基于centos7学习总结 -- shell脚本
shell 脚本必须要以"#!/bin.bash"开头。
脚本建议内容:
#!/bin/bash
# Program:
# This program shows "create 2 day age,1 day age and today filename"
#
#Creat:
# 2021/11/11
#
#Hirstory:
#
#
#Creater/Contact:
# Mr_Chang [email protected]
#
read -p "Please input filename" userfile
userfilename=${userfile:-"filename"}
date1=$(date --date='2 days ago' +%y-%m-%d)
date2=$(date --date='1 days ago' +%y-%m-%d)
date3=$(date +%y-%m-%d)
filename1=${userfilename}-${date1}
filename2=${userfilename}-${date2}
filename3=${userfilename}-${date3}
touch "${filename1}"
touch "${filename2}"
touch "${filename3}"
进行数值运算时需用$(())引起来计算。
$((计算式))
#!/bin/bash
# Program:
# This program shows "multiplay"
#
#Creat:
# 2021/11/11
#
#Hirstory:
#
#
#Creater/Contact:
# Mr_Chang [email protected]
#
read -p "file number:" fNum
read -p "secound number:" sNum
sum=$((${fNum}+${sNum}))
echo "total --> ${sum}"
脚本执行方式的差异(source、sh script 、./script)
source或./script:在当前环境下的shell执行,脚本运行结束后,脚本内的变量在当前shell中依然存在。
sh script:另打开一个子bash shell,运行完后子shell内的变量随着进程结束而消失,要想保留则需export来声明成环境变量。
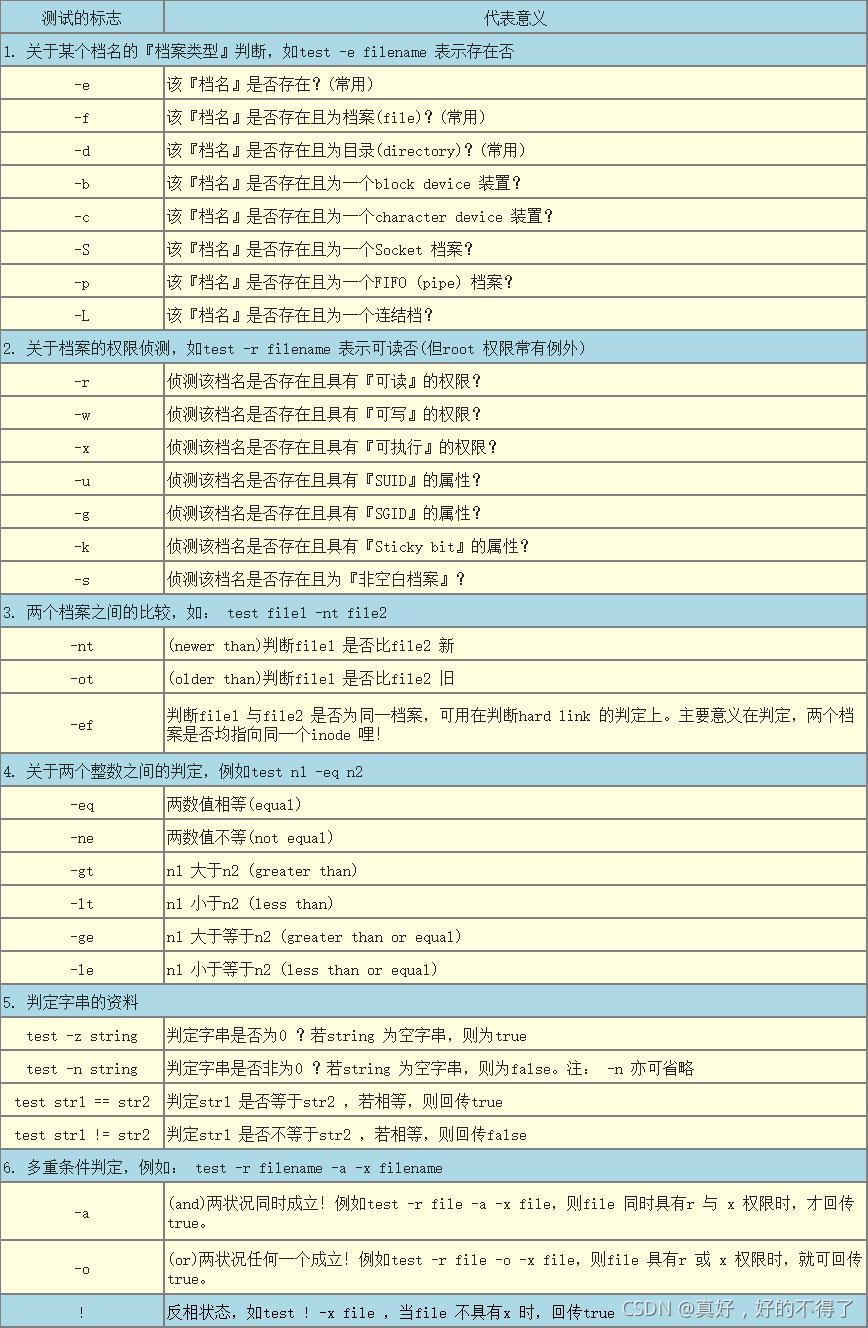
test 判别式
test可以使用 [ ] 来替换
[-z "${HOME}"] ; echo $?
使用 [ ] 时特别注意:
- 中括号内每个组件都需要使用空格来分隔开
- 中括号内的每个变量最好都使用双引号引起来
- 中括号内的常数最好以单或双引号括起来
shell脚本的默认变量
