Windows共享内存与死锁
实验一
一、实验内容或题目:
利用共享内存完成一个生产者进程和一个消费者进程的同步。
二、实验目的与要求:
1、编写程序,使生产者进程和消费者进程通过共享内存和mutex来完成工作同步。
2、了解通过操作系统接口调用,实现通过共享内存进行数据交换。
三、实验步骤:
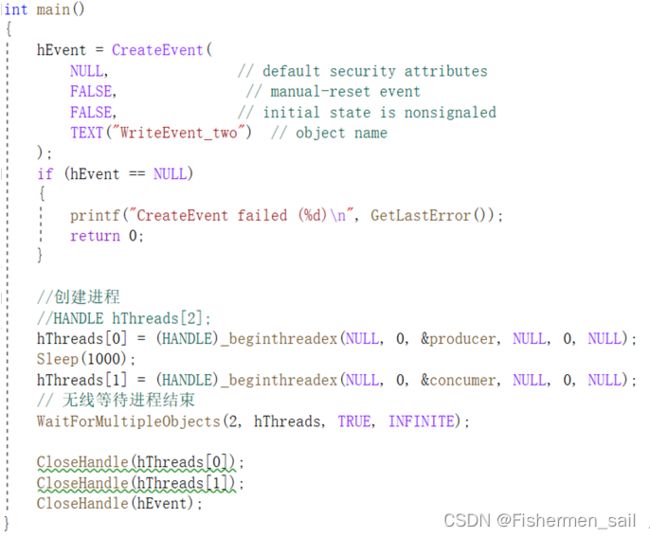
1、分别编写生产者进程和消费者进程,并创建同名的共享内存和mutex
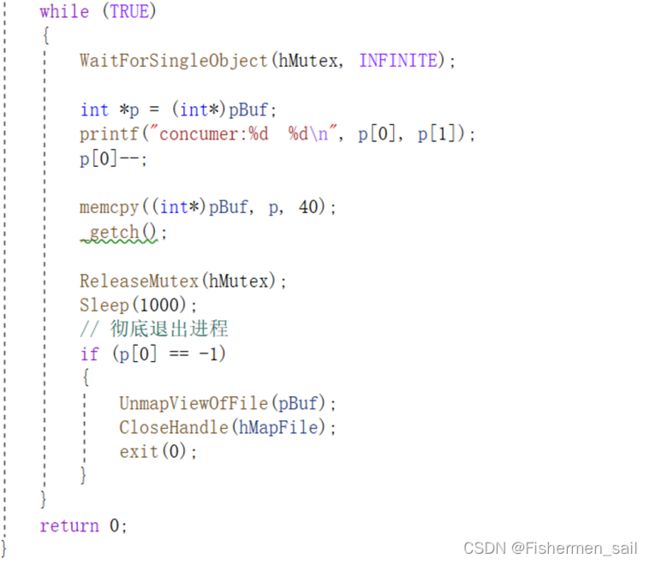
2、生产者加上mutex则向共享内存中增加一条数据,消费者加上mutex则从共享内存中尝试消费一条数据,两者放掉mutex后随机Sleep若干毫秒
3、若生产者接受到一个sigint中断,则向共享内存中写入一个标识后再退出,消费者消费完所有的数据后若发现此标识被置上则同时退出。
需要使用的api:
CreateMutex, CreateFileMapping,MapViewOfFile
共享内存相关example参照:https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/win32/memory/creating-named-shared-memory
提示:
共享内存的相关数据结构可以采用最简单的两个int,第一个int表示数据的数量,第二个int表示生产者是否已经退出。
四、实验结果:
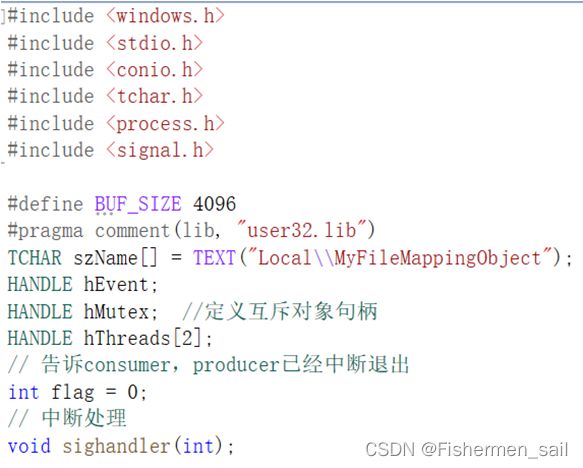
Producer:
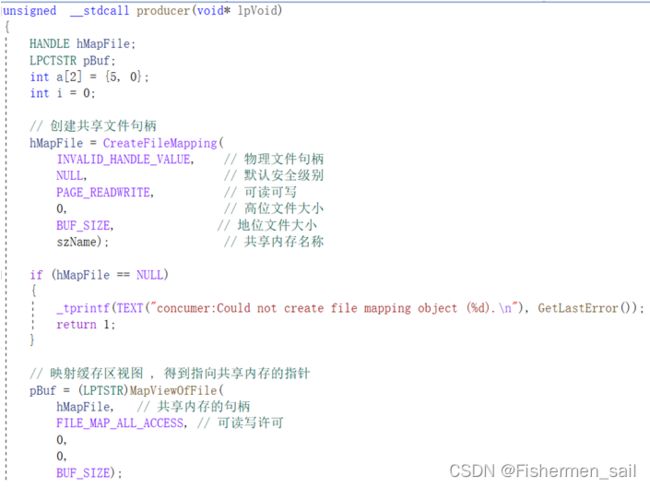


