清华青年AI自强作业2:线性回归预测
清华青年AI自强作业2:线性回归预测
-
- 任务目标
- 任务流程
- 任务详解
- 作业代码
- 参考链接
本文根据《清华青年AI自强计划》课程作业进行剖析,分享出来,与正在学习的同学一起讨论。
任务目标
本次作业任务是根据excel中的数据:身高、收入和喜欢程度,设计一个线性回归算法以进行预测(输入身高和收入,输出是否喜欢),并初步熟悉神经网络的基本流程。
简单说,就是干这件事:
-
输入:data.xls文件中收集的带标签数据
-
过程:搭建最基本的网络及相关模块
-
输出:利用线性回归拟合的一条直线进行预测
任务流程
建模流程
- 训练阶段:学习自动调参
- 输入训练集,读取xls中数据到np数组中
- 采用norm公式将数据归一化
- 设置梯度下降方法:BGD
- 迭代调参
- 内部调用loss和分界函数
- 绘制每次迭代产生的界限划分
- 调用梯度下降法调参
- 计算最终loss
- 推理阶段:定参预测
- 将测试集送入,进行预测
- 输出预测精度
代码架构
- LoadDataFromXLS
- DataPreProcess
- Normalization
- LinearModelTrain
- Sigmoid
- BGD
- LossCal
- ModelPrediction
- Classify
- Visualize
- PlotOriginData
- PlotDecisionBoundary
任务详解
读数据
- xls/csv文件读取
- 按一行不同列读取
- 读取某一列,从某行开始
- 组合到np数据中
详细说明:
- data:第一列身高,第二列工资,第三列喜好;=》对每一列求最大值、最小值、均值,对每一列进行归一化
- X:input data,输入数据,因素、特征:身高工资,仅两列
- y: label,监督学习的标签,结果真实值:喜欢或不喜欢
- y_hat:模型预测值:喜欢或不喜欢
归一化
- 公式:
x_norm = (x - mu) / (x_max - x_min) - numpy求矩阵中行列最值的方法
- np.min(X, axis=0) # 等价于 X.min(0)
- np.min(X, axis=1) # 等价于 X.min(1)
- 最大值求法与之同理。
详细说明:
- 0:输出压缩到1行,输出矩阵每1列的最值
- 1:输出压缩到1列,输出矩阵每1行的最值
随机梯度下降法
sigmoid函数控制输出为0-1,便于与分类标签01区分- 计算误差,代入到公式中更新权重
- 满足迭代次数后,返回权重
- trainMat: 插入第一列全为1,为了与偏置相乘,符合矩阵运算规则,多一维
作业代码
附待完成的作业代码如下,读者可以自行尝试填写请补全部分,并调试观察效果。
import xlrd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
'''
加载 xls 文件
'''
def loadData(filename):
workbook = xlrd.open_workbook(filename)
boyinfo = workbook.sheet_by_index(0)
col_num = boyinfo.ncols
row_num = boyinfo.nrows
col0 = boyinfo.col_values(0)[1:]
data = np.array(col0)
if col_num == 1:
return data
else:
for i in range(col_num-1):
coltemp = boyinfo.col_values(i+1)[1:]
data = np.c_[data, coltemp]
return data
def plotData(X, y):
pos = np.where(y==1)
neg = np.where(y==0)
p1 = plt.plot(X[pos, 0], X[pos, 1], marker='s', markersize=7, color='red')[0]
p2 = plt.plot(X[neg, 0], X[neg, 1], marker='o', markersize=7, color='green')[0]
return p1, p2
'''归一化'''
def normalization(X):
Xmin = np.min(X, axis=0)
Xmax = np.max(X, axis=0)
Xmu = np.mean(X, axis=0)
X_norm = (X - Xmu) / (Xmax - Xmin)
# print(X_norm)
return X_norm
# plot decision boundary:定义一个 plotDecisionBoundaryn 函数,输入参数是 训练集 trainX, 训练集 trainY, 直线斜率截距相关参数 w, 迭代次数 iter_num ,目的是为了画出决策的判断边界
def plotDecisionBoundary(trainX, trainY, w, iter_num = 0):
