系统编程(3):进程
文章目录
- 一、概念
-
- 1.1 什么是进程?
- 1.2 进程ID
- 1.3 进程间通信
- 1.4 进程的三种态的转换
- 二、进程控制
-
- 2.1 创建进程函数:fork函数
-
- 2.1.1 获得pid函数
- 写代码:
-
- 方式一:最简单的
- 方式二:加入while(1)死循环
- 方式三:增加自加逻辑,便于看程序运行逻辑
- 2.2 启动进程函数:exec函数族
-
- 2.2.1 exec函数族的使用场景
- 写代码
- 2.3 ps和kill命令
一、概念
1.1 什么是进程?
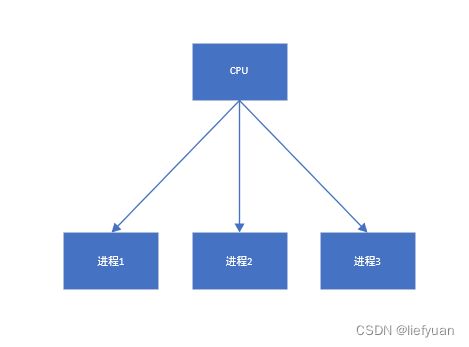
进程指的是正在运行的程序。
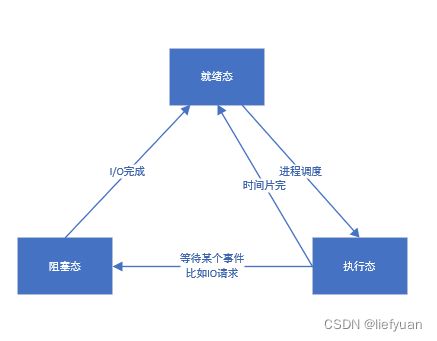
下图是进程的三种状态:
后台进程又叫守护进程。
1.2 进程ID
每个进程都有一个唯一的标识符,即进程ID,简称pid。
1.3 进程间通信
- 管道通信:有名管道,无名管道
- 信号通信:信号的发送,信号的接受,信号的处理
- IPC通信:共享内存,消息队列,信号灯
- Socket通信
1.4 进程的三种态的转换
二、进程控制
2.1 创建进程函数:fork函数
- fork函数
- 头文件:
include - 函数原型:
pid_t fork(void) - 返回值:fork函数有三种返回值。
- 在父进程中,fork返回新创建的子进程的PID
- 在子进程中,fork返回0
- 出现出现错误,fork返回一个负值
2.1.1 获得pid函数
- 获得当前进程的PID:
getpid() - 获得当前进程的父进程的PID:
getppid()
写代码:
方式一:最简单的
#include $ gcc main.c -o main.out
$ ./main.out
This is parent, parent pid is 17937
This is child, child pid is 17938, parent pid is 17937
方式二:加入while(1)死循环
#include $ gcc main.c -o main.out
$ ./main.out
This is parent, parent pid is 18134
This is child, child pid is 18135, parent pid is 18134
This is parent, parent pid is 18134
This is child, child pid is 18135
This is parent, parent pid is 18134
This is child, child pid is 18135
This is parent, parent pid is 18134
This is child, child pid is 18135
This is parent, parent pid is 18134
This is child, child pid is 18135
This is parent, parent pid is 18134
This is child, child pid is 18135
This is parent, parent pid is 18134
This is child, child pid is 18135
This is parent, parent pid is 18134
This is child, child pid is 18135
This is parent, parent pid is 18134
This is child, child pid is 18135
This is parent, parent pid is 18134
This is child, child pid is 18135
This is parent, parent pid is 18134
This is child, child pid is 18135
This is parent, parent pid is 18134
This is child, child pid is 18135
This is parent, parent pid is 18134
This is child, child pid is 18135
This is parent, parent pid is 18134
This is child, child pid is 18135
This is parent, parent pid is 18134
...
方式三:增加自加逻辑,便于看程序运行逻辑
#include 测试运行:
$ gcc main.c -o main.out
$ ./main.out
This is parent, parent pid is 18180
cnt: 1, pid: 18180
This is child, child pid is 18181, parent pid is 18180
cnt: 1, pid: 18181
这里就是说cnt变量在父进程和子进程里面是独立的拷贝,所以结果不是2而是1.
