Java中使用JTS对空间几何计算(读取WKT、距离、点在面内、长度、面积、相交等)
场景
基于GIS相关的集成系统,需要对空间数据做一些判断处理。比如读取WKT数据、点到点、点到线、点到面的距离,
线的长度、面的面积、点是否在面内等处理。
JTS
(Java Topology Suite) Java拓扑套件,是Java的处理地理数据的API。
github地址:
GitHub - locationtech/jts: The JTS Topology Suite is a Java library for creating and manipulating vector geometry.
API文档地址:
org.locationtech.jts:jts-core 1.19.0 API
Maven中央仓库地址:
https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.locationtech.jts/jts-core
特点
实现了OGC关于简单要素SQL查询规范定义的空间数据模型
一个完整的、一致的、基本的二维空间算法的实现,包括二元运算(例如touch和overlap)和空间分析方法(例如intersection和buffer)
一个显示的精确模型,用算法优雅的解决导致dimensional collapse(尺度坍塌–专业名词不知道对不对,暂时这样译)的情况。
健壮的实现了关键计算几何操作
提供著名文本格式的I/O接口
JTS是完全100%由Java写的
JTS支持一套完整的二元谓词操作。二元谓词方法将两个几何图形作为参数,
返回一个布尔值来表示几何图形是否有指定的空间关系。它支持的空间关系有:
相等(equals)、分离(disjoint)、相交(intersect)、相接(touches)、
交叉(crosses)、包含于(within)、包含(contains)、覆盖/覆盖于(overlaps)。
同时,也支持一般的关系(relate)操作符。
relate可以被用来确定维度扩展的九交模型(DE-9IM),它可以完全的描述两个几何图形的关系。
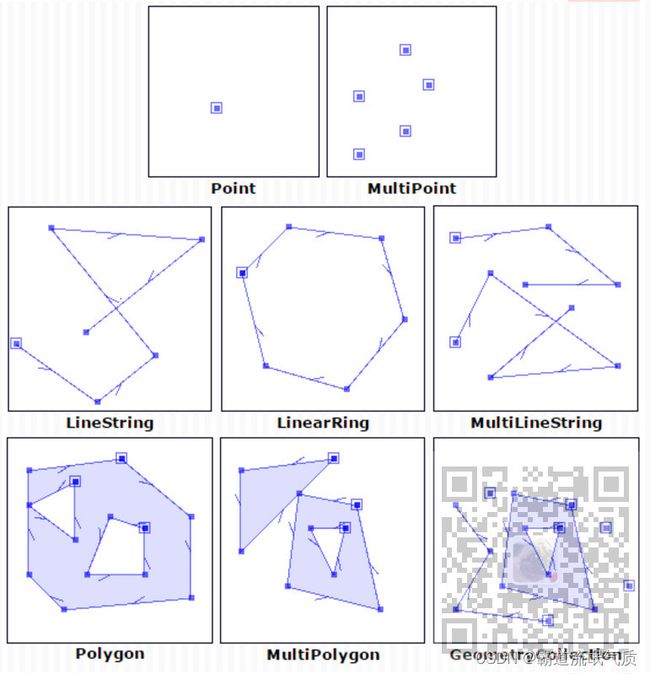
空间数据模型
JTS提供了以下空间数据模型
图形可视化WKT数据
在jts的bin下的testbuilder.bat,双击运行
即可运行WKT数据可视化界面
可以在页面上绘制图形并下方生成wkt数据,以及输入wkt数据,点击右边按钮,图形化显示。
注:
博客:
霸道流氓气质的博客_CSDN博客-C#,架构之路,SpringBoot领域博主
关注公众号
霸道的程序猿
获取编程相关电子书、教程推送与免费下载。
实现
1、项目中引入jts的依赖
org.locationtech.jts
jts-core
1.18.2
2、从WKT字符串中读取几何图形,读取点、线、面
//read a geometry from a WKT string (using the default geometry factory)
//从WKT字符串读取几何图形
Geometry g1 = null;
try {
//读取线
//g1 = new WKTReader().read("LINESTRING (0 0, 10 10, 20 20)");
//读取点
//g1 = new WKTReader().read("POINT (2 2)");
//读取面
g1 = new WKTReader().read("POLYGON((40 100, 40 20, 120 20, 120 100, 40 100))");
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// Arrays.stream(g1.getCoordinates()).forEach(point -> System.out.println("x:"+point.x+" y:"+point.y));
//输出结果:
// x:0.0 y:0.0
// x:10.0 y:10.0
// x:20.0 y:20.0
//Arrays.stream(g1.getCoordinates()).forEach(point ->System.out.println("x:"+point.x+" y:"+point.y));
//输出:x:2.0 y:2.0
//Arrays.stream(g1.getCoordinates()).forEach(point ->System.out.println("x:"+point.x+" y:"+point.y));
//输出:
// x:40.0 y:100.0
// x:40.0 y:20.0
// x:120.0 y:20.0
// x:120.0 y:100.0
// x:40.0 y:100.03、创建点、线
//创建点
Point point = new GeometryFactory().createPoint(new Coordinate(1, 1));
// create a geometry by specifying the coordinates directly
//通过指定坐标创建线
Coordinate[] coordinates = new Coordinate[]{new Coordinate(0, 0),
new Coordinate(10, 10), new Coordinate(20, 20)};
// use the default factory, which gives full double-precision
Geometry g2 = new GeometryFactory().createLineString(coordinates);
//System.out.println("Geometry 2: " + g2);
//输出结果:Geometry 2: LINESTRING (0 0, 10 10, 20 20)4、计算点是否在线上、点是否在面内
//创建点
Point point = new GeometryFactory().createPoint(new Coordinate(1, 1));
//输出结果:POINT (1 1)
//计算点是否在线上
//System.out.println(g1.contains(point));
//输出结果:true
//计算点是否在面内
Point point2 = new GeometryFactory().createPoint(new Coordinate(70, 70));
//System.out.println(g1.contains(point2));
//输出结果: true
Point point3 = new GeometryFactory().createPoint(new Coordinate(20, 10));
//System.out.println(g1.contains(point3));
//输出结果: false5、计算两个几何图形的交点
// compute the intersection of the two geometries
//计算两个几何图形的交点
Geometry g3 = g1.intersection(g2);
//System.out.println("G1 intersection G2: " + g3);