# prepare data
xcord1 = [];ycord1 = [];xcord2 = [];ycord2 = [] # 准备数据,定义四个空的列表,并分别赋值给 xcord1、ycord1、xcord2、ycord2,进行初始化
m, n = np.shape(trainX) # 通过使用 np.shape 函数,得到训练集 trainX 的形状大小,其中,m 为训练集 trainX 的行数,n 为训练集 trainX 的列数
for i in range(m): # 通过使用 for 循环语句,遍历训练集 trainX 所有的行,其中,i 可以取得值分别是 0,1,2,...,m-1,总共是 m 行
if trainY[i] == 1: # 通过使用 if 条件判断语句,如果训练集 trainY(标志)中的元素为 1,那么将训练集 trainX中的 trainX[i,1] 和 trainX[i,2] 分别添加到 xcord1 和 ycord1 列表中
xcord1.append(trainX[i,1]) # 通过 append 的方法,将训练集 trainX中 的 trainX[i,1] 添加到 xcord1 列表中,保存的是 pos 的横坐标, 代表 positive 的数据
ycord1.append(trainX[i,2]) # 通过 append 的方法,将训练集 trainX中 的 trainX[i,2] 添加到 ycord1 列表中,保存的是 pos 的纵坐标, 代表 positive 的数据
else: # 否则,如果训练集 trainY(标志)中的元素不为 1,那么将训练集 trainX中的 trainX[i,1] 和 trainX[i,2] 分别添加到 xcord2 和 ycord2 列表中
xcord2.append(trainX[i,1]) # 通过 append 的方法,将训练集 trainX中 的 trainX[i,1] 添加到 xcord2 列表中,保存的是 neg 的横坐标, 代表 negative 的数据
ycord2.append(trainX[i,2]) # 通过 append 的方法,将训练集 trainX中 的 trainX[i,2] 添加到 ycord2 列表中,保存的是 neg 的纵坐标, 代表 negative 的数据
x_min = min(trainX[:,1]) # 通过使用 min 函数,计算出 trainX[:,1] ,即 trainX 第2列的最小值,并赋值给 x_min
y_min = min(trainX[:,2]) # 通过使用 min 函数,计算出 trainX[:,2] ,即 trainX 第3列的最小值,并赋值给 y_min
x_max = max(trainX[:,1]) # 通过使用 max 函数,计算出 trainX[:,1] ,即 trainX 第2列的最大值,并赋值给 x_max
y_max = max(trainX[:,2]) # 通过使用 max 函数,计算出 trainX[:,2] ,即 trainX 第3列的最大值,并赋值给 y_max
# plot scatter & legend
fig = plt.figure(1) # 通过使用 plt.figure 函数,开始创建一个图形窗口,并赋值给 fig
# 通过使用 plt.scatter 函数,绘制散点图,横坐标为 xcord1, 纵坐标为 ycord1,标记大小为30,颜色为红色,形状样式为 s (正方形),代表 square, 图例标签为 'I like you'
plt.scatter(xcord1, ycord1, s=30, c='red', marker='s', label='I like you')
# 请补全 通过使用 plt.scatter 函数,绘制散点图,横坐标为 xcord2, 纵坐标为 ycord2,标记大小为30,颜色为绿色,形状样式为 o (圆形),代表 circle, 图例标签为 'I don't like you'
plt.scatter(xcord2, ycord2, s=30, c='green', marker='o', label='I don\'t like you')#请补全
plt.legend(loc='upper right') # 设置图例的位置为右上角
# set axis and ticks
delta_x = x_max-x_min # 计算横坐标的极差为横坐标最大值与最小值的差,并赋值给 delta_x
delta_y = y_max-y_min # 计算纵坐标的极差为纵坐标最大值与最小值的差,并赋值给 delta_y
# 设置横坐标的刻度:从 x_min - delta_x / 10 到 x_max + delta_x / 10,使用 np.arange 函数创建数组,步长为 1,并赋值给 my_x_ticks
my_x_ticks = np.arange(x_min - delta_x / 10, x_max + delta_x / 10, 1)
