c++Primer读书笔记(第十二章 动态内存)
12.1 动态内存与智能指针
头文件
12.1.1 shared_ptr


make_shared函数
最安全的分配和使用动态内存的方法是调用一个名为make_shared的标准库函数。
auto p = make_shared<int>(42);
auto q(p);
使用了动态生存期的资源的类
使用动态内存出于以下三种原因:
- 程序不知道自己需要使用多少对象
- 程序不知道所需对象的准确类型
- 程序需要在多个对象间共享数据
class StrBlob{
public:
typedef std::vector<std::string>::size_type size_type;
//构造函数
StrBlob();
StrBlob(std::initializer_list<std::string>il);
//
size_type size() const {return data->size();}
bool empty() const {return data->empty();}
//增删
void push_back(const std::string &t){data->push_back(t);}
void pop_back();
std::string& front();
std::string& back();
private:
std::shared_ptr<std::vector<std::string>>data;
void check(size_type i,const std::string &msg) const
{
if(i>data->size())
throw out_of_range(msg);
}
};
StrBlob::StrBlob():data(make_shared<std::vector<std::string>>()){}
StrBlob::StrBlob(std::initializer_list<std::string>il):data(make_shared<std::vector<std::string>>(il)){}
std::string& StrBlob::front()
{
check(0,"front on empty StrBlob");
return data->front();
}
std::string& StrBlob::back()
{
check(0,"fornt on empty StrBlob");
return data->back();
}
12.1.2 直接管理内存
int *pi=new int;
int *pi=new int(1024);
auto p1=new auto(obj);
动态分配的const对象
const int *pci = new const int(1024);
//动态分配的const对象必须初始化
内存耗尽
int *p1=new int;//如果分配失败,new会抛出一个std::bad_alloc
int *p2=new (nothrow) int;//如果分配失败,new返回一个空指针
带参数的new成为定位new
delete必须和new一一对应
使用动态内存的管理非常容易出错
- 忘记delete内存(内存泄漏)
- 使用已经释放掉的对象。通过在释放内存后将指针置为空,可以检测出这种错误
- 同一块内存释放两次
delete之后重置指针值
delete指针之后指针仍然保存了动态内存的地址,成为空悬指针。
delete指针之后记得置为nullptr
shared_ptr和new结合使用
接收指针参数的构造函数为explicit,所以不能进行隐式转换,必须直接初始化形式来初始化一个智能指针
shared_ptr<int>p2(new int(42));//p2指向一个值为42的int
shared_ptr<int>p2=new int(42);//错误:必须使用直接初始化形式


不要混合使用普通指针和智能指针
普通指针指向的对象交由智能指针后,智能指针一旦将对象释放,那么普通指针便变为了空悬指针
也不要使用get初始化另一个智能指针或者为智能指针赋值
其他shared_ptr操作
12.1.4 智能指针和异常
如果使用智能指针,即使程序块过早结束,智能指针类也能确保在内存不再需要的时候将其释放
智能指针和哑类
没有自己的析构函数,使用shared_ptr管理
使用我们自己的释放操作
默认情况下,shared_ptr假定它们指向的是动态内存。因此当一个shared_ptr被销毁的时候,他默认地对它管理的指针进行delete操作。
有时候我们希望调用自己定义的函数来代替delete。
void end_connection(connection *p){disconnect(*p);}
void f(destination &d)
{
connection c=connect(&d);
shared_ptr<connection>p(&c,end_connection);
//一旦发生异常交由智能指针自己调用end_connection进行释放
}
智能指针的一些陷阱
- 不适用相同的内置指针初始化或者reset多个智能指针
- 不delete get()返回的指针
- 不适用get()初始化或者reset另一个指针指针,和1类似
- 如果你使用了get()返回的指针,当智能指针计数为0销毁后,你使用的指针就变为空悬指针了
- 如果你使用智能指针管理的资源不是new分配的内存,那么记得自己定义删除器
12.1.5 unique_ptr
初始化unique_ptr必须采用直接初始化形式
不支持普通的拷贝或赋值操作
unique_ptr<double>p1;
unique_ptr<int>p2(new int(42));
unique_ptr<string>p2(p1);
unique_ptr<string>p3;
p3=p2;
传递unique_ptr参数和返回unique_ptr
我们可以拷贝或赋值一个将要被销毁的unique_ptr

