2.labelme转yolo格式和MS COCO格式
2.labelme转yolo格式和MS COCO格式
2.1 数据集划分
import os
import random
import shutil
def moveimg(fileDir, tarDir):
pathDir = os.listdir(fileDir) # 取图片的原始路径
filenumber = len(pathDir)
rate = 0.01 # 自定义抽取图片的比例,比方说100张抽10张,那就是0.1
picknumber = int(filenumber * rate) # 按照rate比例从文件夹中取一定数量图片
sample = random.sample(pathDir, picknumber) # 随机选取picknumber数量的样本图片
print(sample)
for name in sample:
shutil.move(fileDir + name, tarDir + "\\" + name)
return
def movelabel(file_list, file_label_train, file_label_val):
for i in file_list:
if (i.endswith('.png') or i.endswith('.jpg') ):
# filename = file_label_train + "\\" + i[:-4] + '.xml' # 可以改成xml文件将’.txt‘改成'.xml'就可以了
# filename = file_label_train + "\\" + i[:-4] + '.txt' # 可以改成xml文件将’.txt‘改成'.xml'就可以了
filename = file_label_train + i[:-4] + '.json'
# print(filename)
if os.path.exists(filename):
shutil.move(filename, file_label_val)
print(i + "处理成功!")
if __name__ == '__main__':
Dataset_name = "Triangle_215_Keypoint_Labelme"
fileDir = r"../data/train/train_pic/" + Dataset_name + "/"# 源图片文件夹路径
tarDir = r"../data/val/val_pic/" + Dataset_name + "/"# 图片移动到新的文件夹路径
if not os.path.exists(tarDir):
os.mkdir(tarDir)
moveimg(fileDir, tarDir)
file_list = os.listdir(tarDir)
file_label_train = r"../data/train/labelme_label/" + Dataset_name + "/"# 源图片标签路径
file_label_val = r"../data/val/labelme_label/" + Dataset_name + "/"# 标签
if not os.path.exists(file_label_val):
os.mkdir(file_label_val)
# 移动到新的文件路径
movelabel(file_list, file_label_train, file_label_val)
2.2 labelme转yolo格式
一个txt文件对应一张图片
2.2.1 yolo格式keypoint annotation txt文件中某一行的意义
这张三角板的yolo格式标注信息及其意义如下:
2.2.2labelme2yolo-keypoint-单个转换
import os
import json
import numpy as np
# 框的类别
bbox_class = {
'sjb_rect':0
}
# 关键点的类别
keypoint_class = ['angle_30', 'angle_60', 'angle_90']
labelme_path = 'DSC_0209.json'
with open(labelme_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
labelme = json.load(f)
img_width = labelme['imageWidth'] # 图像宽度
img_height = labelme['imageHeight'] # 图像高度
# 生成 YOLO 格式的 txt 文件
suffix = labelme_path.split('.')[-2]
yolo_txt_path = suffix + '.txt'
with open(yolo_txt_path, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
for each_ann in labelme['shapes']: # 遍历每个标注
if each_ann['shape_type'] == 'rectangle': # 如果遇到框
yolo_str = ''
## 框的信息
# 框的类别 ID
bbox_class_id = bbox_class[each_ann['label']]
yolo_str += '{} '.format(bbox_class_id)
# 左上角和右下角的 XY 像素坐标
bbox_top_left_x = int(min(each_ann['points'][0][0], each_ann['points'][1][0]))
bbox_bottom_right_x = int(max(each_ann['points'][0][0], each_ann['points'][1][0]))
bbox_top_left_y = int(min(each_ann['points'][0][1], each_ann['points'][1][1]))
bbox_bottom_right_y = int(max(each_ann['points'][0][1], each_ann['points'][1][1]))
# 框中心点的 XY 像素坐标
bbox_center_x = int((bbox_top_left_x + bbox_bottom_right_x) / 2)
bbox_center_y = int((bbox_top_left_y + bbox_bottom_right_y) / 2)
# 框宽度
bbox_width = bbox_bottom_right_x - bbox_top_left_x
# 框高度
bbox_height = bbox_bottom_right_y - bbox_top_left_y