Sighandler(中断信号CTRL + C处理):


Consumer:

Main:
结果:
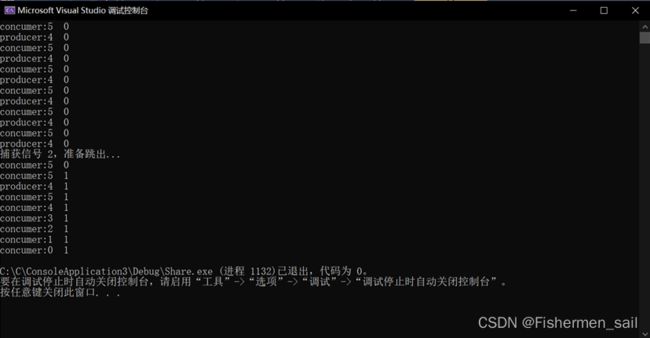
五、总结:
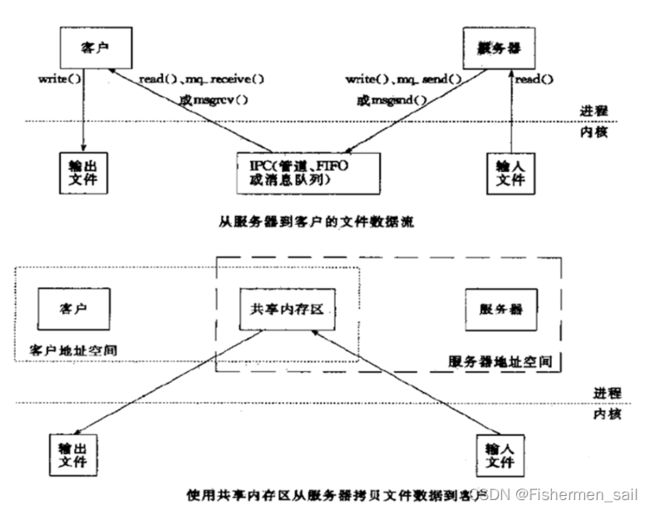
总的来说这个实验还是很难的,花费了很长时间,也遇到了很多问题。首先为什么要映射,这其实是操作系统内存管理的知识,MapViewOfFile就是为了将此内存空间映射到进程的地址空间中。如果两个进程使用相同的DLL,只把DLL的代码页装入内存一次,其他所有映射这个DLL的进程只要共享这些代码页就可以了,如果利用消息机制实现IPC有交换的数据量小、携带的信息少等缺点。
在实验中每次向共享内存放入值后,都必须加“_getch”,否则会出现“Could not open file mapping object”,或者可能导致concumer或producer迟迟无法使用共享内存。这是因为,如果不加“_getch”锁住那个瞬间,那么映射对象将会关闭。

如果你在设定共享内存空间为Global…也是会出错的。这是因为Global保证创建的对象是全局的,对权限要求比较高,而使用local可以保证服务对象仅对当前用户中的进程和线程可见。