/tmp/shell/scriptname opt1 opt2 opt3 opt4
$0 $1 $2 $3 $4
$0:表示脚本名
$1:表示第一个变量
$2:表示第二个变量
.
.
.
$#:表示参数总个数
$@:表示【 “$1” “$2” “$3” “$4” 】之意,每个变数是独立的(用双引号括起来);
$*:表示【 “$1c$2c$3c$4” 】,其中 c 为分隔符,默认为空格, 前面代表【 “$1 $2 $3 $4” 】之意。
shift 造成号码偏移
#!/bin/bash
# Program:
# This program shows shell shift functionasily
#
#Creat:
# 2021/11/11
#
#Hirstory:
#
#
#Creater/Contact:
# Mr_Chang [email protected]
#
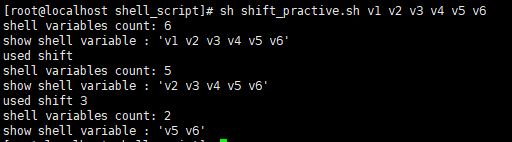
echo "shell variables count: $#"
echo "show shell variable : '$@'"
echo "used shift"
shift
echo "shell variables count: $#"
echo "show shell variable : '$@'"
echo "used shift 3"
shift 3
echo "shell variables count: $#"
echo "show shell variable : '$@'"
条件判别式
if…then
if [ 条件判别式 ]; then
条件成立时可以进入执行的代码
fi
#!/bin/bash
# Program:
# This program shows if else fi. know netstat
#
#Creat:
# 2021/11/11
#
#Hirstory:
#
#
#Creater/Contact:
# Mr_Chang [email protected]
#
#
testfile="/data/shell_script/netstat_data"
#在这里需要注意下,${testfile} 是取出变量值,然后 netstat -tnul 执行结果重定向到 变量值(/data/shell_script/netstat_data)文件内。
netstat -tnul > ${testfile}
testing=$( grep ':80' ${testfile})
if [ "${testing}" != "" ];then
echo "WWW is running in your system."
fi
testing=$( grep ':22' ${testfile})
if [ "${testing}" != "" ];then
echo "SSH is running in your system."