# 框中心点归一化坐标
bbox_center_x_norm = bbox_center_x / img_width
bbox_center_y_norm = bbox_center_y / img_height
# 框归一化宽度
bbox_width_norm = bbox_width / img_width
# 框归一化高度
bbox_height_norm = bbox_height / img_height
yolo_str += '{:.5f} {:.5f} {:.5f} {:.5f} '.format(bbox_center_x_norm, bbox_center_y_norm, bbox_width_norm, bbox_height_norm)
## 找到该框中所有关键点,存在字典 bbox_keypoints_dict 中
bbox_keypoints_dict = {}
for each_ann in labelme['shapes']: # 遍历所有标注
if each_ann['shape_type'] == 'point': # 筛选出关键点标注
# 关键点XY坐标、类别
x = int(each_ann['points'][0][0])
y = int(each_ann['points'][0][1])
label = each_ann['label']
if (x>bbox_top_left_x) & (x<bbox_bottom_right_x) & (y<bbox_bottom_right_y) & (y>bbox_top_left_y): # 筛选出在该个体框中的关键点
bbox_keypoints_dict[label] = [x, y]
## 把关键点按顺序排好
for each_class in keypoint_class: # 遍历每一类关键点
if each_class in bbox_keypoints_dict:
keypoint_x_norm = bbox_keypoints_dict[each_class][0] / img_width
keypoint_y_norm = bbox_keypoints_dict[each_class][1] / img_height
yolo_str += '{:.5f} {:.5f} {} '.format(keypoint_x_norm, keypoint_y_norm, 2) # 2-可见不遮挡 1-遮挡 0-没有点
else: # 不存在的点,一律为0
yolo_str += '0 0 0 '.format(keypoint_x_norm, keypoint_y_norm, 0)
# 写入 txt 文件中
f.write(yolo_str + '\n')
print('{} --> {} 转换完成'.format(labelme_path, yolo_txt_path))
2.2.3labelme2yolo-keypoint-批量转换
目录结构如下:
yolov8/
├─.ipynb_checkpoints/
│ └─labelme2yolo-keypoint-批量转换-checkpoint.ipynb
├─labelme2yolo-keypoint-单个转换/
│ ├─.ipynb_checkpoints/
│ ├─DSC_0209.jpg
│ ├─DSC_0209.json
│ ├─DSC_0209.txt
│ └─labelme2yolo-keypoint-单个转换.ipynb
├─labelme2yolo-keypoint-批量转换.ipynb
└─SJB_25_Dataset/
├─labelme_jsons/
└─labels/
批量转换代码如下:
import os
import json
import shutil
# 函数 处理单个labelme标注json文件
def process_single_json(labelme_path, save_folder='../../labels/train'):
with open(labelme_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
labelme = json.load(f)
img_width = labelme['imageWidth'] # 图像宽度
img_height = labelme['imageHeight'] # 图像高度
# 生成 YOLO 格式的 txt 文件
suffix = labelme_path.split('.')[-2]
yolo_txt_path = suffix + '.txt'
with open(yolo_txt_path, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
for each_ann in labelme['shapes']: # 遍历每个标注
if each_ann['shape_type'] == 'rectangle': # 每个框,在 txt 里写一行
yolo_str = ''
## 框的信息
# 框的类别 ID
bbox_class_id = bbox_class[each_ann['label']]
yolo_str += '{} '.format(bbox_class_id)
# 左上角和右下角的 XY 像素坐标
bbox_top_left_x = int(min(each_ann['points'][0][0], each_ann['points'][1][0]))
bbox_bottom_right_x = int(max(each_ann['points'][0][0], each_ann['points'][1][0]))
bbox_top_left_y = int(min(each_ann['points'][0][1], each_ann['points'][1][1]))
bbox_bottom_right_y = int(max(each_ann['points'][0][1], each_ann['points'][1][1]))
# 框中心点的 XY 像素坐标
bbox_center_x = int((bbox_top_left_x + bbox_bottom_right_x) / 2)
bbox_center_y = int((bbox_top_left_y + bbox_bottom_right_y) / 2)
# 框宽度
bbox_width = bbox_bottom_right_x - bbox_top_left_x
# 框高度
bbox_height = bbox_bottom_right_y - bbox_top_left_y
# 框中心点归一化坐标
bbox_center_x_norm = bbox_center_x / img_width
bbox_center_y_norm = bbox_center_y / img_height
