图像通用操作Python的实现
平时经常会对一个目录下的图像做统一处理,如缩放、旋转等等,之前使用C++处理,有时不是很方便。发现使用Python比较简单,代码量又很少,在Anacanda下执行起来也比较方便。因此,打算在后面遇到图像的常规处理时都将其实现放入到同一个py文件中,用时可随时执行。
所有实现存放在OpenCV_Test/demo/Python的image_generic_operations.py文件中,目前实现的仅有:图像旋转(仅限90,180,270度)、图像缩放,后面会逐渐增加,实现代码如下:
import os
import sys
import cv2
from inspect import currentframe, getframeinfo
import argparse
def get_image_list(path, image_suffix):
image_list = []
for x in os.listdir(path):
if x.endswith(image_suffix):
image_list.append(path+"/"+x)
return image_list
def get_image_name(image_name):
pos = image_name.rfind("/")
image_name = image_name[pos+1:]
return image_name
def image_rotate_clockwise(image_list, degrees, result_path):
print("image rotation ...")
os.makedirs(result_path, exist_ok=True)
if degrees == 90:
rotate_code = cv2.ROTATE_90_CLOCKWISE
elif degrees == 180:
rotate_code = cv2.ROTATE_180
elif degrees == 270:
rotate_code = cv2.ROTATE_90_COUNTERCLOCKWISE
else:
raise Exception("Unsupported rotat degrees: {}, it only supports: clockwise 90, 180, 270; Error Line: {}".format(degrees, getframeinfo(currentframe()).lineno))
for name in image_list:
print(f"\t{name}")
image_name = get_image_name(name)
#print(f"image name:{image_name}"); sys.exit(1)
mat = cv2.imread(name)
mat = cv2.rotate(mat, rotateCode=rotate_code)
cv2.imwrite(result_path+"/"+image_name, mat)
def image_resize(image_list, dst_width, dst_height, result_path):
print("image resize ...")
os.makedirs(result_path, exist_ok=True)
mat = cv2.imread(image_list[0])
h, w, _ = mat.shape
if h > dst_width and w > dst_height:
interpolation = cv2.INTER_AREA
else:
interpolation = cv2.INTER_CUBIC
for name in image_list:
print(f"\t{name}")
image_name = get_image_name(name)
#print(f"image name:{image_name}"); sys.exit(1)
mat = cv2.imread(name)
mat = cv2.resize(mat, (dst_width, dst_height), interpolation=interpolation)
cv2.imwrite(result_path+"/"+image_name, mat)
def parse_args():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="image generic operations", add_help=True)
parser.add_argument("--image_src_path", required=True, type=str, help="the path of the image to be operated, for example: ../../test_images")
parser.add_argument("--operation", required=True, type=str, choices=["rotate", "resize"], help="specifies the operation to take on the image")
parser.add_argument("--image_dst_path", required=True, type=str, help="the path where the resulting image is saved, for example: ../../test_images/result")
parser.add_argument("--degrees", default=90, type=int, choices=[90, 180, 270], help="the degrees by which the image is rotated clockwise")
parser.add_argument("--width", default=256, type=int, help="the width of the image after scaling")
parser.add_argument("--height", default=256, type=int, help="the height of the image after scaling")
parser.add_argument("--image_suffix", default=".png", type=str, help="the suffix of the processed image")
args = parser.parse_args()
return args
if __name__ == "__main__":
args = parse_args()
image_list = get_image_list(args.image_src_path, args.image_suffix)
if args.operation == "rotate":
image_rotate_clockwise(image_list, args.degrees, args.image_dst_path)
if args.operation == "resize":
image_resize(image_list, args.width, args.height, args.image_dst_path)
print("test finish")
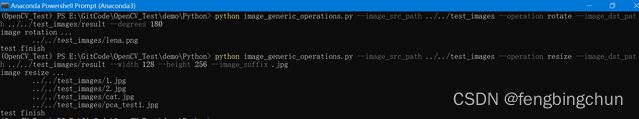
使用如下所示:
GitHub:https://github.com/fengbingchun/OpenCV_Test