在捕获中断信号后,理论上应该让线程1关闭,但是,经过我的尝试,无法实现只关闭进程1而不关闭进程2。之后只能设定一个全局flag,来标志producer已经退出。
六、源码
共享内存:
#include 实验二
一、实验内容或题目:
实现哲学家用餐问题,观察死锁
二、实验目的与要求:
1、使用多线程和mutex模拟实现哲学家用餐问题(课本习题3.14)
2、测试并观察线程数量以及用餐/不用餐时间比对出现死锁概率的影响
三、实验步骤:
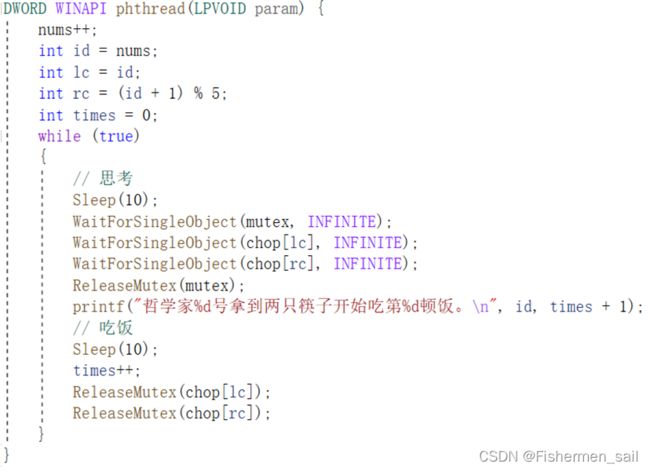
1、创建N个mutex,进行相应的编号
2、创建N个线程,每个线程获得左右两边的mutex后,进行m1时间的用餐(用sleep模拟),放掉mutex后,进行m2时间的休息,再重复上述过程
3、观察死锁的出现
4、调节N以及m1/m2的数值,观察死锁出现的概率与这两个数值的关系
需要使用的api:
CreateMutex, ReleaseMutex
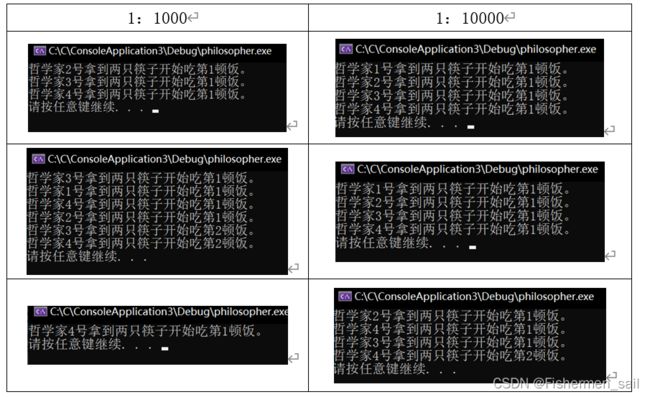
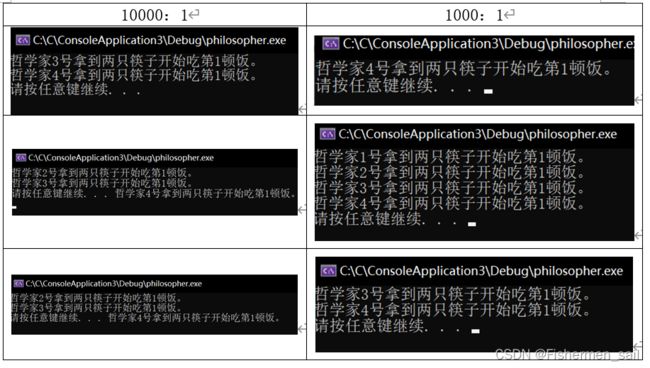
四、实验结果:
五、总结
根据实验结果可以观察出m1/m2越大,越容易出现死锁,用餐时间越长越容易出现死锁,思考时间越长越不容易发生死锁。
六、源码
死锁:
#include 实验三
一、实验内容或题目:
在实验二的基础上,破坏掉一个死锁的必要条件,使死锁得到避免
二、实验目的与要求:
1.理解课本上死锁出现的必要条件
2.破坏掉其中的一个必要条件,使哲学家用餐可以不死锁的持续运行下去,可以尝试以下之一:
1)破坏掉部分分配(拿不到第二个mutex则放掉第一个)
2)破坏掉环路条件(某一个哲学家和其余的取mutex顺序不同)
三、实验步骤:
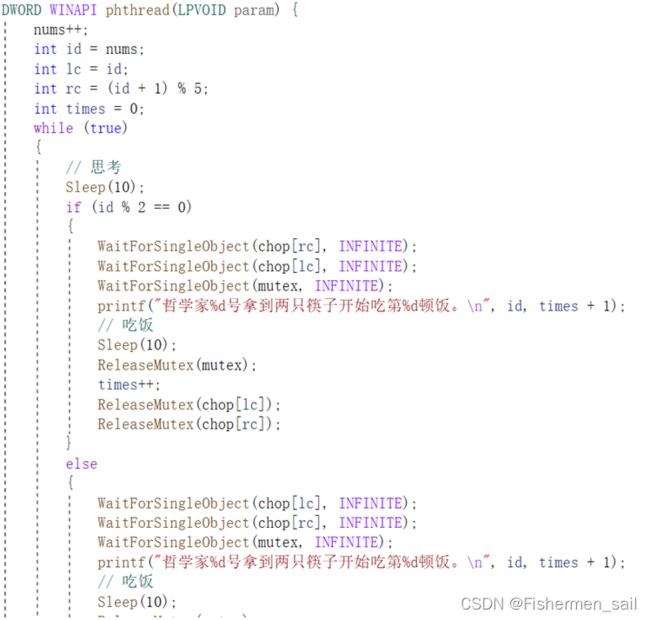
1.设计方法规定,奇数号哲学家只能先拿左边的筷子,而偶数号哲学家相反
2.设计方案实现,保证一个哲学家拿筷子时,将所有的筷子锁住,保证同一时间只有一个哲学家拿筷子。
需要使用的api:
CreateMutex, ReleaseMutex
四、实验结果:
五、总结
通过实验可以发现通过方案奇数号的哲学家先拿起右边的筷子再拿起左边的筷子,偶数号哲学家先拿起左边的筷子,再拿起右边的筷子;保证一个哲学家拿筷子时,将所有的筷子锁住,保证同一时间只有一个哲学家拿筷子,这样都能有效避免哲学家死锁问题。
六、源码
方案一:
#include 方案二:
#include