# 设置纵坐标的刻度:从 y_min - delta_y / 10 到 y_max + delta_y / 10,使用 np.arange 函数创建数组,步长为 1,并赋值给 my_y_ticks
my_y_ticks = np.arange(y_min - delta_y / 10, y_max + delta_y / 10, 1)
plt.xticks(my_x_ticks) # 通过使用 plt.xticks 函数,设置作图的横坐标的刻度为 my_x_ticks
plt.yticks(my_y_ticks) # 通过使用 plt.yticks 函数,设置作图的纵坐标的刻度为 my_y_ticks
# 通过使用 plt.axis 函数,设置作图的横坐标和纵坐标的显示范围,分别是[x_min-delta_x/10, x_max+delta_x/10] 和 [y_min-delta_y/10, y_max+delta_y/10]
plt.axis([x_min-delta_x/10, x_max+delta_x/10, y_min-delta_y/10, y_max+delta_y/10])
# drwa a line:绘制一条直线,用于决策判断
x = np.arange(x_min-delta_x/10, x_max+delta_x/10, 0.01) # 通过使用 np.arange 函数创建数组, 从 x_min - delta_x / 10 到 x_max + delta_x / 10,步长为 0.01,并赋值给 x
y = #请补全 # 通过公式计算得到直线的纵坐标: y = (-w[0]-w[1]*x)/w[2]
plt.plot(x, y.T) # 通过使用 plt.plot 函数绘制图象,其中,横坐标是 x , 纵坐标是 y.T, “.T” 表示的是矩阵的转置,因为绘图时需要横纵坐标的维度一致
# figure name:设置图像的文件名和标题名
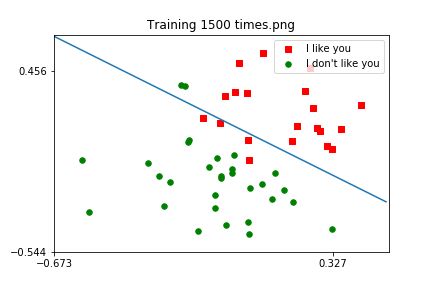
# 设置图像的文件名为 'Training ' + str(iter_num) + ' times.png',其中,str(iter_num) 表示将迭代次数 iter_num 转变成字符串,图片格式为 “png”
fig_name = 'Training ' + str(iter_num) + ' times.png'
# 设置图像的标题名为'Training ' + str(iter_num) + ' times.png',其中,str(iter_num) 表示将迭代次数 iter_num 转变成字符串,图片格式为 “png”
plt.title(fig_name)
fig.savefig(fig_name) # 通过使用 fig.savefig 函数,保存图片,分辨率等参数采取默认值
# plt.show() # 通过使用 plt.show 函数,显示绘制好的图片,注意的是必须关闭图像窗口,才可以进入执行后续的程序
plt.close(fig)
# sigmoid: 定义一个 激活(激励)函数 sigmoid 函数 (activation function),输入参数是 wx, 返回的是 sigmoid 函数值
def sigmoid(wx):
sigmoidV = #请补全 # 请补全 计算激活函数 sigmoid 函数 的函数值,计算公式为:1.0/(1.0+np.exp(-wx))
return sigmoidV
# BGD 批量梯度下降法求最优参数
# 定义一个BGD 函数,即:批量梯度下降法(Batch Gradient Descent,BGD),输入参数是 数据集 X 和 y,
# 迭代次数 iter_num, 学习率 alpha,又写作 lr (learning rate), 它表示每次向着J最陡峭的方向迈步的大小, 返回的是 权重 w
# 通过批量梯度下降法(Batch Gradient Descent,BGD),不断更新权重 W
def BGD(X, y, iter_num, alpha):
trainMat = np.mat(X) # 通过使用 np.mat 函数,将数据集 X 转换成矩阵类型,并赋值给 trainMat
trainY = np.mat(y).T # 通过使用 np.mat 函数,将数据集 y 转换成矩阵类型,并且转置,然后赋值给 trainY
m, n = np.shape(X) # 通过使用 np.shape 函数,得到数据集 X 的形状大小,其中,m 为数据集 X 的行数,n 为数据集 X 的列数
w = np.ones((n,1)) # 通过使用 np.ones 函数,创建元素全为 1 的矩阵,矩阵的大小为 n 行 1 列,并赋值给 w, 即:进行权重 w 的初始化,令其全为 1
for i in range(iter_num): # 通过 for 循环结构,开始进行迭代,其中,i 可取的数依次为:0,1 ,2,....,iter_num-1, 迭代次数总共有 iter_num 次
error = #请补全 # 计算迭代的误差 error:将预测得到的激活函数的数值 sigmoid(trainMat*w) 减去 实际的 trainY 数值
