.name}") // 进行赋值
private String name;
@Value("${tiger.age}")
private Integer age;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Tiger{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
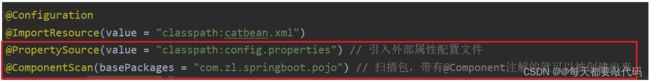
在SpringConfig类当中引入包扫描和使用@PropertyResource注解引入外部属性文件
单元测试:
@Test
public void test05(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
Tiger tiger = applicationContext.getBean("tiger", Tiger.class);
System.out.println(tiger);
}如果此时出现了中文乱码,进行以下设置:
其实以下注解就等同与在xml配置中配置以下信息
@Configuration // 代表xml配置
@ImportResource(value = "classpath:catbean.xml") // 导入其它xml配置
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:config.properties") // 引入外部属性配置文件
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.zl.springboot.pojo") // 扫描包,带有@Component注解的就可以被创建出来与上面是等价的