fi
testing=$( grep ':21' ${testfile})
if [ "${testing}" != "" ];then
echo "ftp is running in your system."
fi
testing=$( grep ':25' ${testfile})
if [ "${testing}" != "" ];then
echo "Mail is running in your system."
fi
在此再强调下," [ ] "符号和变量、常量或比较符之间一定要用空格隔开,否则会引起语法错误。
case…esac
语法:
case $变量名 in
"第一个变量的内容" )
程序段
;;
"第二个变量内容")
程序段
;;
* )
程序段
;;
“*” 表示如果没有匹配到变量内容,默认执行 “*” 下的程序段
#!/bin/bash
# Program:
# This program shows case in operation
#
#Creat:
# 2021/11/11
#
#Hirstory:
#
#
#Creater/Contact:
# Mr_Chang [email protected]
#
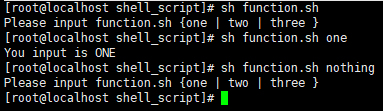
case ${1} in
"one" )
echo "You input is One."
;;
"tow" )
echo "You input is Two."
;;
"three" )
echo "You input is Three"
;;
* )
echo "Please input ${0} {one | two | three }"
;;
esac
shell 中的 function
语法:
function 函数名() {
程序段
{
#!/bin/bash
# Program:
# This program shows function option
#
#Creat:
# 2021/11/11
#
#Hirstory:
#
#
#Creater/Contact:
# Mr_Chang [email protected]
#
function printit(){
echo -n "You input is "
}
case ${1} in
"one" )
printit;echo ${1} | tr 'a-z' 'A-Z'
;;
"two" )
printit;echo ${1} | tr 'a-z' 'A-Z'
;;
"three" )
printit;echo ${1} | tr 'a-z' 'A-Z'
;;
* )
echo "Please input ${0} {one | two | three }"
;;
esac
在function中也是可以传递参数的。
使用 【$1】代表第一个参数,【$2】表示第二个参数
#!/bin/bash
# Program:
# This program shows function parameter option
#
#Creat:
# 2021/11/11
#
#Hirstory:
#
#
#Creater/Contact:
# Mr_Chang [email protected]
#
function printit(){
echo "Your choise is ${1}"
}
case ${1} in
"one" )
printit 1
;;
"two" )
printit 2
;;
"three" )
printit 3
;;
* )
echo "Please input ${0} {one | two | three }"
;;
esac
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
[root@localhost shell_script]# sh function_parm.sh one
Your choise is 1
[root@localhost shell_script]# sh function_parm.sh two
Your choise is 2
[root@localhost shell_script]# sh function_parm.sh three
Your choise is 3
[root@localhost shell_script]# sh function_parm.sh error
Please input function_parm.sh {one | two | three }
当 【 函数名(实参)】 传递给函数值是,函数第一个接收的变量为【$1】,第二个接收的变量为【$2】
循环 while do done 、until do done 和 for do done
while do done 和 until do done 称为不定时循环
while do done
语法:
while [condition]
do
程序段
done
当判别式成立时才会进入循环执行循环体程序段
until do done
语法:
until [condition]
do
程序段
done
当判别式为成立时结束循环
#!/bin/bash
# Program:
# This program shows loop
#
#Creat:
# 2021/11/11
#
#Hirstory:
#
#
#Creater/Contact:
# Mr_Chang [email protected]
#
while [ "${yn}" != "yes" -a "${yn}" != "YES" ]
do
read -p "Pl;ease input yes/YES to stop this program :" yn
done
echo "You input the correct answer!"
--------------------------------------------------------------
[root@localhost shell_script]# sh loop_unit_which.sh
Pl;ease input yes/YES to stop this program :y^Ho
Pl;ease input yes/YES to stop this program :o
Pl;ease input yes/YES to stop this program :y
Pl;ease input yes/YES to stop this program :yes
You input the correct answer!