2.2 启动进程函数:exec函数族
在Linux中并没有exec函数,而是有6个以exec开头的函数族,下面列举了exec函数族的6个函数成员:
int execl(const char *path, const char *arg, ...)int execv(const char *path, char *const arg[], ...)int execle(const char *path, const char *arg, ..., char *const envp[])int execve(const char *path,char *const arg[], ..., char *const envp[])int execlp(const char *file, const char *arg, ...)int execvp(const char *file, char *const arg[], ...)
头文件是:unistd.h
最常用的函数是execl函数
exec函数族可以让子进程执行不同的代码
2.2.1 exec函数族的使用场景
在Linux中使用exec函数族主要有以下两种情况:
- 当进程认为自己不能再为系统和用户做成任何贡献时,就可以调用任何exec函数族让自己重生。
- 如果一个进程想执行另一个程序,那么它就可以调用fork函数新建一个进程,然后调用任何一个exec函数使子进程重生。
写代码
两个代码:
hello.c
#include main.c
#include 测试运行:
liefyuan@ubuntu:~/Linux/app/08-fork$ ./main.out
This is parent, parent pid is 18467
cnt: 1, pid: 18467
This is child, child pid is 18468, parent pid is 18467
Hello World!
只有一次cnt的打印还是父进程打印的,子进程没有cnt打印。
execl函数是“换核不换壳”的,将子进程的内容直接替换成了hello.out程序,而原有的子进程的逻辑就不会再跑了。
2.3 ps和kill命令
ps命令:可以列出系统中当前运行的哪些进程。
举例:
ps aux进程不关联终端ps a和ps u都是进程关联终端的ps x显示所有程序,不以终端来区分ps aux | grep xxx中间竖线是管道的意思,相当是过滤,除了xxx的都不显示
[root@RK356X:/]# ps a
PID TTY STAT TIME COMMAND
765 ttyFIQ0 Ss 0:00 -/bin/sh
3579 ttyFIQ0 R+ 0:00 ps a
[root@RK356X:/]# ps au
USER PID %CPU %MEM VSZ RSS TTY STAT START TIME COMMAND
root 765 0.0 0.1 3168 2068 ttyFIQ0 Ss 11:40 0:00 -/bin/sh
root 3580 0.0 0.0 2992 844 ttyFIQ0 R+ 12:57 0:00 ps au
kill命令:用来杀死进程。
举例:kill -9(SIGKILL) PID
可以是使用kill -l来查看所有的相关命令:
$ kill -l
1) SIGHUP 2) SIGINT 3) SIGQUIT 4) SIGILL 5) SIGTRAP
6) SIGABRT 7) SIGBUS 8) SIGFPE 9) SIGKILL 10) SIGUSR1
11) SIGSEGV 12) SIGUSR2 13) SIGPIPE 14) SIGALRM 15) SIGTERM
16) SIGSTKFLT 17) SIGCHLD 18) SIGCONT 19) SIGSTOP 20) SIGTSTP
21) SIGTTIN 22) SIGTTOU 23) SIGURG 24) SIGXCPU 25) SIGXFSZ
26) SIGVTALRM 27) SIGPROF 28) SIGWINCH 29) SIGIO 30) SIGPWR
31) SIGSYS 34) SIGRTMIN 35) SIGRTMIN+1 36) SIGRTMIN+2 37) SIGRTMIN+3
38) SIGRTMIN+4 39) SIGRTMIN+5 40) SIGRTMIN+6 41) SIGRTMIN+7 42) SIGRTMIN+8
43) SIGRTMIN+9 44) SIGRTMIN+10 45) SIGRTMIN+11 46) SIGRTMIN+12 47) SIGRTMIN+13
48) SIGRTMIN+14 49) SIGRTMIN+15 50) SIGRTMAX-14 51) SIGRTMAX-13 52) SIGRTMAX-12
53) SIGRTMAX-11 54) SIGRTMAX-10 55) SIGRTMAX-9 56) SIGRTMAX-8 57) SIGRTMAX-7
58) SIGRTMAX-6 59) SIGRTMAX-5 60) SIGRTMAX-4 61) SIGRTMAX-3 62) SIGRTMAX-2
63) SIGRTMAX-1 64) SIGRTMAX