redis中的 adlist链表实现
adlist源码解读(基于redis 6.2.7)
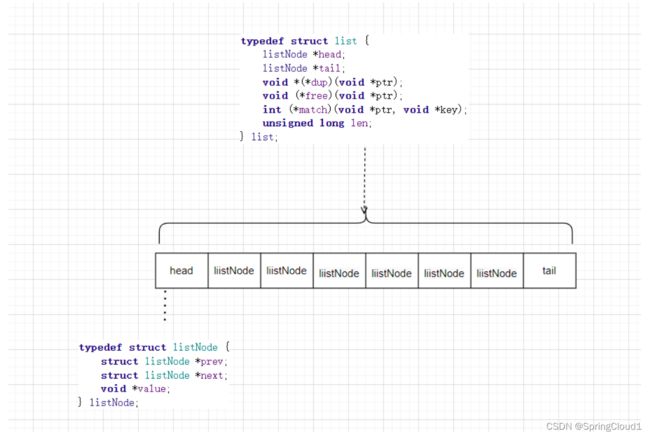
1丶打开源码 adlist.h
typedef struct listNode {
struct listNode *prev;
struct listNode *next;
void *value;
} listNode;
//迭代时 使用
typedef struct listIter {
listNode *next;
int direction; 迭代方向
} listIter;
typedef struct list {
listNode *head;
listNode *tail;
void *(*dup)(void *ptr);
void (*free)(void *ptr);
int (*match)(void *ptr, void *key);
unsigned long len; 连表的长度,O(1)
} list;
可见,list的结构还是比较简单的.listNode,代表每个list的结点, list整体包含了头结点,尾部结点. 而 listIter 则是在迭代操作中使用,下面具体分析.
2丶创建
list *listCreate(void)
{
struct list *list;
//分配空间,分配失败则返回null
if ((list = zmalloc(sizeof(*list))) == NULL)
return NULL;
list->head = list->tail = NULL;
list->len = 0;
list->dup = NULL;
list->free = NULL;
list->match = NULL;
return list;
}
创建比较简单,即分配内存空间. 在我的电脑64位, sizeof(list) = 48; 5个指针一个long类型 = 6 * 8=48
3丶增加节点
3.1头插法
/* Add a new node to the list, to head, containing the specified 'value'
* pointer as value.
* 在list中添加一个新的node,放在头部.包含一个特殊的 "value", value的指针.
* On error, NULL is returned and no operation is performed (i.e. the
* list remains unaltered).
若失败则返回NULL, 没有操作执行
* On success the 'list' pointer you pass to the function is returned.
若成功,则返回入参 传递过来的list指针
*/
list *listAddNodeHead(list *list, void *value)
{
//新增的节点
listNode *node;
if ((node = zmalloc(sizeof(*node))) == NULL)
return NULL;
//新增加点赋值
node->value = value;
//list长度为0,属于刚创建的状态
if (list->len == 0) {
//首位节点都是这个新增的节点
list->head = list->tail = node;
//前后节点都是NULL;
node->prev = node->next = NULL;
} else {
//新增节点的前节点置位NULL,因为是头插法,这个节点作为头结点,肯定没有前置节点.
node->prev = NULL;
//新增节点 后置节点 指向原来的head节点
node->next = list->head;
//原来的head节点, 前置节点指向 这个新增节点.
list->head->prev = node;
//list的头结点设置为新增加点
list->head = node;
}
list->len++;
return list;
}
3.2 尾插法
基本与头插法相似
list *listAddNodeTail(list *list, void *value)
{
listNode *node;
if ((node = zmalloc(sizeof(*node))) == NULL)
return NULL;
node->value = value;
if (list->len == 0) {
list->head = list->tail = node;
node->prev = node->next = NULL;
} else {
node->prev = list->tail;
node->next = NULL;
list->tail->next = node;
list->tail = node;
}
list->len++;
return list;
}
3.3 指定节点前后插入节点
//after为ture则向后面插入
list *listInsertNode(list *list, listNode *old_node, void *value, int after) {
listNode *node;
if ((node = zmalloc(sizeof(*node))) == NULL)
return NULL;
node->value = value;
if (after) {
node->prev = old_node;
node->next = old_node->next;
if (list->tail == old_node) {
list->tail = node;
}
} else {
node->next = old_node;
node->prev = old_node->prev;
if (list->head == old_node) {
list->head = node;
}
}
if (node->prev != NULL) {
node->prev->next = node;
}
if (node->next != NULL) {
node->next->prev = node;
}
list->len++;
return list;
}
4丶删除节点
void listDelNode(list *list, listNode *node)
{
//如果被删除节点有前置节点
if (node->prev)
//前置节点的后置节点设置为 被删除节点的下一个节点
node->prev->next = node->next;
else
//说明被删除节点是头结点, 直接将头结点设置为被删除节点的下一个
list->head = node->next;
//删除节点有后置节点
if (node->next)
node->next->prev = node->prev;
else
//删除节点是尾节点
list->tail = node->prev;
//释放该节点资源
if (list->free) list->free(node->value);
zfree(node);
list->len--;
}
5丶查询节点
listNode *listSearchKey(list *list, void *key)
{
listIter iter;
listNode *node;
//将 iter 的下一个节点设置为头结点
listRewind(list, &iter);
//便利
while((node = listNext(&iter)) != NULL) {
if (list->match) {
if (list->match(node->value, key)) {
return node;
}
} else {
if (key == node->value) {
return node;
}
}
}
return NULL;
}