HarmonyOS学习路之开发篇—Java UI框架(自定义组件与布局 二)
自定义布局
当Java UI框架提供的布局无法满足需求时,可以创建自定义布局,根据需求自定义布局规则
常用接口
Component类相关接口
| 接口名称 |
作用 |
|---|---|
| setEstimateSizeListener |
设置测量组件的侦听器 |
| setEstimatedSize |
设置测量的宽度和高度 |
| onEstimateSize |
测量组件的大小以确定宽度和高度。 |
| EstimateSpec.getChildSizeWithMode |
基于指定的大小和模式为子组件创建度量规范。 |
| EstimateSpec.getSize |
从提供的度量规范中提取大小。 |
| EstimateSpec.getMode |
获取该组件的显示模式。 |
| arrange |
相对于容器组件设置组件的位置和大小 |
ComponentContainer类相关接口
接口名称
作用
setArrangeListener
设置容器组件布局子组件的侦听器
onArrange
通知容器组件在布局时设置子组件的位置和大小
如何实现自定义布局
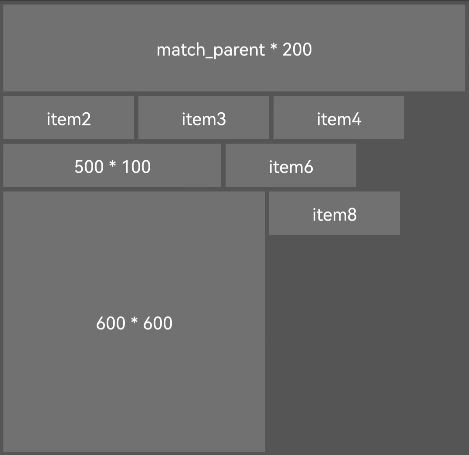
使用自定义布局,实现子组件自动换行功能。
自定义布局的使用效果
1. 创建自定义布局的类,并继承ComponentContainer,添加构造方法。
public class CustomLayout extends ComponentContainer {
public CustomLayout(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
//如需支持xml创建自定义布局,必须添加该构造方法
public CustomLayout(Context context, AttrSet attrSet) {
super(context, attrSet);
}
}2. 实现ComponentContainer.EstimateSizeListener接口,在onEstimateSize方法中进行测量。
public class CustomLayout extends ComponentContainer
implements ComponentContainer.EstimateSizeListener {
...
public CustomLayout(Context context, AttrSet attrSet) {
...
setEstimateSizeListener(this);
}
@Override
public boolean onEstimateSize(int widthEstimatedConfig, int heightEstimatedConfig) {
invalidateValues();
//通知子组件进行测量
measureChildren(widthEstimatedConfig, heightEstimatedConfig);
//关联子组件的索引与其布局数据
for (int idx = 0; idx < getChildCount(); idx++) {
Component childView = getComponentAt(idx);
addChild(childView, idx, EstimateSpec.getSize(widthEstimatedConfig));
}
//测量自身
measureSelf(widthEstimatedConfig, heightEstimatedConfig);
return true;
}
private void measureChildren(int widthEstimatedConfig, int heightEstimatedConfig) {
for (int idx = 0; idx < getChildCount(); idx++) {
Component childView = getComponentAt(idx);
if (childView != null) {
LayoutConfig lc = childView.getLayoutConfig();
int childWidthMeasureSpec;
int childHeightMeasureSpec;
if (lc.width == LayoutConfig.MATCH_CONTENT) {
childWidthMeasureSpec = EstimateSpec.getSizeWithMode(lc.width, EstimateSpec.NOT_EXCEED);
} else if (lc.width == LayoutConfig.MATCH_PARENT) {
int parentWidth = EstimateSpec.getSize(widthEstimatedConfig);
int childWidth = parentWidth - childView.getMarginLeft() - childView.getMarginRight();
childWidthMeasureSpec = EstimateSpec.getSizeWithMode(childWidth, EstimateSpec.PRECISE);
} else {
childWidthMeasureSpec = EstimateSpec.getSizeWithMode(lc.width, EstimateSpec.PRECISE);
}
if (lc.height == LayoutConfig.MATCH_CONTENT) {
childHeightMeasureSpec = EstimateSpec.getSizeWithMode(lc.height, EstimateSpec.NOT_EXCEED);
} else if (lc.height == LayoutConfig.MATCH_PARENT) {
int parentHeight = EstimateSpec.getSize(heightEstimatedConfig);
int childHeight = parentHeight - childView.getMarginTop() - childView.getMarginBottom();
childHeightMeasureSpec = EstimateSpec.getSizeWithMode(childHeight, EstimateSpec.PRECISE);
} else {
childHeightMeasureSpec = EstimateSpec.getSizeWithMode(lc.height, EstimateSpec.PRECISE);
}
childView.estimateSize(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}