# 框归一化宽度
bbox_width_norm = bbox_width / img_width
# 框归一化高度
bbox_height_norm = bbox_height / img_height
yolo_str += '{:.5f} {:.5f} {:.5f} {:.5f} '.format(bbox_center_x_norm, bbox_center_y_norm, bbox_width_norm, bbox_height_norm)
## 找到该框中所有关键点,存在字典 bbox_keypoints_dict 中
bbox_keypoints_dict = {}
for each_ann in labelme['shapes']: # 遍历所有标注
if each_ann['shape_type'] == 'point': # 筛选出关键点标注
# 关键点XY坐标、类别
x = int(each_ann['points'][0][0])
y = int(each_ann['points'][0][1])
label = each_ann['label']
if (x>bbox_top_left_x) & (x<bbox_bottom_right_x) & (y<bbox_bottom_right_y) & (y>bbox_top_left_y): # 筛选出在该个体框中的关键点
bbox_keypoints_dict[label] = [x, y]
## 把关键点按顺序排好
for each_class in keypoint_class: # 遍历每一类关键点
if each_class in bbox_keypoints_dict:
keypoint_x_norm = bbox_keypoints_dict[each_class][0] / img_width
keypoint_y_norm = bbox_keypoints_dict[each_class][1] / img_height
yolo_str += '{:.5f} {:.5f} {} '.format(keypoint_x_norm, keypoint_y_norm, 2) # 2-可见不遮挡 1-遮挡 0-没有点
else: # 不存在的点,一律为0
yolo_str += '0 0 0 '
# 写入 txt 文件中
f.write(yolo_str + '\n')
shutil.move(yolo_txt_path, save_folder)
print('{} --> {} 转换完成'.format(labelme_path, yolo_txt_path))
# 数据集文件夹名称
Dataset_root = 'SJB_25_Dataset'
# 框的类别
bbox_class = {
'sjb_rect':0
}
# 关键点的类别
keypoint_class = ['angle_30', 'angle_60', 'angle_90']
labelme_json_path = Dataset_root+'/labelme_jsons'
if not os.path.exists(Dataset_root+'/labels'):
os.mkdir(Dataset_root+'/labels')
if not os.path.exists(Dataset_root+'/labels/train'):
os.mkdir(Dataset_root+'/labels/train')
if not os.path.exists(Dataset_root+'/labels/val'):
os.mkdir(Dataset_root+'/labels/val')
os.chdir(labelme_json_path)
save_folder = '../labels/train'
for labelme_path in os.listdir():
try:
process_single_json(labelme_path, save_folder=save_folder)
except:
print('******有误******', labelme_path)
print('YOLO格式的txt标注文件已保存至 ', save_folder)
2.3 labelme转MS COCO格式
一个json文件包含数据集的全部标注信息
2.3.1 MS COCO数据集介绍
MS COCO全称是Microsoft Common Objects in Context,是由微软开发维护的大型图像数据集,包括不同检测任务:
- Object Detection([主要处理人、车、大象等])
- DensePose(姿态密度检测)
- Keypoints(关键点检测)
- Captions(字幕标注)
2.3.2 MS COCO数据格式
MS COCO使用JSON存储标注数据
2.3.2.1 data format
这里以关键点检测的验证集为例,查看它的json内容
import json
json_path = r"D:\Python\Jupyter\pytorch\yolov8\MS COCO\annotations\person_keypoints_val2017.json"
json_labels = json.load(open(json_path, "r"))
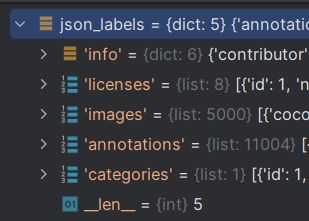
第一层结构如下,包含info、licenses、images、annotations、categories,共五个对象
info保存数据集的信息
licenses保存数据集的许可协议
annotations保存标注信息:
| 参数 | 参数含义 |
|---|---|
segmentation |
保存polygon数据 |
num_keypoints |
表示给定对象的标记关键点数量(对象集合或小对象的num_keypoints值为0) |
area |
保存目标面积 |
iscrowd |
值为0表示单个对象,值为1表示对象集合 |
keypoints |
是一个长度为3k的数组,其中k是定义的关键点类别总数(在MS COCO中k=17)。每个关键点按顺序依次存储横坐标x,纵坐标y和关键点可见性v。v=0:未标记(此情况下,x=y=0),v=1:标记但不可见,v=2:标记且可见。如果关键点位于上面segmentation的框内,则该关键点被视为可见 |
image_id |
表示MS COCO数据集的图片id |
bbox |
保存边界框(bounding box)左上角点的横纵坐标、宽度和高度 |
category_id |
表示类别id |
id |
表示label的id,也就是每一个label(人、等车实例对应的bbox)都有一个和它一一对应的id。一个image_id可以对应多个id(一张图片上有多个label),而一个id只能对应一个image_id |