[root@localhost shell_script]#
for do done
语法1:
for var in list
do
程序段
done
语法1有点类似类似于java的增强for循环,循环依次拿出集合中的值。
在此,循环一次从list中拿出一个值赋给变量【var】
语法2:
for((起始值; 判别式; 赋值运算))
do
程序段
done
语法2是针对固定循环次数的循环,指定循环多少次的意思。
例题1:随机选出今天去哪家店吃午餐
#!/bin/bash
# Program:
# This program shows loop for which choise one shops
#
#Creat:
# 2021/11/11
#
#Hirstory:
#
#
#Creater/Contact:
# Mr_Chang [email protected]
#
eat[1]="賣噹噹漢堡" # 寫下你所收集到的店家!
eat[2]="肯爺爺炸雞"
eat[3]="彩虹日式便當"
eat[4]="越油越好吃大雅"
eat[5]="想不出吃啥學餐"
eat[6]="太師父便當"
eat[7]="池上便當"
eat[8]="懷念火車便當"
eat[9]="一起吃泡麵"
index=9
randoms=$(( ${RANDOM}*${index}/32767 +1))
echo "Today we choice ${eat[${randoms}]}"
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
[root@localhost shell_script]# sh loop_for_random_choice.sh
Today we choice 池上便當
[root@localhost shell_script]# sh loop_for_random_choice.sh
Today we choice 懷念火車便當
[root@localhost shell_script]# sh loop_for_random_choice.sh
Today we choice 想不出吃啥學餐
[root@localhost shell_script]# sh loop_for_random_choice.sh
Today we choice 太師父便當
[root@localhost shell_script]# sh loop_for_random_choice.sh
Today we choice 池上便當
[root@localhost shell_script]# sh loop_for_random_choice.sh
Today we choice 越油越好吃大雅
例题2:随机选出今天三家店
#!/bin/bash
# Program:
# This program shows loop for while choise three shops
#
#Creat:
# 2021/11/11
#
#Hirstory:
#
#
#Creater/Contact:
# Mr_Chang [email protected]
#
eat[1]="賣噹噹漢堡" # 寫下你所收集到的店家!
eat[2]="肯爺爺炸雞"
eat[3]="彩虹日式便當"
eat[4]="越油越好吃大雅"
eat[5]="想不出吃啥學餐"
eat[6]="太師父便當"
eat[7]="池上便當"
eat[8]="懷念火車便當"
eat[9]="一起吃泡麵"
index=9
eated=0
while [ "${eated}" -lt 3 ]
do
mycheck=0
check=$(( ${RANDOM}*${index}/32767 +1))
if [ "${eated}" -ge 1 ]; then
for i in $(seq 1 ${eated})
do
if [ "${eatedcon[$i]}" == ${check} ];then
mycheck=1
fi
done
fi
done
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
[root@localhost shell_script]# sh loop_for_random_choice1.sh
choice 肯爺爺炸雞
choice 太師父便當
choice 彩虹日式便當
[root@localhost shell_script]# sh loop_for_random_choice1.sh
choice 池上便當
choice 越油越好吃大雅
choice 想不出吃啥學餐
[root@localhost shell_script]# sh loop_for_random_choice1.sh
choice 肯爺爺炸雞
choice 一起吃泡麵
choice 太師父便當
shell脚本的调试
sh [-nvx] script.sh
-n 仅进行语法检测,不执行脚本
-v 在执行前,先查看脚本内容
-x 将使用到的脚本内容显示到屏幕上,类似于debug
为了简单说明各参数的租用,这里使用相对较为简单例子说明
#!/bin/bash
# Program:
# This program shows "input you firstname and lastname. Program shows your full name" in you screen
#
#Creat:
# 2021/11/11 17:18
#
#Hirstory:
#
#
#Creater/Contact:
# Mr_Chang [email protected]
#
read -p "Please input your fistname:" firstname
read -p "Please inout your lastname" lastname
echo "Your name is ${firstname}${lastname}"
exit 0