Kotlin|Kotlin反射
文章目录
- 1. Kotlin 反射
-
- 1.1 Kotlin 反射类图
- 2.创建实例
-
- 无参构造
- 有参构造
- 说明
- 例子
- 3.通过反射调用方法 KFunction
- 4. 通过反射获取属性
- 5.获取实例的 companion
- 6. 获取注解
- 7.获取内部类
- 8.完整的代码
- 9. 问题
-
- 9.1 打包混淆问题
1. Kotlin 反射
Kotlin 的反射需要集成 org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-reflect 仓库,版本保持与 kotlin 一致。
implementation "org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-reflect:$kotlin_version"
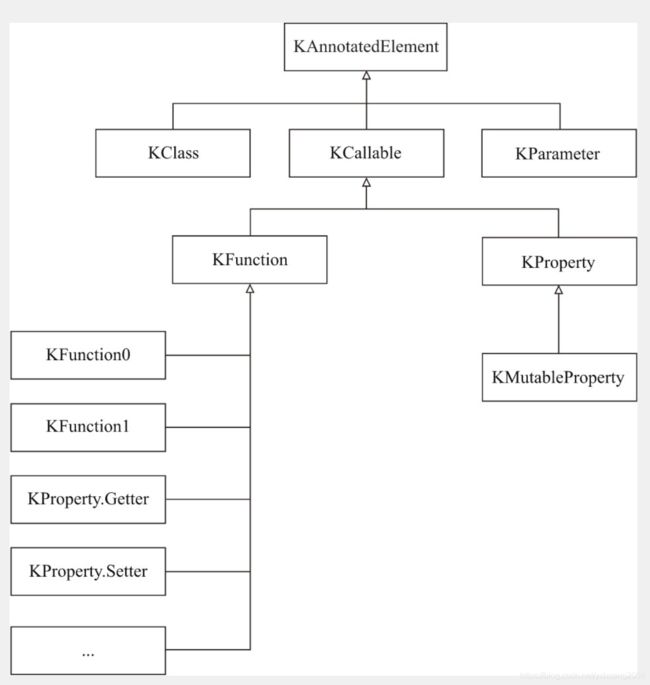
1.1 Kotlin 反射类图
图片引用《Kotlin 核心编程》
通过 kotlin 和 java 的对比,更容易理解 kotlin 的反射
- Kotlin 的反射类都是基于
KAnnotatedElement, 而 Java 的反射类都是基于AnnotateElement; - Kotlin 的 KCallable 和 Java 的 AccessiableObject 都是可用元素;
- Kotlin 的 KProperty 和 Java 的 Field 不太相同。 Kotlin 的 KProperty 通常指相应的 Getter 和 Setter 整体作为一个 KProperty(不存在字段的概念),而 Java 的 Field 通常仅仅指字段本身。
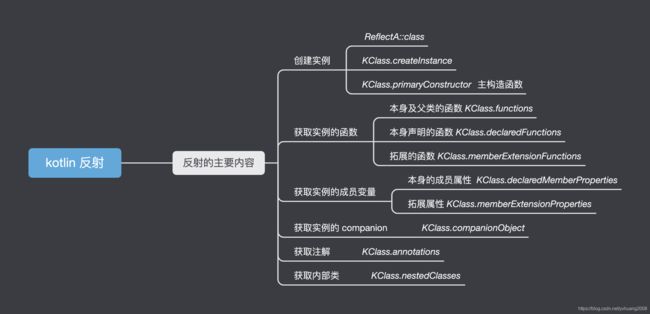
日常使用的 Kotlin 反射
-
创建实例
- ReflectA::class
- KClass.createInstance
- KClass.primaryConstructor 主构造函数
-
获取实例的函数
- 本身及父类的函数 KClass.functions
- 本身声明的函数 KClass.declaredFunctions
- 拓展的函数 KClass.memberExtensionFunctions
-
获取实例的成员变量
- 本身的成员属性 KClass.declaredMemberProperties
- 拓展属性 KClass.memberExtensionProperties
-
获取实例的 companion
KClass.companionObject -
获取注解
KClass.annotations -
获取内部类
KClass.nestedClasses
2.创建实例
无参构造
val clazz = ReflectA::class
val inst2 = clazz.createInstance()
有参构造
val cons1 = clazz.primaryConstructor
val inst1 = cons1?.call(参入参数)
// 或者
val cons2 = clazz.constructors
cons2.get[i].call(参入参数)
说明
- KClass.createInstance 是调用无参数的构造函数
- KClass.primaryConstructor 是主构造函数,如果有参数,可以调用它的 call 方法传入参数
例子
后面的例子都是以 ReflectA 类为例
//定义注解
annotation class Anno
@Deprecated("该类已经不推荐使用")
@Anno
class ReflectA(val name: String) {
companion object{
const val TAG = "ReflectA"
fun show(){
}
}
var age: Int = 0
constructor() : this("ReflectA_")
constructor(name: String, age: Int) : this(name) {
this.age = age
}
fun print(str: String) {
println("ReflectA print str $str")
}
fun sayHi(): String {
println("ReflectA sayHi")
return "sayHi"
}
class InnerClass
}
// 拓展方法
fun ReflectA.exfun() {
println("exfun")
}
// 拓展属性
val ReflectA.foo: Double
get() = 3.14
调用的例子:
println("---------- 创建对象 ---------")
println(" ")
println("createInstance 创建实例")
// createInstance() 方法调用无参数的构造器创建实例