w = #请补全 # 更新权重 w , BGD 批量梯度下降法 的核心, w = w - (1.0/m)*alpha*trainMat.T*error
return w # 返回 w
# loss fuc Y_ 预测值 Y 真值
def loss(X, Y, w): # 定义一个 损失函数 loss 函数 (loss function),输入参数是 X, Y, w, 返回的是 损失函数的值
m, n = np.shape(X) # 通过使用 np.shape 函数,得到数据集 X 的形状大小,其中,m 为数据集 X 的行数,n 为数据集 X 的列数
trainMat = np.mat(X) # 通过使用 np.mat 函数,将数据集 X 转变成矩阵类型,并赋值给 trainMat
Y_ = [] # 准备数据,定义一个空的列表,并赋值给 Y_,进行初始化, 后续会通过 append 的方法向空列表内不断添加新的元素
for i in np.arange(m): # 通过 for 循环结构,遍历数据集 X 所有的行,其中,i 可取的数依次为:0,1 ,2,....,m-1, 数据集 X总共有 m 行
# 通过 append 的方法向空列表 Y_ 内不断添加新的元素,新元素是通过 训练的矩阵数据集 trainMat[i] 乘以权重 w 之后,再计算激活函数 sigmoid 的函数值
Y_.append(sigmoid(trainMat[i]*w))
m = np.shape(Y_)[0] # 通过使用 np.shape 函数,得到数据集 X 的形状大小,其中,np.shape(Y_)[0] 为数据集 X 的行数,并赋值给 m
sum_err = 0.0 # 初始化误差的总和为 0.0, 赋值给 sum_err, 后续会不断更新 误差的总和 sum_err 的数值
for i in range(m): # 通过 for 循环结构,遍历数据集 Y_ 所有的行,其中,i 可取的数依次为:0,1 ,2,....,m-1, 数据集 Y_ 总共有 m 行
# 请补全 更新误差的总和 sum_err 的数值, 每次 误差的总和 sum_err 递减 Y[i]*np.log(Y_[i])+(1-Y[i])*np.log(1-Y_[i]),这是 交叉熵损失函数( Cross Entropy Loss )的计算公式
sum_err = #请补全
return sum_err/m # 返回 sum_err
# classify:定义一个 classify 函数,输入参数是 wx, 返回的是标志 1 或者 0
def classify(wx):
prob = sigmoid(wx) # 计算概率:将激活函数 sigmoid(wx) 的数值作为预测的概率,并赋值给 prob
if prob > 0.5: # 如果 概率 prob 大于 0.5, 那么返回数值 1
return 1
else: # 否则,如果 概率 prob 不大于 0.5, 那么返回数值 0
return 0
# predict:定义一个 predict 函数,输入参数是 测试集 testX 和权重 w, 返回的是预测的结果 result
def predict(testX, w):
m, n = np.shape(testX) # 通过使用 np.shape 函数,得到测试集 testX 的形状大小,其中,m 为测试集 testX 的行数,n 为测试集 testX 的列数
testMat = np.mat(testX) # 通过使用 np.mat 函数,将测试集 testX 转换成矩阵类型,并赋值给 testMat
result = [] # 准备数据,定义一个空的列表,并赋值给结果 result,进行初始化, 后续会通过 append 的方法向空列表内不断添加新的元素
for i in np.arange(m): # 通过 for 循环结构,遍历测试集 testX 所有的行,其中,i 可取的数依次为:0,1 ,2,....,m-1, 测试集 testX 总共有 m 行
# 通过 append 的方法向空列表 result 内不断添加新的元素,新元素是通过调用 classify 函数进行预测得到,将返回的浮点型的 1 或者 0 添加到 空列表 result 内
result.append(classify(float(testMat[i]*w)))
return result # 返回预测结果result
# Precision:定义一个 Precision 函数,输入参数是数据集 X, Y 和权重 w, 返回的是 测试集的正确率
def Precision(X, Y, w):
result = predict(X, w) # 通过调用 predict 函数,输入测试集 X 和权重 w, 计算得到预测结果,并把返回的结果赋值给 result
right_sum = 0 # 进行初始化预测正确的数目,赋值 0 给 right_sum,后续如果预测正确,会不断增加 1
# 通过 for 循环结构,开始进行遍历,其中,i 可取的数依次为:0,1 ,2,....,len(result)-1, 预测结果 result 内元素的个数总和为 len(result)
for i in range(len(result)):
