编译原理 实验四 LR(1)分析法程序
源代码仓库:CompilePrincipleLearning/experiment_4 · yusixian/CompilePrincipleLearning (github.com)
源代码在demo文件夹中~
一. 实验目的
- 掌握LR(1)分析法的基本原理
- 掌握LR(1)分析表的构造方法
- 掌握LR(1)驱动程序的构造方法
二. 实验内容及要求
构造LR(1)分析程序,利用它进行语法分析,判断给出的符号串是否为该文法识别的句子,了解LR(K)分析方法是严格的从左向右扫描,和自底向上的语法分析方法。
根据某一文法编制调试LR(1)分析程序,以便对任意输入的符号串进行分析。本次实验的目的主要是加深对LR(1)分析法的理解。
对下列文法,用LR(1)分析法对任意输入的符号串进行分析:
(0)S’->E
(1)E->E+T
(2)E->T
(3)T->T*F
(4)T->F
(5)F->(E)
(6)F->i
输出的格式如下:
(1)LR(1)分析程序,编制人:姓名,学号,班级
(2)输入一以#结束的符号串(包括±*/()i#):在此位置输入符号串
(3)输出过程如下:
| 步骤 | 状态栈 | 符号栈**** | 剩余输入串 | 动作 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | # | i+i*i# | 移进 |
(4)输入符号串为非法符号串或合法符号串
注意:
1.表达式中允许使用运算符(+|*)、分割符(括号)、字符i,结束符#;
2.如果遇到错误的表达式,应输出错误提示信息(该信息越详细越好);
3.对学有余力的同学,测试用的表达式事先放在文本文件中,一行存放一个表达式,同时以分号分割。同时将预期的输出结果写在另一个文本文件中,以便和输出进行对照;
