emd,eemd,vmd,频谱图,分解图对比matlab代码
作为自己学习的一个记录吧。
对这个信号进行实验,其中公式是截图截的,懒得改了,f1就是s1。
对这个s信号进行分解。下面开始代码操作:
原始信号生成:运行该段代码,生成一个s.mat数据,并作图。
clear
clc
close all
t = 0:0.001:2;
s1 = cos(4*pi.*t);
figure
plot(t,s1)
%%
s2 = 1/4*cos(48*pi.*t);
figure
plot(t,s2)
%%
s3 = 1/16*cos(576*pi.*t);
figure
plot(t,s3)
%%
s4 = 3*wgn(1,length(t),10*log10(0.01));
figure
plot(t,s4)
figure
s = s1+s2+s3+s4;
plot(t,s)
save s.mat s
先上main_emd的主函数
这段代码就是对原始信号s进行emd分解,并出图。
clear
clc
close all
load s.mat
%% EEMD分解
[u its]=emd(s);
t = 0:0.001:2;
% [a b]=size(u);
a = 8;
figure(1);
imfn=u;
subplot(a+1,1,1);
plot(t,s); %故障信号
ylabel('s','fontsize',12,'fontname','宋体');
for n1=1:a
subplot(a+1,1,n1+1);
plot(t,u(n1,:));%输出IMF分量,a(:,n)则表示矩阵a的第n列元素,u(n1,:)表示矩阵u的n1行元素
ylabel(['IMF' int2str(n1)]);%int2str(i)是将数值i四舍五入后转变成字符,y轴命名
end
xlabel('时间\itt/s','fontsize',12,'fontname','宋体');
%%
figure('Name','频谱图','Color','white');
K = a;
L = length(t);
fs = 2001;
for i = 1:K
p=abs(fft(u(i,:))); %并fft,得到p,就是包络线的fft---包络谱
subplot(K,1,i);
plot((0:L-1)*fs/L,p) %绘制包络谱
xlim([0 fs/2]) %展示包络谱低频段,这句代码可以自己根据情况选择是否注释
if i ==1
title('频谱图'); ylabel(['IMF' int2str(i)]);%int2str(i)是将数值i四舍五入后转变成字符,y轴命名
elseif i==K
xlabel('频率'); ylabel(['IMF' int2str(i)]);%int2str(i)是将数值i四舍五入后转变成字符,y轴命名
else
ylabel(['IMF' int2str(i)]);%int2str(i)是将数值i四舍五入后转变成字符,y轴命名
end
end
set(gcf,'color','w');
再上main_eemd的主函数
这段代码就是对原始信号s进行eemd分解,并出图。其实和emd的主函数差不多。
clear
clc
% close all
load s.mat
%% EEMD分解
Nstd = 0.5;
NR = 500;
MaxIter = 5000;
[u its]=eemd(s,Nstd ,NR,MaxIter);
t = 0:0.001:2;
% [a b]=size(u);
a = 8;
figure(1);
imfn=u;
subplot(a+1,1,1);
plot(t,s); %故障信号
ylabel('s','fontsize',12,'fontname','宋体');
for n1=1:a
subplot(a+1,1,n1+1);
plot(t,u(n1,:));%输出IMF分量,a(:,n)则表示矩阵a的第n列元素,u(n1,:)表示矩阵u的n1行元素
ylabel(['IMF' int2str(n1)]);%int2str(i)是将数值i四舍五入后转变成字符,y轴命名
end
xlabel('时间\itt/s','fontsize',12,'fontname','宋体');
%%
figure('Name','频谱图','Color','white');
K = a;
L = length(t);
fs = 2001;
for i = 1:K
p=abs(fft(u(i,:))); %并fft,得到p,就是包络线的fft---包络谱
subplot(K,1,i);
plot((0:L-1)*fs/L,p) %绘制包络谱
xlim([0 fs/2]) %展示包络谱低频段,这句代码可以自己根据情况选择是否注释
if i ==1
title('频谱图'); ylabel(['IMF' int2str(i)]);%int2str(i)是将数值i四舍五入后转变成字符,y轴命名
elseif i==K
xlabel('频率'); ylabel(['IMF' int2str(i)]);%int2str(i)是将数值i四舍五入后转变成字符,y轴命名
else
ylabel(['IMF' int2str(i)]);%int2str(i)是将数值i四舍五入后转变成字符,y轴命名
end
end
set(gcf,'color','w');
然后是main_vmd的主函数
clear
clc
close all
load s.mat
X = s;
t = 0:0.0005:1;
%--------- some sample parameters forVMD:对于VMD样品参数进行设置---------------
alpha = 2000; % moderate bandwidth constraint:适度的带宽约束/惩罚因子
tau = 0; % noise-tolerance (no strict fidelity enforcement):噪声容限(没有严格的保真度执行)