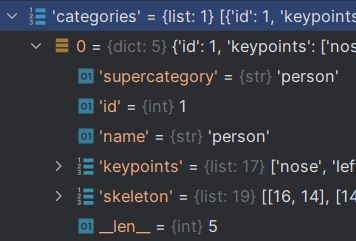
categories保存类别信息:
关键点检测的JSON结构如下:
{
"info" : {
"year" : int,
"version" : str,
"description" : str,
"contributor" : str,
"url" : str,
"date_created" : datetime,
},
"licenses" : {
"id" : int,
"name" : str,
"url" : str,
},
"images" : {
"id" : int,
"width" : int,
"height" : int,
"file_name" : str,
"license" : int,
"flickr_url" : str,
"coco_url" : str,
"date_captured" : datetime,
},
"annotations" : {
"segmentation" : RLE or [polygon],
"num_keypoints" : int,
"area" : float,
"iscrowd" : 0 or 1,
"keypoints" : [x1,y1,v1,...],
"image_id" : int,
"bbox" : [x,y,width,height],
"category_id" : int,
"id" : int,
},
"categories" : {
"supercategory" : str,
"id" : int,
"name" : str,
"keypoints" : [str],
"skeleton" : [edge],
},
}
2.3.2.1 result format
还是只展示关键点检测的结果
[{
"image_id": int,
"category_id": int,
"keypoints": [x1,y1,v1,...,xk,yk,vk],
"score": float,
}]
2.3.3 labelme2MSCOCO-keypoint-单个转换
import os
import json
import numpy as np
# 函数-处理单个labelme标注json文件
def process_single_json(labelme, image_id=1):
'''
输入labelme的json数据,输出coco格式的每个框的关键点标注信息
'''
global ANN_ID
coco_annotations = []
for each_ann in labelme['shapes']: # 遍历该json文件中的所有标注
if each_ann['shape_type'] == 'rectangle': # 筛选出框
# 该框元数据
bbox_dict = {}
bbox_dict['category_id'] = 1
bbox_dict['segmentation'] = []
bbox_dict['iscrowd'] = 0
bbox_dict['segmentation'] = []
bbox_dict['image_id'] = image_id
bbox_dict['id'] = ANN_ID
# print(ANN_ID)
ANN_ID += 1
# 获取该框坐标
bbox_left_top_x = min(int(each_ann['points'][0][0]), int(each_ann['points'][1][0]))
bbox_left_top_y = min(int(each_ann['points'][0][1]), int(each_ann['points'][1][1]))
bbox_right_bottom_x = max(int(each_ann['points'][0][0]), int(each_ann['points'][1][0]))
bbox_right_bottom_y = max(int(each_ann['points'][0][1]), int(each_ann['points'][1][1]))
bbox_w = bbox_right_bottom_x - bbox_left_top_x
bbox_h = bbox_right_bottom_y - bbox_left_top_y
bbox_dict['bbox'] = [bbox_left_top_x, bbox_left_top_y, bbox_w, bbox_h] # 左上角x、y、框的w、h
bbox_dict['area'] = bbox_w * bbox_h
# 筛选出分割多段线
for each_ann in labelme['shapes']: # 遍历所有标注
if each_ann['shape_type'] == 'polygon': # 筛选出分割多段线标注
# 第一个点的坐标
first_x = each_ann['points'][0][0]
first_y = each_ann['points'][0][1]
if (first_x>bbox_left_top_x) & (first_x<bbox_right_bottom_x) & (first_y<bbox_right_bottom_y) & (first_y>bbox_left_top_y): # 筛选出在该个体框中的关键点
bbox_dict['segmentation'] = list(map(lambda x: list(map(lambda y: round(y, 2), x)), each_ann['points'])) # 坐标保留两位小数
# bbox_dict['segmentation'] = each_ann['points']
# 筛选出该个体框中的所有关键点
bbox_keypoints_dict = {}
for each_ann in labelme['shapes']: # 遍历所有标注
if each_ann['shape_type'] == 'point': # 筛选出关键点标注
# 关键点横纵坐标
x = int(each_ann['points'][0][0])
y = int(each_ann['points'][0][1])
label = each_ann['label']
if (x>bbox_left_top_x) & (x<bbox_right_bottom_x) & (y<bbox_right_bottom_y) & (y>bbox_left_top_y): # 筛选出在该个体框中的关键点
bbox_keypoints_dict[label] = [x, y]
bbox_dict['num_keypoints'] = len(bbox_keypoints_dict)
# print(bbox_keypoints_dict)
# 把关键点按照类别顺序排好
bbox_dict['keypoints'] = []
