链表(简单)
链表(简单)-- Java
1、输入一个链表的头节点,从尾到头反过来返回每个节点的值(用数组返回)。
原文链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/cong-wei-dao-tou-da-yin-lian-biao-lcof
示例 1:
输入:head = [1,3,2]
输出:[2,3,1]
限制:
0 <= 链表长度 <= 10000
题目解读:
实现代码中定义好的ListNode,val指的是当前位置存放的值,next类似c语言中的指针用法(即下一指针位置存放的ListNode类型数据)
思路:(扫描两次)
1.由于返回数组,需要先计算head中有多少个数据,用于数组初始化长度。
2.根据数据个数初始化数组长度后,直接以数组下标倒序依次插入head数据
实现代码:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int[] reversePrint(ListNode head) {
ListNode node = head;
int count = 0;
while (node != null){
count++;
node = node.next;
}
int[] ints = new int[count];
for (int j=count-1; j>=0; j--){
ints[j] = head.val;
head = head.next;
}
return ints;
}
}
2、定义一个函数,输入一个链表的头节点,反转该链表并输出反转后链表的头节点。
原文链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/fan-zhuan-lian-biao-lcof
示例:
输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL
输出: 5->4->3->2->1->NULL
限制:
0 <= 节点个数 <= 5000
思路:
1.双指针法
此题采用双指针方式进行解析时,可以理解为,初始时指针由1依次指向5,最后是null;最后要实现的结果是由5依次指向1,最后是null。就相当于将当前元素的next选定为前一个元素。
即,原本1的next为2,2的next为3…5的next为null;链表反转后,1的next为null,2的next为1…5的next为4
2.递归法
递归法是先将指针指向倒数第二个元素,然后在指定最后一个元素的next指向自身,再将自身的next指向null,依次在回溯的过程中当回溯到1时程序结束。思路解析图如下:
实现代码:
// 双指针法
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode cur = head, pre = null;
while(cur != null) {
ListNode tmp = cur.next; // 暂存后继节点 cur.next
cur.next = pre; // 修改 next 引用指向
pre = cur; // pre 暂存 cur
cur = tmp; // cur 访问下一节点
}
return pre;
}
}
// 递归法
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
while(head == null || head.next == null){
return head;
}
ListNode node = reverseList(head.next);
head.next.next = head;
head.next = null;
return node;
}
}
/**
* 递归法中难点:
* head.next.next = head
* 此处可以理解为:head.next = tmp; tmp.next = head
* 即,将当前元素的下一元素指针逆转,原本是4->5,变为5->4
*
* head.next = null
* 可以理解为 4->null
*/
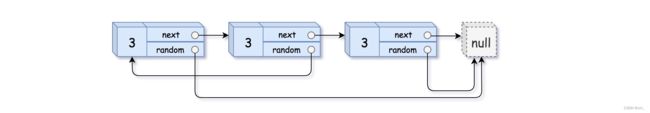
3、(复杂链表的复制) 请实现 copyRandomList 函数,复制一个复杂链表。在复杂链表中,每个节点除了有一个 next 指针指向下一个节点,还有一个 random 指针指向链表中的任意节点或者 null。
输入:head = [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
输出:[[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
示例 2:
输入:head = [[1,1],[2,1]]
输出:[[1,1],[2,1]]
示例 3:
输出:[[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]]
示例 4:
输入:head = []
输出:[]
解释:给定的链表为空(空指针),因此返回 null。
原文链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/fu-za-lian-biao-de-fu-zhi-lcof
题目解读:
题目的实际意思可以理解为,讲一个存有对象的链表复制出来,只是该对象的属性全部都为链表中元素值。
思路:
使用哈希表的做法,先将链表节点的值一个个对应放入Map中,再对应将节点的next和random属性赋值进新节点中。
实现代码:
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
int val;
Node next;
Node random;
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
this.random = null;
}
}
*/
class Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
if (head == null){
return null;
}
Node cur = head;
Map map = new HashMap<>();
while (cur != null) {
map.put(cur, new Node(cur.val));
cur = cur.next;
}
cur = head;
while (cur != null){
map.get(cur).next = map.get(cur.next);
map.get(cur).random = map.get(cur.random);
cur = cur.next;
}
return map.get(head);
}
}