向unique_ptr传递删除器
12.1.6 weak_ptr
弱智能指针 讲一个weak_ptr绑到一个shared_ptr不会改变其引用计数
12.2动态数组
12.2.1 new和数组
int *p=new int[get_size()];
typedef int arrT[42];
int *p = new arrT;
初始化动态分配的对象的数组
int *pia=new int[10];//10个未初始化的int
int *pia2=new int[10]();//10个0
string *psa=new string[10];//10个空的string
string *pas2=new string[10]();//10个空的string
可以用花括号进行初始化列表,缺补默认值 多报异常
动态分配一个空数组是合法的
char arr[0];//不合法
char *cp = new char[0];//合法
释放动态数组
delete p;
delete [] pa;
智能指针和动态数组
unique_ptr<int[]>up(new int[10]);
up.release();//自动调用delete[]
管理动态数组的unique_ptr不能用.或者->,直接用下标访问
shared_ptr管理动态数组的话必须提供一个删除器,调用delete[]
shared_ptr<int>sp(new int[10],[](int *p){delete [] p;})
sp.reset();
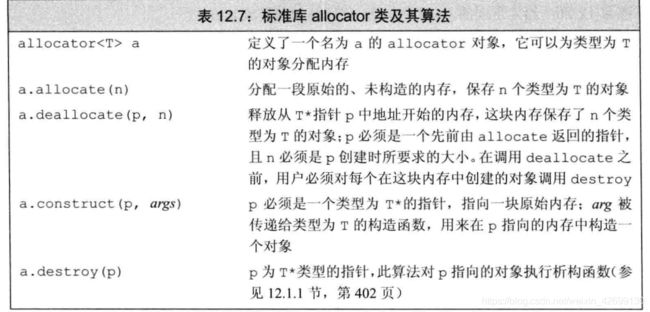
12.2.2 allocator 427
12.3 使用标准库:文本查询查询
需要完成的任务
- 当程序读取输入文件的时候,记住单词出现的行,需要逐行读取输入文件,并将每一行分解为独立的单词
- 输出:必须能提取每个单词关联的行号、行号必须按升序出现而且没有重复、他必须能打印给定行号中的文本
实现的工具
- 使用一个vector< string >来保存文件的一行,下标就是行号
- 使用一个istringstream来将每一行分解为单词
- 使用一个set保存每一个单词在输入文本中出现的行号,保证对于每一个单词同一个行号只会出现一次并且按升序排列(set是有序的无重复集合)
- 使用map存储每一个单词和对应的行号set集合,方便通过任意一个单词提取它的行数set集合
在类之间共享数据
- QueryResult类对象用来保存TextQuery输出的结果,那么如果不进行特殊处理,则需要进行拷贝set甚至是vector,而我们不希望进行拷贝操作。
- 所以我们可以返回指向TextQuery内部对象的迭代器或者指针,这样可以避免拷贝的出现
- 新的问题出现:如何直到指向的对象是否存活?如果已经提前销毁,那么QueryResult就会对一个已经不存在的对象进行操作
- 对于生存周期进行监视这一操作已经暗示了答案,我们可以使用shared_ptr作为对象,反应数据结构中这种共享关系
- main.cpp
- ostream对象的用法
- !(std::cin>>s)遇到文件尾部返回false
- ifstream读入文件用法
#include "TextQuery.hpp"
#include "QueryResult.hpp"
#include - 文本查询类程序TextQuery
TextQuery.hpp
#ifndef TEXTQUERY_HPP
#define TEXTQUERY_HPP
#include TextQuery.cpo
- istringstream的使用
- map下标操作返回对应的元素
- 设置一个静态的set指针 ,用来给每次没有找到sought用作返回值
- 当map用来查找元素的时候使用find而不是下标,避免将不存在的关键字插入map中
#include "TextQuery.hpp"
#include >
if(!lines)//如果为空,说明单词第一次出现,创建一个新的set
lines.reset(new std::set<line_no>);
lines->insert(n);//将当前行号插入set
}
}
}
QueryResult TextQuery::query(const std::string &sought)const
{
//如果没有找到sought,我们将返回一个指向此set的指针
static std::shared_ptr<std::set<line_no>>nodata(new std::set<line_no>);
//使用find而不是下标运算符来查找查找单词,避免将单词添加到wm中
auto loc=wn.find(sought);
if(loc == wn.end())
return QueryResult(sought,nodata,file);
else
return QueryResult(sought,loc->second,file);
}
- QueryResult
#ifndef QUERYRESULT_HPP
#define QUERYRESULT_HPP
#include