多叉树的构建,条件查询,修改删除节点
多叉树的构建查询,新增,修改,删除
文章目录
- 多叉树的构建查询,新增,修改,删除
-
- 一,数据库表设计
- 二、新增相对应数据库表的实体类
- 三、新建多叉树树工具类
- 四、多叉树树的条件查询
- 五、多叉树的节点新增
- 六、多叉树的节点删除
- 七、多叉树修改
一,数据库表设计
一般树型的节点信息管理表只需要一个id(当前节点id)以及一个parent_id(父节点id即可),其他的基础信息字段按照需求来
注意这里我 给parent_id字段设置了默认值-1,代表不在这颗树中,parent_id为0即代表为根节点。
例如这里一个管理模块对这张表进行了维护,可新增节点2和可新增节点3都目前都不在这棵树中但是后续可以把它添加到树中(添加的时候只查询parent_id为-1的数据,表示这些数据可作为节点新增到树中,新增其实就是前端传id和parent_id,然后根据id更新掉parent_id即可)
二、新增相对应数据库表的实体类
实体类的这部分代码逻辑都差不多,这里的代码是参考下面这篇博客的代码:
多叉树操作博客
public class TreeNode implements Serializable {
private int parentId;
private int selfId;
protected String nodeName;
protected Object obj;
protected TreeNode parentNode;
protected List<TreeNode> childList;
public TreeNode() {
initChildList();
}
public TreeNode(TreeNode parentNode) {
this.getParentNode();
initChildList();
}
public boolean isLeaf() {
if (childList == ) {
return true;
} else {
if (childList.isEmpty()) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
}
/* 插入一个child节点到当前节点中 */
public void addChildNode(TreeNode treeNode) {
initChildList();
childList.add(treeNode);
}
public void initChildList() {
if (childList == )
childList = new ArrayList<TreeNode>();
}
public boolean isValidTree() {
return true;
}
/* 返回当前节点的父辈节点集合 */
public List<TreeNode> getElders() {
List<TreeNode> elderList = new ArrayList<TreeNode>();
TreeNode parentNode = this.getParentNode();
if (parentNode == ) {
return elderList;
} else {
elderList.add(parentNode);
elderList.addAll(parentNode.getElders());
return elderList;
}
}
/* 返回当前节点的晚辈集合 */
public List<TreeNode> getJuniors() {
List<TreeNode> juniorList = new ArrayList<TreeNode>();
List<TreeNode> childList = this.getChildList();
if (childList == ) {
return juniorList;
} else {
int childNumber = childList.size();
for (int i = 0; i < childNumber; i++) {
TreeNode junior = childList.get(i);
juniorList.add(junior);
juniorList.addAll(junior.getJuniors());
}
return juniorList;
}
}
/* 返回当前节点的孩子集合 */
public List<TreeNode> getChildList() {
return childList;
}
/* 删除节点和它下面的晚辈 */
public void deleteNode() {
TreeNode parentNode = this.getParentNode();
int id = this.getSelfId();
if (parentNode != ) {
parentNode.deleteChildNode(id);
}
}
/* 删除当前节点的某个子节点 */
public void deleteChildNode(int childId) {
List<TreeNode> childList = this.getChildList();
int childNumber = childList.size();
for (int i = 0; i < childNumber; i++) {
TreeNode child = childList.get(i);
if (child.getSelfId() == childId) {
childList.remove(i);
return;
}
}
}
/* 动态的插入一个新的节点到当前树中 */
public boolean insertJuniorNode(TreeNode treeNode) {
int juniorParentId = treeNode.getParentId();
if (this.parentId == juniorParentId) {
addChildNode(treeNode);
return true;
} else {
List<TreeNode> childList = this.getChildList();
int childNumber = childList.size();
boolean insertFlag;
for (int i = 0; i < childNumber; i++) {