K = 8; % modes:分解的模态数,可以自行设置,这里以8为例。
DC = 0; % no DC part imposed:无直流部分
init = 1; % initialize omegas uniformly :omegas的均匀初始化
tol = 1e-10;
%--------------- Run actual VMD code:数据进行vmd分解---------------------------
% [u,omega] = pVMD(s,fs, alpha, K, tol);
[u, u_hat, omega] = VMD(X, alpha, tau, K, DC, init, tol); %其中u为分解得到的IMF分量
a = K;
figure(1);
imfn=u;
subplot(a+1,1,1);
plot(t,s); %故障信号
ylabel('s','fontsize',12,'fontname','宋体');
for n1=1:a
subplot(a+1,1,n1+1);
plot(t,u(n1,:));%输出IMF分量,a(:,n)则表示矩阵a的第n列元素,u(n1,:)表示矩阵u的n1行元素
ylabel(['IMF' int2str(n1)]);%int2str(i)是将数值i四舍五入后转变成字符,y轴命名
end
xlabel('时间\itt/s','fontsize',12,'fontname','宋体');
%%
figure('Name','频谱图','Color','white');
K = a;
L = length(t);
fs = 2001;
for i = 1:K
p=abs(fft(u(i,:))); %并fft,得到p,就是包络线的fft---包络谱
subplot(K,1,i);
plot((0:L-1)*fs/L,p) %绘制包络谱
xlim([0 fs/2]) %展示包络谱低频段,这句代码可以自己根据情况选择是否注释
if i ==1
title('频谱图'); ylabel(['IMF' int2str(i)]);%int2str(i)是将数值i四舍五入后转变成字符,y轴命名
elseif i==K
xlabel('频率'); ylabel(['IMF' int2str(i)]);%int2str(i)是将数值i四舍五入后转变成字符,y轴命名
else
ylabel(['IMF' int2str(i)]);%int2str(i)是将数值i四舍五入后转变成字符,y轴命名
end
end
set(gcf,'color','w');最后再上emd、eemd、vmd的函数代码
首先是emd的:
function [imf,ort,nbits] = emd(varargin)
[x,t,sd,sd2,tol,MODE_COMPLEX,ndirs,display_sifting,sdt,sd2t,r,imf,k,nbit,NbIt,MAXITERATIONS,FIXE,FIXE_H,MAXMODES,INTERP,mask] = init(varargin{:});
if display_sifting
fig_h = figure;
end
%main loop : requires at least 3 extrema to proceed
while (~stop_EMD(r,MODE_COMPLEX,ndirs) && (k < MAXMODES+1 || MAXMODES == 0) && ~any(mask))
% current mode
m = r;
% mode at previous iteration
mp = m;
%computation of mean and stopping criterion
if FIXE
[stop_sift,moyenne] = stop_sifting_fixe(t,m,INTERP,MODE_COMPLEX,ndirs);
elseif FIXE_H
stop_count = 0;
[stop_sift,moyenne] = stop_sifting_fixe_h(t,m,INTERP,stop_count,FIXE_H,MODE_COMPLEX,ndirs);
else
[stop_sift,moyenne] = stop_sifting(m,t,sd,sd2,tol,INTERP,MODE_COMPLEX,ndirs);
end
% in case the current mode is so small that machine precision can cause
% spurious extrema to appear
if (max(abs(m))) < (1e-10)*(max(abs(x)))
if ~stop_sift
warning('emd:warning','forced stop of EMD : too small amplitude')
else
disp('forced stop of EMD : too small amplitude')
end
break
end
% sifting loop
while ~stop_sift && nbitMAXITERATIONS/5 && mod(nbit,floor(MAXITERATIONS/10))==0 && ~FIXE && nbit > 100)
disp(['mode ',int2str(k),', iteration ',int2str(nbit)])
if exist('s','var')
disp(['stop parameter mean value : ',num2str(s)])
end
[im,iM] = extr(m);
disp([int2str(sum(m(im) > 0)),' minima > 0; ',int2str(sum(m(iM) < 0)),' maxima < 0.'])