val inst2 = clazz.createInstance()
println(inst2.name)
println(inst2.age)
println(" ")
// primaryConstructor 主构造函数
val cons1 = clazz.primaryConstructor
val inst1 = cons1?.call("hello reflect") // 参入参数
println(inst1)
println("inst1 " + inst1?.name)
println(" ")
println("第一个构造函数")
val cons2 = clazz.constructors.first()
println(cons2)
println(" ")
println("-------调用方法------")
val funs3 = clazz.declaredFunctions
val inst3 = clazz.createInstance()
println("ReflectA 本身声明的全部方法如下:")
funs3.forEach { println(it) }
for (f in funs3) {
if (f.name == "sayHi") {
f.call(inst3)
}
if (f.name == "print") {
f.call(inst3, "反射打印")
}
}
输出
---------- 创建对象 ---------
createInstance 创建实例
ReflectA_
0
com.yxhuang.androiddailydemo.reflect.ReflectA@7b9a4292
inst1 hello reflect
第一个构造函数
fun (): com.yxhuang.androiddailydemo.reflect.ReflectA
3.通过反射调用方法 KFunction
通过 KClass.declaredFunctions 获取,返回是一个 KFunction 列表
println("-------调用方法------")
val funs3 = clazz.declaredFunctions
val inst3 = clazz.createInstance()
println("ReflectA 本身声明的全部方法如下:")
funs3.forEach { println(it) }
for (f in funs3) {
if (f.name == "sayHi") {
f.call(inst3) // 调用无参函数
}
if (f.name == "print") {
f.call(inst3, "反射打印") // 传入参数
}
}
输出
-------调用方法------
ReflectA 本身声明的全部方法如下:
fun com.yxhuang.androiddailydemo.reflect.ReflectA.print(kotlin.String): kotlin.Unit
fun com.yxhuang.androiddailydemo.reflect.ReflectA.sayHi(): kotlin.String
ReflectA print str 反射打印
ReflectA sayHi
4. 通过反射获取属性
通过 KClass.declaredMemberProperties 获取,返回是 KProperty1 列表。
KProperty 代码属性,它是 KCallable 的子类,
主要接口有
public actual interface KProperty<out V> : KCallable<V> {
/**
* `true` if this property is `lateinit`.
* 是否是 lateinit
*/
@SinceKotlin("1.1")
public val isLateinit: Boolean
/**
* `true` if this property is `const`.
* 是否是 const
*/
@SinceKotlin("1.1")
public val isConst: Boolean
/** The getter of this property, used to obtain the value of the property. */
public val getter: Getter<V>
/**
* Represents a property accessor, which is a `get` or `set` method declared alongside the property.
*/
public interface Accessor<out V> {
/** The property which this accessor is originated from. */
public val property: KProperty<V>
}
/**
* Getter of the property is a `get` method declared alongside the property.