TreeNode childNode = childList.get(i);
insertFlag = childNode.insertJuniorNode(treeNode);
if (insertFlag == true)
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
/* 找到一颗树中某个节点 */
public TreeNode findTreeNodeById(int id) {
if (this.selfId == id)
return this;
if (childList.isEmpty() || childList == ) {
return ;
} else {
int childNumber = childList.size();
for (int i = 0; i < childNumber; i++) {
TreeNode child = childList.get(i);
TreeNode resultNode = child.findTreeNodeById(id);
if (resultNode != ) {
return resultNode;
}
}
return ;
}
}
/* 遍历一棵树,层次遍历 */
public void traverse() {
if (selfId < 0)
return;
print(this.selfId);
if (childList == || childList.isEmpty())
return;
int childNumber = childList.size();
for (int i = 0; i < childNumber; i++) {
TreeNode child = childList.get(i);
child.traverse();
}
}
public void print(String content) {
System.out.println(content);
}
public void print(int content) {
System.out.println(String.valueOf(content));
}
public void setChildList(List<TreeNode> childList) {
this.childList = childList;
}
public int getParentId() {
return parentId;
}
public void setParentId(int parentId) {
this.parentId = parentId;
}
public int getSelfId() {
return selfId;
}
public void setSelfId(int selfId) {
this.selfId = selfId;
}
public TreeNode getParentNode() {
return parentNode;
}
public void setParentNode(TreeNode parentNode) {
this.parentNode = parentNode;
}
public String getNodeName() {
return nodeName;
}
public void setNodeName(String nodeName) {
this.nodeName = nodeName;
}
public Object getObj() {
return obj;
}
public void setObj(Object obj) {
this.obj = obj;
}
}
三、新建多叉树树工具类
通过前面这三步其实就已经构建起来了一颗多叉树,以及多叉树的一些基本操作。
例如这里的TreeNode root节点其实就是已经构建好的树,并存在了这个属性中。
public class TreeHelper {
private TreeNode root;
private List<TreeNode> tempNodeList;
private boolean isValidTree = true;
public TreeHelper() {
}
public TreeHelper(List<TreeNode> treeNodeList) {
tempNodeList = treeNodeList;
generateTree();
}
public static TreeNode getTreeNodeById(TreeNode tree, int id) {
if (tree == )
return ;
TreeNode treeNode = tree.findTreeNodeById(id);
return treeNode;
}
/** generate a tree from the given treeNode or entity list */
public void generateTree() {
HashMap nodeMap = putNodesIntoMap();
putChildIntoParent(nodeMap);
}
/**
* put all the treeNodes into a hash table by its id as the key
*
* @return hashmap that contains the treenodes
*/
protected HashMap putNodesIntoMap() {
int maxId = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
HashMap nodeMap = new HashMap<String, TreeNode>();
Iterator it = tempNodeList.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
TreeNode treeNode = (TreeNode) it.next();
int id = treeNode.getSelfId();
if (id < maxId) {
maxId = id;
this.root = treeNode;
}
String keyId = String.valueOf(id);