end
%sifting
m = m - moyenne;
%computation of mean and stopping criterion
if FIXE
[stop_sift,moyenne] = stop_sifting_fixe(t,m,INTERP,MODE_COMPLEX,ndirs);
elseif FIXE_H
[stop_sift,moyenne,stop_count] = stop_sifting_fixe_h(t,m,INTERP,stop_count,FIXE_H,MODE_COMPLEX,ndirs);
else
[stop_sift,moyenne,s] = stop_sifting(m,t,sd,sd2,tol,INTERP,MODE_COMPLEX,ndirs);
end
% display
if display_sifting && ~MODE_COMPLEX
NBSYM = 2;
[indmin,indmax] = extr(mp);
[tmin,tmax,mmin,mmax] = boundary_conditions(indmin,indmax,t,mp,mp,NBSYM);
envminp = interp1(tmin,mmin,t,INTERP);
envmaxp = interp1(tmax,mmax,t,INTERP);
envmoyp = (envminp+envmaxp)/2;
if FIXE || FIXE_H
display_emd_fixe(t,m,mp,r,envminp,envmaxp,envmoyp,nbit,k,display_sifting)
else
sxp=2*(abs(envmoyp))./(abs(envmaxp-envminp));
sp = mean(sxp);
display_emd(t,m,mp,r,envminp,envmaxp,envmoyp,s,sp,sxp,sdt,sd2t,nbit,k,display_sifting,stop_sift)
end
end
mp = m;
nbit=nbit+1;
NbIt=NbIt+1;
if(nbit==(MAXITERATIONS-1) && ~FIXE && nbit > 100)
if exist('s','var')
warning('emd:warning',['forced stop of sifting : too many iterations... mode ',int2str(k),'. stop parameter mean value : ',num2str(s)])
else
warning('emd:warning',['forced stop of sifting : too many iterations... mode ',int2str(k),'.'])
end
end
end % sifting loop
imf(k,:) = m;
if display_sifting
disp(['mode ',int2str(k),' stored'])
end
nbits(k) = nbit;
k = k+1;
r = r - m;
nbit=0;
end %main loop
if any(r) && ~any(mask)
imf(k,:) = r;
end
ort = io(x,imf);
if display_sifting
close
end
end
%---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
% tests if there are enough (3) extrema to continue the decomposition
function stop = stop_EMD(r,MODE_COMPLEX,ndirs)
if MODE_COMPLEX
for k = 1:ndirs
phi = (k-1)*pi/ndirs;
[indmin,indmax] = extr(real(exp(i*phi)*r));
ner(k) = length(indmin) + length(indmax);
end
stop = any(ner < 3);
else
[indmin,indmax] = extr(r);
ner = length(indmin) + length(indmax);
stop = ner < 3;
end
end
%---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
% computes the mean of the envelopes and the mode amplitude estimate
function [envmoy,nem,nzm,amp] = mean_and_amplitude(m,t,INTERP,MODE_COMPLEX,ndirs)
NBSYM = 2;
if MODE_COMPLEX
switch MODE_COMPLEX
case 1
for k = 1:ndirs
phi = (k-1)*pi/ndirs;
y = real(exp(-i*phi)*m);
[indmin,indmax,indzer] = extr(y);
nem(k) = length(indmin)+length(indmax);
nzm(k) = length(indzer);
[tmin,tmax,zmin,zmax] = boundary_conditions(indmin,indmax,t,y,m,NBSYM);
envmin(k,:) = interp1(tmin,zmin,t,INTERP);
envmax(k,:) = interp1(tmax,zmax,t,INTERP);
end
envmoy = mean((envmin+envmax)/2,1);
if nargout > 3
amp = mean(abs(envmax-envmin),1)/2;
end
case 2
for k = 1:ndirs
phi = (k-1)*pi/ndirs;
y = real(exp(-i*phi)*m);
[indmin,indmax,indzer] = extr(y);
nem(k) = length(indmin)+length(indmax);
nzm(k) = length(indzer);
[tmin,tmax,zmin,zmax] = boundary_conditions(indmin,indmax,t,y,y,NBSYM);