}
}
private void measureSelf(int widthEstimatedConfig, int heightEstimatedConfig) {
int widthSpce = EstimateSpec.getMode(widthEstimatedConfig);
int heightSpce = EstimateSpec.getMode(heightEstimatedConfig);
int widthConfig = 0;
switch (widthSpce) {
case EstimateSpec.UNCONSTRAINT:
case EstimateSpec.PRECISE:
int width = EstimateSpec.getSize(widthEstimatedConfig);
widthConfig = EstimateSpec.getSizeWithMode(width, EstimateSpec.PRECISE);
break;
case EstimateSpec.NOT_EXCEED:
widthConfig = EstimateSpec.getSizeWithMode(maxWidth, EstimateSpec.PRECISE);
break;
default:
break;
}
int heightConfig = 0;
switch (heightSpce) {
case EstimateSpec.UNCONSTRAINT:
case EstimateSpec.PRECISE:
int height = EstimateSpec.getSize(heightEstimatedConfig);
heightConfig = EstimateSpec.getSizeWithMode(height, EstimateSpec.PRECISE);
break;
case EstimateSpec.NOT_EXCEED:
heightConfig = EstimateSpec.getSizeWithMode(maxHeight, EstimateSpec.PRECISE);
break;
default:
break;
}
setEstimatedSize(widthConfig, heightConfig);
}
}注意:
- 容器类组件在自定义测量过程不仅要测量自身,也要递归的通知各子组件进行测量。
- 测量出的大小需通过setEstimatedSize通知组件,并且必须返回true使测量值生效。
3. 测量时,需要确定每个子组件大小和位置的数据,并保存这些数据。
private int xx = 0;
private int yy = 0;
private int maxWidth = 0;
private int maxHeight = 0;
private int lastHeight = 0;
// 子组件索引与其布局数据的集合
private final Map axis = new HashMap<>();
private static class Layout {
int positionX = 0;
int positionY = 0;
int width = 0;
int height = 0;
}
...
private void invalidateValues() {
xx = 0;
yy = 0;
maxWidth = 0;
maxHeight = 0;
axis.clear();
}
private void addChild(Component component, int id, int layoutWidth) {
Layout layout = new Layout();
layout.positionX = xx + component.getMarginLeft();
layout.positionY = yy + component.getMarginTop();
layout.width = component.getEstimatedWidth();
layout.height = component.getEstimatedHeight();
if ((xx + layout.width) > layoutWidth) {
xx = 0;
yy += lastHeight;
lastHeight = 0;
layout.positionX = xx + component.getMarginLeft();
layout.positionY = yy + component.getMarginTop();
}
axis.put(id, layout);
lastHeight = Math.max(lastHeight, layout.height + component.getMarginBottom());
xx += layout.width + component.getMarginRight();
maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth, layout.positionX + layout.width + component.getMarginRight());
maxHeight = Math.max(maxHeight, layout.positionY + layout.height + component.getMarginBottom());
} 4. 实现ComponentContainer.ArrangeListener接口,在onArrange方法中排列子组件。
public class CustomLayout extends ComponentContainer
implements ComponentContainer.EstimateSizeListener,
ComponentContainer.ArrangeListener {
...
public CustomLayout(Context context
, AttrSet attrSet
) {
...
setArrangeListener(this);
}
@Override
public boolean onArrange(int left, int top, int width, int height) {
// 对各个子组件进行布局
for (int idx = 0; idx < getChildCount(); idx++) {
Component childView = getComponentAt(idx);
Layout layout = axis.get(idx);
if (layout != null) {
childView.arrange(layout.positionX, layout.positionY, layout.width, layout.height);
}
}
return true;
}
}5. 在xml文件中创建此布局,并添加若干子组件。