*/
public interface Getter<out V> : Accessor<V>, KFunction<V>
}
获取例子
println("-------访问属性------")
//通过decaredMemberProperties获取全部成员属性
val memberProperties2 = clazz.declaredMemberProperties
val inst4 = clazz.createInstance()
println("ReflectA 本身声明的成员属性如下:")
memberProperties2.forEach { println(it) }
println("inst4 name: ${inst4.name}")
memberProperties2.forEach {
if (it.name == "age") {
it as KMutableProperty1<ReflectA, Int>
it.isAccessible = true
it.set(inst4, 20)
println(it.get(inst4))
}
}
输出
-------访问属性------
ReflectA 本身声明的成员属性如下:
var com.yxhuang.androiddailydemo.reflect.ReflectA.age: kotlin.Int
val com.yxhuang.androiddailydemo.reflect.ReflectA.name: kotlin.String
inst4 name: ReflectA_
20
5.获取实例的 companion
通过 KClass.companionObject 获取,返回也是一个 KClass 对象
println("---------- companion 对象 ---------") //
val companion = clazz.companionObject // 返回也是一个 KClass
if (companion != null){
println("companion $companion")
companion.declaredMemberProperties.forEach {
println("companion declaredMemberProperties: $it")
}
companion.declaredFunctions.forEach {
println("companion declaredFunctions: $it")
}
}
输出
---------- companion 对象 ---------
companion class com.yxhuang.androiddailydemo.reflect.ReflectA$Companion
companion declaredMembers: val com.yxhuang.androiddailydemo.reflect.ReflectA.Companion.TAG: kotlin.String
companion declaredFunctions: fun com.yxhuang.androiddailydemo.reflect.ReflectA.Companion.show(): kotlin.Unit
6. 获取注解
通过 KClass.annotations 获取注解,返回是一个Annotation列表
//通过annotations属性获取该KClass对象所对应类的全部注解
val anns = clazz.annotations
println("ReflectA 的全部注解如下:")
anns.forEach { println(it) }
println("该KClass元素上的@Annot注解为:${clazz.findAnnotation<Anno>()}")
输出
ReflectA 的全部注解如下:
@kotlin.Deprecated(level=WARNING, [email protected](imports=[], expression=), message=该类已经不推荐使用)
@com.yxhuang.androiddailydemo.reflect.Anno()
该KClass元素上的@Annot注解为:@com.yxhuang.androiddailydemo.reflect.Anno()
7.获取内部类
通过 KClass.nestedClasses 获取,返回是一个内部类的 KClass 列表
//通过nestedClasses属性获取所对应的全部嵌套类
val inners = clazz.nestedClasses
println("ReflectA 的全部内部类如下:")
inners.forEach { println(it) }
输出
ReflectA 的全部内部类如下:
class com.yxhuang.androiddailydemo.reflect.ReflectA$Companion
class com.yxhuang.androiddailydemo.reflect.ReflectA$InnerClass
8.完整的代码
package com.yxhuang.androiddailydemo.reflect
import kotlin.reflect.KMutableProperty1
import kotlin.reflect.full.*
import kotlin.reflect.jvm.isAccessible
/**
* Created by yxhuang
* Date: 2021/7/30
* Description:
*/
//定义注解
annotation class Anno
@Deprecated("该类已经不推荐使用")
@Anno
class ReflectA(val name: String) {
companion object{
const val TAG = "ReflectA"
fun show(){
}
}
var age: Int = 0
constructor() : this("ReflectA_")
constructor(name: String, age: Int) : this(name) {
this.age = age
}
fun print(str: String) {
println("ReflectA print str $str")
}
fun sayHi(): String {
println("ReflectA sayHi")
return "sayHi"
}
class InnerClass
}
// 拓展方法
fun ReflectA.exfun() {
println("exfun")
}
// 拓展属性
val ReflectA.foo: Double
get() = 3.14
fun main() {
println("Hello word")
val clazz = ReflectA::class
println(clazz)
println("ReflectA 的全部构造器如下:")
clazz.constructors.forEach {
println(it)
}
println("ReflectA 的主构造器如下:")
println(clazz.primaryConstructor)
println(" ")
//通过functions属性获取该KClass对象所对应类的全部方法