envmin(k,:) = exp(i*phi)*interp1(tmin,zmin,t,INTERP);
envmax(k,:) = exp(i*phi)*interp1(tmax,zmax,t,INTERP);
end
envmoy = mean((envmin+envmax),1);
if nargout > 3
amp = mean(abs(envmax-envmin),1)/2;
end
end
else
[indmin,indmax,indzer] = extr(m);
nem = length(indmin)+length(indmax);
nzm = length(indzer);
[tmin,tmax,mmin,mmax] = boundary_conditions(indmin,indmax,t,m,m,NBSYM);
envmin = interp1(tmin,mmin,t,INTERP);
envmax = interp1(tmax,mmax,t,INTERP);
envmoy = (envmin+envmax)/2;
if nargout > 3
amp = mean(abs(envmax-envmin),1)/2;
end
end
end
%-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
% default stopping criterion
function [stop,envmoy,s] = stop_sifting(m,t,sd,sd2,tol,INTERP,MODE_COMPLEX,ndirs)
try
[envmoy,nem,nzm,amp] = mean_and_amplitude(m,t,INTERP,MODE_COMPLEX,ndirs);
sx = abs(envmoy)./amp;
s = mean(sx);
stop = ~((mean(sx > sd) > tol | any(sx > sd2)) & (all(nem > 2)));
if ~MODE_COMPLEX
stop = stop && ~(abs(nzm-nem)>1);
end
catch
stop = 1;
envmoy = zeros(1,length(m));
s = NaN;
end
end
%-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
% stopping criterion corresponding to option FIX
function [stop,moyenne]= stop_sifting_fixe(t,m,INTERP,MODE_COMPLEX,ndirs)
try
moyenne = mean_and_amplitude(m,t,INTERP,MODE_COMPLEX,ndirs);
stop = 0;
catch
moyenne = zeros(1,length(m));
stop = 1;
end
end
%-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
% stopping criterion corresponding to option FIX_H
function [stop,moyenne,stop_count]= stop_sifting_fixe_h(t,m,INTERP,stop_count,FIXE_H,MODE_COMPLEX,ndirs)
try
[moyenne,nem,nzm] = mean_and_amplitude(m,t,INTERP,MODE_COMPLEX,ndirs);
if (all(abs(nzm-nem)>1))
stop = 0;
stop_count = 0;
else
stop_count = stop_count+1;
stop = (stop_count == FIXE_H);
end
catch
moyenne = zeros(1,length(m));
stop = 1;
end
end
%-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
% displays the progression of the decomposition with the default stopping criterion
function display_emd(t,m,mp,r,envmin,envmax,envmoy,s,sb,sx,sdt,sd2t,nbit,k,display_sifting,stop_sift)
subplot(4,1,1)
plot(t,mp);hold on;
plot(t,envmax,'--k');plot(t,envmin,'--k');plot(t,envmoy,'r');
title(['IMF ',int2str(k),'; iteration ',int2str(nbit),' before sifting']);
set(gca,'XTick',[])
hold off
subplot(4,1,2)
plot(t,sx)
hold on
plot(t,sdt,'--r')
plot(t,sd2t,':k')
title('stop parameter')
set(gca,'XTick',[])
hold off
subplot(4,1,3)
plot(t,m)
title(['IMF ',int2str(k),'; iteration ',int2str(nbit),' after sifting']);
set(gca,'XTick',[])
subplot(4,1,4);
plot(t,r-m)
title('residue');
disp(['stop parameter mean value : ',num2str(sb),' before sifting and ',num2str(s),' after'])
if stop_sift
disp('last iteration for this mode')
end
if display_sifting == 2
pause(0.01)
else
pause
end
end
%---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
% displays the progression of the decomposition with the FIX and FIX_H stopping criteria