4.可采用的其它的文法,但是必须是LR1分析方法。
三. 实验过程
1、构造识别LR(1)文法活前缀的DFA
如图:新标签页打开,不糊的。
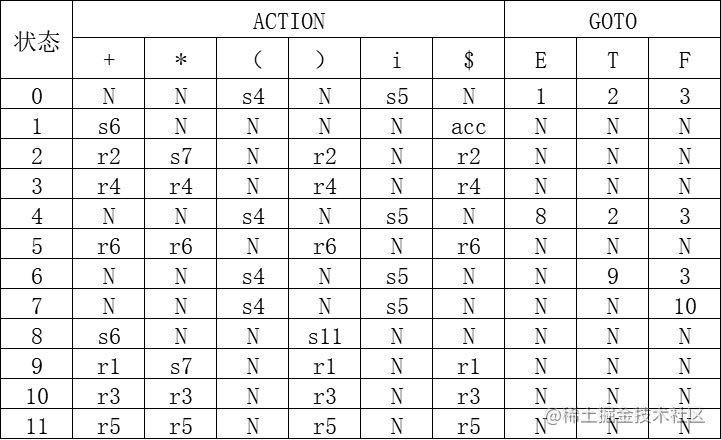
action表和goto表如下:
2、采用的数据结构
// ACTION表
// + * ( ) i #
string action[12][6];
// goto表
// a b #
int _goto[12][3];
string vt = "+*()i#"; // 终结符表
string vn = "ETF"; // 非终结符表
string LR[6] = { "E->E+T", "E->T", "T->T*F", "T->F", "F->(E)", "F->i" }; // 存放产生式
stack<char> chars; // 符号栈
stack<int> state; // 状态栈
3、头文件声明和全局变量定义
如下。
#include 4、函数汇总
(1)函数汇总表
| 函数名称 | 功能简述 |
|---|---|
readFile |
读取文件函数,返回一个string动态数组,以行数分割 |
init |
初始化函数,在该函数中进行goto表和action表的初始化 |
printActions / printGotos |
输出goto表与action表 |
isTerminator |
判断当前字符c是否是终结符 |
findTerminator |
返回终结符所处下标 |
findNonTerminator |
返回非终结符所处下标 |
s2string |
将栈转换为字符串返回,方便输出步骤 |
analyzeLR1 |
利用LR1分析法分析字符串exp,输出其分析步骤 |
