c++系列之string类的常用接口函数
博客:小怡同学
个人简介:编程小萌新
如果博客对大家有用的话,请点赞关注再收藏
string
string时表示字符串的字符类
//使用 string类包含#include 头文件 以及 using namespace std
string类的常见构造
#include string
string容量相关接口 (size(),capacity(),clear(),empty)
1.size()是元素个数
//. size()与length()方法底层实现原理完全相同,引入size()的原因是为了与其他容器的接口保持一致,一般情况下基本都是用size()。
2.capacity()是容积
3.clear()将字符串清空,但不改变底层空间大小 //clear()只是将string中有效字符清空,不改变底层空间大小。
4.empty()检测字符串是否为空是返回true ,否则返回false
resize()接口函数
resize(size_t n) 与 resize(size_t n, char
c)都是将字符串中有效字符个数改变到n个,不同的是当字符个数增多时:resize(n)用0来填充多出的元素空间,resize(size_t n, char
c)用字符c来填充多出的元素空间。注意:resize在改变元素个数时,如果是将元素个数增多,可能会改变底层容量的大小,如果是将元素个数减少,底层空间总大小不变。
int main()
{
string s1("hello world");
cout << s1.size() <<endl;
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;
s1.resize(34,'y');// 将s1中有效字符个数增加到34个,多出位置用'y'进行填充
s1.resize(13);
cout << s1.size() << endl;
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;
cout << s1 << endl;
s1.resize(3, 'y');
cout << s1.size() << endl;
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;
cout << s1 << endl;
return 0;
}
reserve()
//reserve(size_t res_arg=0)
为string预留空间,不改变有效元素个数,当reserve的参数小于string的底层空间总大小时,reserver不会改变容量大小。
string类对象的访问及遍历操作
//operator[]
//迭代器->begin(),end() / rbegin() ,rend()
//for
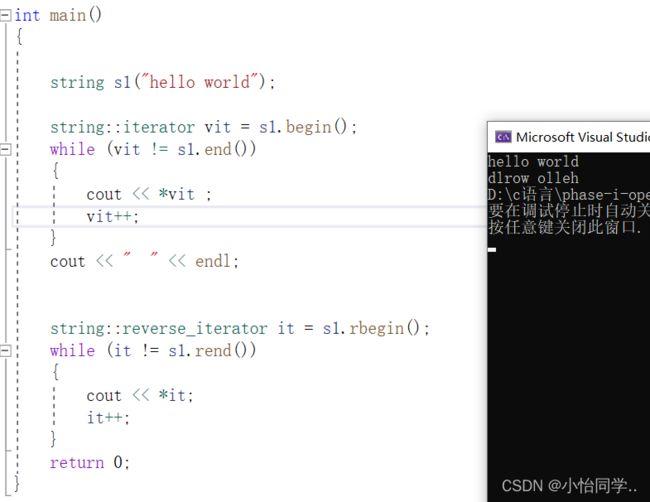
int main()
{
string s1("hello world");
string::iterator vit = s1.begin();
while (vit != s1.end())
{
cout << *vit ;
vit++;
}
cout << " " << endl;
string::reverse_iterator it = s1.rbegin();
while (it != s1.rend())
{
cout << *it;
it++;
}
return 0;
}
int main()
{
string s1("hello world");
for (auto tmp: s1)//tmp只是原数组拷贝 不改变原数就改成引用会改变
{
cout << ++tmp;
}
cout << " " << endl;
for (auto& tmp : s1)
{
cout << ++tmp ;
}
return 0;
}
string类对象的修改和操作
插入(拼接)方式
push_back() //加字符
append()//加字符串
operator()//加字符或字符串都行
int main()
{
string s1("hello world");
s1.push_back('a');
s1.append("asddfs");
s1 += 'a';
s1 += "sfasd";
cout << s1;
return 0;
}
正向和反向查找:find() + rfind()
int main()
{
string s1("hello.world");
int pos1 = s1.find('.');
string s ("string.cpp");
int pos = s.rfind('.');
string s2("aahello.world");
int pos = s2.find(s1);//查找字符串
//返回下标
string s1("hello.worl.d");
int pos = s1.find('.',6 );
//第一个参数是要找的字符、字符串,第二个参数是从下标n开始查找
cout << pos;
return 0;
// npos是string里面的一个静态成员变量
// static const size_t npos = -1;
//如果未找到匹配项,则该函数返回string::npos。
}
截取子串:substr()
string substr (size_t pos = 0, size_t len = npos) const
int main()
{
string s1("hello.world");
int pos1 = s1.find('.');
string s2("aahello.world");
string s3( s1.substr(1, 5));
cout << s3 << endl;
//从下标pos ,截取n个
return 0;
//返回字符串对象
}
getline()
//非字符类的接口函数
istream& getline (istream& is, string& str)
int main()
{
string s1;
getline(cin,s1);
cout << s1 << endl;
return 0;
}
reverse用法
//非string接口函数,常用于字符串反转 void reverse (BidirectionalIterator first,BidirectionalIterator last); 参数是迭代器 (左闭右开)
#include //begin()是字符串第一个字符
//end()是字符串最后一个字符的下一位
//rbegin()是最后一个元素
//rend()是第一个元素