function display_emd_fixe(t,m,mp,r,envmin,envmax,envmoy,nbit,k,display_sifting)
subplot(3,1,1)
plot(t,mp);hold on;
plot(t,envmax,'--k');plot(t,envmin,'--k');plot(t,envmoy,'r');
title(['IMF ',int2str(k),'; iteration ',int2str(nbit),' before sifting']);
set(gca,'XTick',[])
hold off
subplot(3,1,2)
plot(t,m)
title(['IMF ',int2str(k),'; iteration ',int2str(nbit),' after sifting']);
set(gca,'XTick',[])
subplot(3,1,3);
plot(t,r-m)
title('residue');
if display_sifting == 2
pause(0.01)
else
pause
end
end
%---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
% defines new extrema points to extend the interpolations at the edges of the
% signal (mainly mirror symmetry)
function [tmin,tmax,zmin,zmax] = boundary_conditions(indmin,indmax,t,x,z,nbsym)
lx = length(x);
if (length(indmin) + length(indmax) < 3)
error('not enough extrema')
end
% boundary conditions for interpolations :
if indmax(1) < indmin(1)
if x(1) > x(indmin(1))
lmax = fliplr(indmax(2:min(end,nbsym+1)));
lmin = fliplr(indmin(1:min(end,nbsym)));
lsym = indmax(1);
else
lmax = fliplr(indmax(1:min(end,nbsym)));
lmin = [fliplr(indmin(1:min(end,nbsym-1))),1];
lsym = 1;
end
else
if x(1) < x(indmax(1))
lmax = fliplr(indmax(1:min(end,nbsym)));
lmin = fliplr(indmin(2:min(end,nbsym+1)));
lsym = indmin(1);
else
lmax = [fliplr(indmax(1:min(end,nbsym-1))),1];
lmin = fliplr(indmin(1:min(end,nbsym)));
lsym = 1;
end
end
if indmax(end) < indmin(end)
if x(end) < x(indmax(end))
rmax = fliplr(indmax(max(end-nbsym+1,1):end));
rmin = fliplr(indmin(max(end-nbsym,1):end-1));
rsym = indmin(end);
else
rmax = [lx,fliplr(indmax(max(end-nbsym+2,1):end))];
rmin = fliplr(indmin(max(end-nbsym+1,1):end));
rsym = lx;
end
else
if x(end) > x(indmin(end))
rmax = fliplr(indmax(max(end-nbsym,1):end-1));
rmin = fliplr(indmin(max(end-nbsym+1,1):end));
rsym = indmax(end);
else
rmax = fliplr(indmax(max(end-nbsym+1,1):end));
rmin = [lx,fliplr(indmin(max(end-nbsym+2,1):end))];
rsym = lx;
end
end
tlmin = 2*t(lsym)-t(lmin);
tlmax = 2*t(lsym)-t(lmax);
trmin = 2*t(rsym)-t(rmin);
trmax = 2*t(rsym)-t(rmax);
% in case symmetrized parts do not extend enough
if tlmin(1) > t(1) || tlmax(1) > t(1)
if lsym == indmax(1)
lmax = fliplr(indmax(1:min(end,nbsym)));
else
lmin = fliplr(indmin(1:min(end,nbsym)));
end
if lsym == 1
error('bug')
end
lsym = 1;
tlmin = 2*t(lsym)-t(lmin);
tlmax = 2*t(lsym)-t(lmax);
end
if trmin(end) < t(lx) || trmax(end) < t(lx)
if rsym == indmax(end)
rmax = fliplr(indmax(max(end-nbsym+1,1):end));
else
rmin = fliplr(indmin(max(end-nbsym+1,1):end));
end
if rsym == lx
error('bug')
end
rsym = lx;
trmin = 2*t(rsym)-t(rmin);
trmax = 2*t(rsym)-t(rmax);
end
zlmax =z(lmax);
zlmin =z(lmin);
zrmax =z(rmax);
zrmin =z(rmin);
tmin = [tlmin t(indmin) trmin];
tmax = [tlmax t(indmax) trmax];
zmin = [zlmin z(indmin) zrmin];
zmax = [zlmax z(indmax) zrmax];
end
%---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