if result[i]-int(Y[i]) == 0: # 通过条件判断语句 if, 如果结果 result 的元素与 int(Y[i])相等,即:预测正确! 那么更新预测正确的数目 right_sum
right_sum += 1 # 如果预测正确! 那么更新预测正确的数目 right_sum,每次递增加 1
# 最后返回测试集预测的正确率,计算公式为:1.0*right_sum/len(Y),注意:乘以 1.0 的原因是把正确率变成浮点型,当然也可以直接用 float 强制转换
return 1.0*right_sum/len(Y)
if __name__ == "__main__":
data = loadData('data.xls')
X = data[:,:2]
y = data[:,2]
plt_data = plt.figure(1)
p1, p2 = plotData(X, y)
plt.xlabel('tall')
plt.ylabel('salary')
plt.legend((p1, p2), ('I like you', "I do not like you"), numpoints=1, handlelength=0)
plt_data.savefig('visualization_org.png') # 通过调用 plt.savefig 函数,保存图像,并且图像的文件名为:'visualization_org.jpg',其中,图片的格式为 'jpg'
# plt.show() # 通过调用 plt.show 函数,显示图像
plt.close(plt_data) # 通过调用 plt.close 来关闭窗口
'''将数据X归一化'''
X_norm = normalization(X)
plt_norm = plt.figure(1)
# print(X_norm)
p1_norm, p2_norm = plotData(X_norm, y)
# print(p1_norm)
# print(p2_norm)
plt.xlabel('tall')
plt.ylabel('salary')
plt.legend((p1_norm, p2_norm), ('I like you', 'I do not like you'), numpoints = 1, handlelength=0)
plt_norm.savefig("visualization_norm.png")
# plt.show(plt_norm) # 通过调用 plt.show 函数,显示图像
plt.close(plt_norm)
'''optimizing by BSD'''
iter_num = 1
lr = 0.05
m, n = np.shape(data)
offset = np.ones((m, 1))
trainMat = np.c_[offset, X_norm]
theta = BGD(trainMat, y, iter_num, lr)
# 通过调用 plotDecisionBoundary 函数,绘制分类决策的直线,其中,输入参数分别是:训练集 trainMat, 标签 y, 最优化后的权重 theta 和 迭代次数 iter_num
plotDecisionBoundary(trainMat, y, theta, iter_num)
cost = loss(trainMat, y, theta) # 通过调用 loss 函数,计算出本模型算法的损失函数,其中, 输入参数分别是: 训练集 trainMat, 标签 y 和 最优化后的权重 theta, 并赋值给 cost
print('Cost theta: {0}'.format(cost)) # 在屏幕上输出 损失函数的数值,其中,.format(cost) 的格式是更加规范的输出格式,当然也可以用转义字符 %s
# Compute accuracy on our training set
p = Precision(trainMat, y, theta) # 通过调用 Precision 函数,计算出预测 测试集结果的正确率,其中,输入参数分别是: 训练集 trainMat, 标签 y 和 最优化后的权重 theta, 并赋值给 p
print('Train Accuracy: {0}'.format(p)) # 在屏幕上输出 测试集正确率的数值,其中,.format(p) 的格式是更加规范的输出格式,当然也可以用转义字符 %s
print('finished!') # 在屏幕上输出完成的信息,'finished!'
其中,务必要注意的相关矩阵变量维度,整理如下,以便对照:
mat: m*n
w: n*1
mat.T: n*m
error: m*1
sigmoid: m*1
trainY: m*1
Y: 1*m
限于篇幅,完整作业代码参考见公众号:来知晓,后台回复:青年AI,即可获取。
参考链接
- 文科生都能零基础学AI?清华这门免费课程让我信了,link