for each_class in class_list['keypoints']:
if each_class in bbox_keypoints_dict:
bbox_dict['keypoints'].append(bbox_keypoints_dict[each_class][0])
bbox_dict['keypoints'].append(bbox_keypoints_dict[each_class][1])
bbox_dict['keypoints'].append(2) # 2-可见不遮挡 1-遮挡 0-没有点
else: # 不存在的点,一律为0
bbox_dict['keypoints'].append(0)
bbox_dict['keypoints'].append(0)
bbox_dict['keypoints'].append(0)
coco_annotations.append(bbox_dict)
return coco_annotations
# 使用函数处理单个labelme格式的json标注文件
labelme_json_path = 'DSC_0209.json'
with open(labelme_json_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
labelme = json.load(f)
process_single_json(labelme)
# 添加images和annotations
IMG_ID = 0
ANN_ID = 0
# 遍历所有 labelme 格式的 json 文件
for labelme_json in os.listdir():
if labelme_json.split('.')[-1] == 'json':
with open(labelme_json, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
labelme = json.load(f)
## 提取图像元数据
img_dict = {}
img_dict['file_name'] = labelme['imagePath']
img_dict['height'] = labelme['imageHeight']
img_dict['width'] = labelme['imageWidth']
img_dict['id'] = IMG_ID
coco['images'].append(img_dict)
## 提取框和关键点信息
coco_annotations = process_single_json(labelme, image_id=IMG_ID)
coco['annotations'] += coco_annotations
IMG_ID += 1
print(labelme_json, '已处理完毕')
else:
pass
# 保存生成的文件
if not os.path.exists('output_coco'):
os.mkdir('output_coco')
print('创建新目录 output_coco')
coco_path = 'output_coco/coco_sample.json'
with open(coco_path, 'w') as f:
json.dump(coco, f, indent=2)
# 验证MS COCO格式的标注
from pycocotools.coco import COCO
my_coco = COCO(coco_path)
2.3.4 labelme2MSCOCO-keypoint-批量转换
目录结构如下:
labelme2MSCOCO-keypoint-单个转换/
├─.ipynb_checkpoints/
│ └─labelme2MSCOCO-keypoint-单个转换-checkpoint.ipynb
├─DSC_0209.jpg
├─DSC_0209.json
├─labelme2MSCOCO-keypoint-单个转换.ipynb
└─output_coco/
└─coco_sample.json
转换代码如下:
import os
import json
Dataset_root = 'SJB_25_Dataset'
labelme_json_path = Dataset_root+'/labelme_jsons'
class_list = {
'supercategory': 'sjb_rect',
'id': 1,
'name': 'sjb_rect',
'keypoints': ['angle_30', 'angle_60', 'angle_90'], # 大小写敏感
'skeleton':[[0,1], [0,2], [1,2]]
}
if not os.path.exists(Dataset_root+'/MSCOCO_labels'):
os.mkdir(Dataset_root+'/MSCOCO_labels')
if not os.path.exists(Dataset_root+'/MSCOCO_labels/train'):
os.mkdir(Dataset_root+'/MSCOCO_labels/train')
if not os.path.exists(Dataset_root+'/MSCOCO_labels/val'):
os.mkdir(Dataset_root+'/MSCOCO_labels/val')
def process_single_json(labelme, image_id=1):
'''
输入labelme的json数据,输出coco格式的每个框的关键点标注信息
'''
global ANN_ID
coco_annotations = []
for each_ann in labelme['shapes']: # 遍历该json文件中的所有标注
if each_ann['shape_type'] == 'rectangle': # 筛选出个体框
# 个体框元数据
bbox_dict = {}
bbox_dict['category_id'] = 1
bbox_dict['segmentation'] = []
bbox_dict['iscrowd'] = 0
bbox_dict['segmentation'] = []
bbox_dict['image_id'] = image_id
bbox_dict['id'] = ANN_ID
# print(ANN_ID)
ANN_ID += 1
# 获取个体框坐标
bbox_left_top_x = min(int(each_ann['points'][0][0]), int(each_ann['points'][1][0]))
bbox_left_top_y = min(int(each_ann['points'][0][1]), int(each_ann['points'][1][1]))