%extracts the indices of extrema
function [indmin, indmax, indzer] = extr(x,t)
if(nargin==1)
t=1:length(x);
end
m = length(x);
if nargout > 2
x1=x(1:m-1);
x2=x(2:m);
indzer = find(x1.*x2<0);
if any(x == 0)
iz = find( x==0 );
indz = [];
if any(diff(iz)==1)
zer = x == 0;
dz = diff([0 zer 0]);
debz = find(dz == 1);
finz = find(dz == -1)-1;
indz = round((debz+finz)/2);
else
indz = iz;
end
indzer = sort([indzer indz]);
end
end
d = diff(x);
n = length(d);
d1 = d(1:n-1);
d2 = d(2:n);
indmin = find(d1.*d2<0 & d1<0)+1;
indmax = find(d1.*d2<0 & d1>0)+1;
% when two or more successive points have the same value we consider only one extremum in the middle of the constant area
% (only works if the signal is uniformly sampled)
if any(d==0)
imax = [];
imin = [];
bad = (d==0);
dd = diff([0 bad 0]);
debs = find(dd == 1);
fins = find(dd == -1);
if debs(1) == 1
if length(debs) > 1
debs = debs(2:end);
fins = fins(2:end);
else
debs = [];
fins = [];
end
end
if length(debs) > 0
if fins(end) == m
if length(debs) > 1
debs = debs(1:(end-1));
fins = fins(1:(end-1));
else
debs = [];
fins = [];
end
end
end
lc = length(debs);
if lc > 0
for k = 1:lc
if d(debs(k)-1) > 0
if d(fins(k)) < 0
imax = [imax round((fins(k)+debs(k))/2)];
end
else
if d(fins(k)) > 0
imin = [imin round((fins(k)+debs(k))/2)];
end
end
end
end
if length(imax) > 0
indmax = sort([indmax imax]);
end
if length(imin) > 0
indmin = sort([indmin imin]);
end
end
end
%---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
function ort = io(x,imf)
% ort = IO(x,imf) computes the index of orthogonality
%
% inputs : - x : analyzed signal
% - imf : empirical mode decomposition
n = size(imf,1);
s = 0;
for i = 1:n
for j =1:n
if i~=j
s = s + abs(sum(imf(i,:).*conj(imf(j,:)))/sum(x.^2));
end
end
end
ort = 0.5*s;
end
%---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
function [x,t,sd,sd2,tol,MODE_COMPLEX,ndirs,display_sifting,sdt,sd2t,r,imf,k,nbit,NbIt,MAXITERATIONS,FIXE,FIXE_H,MAXMODES,INTERP,mask] = init(varargin)
x = varargin{1};
if nargin == 2
if isstruct(varargin{2})
inopts = varargin{2};
else
error('when using 2 arguments the first one is the analyzed signal X and the second one is a struct object describing the options')
end
elseif nargin > 2
try
inopts = struct(varargin{2:end});
catch
error('bad argument syntax')
end
end
% default for stopping
defstop = [0.05,0.5,0.05];
opt_fields = {'t','stop','display','maxiterations','fix','maxmodes','interp','fix_h','mask','ndirs','complex_version'};
defopts.stop = defstop;
defopts.display = 0;
defopts.t = 1:max(size(x));
defopts.maxiterations = 2000;
defopts.fix = 0;
defopts.maxmodes = 0;
defopts.interp = 'spline';
defopts.fix_h = 0;
defopts.mask = 0;
defopts.ndirs = 4;
defopts.complex_version = 2;
opts = defopts;
if(nargin==1)
inopts = defopts;
elseif nargin == 0
error('not enough arguments')
end
names = fieldnames(inopts);
for nom = names'