main |
主程序入口,调用读取文件函数开始分析 |
(2)函数的调用关系
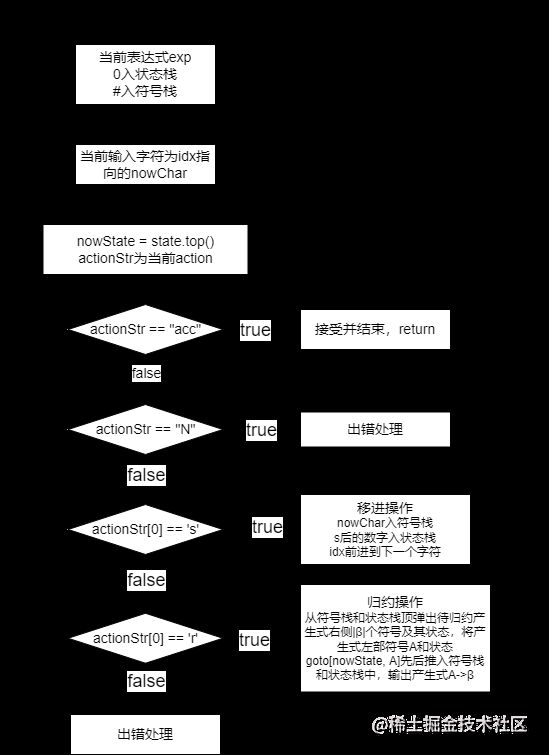
(3)流程图
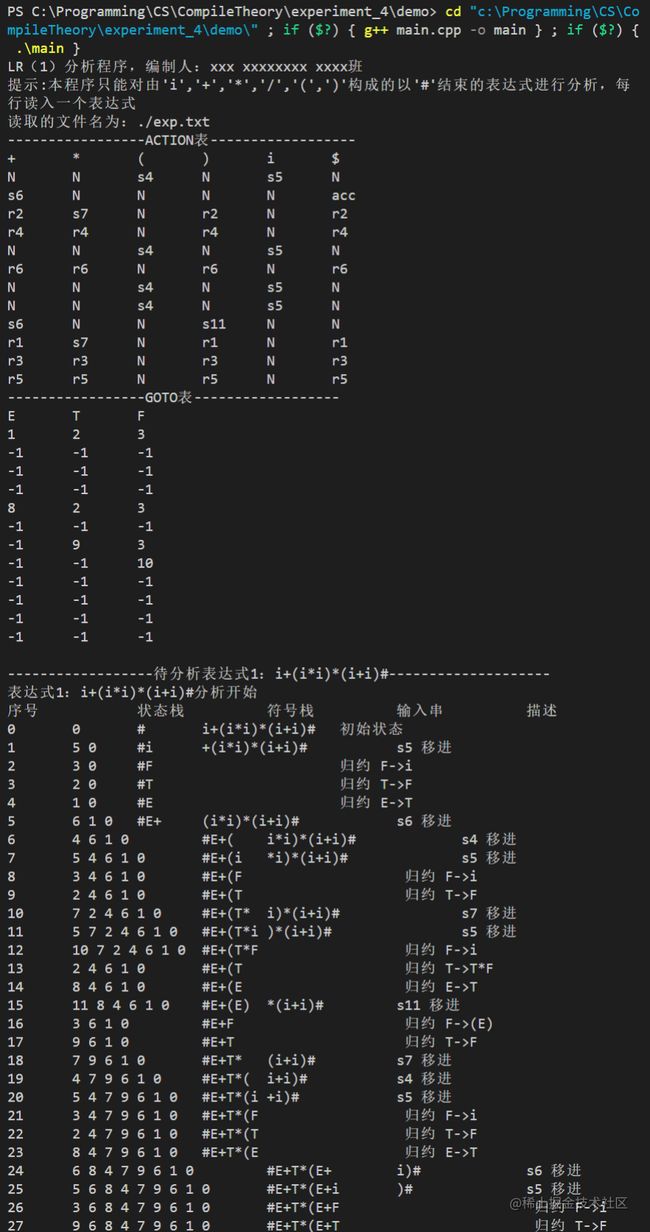
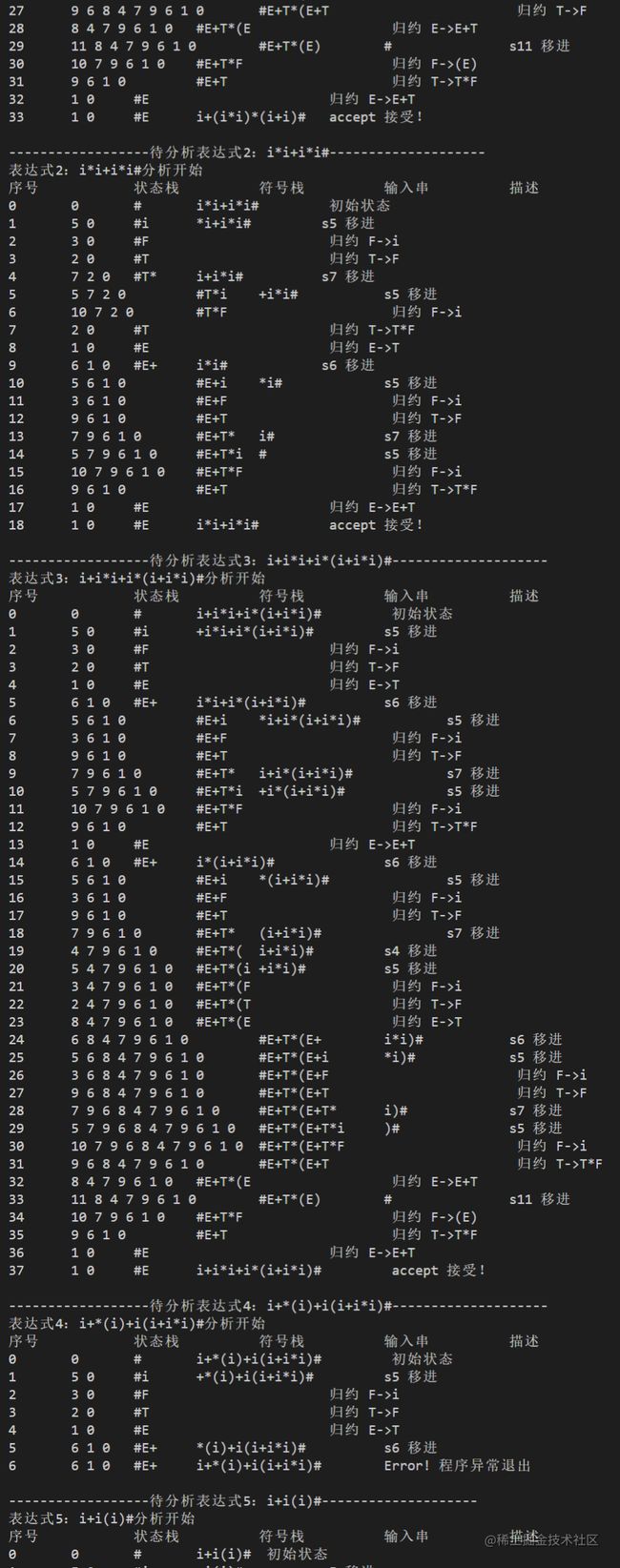
5、实验结果
输入
action.txt文件
N N s4 N s5 N
s6 N N N N acc
r2 s7 N r2 N r2
r4 r4 N r4 N r4
N N s4 N s5 N
r6 r6 N r6 N r6
N N s4 N s5 N
N N s4 N s5 N
s6 N N s11 N N
r1 s7 N r1 N r1
r3 r3 N r3 N r3
r5 r5 N r5 N r5
goto.txt文件
1 2 3
N N N
N N N
N N N
8 2 3
N N N
N 9 3
N N 10
N N N
N N N
N N N
N N N
exp.txt文件
i+(i*i)*(i+i)#
i*i+i*i#
i+i*i+i*(i+i*i)#
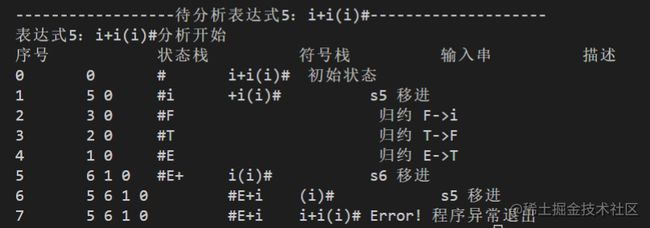
i+*(i)+i(i+i*i)#
i+i(i)#
输出
完整代码
/*
* @Author: cos
* @Date: 2022-04-30 14:20:51
* @LastEditTime: 2022-05-01 02:34:12
* @LastEditors: cos
* @Description: 实验4 LR(1) 分析法
* @FilePath: \CompileTheory\experiment_4\demo\main.cpp
*/
#include