bbox_right_bottom_x = max(int(each_ann['points'][0][0]), int(each_ann['points'][1][0]))
bbox_right_bottom_y = max(int(each_ann['points'][0][1]), int(each_ann['points'][1][1]))
bbox_w = bbox_right_bottom_x - bbox_left_top_x
bbox_h = bbox_right_bottom_y - bbox_left_top_y
bbox_dict['bbox'] = [bbox_left_top_x, bbox_left_top_y, bbox_w, bbox_h] # 左上角x、y、框的w、h
bbox_dict['area'] = bbox_w * bbox_h
# 筛选出分割多段线
for each_ann in labelme['shapes']: # 遍历所有标注
if each_ann['shape_type'] == 'polygon': # 筛选出分割多段线标注
# 第一个点的坐标
first_x = each_ann['points'][0][0]
first_y = each_ann['points'][0][1]
if (first_x>bbox_left_top_x) & (first_x<bbox_right_bottom_x) & (first_y<bbox_right_bottom_y) & (first_y>bbox_left_top_y): # 筛选出在该个体框中的关键点
bbox_dict['segmentation'] = list(map(lambda x: list(map(lambda y: round(y, 2), x)), each_ann['points'])) # 坐标保留两位小数
# bbox_dict['segmentation'] = each_ann['points']
# 筛选出该个体框中的所有关键点
bbox_keypoints_dict = {}
for each_ann in labelme['shapes']: # 遍历所有标注
if each_ann['shape_type'] == 'point': # 筛选出关键点标注
# 关键点横纵坐标
x = int(each_ann['points'][0][0])
y = int(each_ann['points'][0][1])
label = each_ann['label']
if (x>bbox_left_top_x) & (x<bbox_right_bottom_x) & (y<bbox_right_bottom_y) & (y>bbox_left_top_y): # 筛选出在该个体框中的关键点
bbox_keypoints_dict[label] = [x, y]
bbox_dict['num_keypoints'] = len(bbox_keypoints_dict)
# print(bbox_keypoints_dict)
# 把关键点按照类别顺序排好
bbox_dict['keypoints'] = []
for each_class in class_list['keypoints']:
if each_class in bbox_keypoints_dict:
bbox_dict['keypoints'].append(bbox_keypoints_dict[each_class][0])
bbox_dict['keypoints'].append(bbox_keypoints_dict[each_class][1])
bbox_dict['keypoints'].append(2) # 2-可见不遮挡 1-遮挡 0-没有点
else: # 不存在的点,一律为0
bbox_dict['keypoints'].append(0)
bbox_dict['keypoints'].append(0)
bbox_dict['keypoints'].append(0)
coco_annotations.append(bbox_dict)
return coco_annotations
def process_folder():
IMG_ID = 0
ANN_ID = 0
# 遍历所有 labelme 格式的 json 文件
for labelme_json in os.listdir():
if labelme_json.split('.')[-1] == 'json':
with open(labelme_json, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
labelme = json.load(f)
## 提取图像元数据
img_dict = {}
img_dict['file_name'] = labelme['imagePath']
img_dict['height'] = labelme['imageHeight']
img_dict['width'] = labelme['imageWidth']
img_dict['id'] = IMG_ID
coco['images'].append(img_dict)
## 提取框和关键点信息
coco_annotations = process_single_json(labelme, image_id=IMG_ID)
coco['annotations'] += coco_annotations
IMG_ID += 1
print(labelme_json, '已处理完毕')
else:
pass
coco = {}
coco['categories'] = []
coco['categories'].append(class_list)
coco['images'] = []
coco['annotations'] = []
IMG_ID = 0
ANN_ID = 0
path = os.path.join(Dataset_root, 'labelme_jsons')
os.chdir(path)
process_folder()
# 保存coco标注文件
coco_path = '../MSCOCO_labels/train/train_coco.json'
with open(coco_path, 'w') as f:
json.dump(coco, f, indent=2)
os.chdir('../../')
参考资料
- 同济子豪兄-两天带你搞定关键点检测毕业设计全流程
- https://cocodataset.org/#format-data
- MS COCO数据集介绍以及pycocotools简单使用
- MSCOCO api详解 —— Keypoints
- 目标检测数据集MSCOCO详解