if ~any(strcmpi(char(nom), opt_fields))
error(['bad option field name: ',char(nom)])
end
if ~isempty(eval(['inopts.',char(nom)])) % empty values are discarded
eval(['opts.',lower(char(nom)),' = inopts.',char(nom),';'])
end
end
t = opts.t;
stop = opts.stop;
display_sifting = opts.display;
MAXITERATIONS = opts.maxiterations;
FIXE = opts.fix;
MAXMODES = opts.maxmodes;
INTERP = opts.interp;
FIXE_H = opts.fix_h;
mask = opts.mask;
ndirs = opts.ndirs;
complex_version = opts.complex_version;
if ~isvector(x)
error('X must have only one row or one column')
end
if size(x,1) > 1
x = x.';
end
if ~isvector(t)
error('option field T must have only one row or one column')
end
if ~isreal(t)
error('time instants T must be a real vector')
end
if size(t,1) > 1
t = t';
end
if (length(t)~=length(x))
error('X and option field T must have the same length')
end
if ~isvector(stop) || length(stop) > 3
error('option field STOP must have only one row or one column of max three elements')
end
if ~all(isfinite(x))
error('data elements must be finite')
end
if size(stop,1) > 1
stop = stop';
end
L = length(stop);
if L < 3
stop(3)=defstop(3);
end
if L < 2
stop(2)=defstop(2);
end
if ~ischar(INTERP) || ~any(strcmpi(INTERP,{'linear','cubic','spline'}))
error('INTERP field must be ''linear'', ''cubic'', ''pchip'' or ''spline''')
end
%special procedure when a masking signal is specified
if any(mask)
if ~isvector(mask) || length(mask) ~= length(x)
error('masking signal must have the same dimension as the analyzed signal X')
end
if size(mask,1) > 1
mask = mask.';
end
opts.mask = 0;
imf1 = emd(x+mask,opts);
imf2 = emd(x-mask,opts);
if size(imf1,1) ~= size(imf2,1)
warning('emd:warning',['the two sets of IMFs have different sizes: ',int2str(size(imf1,1)),' and ',int2str(size(imf2,1)),' IMFs.'])
end
S1 = size(imf1,1);
S2 = size(imf2,1);
if S1 ~= S2
if S1 < S2
tmp = imf1;
imf1 = imf2;
imf2 = tmp;
end
imf2(max(S1,S2),1) = 0;
end
imf = (imf1+imf2)/2;
end
sd = stop(1);
sd2 = stop(2);
tol = stop(3);
lx = length(x);
sdt = sd*ones(1,lx);
sd2t = sd2*ones(1,lx);
if FIXE
MAXITERATIONS = FIXE;
if FIXE_H
error('cannot use both ''FIX'' and ''FIX_H'' modes')
end
end
MODE_COMPLEX = ~isreal(x)*complex_version;
if MODE_COMPLEX && complex_version ~= 1 && complex_version ~= 2
error('COMPLEX_VERSION parameter must equal 1 or 2')
end
% number of extrema and zero-crossings in residual
ner = lx;
nzr = lx;
r = x;
if ~any(mask) % if a masking signal is specified "imf" already exists at this stage
imf = [];
end
k = 1;
% iterations counter for extraction of 1 mode
nbit=0;
% total iterations counter
NbIt=0;
end 然后是eemd的,注意eemd的调用了emd的函数,所以eemd不要单独使用哦。
function [modos its]=eemd(x,Nstd,NR,MaxIter)
%--------------------------------------------------------------------------
%WARNING: this code needs to include in the same
%directoy the file emd.m developed by Rilling and Flandrin.
