C++的IO流与操作
一. C++IO流
IO的定义: 向设备输入数据和输出数据
设备:
- 文件
- 控制台
- 特定的数据类型(stringstream)
c++中,必须通过特定的已经定义好的类, 来处理IO(输入输出),一共11个类。
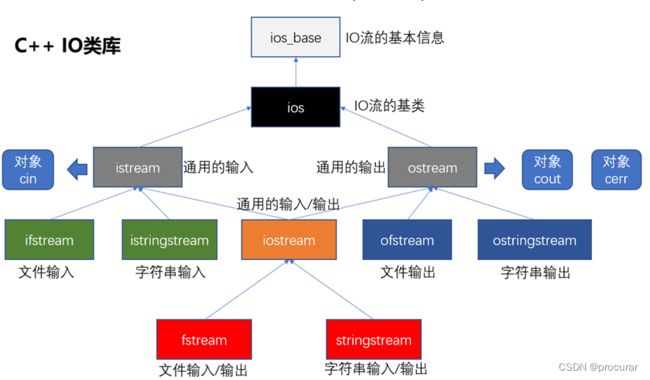
二.文件流打开、读写文件
- 文件流: 对文件进行读写操作
- 头文件: fstream
- 类库:
ifstream 对文件输入(读文件)
ofstream 对文件输出(写文件)
fstream 对文件输入或输出
文件打开方式:
| 模式标志 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| ios::in | 读方式打开文件 |
| ios:out | 写方式打开文件 |
| ios::trunc | 如果此文件已经存在, 就会打开文件之前把文件长度截断为0 |
| ios::app | 尾部追加加方式(在尾部写入) |
| ios::ate | 文件打开后, 定位到文件尾 |
| ios::binary | 二进制方式(默认是文本方式) |
以上打开方式, 可以使用位操作 | 组合起来
1.对文本文件流读写
①写文本文件
#include ②读文本文件
#include 2.对二进制文件流读写
文本文件和二进制文件的区别?
文本文件: 写数字1, 实际写入的是 ‘1’
二进制文件:写数字1, 实际写入的是 整数1(4个字节,最低字节是1, 高3个字节都是0);写字符‘R’实际输入的还是‘R’
①写二进制文件
使用文件流对象的write方法写入二进制数据.
#include 注意:如果用这种方式outfile << age << endl;那么文件中显示的将是整数对应的字符。
②读二进制文件
使用文件流对象的read方法.
#include 3.对文件流按格式读写取数据
使用stringstream
①按指定格式写文件
#include ②按指定格式读文件
C语言中有fscanf可以用,但是C++没有很好的解决方案, 需使用C语言的sscanf
#include 4.文件流的状态检查
- s.is_open( )
文件流是否打开成功,
- s.eof( )
流s是否结束
- s.fail( )
流s的failbit或者badbit被置位时, 返回true
failbit: 出现非致命错误,可挽回, 一般是软件错误
badbit置位, 出现致命错误, 一般是硬件错误或系统底层错误, 不可挽回
- s.bad( )
流s的badbit置位时, 返回true
- s.good( )
流s处于有效状态时, 返回true
- s.clear( )
流s的所有状态都被复位
补充:
- cin.ignore(count, c)
从输入流中提取并丢弃字符,直到遇到下列三种情况
1.提取的字符达到了参数count指定的数量
2.在输入序列中遇到文件结束(EOF)
3.输入序列中的下一个字符为参数c指定的字符(这个字符会被提取并丢弃)
count常常取:
std::numeric_limitsstd::streamsize::max() 相当于IO流的最大字符个数
常见用法:(把标准输入缓冲区cin的所有数据都清空)
cin.ignore(std::numeric_limits::max(), ‘\n’);
cin.ignore();
一般用于用完cin后面又用getline等会读取换行符的输入。
5.随机读写:文件流的定位
①seekg
偏移量 起始位置
seekg( off_type offset, ios::seekdir origin );
作用:设置输入流的位置
参数1: 偏移量
参数2: 相对位置
beg 相对于开始位置
cur 相对于当前位置
end 相对于结束位置
读取当前程序的最后50个字符
#include ②tellg
返回该输入流的当前位置(距离文件的起始位置的偏移量)
获取当前文件的长度
#include ③seekp
设置该输出流的位置
先向新文件写入:“123456789”
然后再在第4个字符位置写入“ABC”
#include 总结:
- 文件没有关闭 :文件没有关闭, close(),可能导致写文件失败
- 文件打开方式不合适
- 在VS2015的部分版本中,当sscanf和sscanf_s的格式字符串中含有中文时,可能会读取失败。在vs2019中未发现该类问题。