//输出结果:G1 intersection G2: MULTILINESTRING ((0 0, 10 10), (10 10, 20 20))6、创建一个MultiPoint多点
// create a factory using default values (e.g. floating precision)
//创建一个MultiPoint多点
GeometryFactory fact = new GeometryFactory();
// Point p1 = fact.createPoint(new Coordinate(0,0));
// System.out.println(p1);
//
// Point p2 = fact.createPoint(new Coordinate(1,1));
// System.out.println(p2);
//
// MultiPoint mpt = fact.createMultiPointFromCoords(new Coordinate[] { new Coordinate(0,0), new Coordinate(1,1) } );
// System.out.println(mpt);
//输出结果:
// POINT (0 0)
// POINT (1 1)
// MULTIPOINT ((0 0), (1 1))7、创建闭合线LinearRing
//创建闭合线-LinearRing
LinearRing lr = new GeometryFactory().createLinearRing(new Coordinate[]{new Coordinate(0, 0), new Coordinate(0, 10), new Coordinate(10, 10), new Coordinate(10, 0), new Coordinate(0, 0)});
//System.out.println(lr);
//输出结果:LINEARRING (0 0, 0 10, 10 10, 10 0, 0 0)8、创建几何集合列表
//创建几何集合列表
Geometry[] garray = new Geometry[]{g1,g2};
GeometryCollection gc = fact.createGeometryCollection(garray);
//System.out.println(gc.toString());
//输出结果:GEOMETRYCOLLECTION (POLYGON ((40 100, 40 20, 120 20, 120 100, 40 100)), LINESTRING (0 0, 10 10, 20 20))9、几何关系判断
//几何关系判断,是否相交intersection
//其他方法类似
// 相等(Equals): 几何形状拓扑上相等。
// 不相交(Disjoint): 几何形状没有共有的点。
// 相交(Intersects): 几何形状至少有一个共有点(区别于脱节)
// 接触(Touches): 几何形状有至少一个公共的边界点,但是没有内部点。
// 交叉(Crosses): 几何形状共享一些但不是所有的内部点。
// 内含(Within): 几何形状A的线都在几何形状B内部。
// 包含(Contains): 几何形状B的线都在几何形状A内部(区别于内含)
// 重叠(Overlaps): 几何形状共享一部分但不是所有的公共点,而且相交处有他们自己相同的区域。
WKTReader reader = new WKTReader(fact);
LineString geometry1 = null;
try {
geometry1 = (LineString) reader.read("LINESTRING(0 0, 2 0, 5 0)");
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
LineString geometry2 = null;
try {
geometry2 = (LineString) reader.read("LINESTRING(0 0, 0 2)");
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
Geometry interPoint = geometry1.intersection(geometry2);//相交点
//System.out.println(interPoint.toText());
//输出结果: POINT (0 0)10、计算距离distance
//计算距离distance
Point p1 = fact.createPoint(new Coordinate(0,0));
//System.out.println(p1);
Point p2 = fact.createPoint(new Coordinate(3,4));
///System.out.println(p2);
//System.out.println(p1.distance(p2));
//输出结果
// POINT (0 0)
// POINT (3 4)
// 5.011、计算长度和面积
Geometry g5 = null;
Geometry g6 = null;
try {
//读取面
g5 = new WKTReader().read("POLYGON((40 100, 40 20, 120 20, 120 100, 40 100))");
g6 = new WKTReader().read("LINESTRING(0 0, 0 2)");
//计算面积getArea()
//System.out.println(g5.getArea());
//输出结果:6400.0
//计算长度getLength()
//System.out.println(g6.getLength());
//输出结果:2.0
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}12、求点到线、点到面的最近距离
GeometryFactory gf = new GeometryFactory();
WKTReader reader2 = new WKTReader(gf);
Geometry line2 = null;
Geometry g7 = null;
try {
line2 = reader2.read("LINESTRING(0 0, 10 0, 10 10, 20 10)");
g7 = new WKTReader().read("POLYGON((40 100, 40 20, 120 20, 120 100, 40 100))");
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
Coordinate c = new Coordinate(5, 5);
PointPairDistance ppd = new PointPairDistance();
//求点到线的最近距离
//DistanceToPoint.computeDistance(line2,c,ppd);
//输出结果:5.0
//求点到面的最近距离
DistanceToPoint.computeDistance(g7,c,ppd);
System.out.println(ppd.getDistance());
//输出结果38.0788655293195413、其他api可以参考其官方文档或者示例代码中进行使用。