% -------------------------------------------------------------------------
% OUTPUT
% modos: contain the obtained modes in a matrix with the rows being the modes
% its: contain the iterations needed for each mode for each realization
%
% INPUT
% x: signal to decompose
% Nstd: noise standard deviation
% NR: number of realizations
% MaxIter: maximum number of sifting iterations allowed.
% -------------------------------------------------------------------------
% Syntax
%
% modos=eemd(x,Nstd,NR,MaxIter)
% [modos its]=eemd(x,Nstd,NR,MaxIter)
% -------------------------------------------------------------------------
% NOTE: if Nstd=0 and NR=1, the EMD decomposition is obtained.
% -------------------------------------------------------------------------
desvio_estandar=std(x);
x=x/desvio_estandar;
xconruido=x+Nstd*randn(size(x));
[modos, o, it]=emd(xconruido,'MAXITERATIONS',MaxIter);
modos=modos/NR;
iter=it;
if NR>=2
for i=2:NR
xconruido=x+Nstd*randn(size(x));
[temp, ort, it]=emd(xconruido,'MAXITERATIONS',MaxIter);
temp=temp/NR;
lit=length(it);
[p liter]=size(iter);
if litalto
modos=[modos; zeros(abs(diferencia),ancho)];
end;
if alto>filas
temp=[temp;zeros(abs(diferencia),ancho)];
end;
modos=modos+temp;
end;
end;
its=iter;
modos=modos*desvio_estandar;
end VMD的脚本函数之前文章有说过,有需要的来这里粘贴吧 ,只粘贴vmd.m即可哦。
(52条消息) VMD分解,matlab代码,包络线,包络谱,中心频率,峭度值,能量熵,近似熵,包络熵,频谱图,希尔伯特变换,包含所有程序MATLAB代码,-西储大学数据集为例_包络谱绘制_今天吃饺子的博客-CSDN博客
也不能光上代码,结果图全部都在这里哦
首先是原始信号的图,原谅我太懒,没整坐标轴。这里简单说一下,从上往下依次是s1,s2,s3,s4,s,这里就是对s信号进行的分解哦。
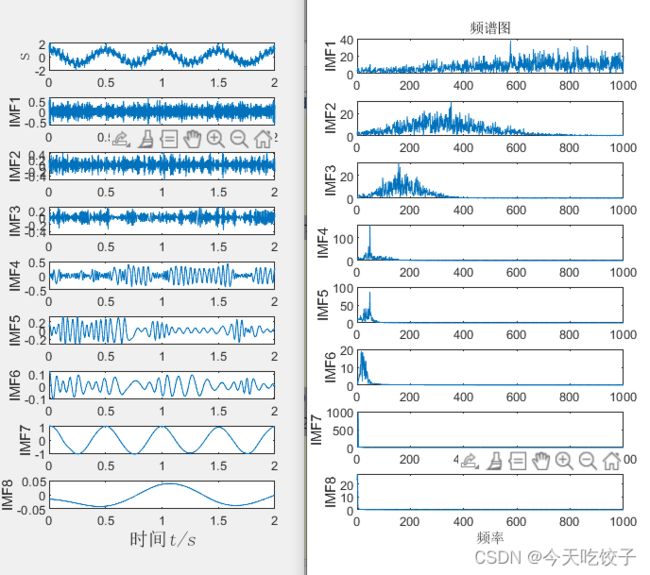
然后是emd信号的分解图和频谱图
eemd的分解图和频谱图
VMD信号的分解图和频谱图
话说emd和eemd的差别看似不大哦,但是多少还是有点区别的,稍微降低了一些模态重叠。反观VMD在模态重叠这方面,确实无敌哦,基本无重叠。
okkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkk,祝大家代码永不出错!