nodeMap.put(keyId, treeNode);
// System.out.println("keyId: " +keyId);
}
return nodeMap;
}
/**
* set the parent nodes point to the child nodes
*
* @param nodeMap
* a hashmap that contains all the treenodes by its id as the key
*/
protected void putChildIntoParent(HashMap nodeMap) {
Iterator it = nodeMap.values().iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
TreeNode treeNode = (TreeNode) it.next();
int parentId = treeNode.getParentId();
String parentKeyId = String.valueOf(parentId);
if (nodeMap.containsKey(parentKeyId)) {
TreeNode parentNode = (TreeNode) nodeMap.get(parentKeyId);
if (parentNode == ) {
this.isValidTree = false;
return;
} else {
parentNode.addChildNode(treeNode);
// System.out.println("childId: " +treeNode.getSelfId()+" parentId: "+parentNode.getSelfId());
}
}
}
}
/** initialize the tempNodeList property */
protected void initTempNodeList() {
if (this.tempNodeList == ) {
this.tempNodeList = new ArrayList<TreeNode>();
}
}
/** add a tree node to the tempNodeList */
public void addTreeNode(TreeNode treeNode) {
initTempNodeList();
this.tempNodeList.add(treeNode);
}
/**
* insert a tree node to the tree generated already
*
* @return show the insert operation is ok or not
*/
public boolean insertTreeNode(TreeNode treeNode) {
boolean insertFlag = root.insertJuniorNode(treeNode);
return insertFlag;
}
/**
* adapt the entities to the corresponding treeNode
*
* @param entityList
* list that contains the entities
*@return the list containg the corresponding treeNodes of the entities
*/
public static List<TreeNode> changeEnititiesToTreeNodes(List entityList) {
OrganizationEntity orgEntity = new OrganizationEntity();
List<TreeNode> tempNodeList = new ArrayList<TreeNode>();
TreeNode treeNode;
Iterator it = entityList.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
orgEntity = (OrganizationEntity) it.next();
treeNode = new TreeNode();
treeNode.setObj(orgEntity);
treeNode.setParentId(orgEntity.getParentId());
treeNode.setSelfId(orgEntity.getOrgId());
treeNode.setNodeName(orgEntity.getOrgName());
tempNodeList.add(treeNode);
}
return tempNodeList;
}
public boolean isValidTree() {
return this.isValidTree;
}
public TreeNode getRoot() {
return root;
}
public void setRoot(TreeNode root) {
this.root = root;
}
public List<TreeNode> getTempNodeList() {
return tempNodeList;
}
public void setTempNodeList(List<TreeNode> tempNodeList) {
this.tempNodeList = tempNodeList;
}
}
四、多叉树树的条件查询
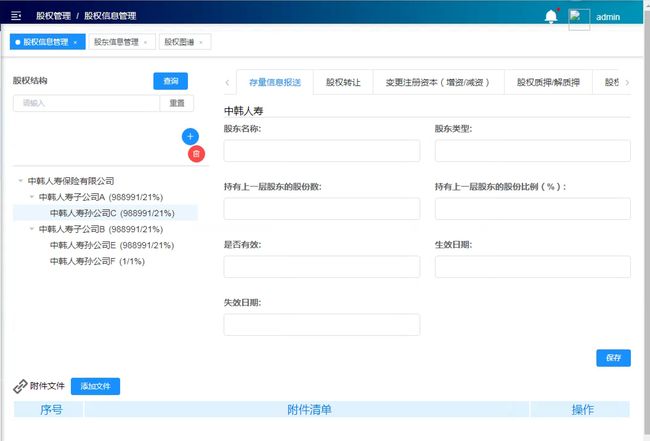
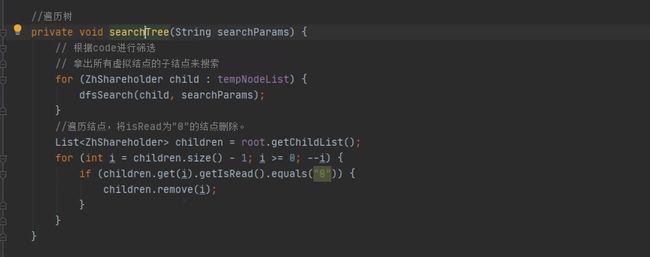
这里是参考我自己改写的代码,由于在云桌面里面,所以上了截图,逻辑跟上面的代码是可以衔接起来的,
比如这列构建一棵股东树,并根据股东名称对树进行查询,首先在实体类里面新加一个isRead字段默认为0,查询搜索到之后就会把它设为1,最后删除掉所有子节点中isRead为0的节点反给前端。
五、多叉树的节点新增
六、多叉树的节点删除
这里做的比较简单,前端传当前节点id,删除时看有没有parent_id为当前节点id的节点,如果有则不让删除当前节点,提醒用户先删除下层节点。
七、多叉树修改
这里目前也比较简单只让他修改节点的基础信息,前端传节点id然后修改就行了。