val funs = clazz.functions
println("ReflectA 的全部方法如下:")
funs.forEach { println(it) }
println(" ")
//通过 declaredFunctions 属性获取该KClass对象声明的全部方法
val funs2 = clazz.declaredFunctions
println("ReflectA 本身声明的全部方法如下:")
funs2.forEach { println(it) }
println(" ")
//通过 memberExtensionFunctions 属性获取全部扩展方法
val exetensionFunctions = clazz.memberExtensionFunctions
println("ReflectA 声明的扩展方法如下:")
exetensionFunctions.forEach { println(it) }
println(" ")
//通过decaredMemberProperties获取全部成员属性
var memberProperties = clazz.declaredMemberProperties
println("ReflectA 本身声明的成员属性如下:")
memberProperties.forEach { println(it) }
println(" ")
//通过memberExtensionProperties属性获取该KClass对象的全部扩展属性
var exProperties = clazz.memberExtensionProperties
println("ReflectA 本身声明的扩展属性如下:")
exProperties.forEach { println(it) }
println(" ")
//通过annotations属性获取该KClass对象所对应类的全部注解
val anns = clazz.annotations
println("ReflectA 的全部注解如下:")
anns.forEach { println(it) }
println("该KClass元素上的@Annot注解为:${clazz.findAnnotation<Anno>()}")
println(" ")
//通过nestedClasses属性获取所对应的全部嵌套类
val inners = clazz.nestedClasses
println("ReflectA 的全部内部类如下:")
inners.forEach { println(it) }
println(" ")
//通过supertypes属性获取该类的所有父类型
println("KClassTest的父类型为:${clazz.supertypes}")
println(" ")
println("---------- companion 对象 ---------") //
val companion = clazz.companionObject // 返回也是一个 KClass
if (companion != null){
println("companion $companion")
companion.declaredMemberProperties.forEach {
println("companion declaredMemberProperties: $it")
}
companion.declaredFunctions.forEach {
println("companion declaredFunctions: $it")
}
}
println(" ")
println("---------- 创建对象 ---------")
println(" ")
println("createInstance 创建实例")
// createInstance() 方法调用无参数的构造器创建实例
val inst2 = clazz.createInstance()
println(inst2.name)
println(inst2.age)
println(" ")
// primaryConstructor 主构造函数
val cons1 = clazz.primaryConstructor
val inst1 = cons1?.call("hello reflect") // 参入参数
println(inst1)
println("inst1 " + inst1?.name)
println(" ")
println("第一个构造函数")
val cons2 = clazz.constructors.first()
println(cons2)
println(" ")
println("-------调用方法------")
val funs3 = clazz.declaredFunctions
val inst3 = clazz.createInstance()
println("ReflectA 本身声明的全部方法如下:")
funs3.forEach { println(it) }
for (f in funs3) {
if (f.name == "sayHi") {
f.call(inst3)
}
if (f.name == "print") {
f.call(inst3, "反射打印")
}
}
println("\n")
println("-------访问属性------")
//通过decaredMemberProperties获取全部成员属性
val memberProperties2 = clazz.declaredMemberProperties
val inst4 = clazz.createInstance()
println("ReflectA 本身声明的成员属性如下:")
memberProperties2.forEach { println(it) }
println("inst4 name: ${inst4.name}")
memberProperties2.forEach {
if (it.name == "age") {
it as KMutableProperty1<ReflectA, Int>
it.isAccessible = true
it.set(inst4, 20)
println(it.get(inst4))
}
}
}
9. 问题
9.1 打包混淆问题
在打包混淆之后,如果出现问题
java.lang.IllegalStateException: No BuiltInsLoader implementation was found. Please ensure that the META-INF/services/ is not stripped from your application and that the Java virtual machine is not running under a security manager
这是由于混淆导致的,解决办法是在 proguard-rules.pro 中添加下面的规矩即可
-keep class kotlin.reflect.jvm.internal.impl.**
-keep class kotlin.Metadata {*; }
-keepclassmembers class kotlin.Metadata { public ;}